Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Kinematics of Machinery
Загружено:
Sri RИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Kinematics of Machinery
Загружено:
Sri RАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code: 9A03401
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, April/May 2013
KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY
(Mechanical Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70
Answer any FIVE questions
All questions carry equal marks
*****
Contd. in Page 2
Page 1 of 2
1 (a) Define the term kinematic link. Explain different types of links with the help of
examples.
(b) Explain different inversions of four bar chain with the of line diagrams.
2 (a) Sketch and describe the Harts straight line mechanism indicating clearly the
conditions under which the point P on the corners of the rhombus of the mechanism
generates a straight line.
(b) Prove geometrically that the above mechanism is capable of producing straight line.
3 (a) Draw and explain Kliens construction for determining the velocity and acceleration
of the piston in a slider crank mechanism.
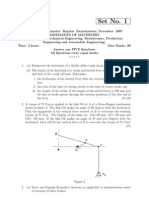
(b) In a pin jointed four bar mechanism, as shown in fig. AB =300 mm, BC =CD =360
mm, and AD =600 mm, the angle BAD =60
0
. The crank AB rotates uniformly at 100
r.p.m. locate ball the instantaneous centers and find the angular velocity of the link
BC.
4 (a) What is fundamental equation of steering gears? Which steering gear fulfils this
condition?
(b) In a double universal coupling joining two shafts, the intermediate shaft is inclined at
10
0
to each. The input and the output forks on the intermediate shaft have been
assembled inadvertently at 90
0
to one another. Determine the maximum and the
least velocities of the output shaft if the speed of the input shaft is 500 r.p.m. Also
find the coefficient of fluctuation in speed.
1
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net www.android.jntuworld.com
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code: 9A03401
*****
Page 2 of 2
5 (a) Why a roller follower is preferred to that of a knife-edged follower.
(b) From the following data draw the profile of a cam in which the follower moves
with S.H.M. during ascent while it moves uniformly accelerated motion during
descent:
Lift of follower =4 cm; Least radius of cam =5 cm; Angle of ascent =48
0
; Angle
of dwell between ascent and descent =42
0
; Angle of descent =60
0
; The diameter
of roller =3 cm; Distance between line of action of the follower and the axes of
cam =2 cm. If the cam rotates at 360 r.p.m. anticlockwise, find the maximum
velocity and acceleration of the follower during descent.
6 (a) State and prove the law of gear tooth action for constant velocity ratio and show
how the involute teeth profile satisfies the condition.
(b) Derive an expression for the velocity of sliding between a pair of in volute teeth.
State the advantages of in volute profile as a gear tooth profile.
7 In a flat belt drive the initial tension is 2000 N, the coefficient of friction between
the belt and the pulley is 0.3 and the angle of lap on the smaller pulley is 150
0
.
The smaller pulley has a radius of 200 mm and rotates at 500 r.p.m. find the
power in KW transmitted by the belt.
8 In an epicyclic gear train, the internal wheels A and B and the compound wheels
C and D rotate independently about axis O. the wheels E and F rotate on pins
fixed to the arm G.E gear with A and C and F gear with B and D. All wheels have
the same module and the number of teeth are: T
C
=28
,
T
D
=26, T
E
=T
F
=18
(i) Sketch the arrangement ;
(ii) Find the number of teeth on A and B;
(iii) If the arm G makes 100 r.p.m clockwise and A is fixed, find the speed B;
(iv) If the arm G makes100 r.p.m clockwise and wheel A makes 10 r.p.m counter
clockwise, find the speed of wheel B.
1
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net www.android.jntuworld.com
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code: 9A03401
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, April/May 2013
KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY
(Mechanical Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70
Answer any FIVE questions
All questions carry equal marks
*****
Contd. in Page 2
Page 1 of 2
1 (a) Differentiate between: (i) Lower pair and higher pair. (ii) Turning pair and sliding pair.
(iii) Screw pair and spherical pair. (iv) Closed pair and unclosed pair.
(b) With a neat sketch explain the Whitworth Quick Return Mechanism.
2 (a) Describe the Watts parallel mechanism for straight line motion and derive the condition
under which the straight line is traced.
(b) Describe Harts mechanism with a neat sketch and prove that the tracing point describes
a straight line path
3 The crank of a slider crank mechanism is 15 cm and the connecting rod is 60 cm long.
The crank makes 300 r.p.m in the clock wise direction. When it has turned 45 from the
inner dead centre position, determine; (i) Acceleration of the mid-point of the connecting
rod and (ii) Angular acceleration of the connecting rod.
4 (a) Describe with a neat sketch the working of Davis steering gear mechanism. Also prove
that for Davis steering gear Tan = w/2L.
