Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Basic Biology
Загружено:
meemansa12Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Basic Biology
Загружено:
meemansa12Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 1
Basic Biology
Cells are the basic structural units and the building blocks of living organisms.
Discovery of the Cell
Cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 after observing a
piece of cork under a magnifying device.
Robert Hooke coined the term cell.
Schleiden and Schwann proposed the cell theory. According to cell
theory-
1. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells
2. Cells are the basic structural and functional unit of life.
3. New cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Number of Cells
Organisms made of only a single cell are called unicellular organisms.
For example: Amoeba and Paramecium
Single cell in these organisms performs all the basic functions such as
digestion, respiration, and excretion.
Organisms made up of more than one cells are called multicellular
organisms.
For example: Humans, cow, rose
In these organisms, the cells show division of labour as particular set of
cells are involved in performing a specific body function.
Shape of the Cells
Most of the cells have a definite shape.
Some cells such as that in Amoeba have no definite shape.
The human red blood cell (RBC) is spherical-shaped.
The muscle cells in humans are spindle-shaped.
The human nerve cells have elongated branched structure.
In plants and bacteria, the cell is enclosed in a protective covering called
cell wall, which gives shape and rigidity to the cells.
Size of the Cells
The smallest cell is 0.1 to 0.5 mm in bacteria.
The largest cell is of size 170 mm 130 mm, which is the egg of an
ostrich.
Size of a cell has no relation with the size of an organism.
Cell Structure and Functions
In multicellular organisms, each organ system is made up of several
organs.
Organs are further made up of tissues.
Tissues are groups of similar cells performing a specific function.
Components of the Cell
Cell Membrane
1. A cell is composed of cell membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus.
2. The cytoplasm and nucleus enclosed in the cell membrane
together constitute plasma membrane. It checks the transport of
substances in the cell.
3. The cell membrane is selectively permeable i.e. it allows the
movement of certain substances through it while restricts the
movement of others.
4. It gives a definite shape to the cell and protects its internal
contents.
Cell Wall
1. In plants, an extra protective covering known as cellulose is
present.
2. It is called cell wall and protects plant cells from environment
variations.
3. Cell wall is made up of a complex carbohydrate called cellulose
and it imparts rigidity to the plant cell.
Cytoplasm
1. It is a jelly-like substance present between cell membrane and
nucleus.
2. It contains various cell organelles such as mitochondria, golgi
body, etc.
Nucleus
1. It is a dense spherical body located at the centre of the cell.
2. It is surrounded by porous nuclear membrane.
3. Inside the nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm is present which
contains spherical body called nucleolus and thread-like
structures called chromosomes.
4. Chromosomes are the structures that carry genes and play an
important role in inheritance.
5. The entire living substance in a cell is known as protoplast.
Vacuoles
1. Vacuoles are fluid-filled membrane-bound structures in the cell.
2. In plant cells, a single large vacuole is present.
3. In animal cells, numerous small vacuoles are present.
4. The membrane of the vacuole is called tonoplast. This membrane
encloses a fluis called cell sap.
Plastids
1. They are present in plant cells.
2. Chloroplast is a plastid containing green pigment called
chlorophyll that is required in photosynthesis.
3. Plastids are of two types leucoplasts and chromoplasts
4. Leucoplasts are colourless and are used to store food while
chromoplasts are plastids containing pigments. Chloroplasts are a
type of chromoplasts only
5. Chloroplasts consist of two regions grana (stacks of sac like
membrane bound structures that contain pigment chlorophyll)
and stroma (ground substance containing enzymes and starch
grains)
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
They are of two types:
1. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) is important for
synthesis and packaging of proteins.
2. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) acts as storage
organelle. It also helps in lipid (fat) synthesis.
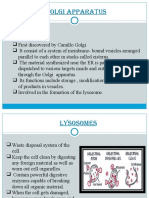
Golgi Apparatus
1. It is made up of parallel arranged membrane-bound vesicles
called cisternae.