(b) A Hookes joint is used to connect two shafts. The driving shaft is rotating uniformly with
a speed of 600 r.p.m the maximum speed of the driven shaft is 630 r.p.m. Determine the
greatest permissible angle between the two shafts. Also find the minimum speed of the
driven shaft.
5 Draw the profile of a cam operating a knife-edge follower when the axis of the follower
passes through the axis of the cam shaft from the following data:
(i) Follower to move outwards through 30 mm during 90 of cam rotation,
(ii) Follower to dwell for the next 45,
(iii) Follower to return to its original position during next 60,
(iv) Follower to dwell for the rest of the cam rotation.
The displacement of the follower is to take place with simple harmonic motion during
both the outward and the return strokes. The least radius of the cam is 50 mm. if the
cam rotates at 600 r.p.m. Determine the maximum velocity and acceleration of the
follower during outward stroke and return stroke.
2
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net www.android.jntuworld.com
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code: 9A03401
*****
Page 2 of 2
6 (a) Prove that the velocity of sliding is proportional to the distance of the point of contact
from the pitch point.
(b) Two in volute gears of 20
0
pressure angle are in mesh. The number of teeth on pinion
is 20 and the gear ratio is 2. If the pitch expressed in module is 5 mm and the pitch
line speed is 1.2 m/s, assuming addendum as standard and equal to one module,
find: (i) The angle turned through by pinion when one pair of teeth is in mesh; and
(ii) The maximum velocity of sliding.
7 (a) Distinguish between slip and creep in a belt drive. Derive an expression for the ratio of
tensions in the tight and slack sides in terms of and , when the belt is just on the
point of slipping.
(b) A shaft running at 120 r.p.m is to drive a parallel shaft at 180 r.p.m the pulley on the
driving shaft is 75 cm in diameter, calculate the diameter of the pulley on the driven
shaft (i) neglecting belt thickness (ii) taking belt thickness into account which is 15
mm, (iii) assuming in the latter case a total slip of 4 %.
8 Two parallel shafts are connected with the help of two gears one gear on each shaft.
The number of teeth on one gear is 40 and speed of the shaft is 500 r.p.m. If the
speed ratio is 2.5 and circular pitch of the gears is 24 mm, and then find;
(i) Number of teeth and speed of other shaft and
(ii) Centre distance between the two shafts.
2
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net www.android.jntuworld.com
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code: 9A03401
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, April/May 2013
KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY
(Mechanical Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70
Answer any FIVE questions
All questions carry equal marks
*****
Contd. in Page 2
Page 1 of 2
1 (a) Define the term Inversion of a mechanism. Explain any one inversion of a double
slider crank mechanism.
(b) In a crank and slotted lever quick return mechanism, the distance between the fixed
centres is 150 mm and the driving crank is 75 mm long. Determine the ratio of the time
taken on the cutting and return strokes.
2 (a) What do you mean by straight line mechanism? Name the different mechanisms which
are used for exact straight line motion
(b) Describe any one type of exact straight line motion mechanism with the help of a
sketch.
3 (a) What do you mean by Coriolis component of acceleration? When it will exist?
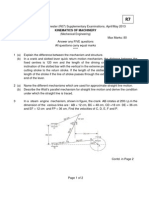
(b) Locate all the instantaneous centers of the slider crank mechanism as shown in figure.
The lengths of cranks OB and connecting rod AB are 100 mm and 400 mm
respectively. If the crank rotates clockwise with an angular velocity of 10 rad/s, find:
(i) Velocity of the slider A, and (ii) Angular velocity of the connecting rod AB.
4 (a) What is a Hookes joint? Where is it used? Sketch a polar velocity diagram of a
Hookes joint and mark its salient features.
(b) Derive an expression for the ratio of angular velocities of the shafts of a Hookes joint.
3
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net www.android.jntuworld.com
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code: 9A03401
*****
Page 2 of 2
5 Differentiate between:
(a) Pitch point and trace point and
(b) Period of ascent and period of decent.
(c) Draw the profile of a cam which raises a value with S.H.M. through 3 cm in 1/3 of
revolution, keep it fully raised through 1/12 revolution and it is closed in next 1/3
revolution with S.H.M. the valve remains closed during the rest of the revolution. The
diameter of the roller is 1 cm and minimum radius of the cam is to be 2 cm. The axis
of the valve rod is offset by 1.0 cm from the axis of cam shaft.
6 (a) Derive an expression for the centre distance of a pair of spiral gears.
(b) The pitch circle diameter of the smaller of the two spur wheels which mesh externally
and have involute teeth is 100 mm. The numbers of teeth are 16 and 32. The
pressure angle is 20
0
and the addendum is 0.32 of the circular pitch. Find the length
of the path of contact of the pair of teeth.
7 The following data relate to a flat belt drive:
Power transmitted =18 kW.
Pulley diameter =180 cm.
Angle of contact =175
0
.
Speed of pulley =300 r.p.m.
Coefficient of friction between belt and pulley surface =0.30.
Permissible stress for belt =300 N/cm
2
.
Thickness of belt =8 mm.
Density of belt material =0.95 x 10
-3
gm/cm
3
.
Determine the width of belt required taking centrifugal tension into account.
8 (a) Explain the term, sun and planet gears. With a neat sketch explain the working of an
epicyclic gear train with a sun and planet gear.
(b) Two parallel shafts are to be connected by spur gearing. The approximate distance
between the shafts is 600 mm. If one shaft runs at 120 r.p.m and other at 360 r.p.m.
Find number of teeth on each wheel if module is 8 mm. Also determine the exact
distance apart of the shafts.
3
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net www.android.jntuworld.com
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code: 9A03401
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, April/May 2013
KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY
(Mechanical Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70
Answer any FIVE questions
All questions carry equal marks
*****
Contd. in Page 2
Page 1 of 2
1 (a) What is a machine? Giving example, differentiate between a machine and structure.
(b) Sketch and describe the working of two different types of quick return mechanisms.
Give examples of their applications. Derive an expression for the ratio of times taken in
forward and return stroke for one of these mechanisms.
2 (a) Sketch and describe the Peaucellier straight line mechanism indicating clearly the
conditions under which the point P on the corners of the rhombus of the mechanism
generates a straight line.
(b) Prove geometrically that the above mechanism is capable of producing straight line.
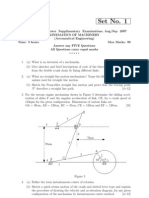
3 In a four bar chain ABCD, AD is fixed and is 15 cm long. The crank AB is 4 cm long
and rotates at 120 r.p.m clockwise, while the link CD (8 cm) oscillates about D. BC and
AD are of equal length. Find:
(i) The angular velocity and angular acceleration of link CD when angle BAD =60.
(ii) The velocity and acceleration of the points B and C.
4 (a) An Ackermann steering gear does not satisfy the fundamental equation of steering
gear at all positions. Yet it is widely used. Why?
(b) The driving shaft of a double Hookes joint rotates at 400 rpm. The angle of the driving
and of the driven shaft with the intermediate shaft is 20
0
. If somehow the forks of the
intermediate shaft lie in planes perpendicular to each other. Determine the maximum
and the minimum velocities of the driven shaft.
5 Draw the profile for the disc cam offset 20 mm to the right of the centre of the cam
shaft. The base circle diameter is 75 mm and the diameter of the roller is 10 mm, the
follower is to move outward a distance of 40 mm with S.H.M. in 140
0
of the cam
rotation to dwell for 40
0
of cam rotation to move inward with 150
0
of cam rotation with
uniform acceleration and retardation. Calculate the maximum velocity and acceleration
of the follower during each stroke if the cam shaft rotates at 90 r.p.m.
4
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net www.android.jntuworld.com
J
N
T
U
W
O
R
L
D
Code: 9A03401
*****
Page 2 of 2
6 (a) Explain what interference is and how it is prevented.
(b) A spur gear has a module of 3 mm and its pitch line velocity is 942.45 mm/s. if the
number of teeth of this spur gear is 20, find the speed of the gear. Also determine its
circular pitch.
7 A leather belt 200 mm x 10 mm is of density 1.1 gm /cc. its maximum permissible
tension is 200 N/ cm
2
. If the ratio of tensions is 1.8, determine at what velocity should
it be run so as to transmit maximum power? Also, determine the maximum power
transmitted.
8
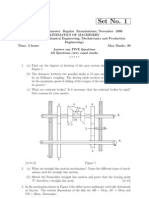
An epicyclic train is shown in figure Internal gear A is keyed to the driving shaft and
has 30 teeth. Compound wheel C and D of 20 and 22 teeth respectively are free to
rotate on the pin fixed to the arm P which is rigidly connected to the driven shaft.
Internal gear B which has 32 teeth is fixed. If the driving shaft runs at 60 r.p.m.
clockwise, determine the speed of the driven shaft. What is the direction of rotation of
driven shaft with reference to driving shaft?