2. It helps in storage, modification, and packaging of products in
vesicles.
3. It helps in formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids.
Lysosomes
1. It is a membrane-bound structure that holds variety of enzymes.
2. Rich in all types of hydrolytic enzymes, which are active at acidic
pH
3. It is involved in digestion of carbohydrate, proteins, lipids, and
nucleic acids.
Mitochondria
1. It is a double membrane-bound structure.
2. The inner membrane of mitochondria is deeply folded to form
cristae.
3. Cristae increase the surface area in the organelle.
4. It is the site of cellular respiration and hence known as power
house of cell.
5. They have their own single circular DNA.
6. They divide by fission.
Differences between Plant and Animal cells
Plant Cell Animal Cells
1. Cell wall is present. 1. Cell wall is absent.
2. Nucleus is located in the
periphery of the cell.
2. Nucleus is located in the centre of
the cells.
3. Numerous chloroplasts are
present.
3. Chloroplast is absent.
4. A large single vacuole is present. 4. Numerous small vacuoles are
present in the cytoplasm.
Contribute to this Revision Note:
If you find anything of importance missing from this note, email it to us at revision-notes@meritnation.com, and
well add it to this note under your name!
Вам также может понравиться
- The Christmas LessonДокумент4 страницыThe Christmas Lessonmeemansa12Оценок пока нет
- Du List 2016Документ18 страницDu List 2016meemansa12Оценок пока нет
- Graphical User InterfaceДокумент3 страницыGraphical User Interfacemeemansa12Оценок пока нет
- GK Indian Quiz QuestionsДокумент3 страницыGK Indian Quiz Questionsmeemansa12Оценок пока нет
- Chief Ministers & Governors of Indian StatesДокумент2 страницыChief Ministers & Governors of Indian Statesmeemansa12Оценок пока нет
- Computer Technology QuizДокумент5 страницComputer Technology Quizmeemansa120% (1)
- 15 Quiz Questions On IndiaДокумент4 страницы15 Quiz Questions On Indiameemansa12Оценок пока нет
- Current Affairs QuizДокумент3 страницыCurrent Affairs Quizmeemansa12Оценок пока нет
- Code P AipmtДокумент19 страницCode P Aipmt27rocketgirlОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Major CharactersДокумент3 страницыAnalysis of Major CharactersZaib RehmanОценок пока нет
- Derek IndiaДокумент20 страницDerek Indiameemansa12Оценок пока нет
- Electricity PDFДокумент4 страницыElectricity PDFmeemansa12Оценок пока нет
- Motion in A Straight Line Test 1Документ10 страницMotion in A Straight Line Test 1meemansa12Оценок пока нет
- M2 NQ 8 F1 U LUt P@pho T0 ERx Z6 VVQ ZTTS28 QTF SNGD 9 e 68!Документ3 страницыM2 NQ 8 F1 U LUt P@pho T0 ERx Z6 VVQ ZTTS28 QTF SNGD 9 e 68!deep.deepkОценок пока нет
- Respiration and Excretion in AnimalsДокумент3 страницыRespiration and Excretion in Animalsmeemansa12Оценок пока нет
- Movements in Plants and AnimalsДокумент2 страницыMovements in Plants and Animalsmeemansa12Оценок пока нет
- Life Processes NutritionДокумент3 страницыLife Processes Nutritionmeemansa12Оценок пока нет
- Life Under The MicroscopeДокумент3 страницыLife Under The Microscopemeemansa12Оценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Plant PhysiologyДокумент95 страницPlant PhysiologyAlvin B BuenconsejoОценок пока нет
- Class 9th Cell - The Unit of LifeДокумент40 страницClass 9th Cell - The Unit of LifeKabir RaiОценок пока нет
- Content in Demo TeachingДокумент6 страницContent in Demo TeachingAgustines, Marie Char C.Оценок пока нет
- CellsДокумент31 страницаCellsPranav ShindeОценок пока нет
- PLASTIDSДокумент4 страницыPLASTIDSaroojОценок пока нет
- Selina Solutions For Class 9 Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Unit of LifeДокумент15 страницSelina Solutions For Class 9 Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Unit of LifePrashun PriyadarshiОценок пока нет
- CLS Aipmt-18-19 XIII Bot Study-Package-1 SET-1 Chapter-1 PDFДокумент38 страницCLS Aipmt-18-19 XIII Bot Study-Package-1 SET-1 Chapter-1 PDFKunal GuptaОценок пока нет
- Cell Organeeles IДокумент7 страницCell Organeeles ISaumya GopalОценок пока нет
- Cell 7Документ6 страницCell 7XI-A Vishal BishnoiОценок пока нет
- Cell OrganelleДокумент9 страницCell OrganelleGwencytech DomingoОценок пока нет
- Raven Biology of Plants: Eighth EditionДокумент63 страницыRaven Biology of Plants: Eighth EditionMoath EnnabОценок пока нет
- Science7 Q2 Mod4 EggsAreWhiteLemonsAreYellowLikeMeAndYouTheyreMadeOfCellsToo V3.1 TessOKДокумент34 страницыScience7 Q2 Mod4 EggsAreWhiteLemonsAreYellowLikeMeAndYouTheyreMadeOfCellsToo V3.1 TessOKEspher Macabitas100% (6)
- محاضرة 2Документ41 страницаمحاضرة 2AbdulОценок пока нет
- Byjus Com Biology Cell OrganellesДокумент26 страницByjus Com Biology Cell OrganellesᏗᏕᎥᎷ ᏗᏝᎥОценок пока нет
- Lakhmir Singh Biology Class 9 Solutions CH 2Документ7 страницLakhmir Singh Biology Class 9 Solutions CH 2DarshilОценок пока нет
- Group 2-Excercise 1Документ7 страницGroup 2-Excercise 1James Carbonell Dela PeñaОценок пока нет
- VMC - SOSE IX HRT - 1 (Question Paper)Документ14 страницVMC - SOSE IX HRT - 1 (Question Paper)Harsh Ranjan77% (13)
- 9 Cbse - Term-1 - ScienceДокумент13 страниц9 Cbse - Term-1 - ScienceSHUAIN PARAMBIL (EMP324)Оценок пока нет
- Laboratory Exercise 1Документ2 страницыLaboratory Exercise 1Markie Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Cell Organelles - Biology Class 11 - NEETДокумент18 страницCell Organelles - Biology Class 11 - NEETsanjОценок пока нет
- 9th Class Notes Cell - The Fundamental Unit of LifeДокумент6 страниц9th Class Notes Cell - The Fundamental Unit of LifepralexprajapatiОценок пока нет
- Introduction To The Vascular Plant BodyДокумент15 страницIntroduction To The Vascular Plant BodyEula Trixie DenulanОценок пока нет
- Cbiescpl 03Документ10 страницCbiescpl 03Kanika MaheshwariОценок пока нет
- Cell Organelles: Structures and FunctionsДокумент6 страницCell Organelles: Structures and FunctionsSai Deekshita VijayakumarОценок пока нет
- Cell Organelles ProjectДокумент18 страницCell Organelles Projecthana fathimaОценок пока нет
- Cells PDFДокумент12 страницCells PDFkyla mae adlawonОценок пока нет
- 2014 Test Paper DR Homi BhabhaДокумент9 страниц2014 Test Paper DR Homi BhabhaDr Mohan Savade100% (1)
- Lecture 1Документ39 страницLecture 1Mohammed SindiОценок пока нет
- Biology Class Ix Reference Study Material PDFДокумент219 страницBiology Class Ix Reference Study Material PDFVishal50% (2)
- Etan Bar-1995-PigmentДокумент8 страницEtan Bar-1995-PigmentKarenParadaОценок пока нет