4
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jwjobs.net www.android.jntuworld.com
Вам также может понравиться
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3От EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Design Optimization of Fluid Machinery: Applying Computational Fluid Dynamics and Numerical OptimizationОт EverandDesign Optimization of Fluid Machinery: Applying Computational Fluid Dynamics and Numerical OptimizationОценок пока нет
- Electrician Mostly Asked MCQ For RRB ALP PDFДокумент32 страницыElectrician Mostly Asked MCQ For RRB ALP PDFSajid Faniband100% (1)
- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesДокумент22 страницыEquilibrium of Rigid BodiesSpiro DourbalyОценок пока нет
- Sivudu Complete SerialДокумент218 страницSivudu Complete SerialSri R80% (10)
- SHS-General Chemistry 1Документ32 страницыSHS-General Chemistry 1JC PerezОценок пока нет
- Fin Plate Beam-To-column-flange Connection (GB)Документ16 страницFin Plate Beam-To-column-flange Connection (GB)Vlad MosОценок пока нет
- 9A03401 Kinematics of MachineryДокумент8 страниц9A03401 Kinematics of MachinerysivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- 9A14402 Theory of MachinesДокумент8 страниц9A14402 Theory of MachinessivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of MachineryДокумент9 страницKinematics of MachineryChinmay SahooОценок пока нет
- 9A14402 Theory of MachinesДокумент8 страниц9A14402 Theory of MachinessivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- ME2203 M.J 2007Документ0 страницME2203 M.J 2007Venkatesh RajamaniОценок пока нет
- R7220302 Kinematics of MachineryДокумент2 страницыR7220302 Kinematics of MachinerysivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- 9A03401 Kinematics of MachineryДокумент8 страниц9A03401 Kinematics of MachinerysivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- Rr222105 Kinematics of MachineryДокумент11 страницRr222105 Kinematics of MachinerySrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- 1424R05310304 Kinematics of MacДокумент10 страниц1424R05310304 Kinematics of Macأحمد جمالОценок пока нет
- r05310304 Kinematics of MachineryДокумент10 страницr05310304 Kinematics of MachinerySRINIVASA RAO GANTAОценок пока нет
- Me1252 Kinematics of MachineryДокумент3 страницыMe1252 Kinematics of MachineryManikandan SelvamОценок пока нет
- Upto 2010 KomДокумент36 страницUpto 2010 KompsnasabariОценок пока нет
- EMG 2208 - Mechanics of Machines - Assignment - MMU Sept 2012Документ4 страницыEMG 2208 - Mechanics of Machines - Assignment - MMU Sept 2012Charles OndiekiОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of Machinery November Am Rr222105Документ12 страницKinematics of Machinery November Am Rr222105Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryОценок пока нет
- 9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignДокумент8 страниц9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignsivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- Me6401 Kinematics of Machinery UNIT-I (Basics of Mechanism)Документ8 страницMe6401 Kinematics of Machinery UNIT-I (Basics of Mechanism)Ãraviñdhañ RändýОценок пока нет
- NR 220304 Kinematics of MachineryДокумент11 страницNR 220304 Kinematics of MachinerySrinivasa Rao GОценок пока нет
- 133BB112017Документ3 страницы133BB112017prempragupta123Оценок пока нет
- Unit-1: Introduction: Question BankДокумент12 страницUnit-1: Introduction: Question BankAmit BharadwajОценок пока нет
- Cms College of Engineering, Namakkal: Unit 1 - Basics of MechanismsДокумент17 страницCms College of Engineering, Namakkal: Unit 1 - Basics of MechanismsRajueswarОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of Machinery Question BankДокумент7 страницKinematics of Machinery Question BankpanneerthambiОценок пока нет
- rr310304 Kinematics of MachineryДокумент12 страницrr310304 Kinematics of MachinerySrinivasa Rao GОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological UniversityДокумент3 страницыGujarat Technological UniversityKrinal AdakiОценок пока нет
- Assignment Unit - 1: 2) .A Pair of Involute Gears Is in Mesh. The Application Restricts The Space To Accommodate TheseДокумент4 страницыAssignment Unit - 1: 2) .A Pair of Involute Gears Is in Mesh. The Application Restricts The Space To Accommodate TheserahulОценок пока нет
- rr310304 Kinematics of MachineryДокумент11 страницrr310304 Kinematics of MachinerySRINIVASA RAO GANTAОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of Machinery May2006 Rr222105Документ11 страницKinematics of Machinery May2006 Rr222105Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryОценок пока нет
- Mechanisms and Mechanical DesignДокумент9 страницMechanisms and Mechanical DesignNizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of MachinesДокумент2 страницыKinematics of Machinessameer_m_daniОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of Machinery Question BankДокумент5 страницKinematics of Machinery Question BankSree MurthyОценок пока нет
- Upto 2010 KomДокумент36 страницUpto 2010 KomRajueswarОценок пока нет
- Marks:: 3. (A) in (I) (Ir) (Iir) Rod. (B) TheoremДокумент3 страницыMarks:: 3. (A) in (I) (Ir) (Iir) Rod. (B) TheoremSaikumar reddyОценок пока нет
- A.R Engineering College: Villupuram Department of Mechanical EngineeringДокумент14 страницA.R Engineering College: Villupuram Department of Mechanical EngineeringVENKATESHОценок пока нет
- Unit Wise 16 Mark QuestionsДокумент29 страницUnit Wise 16 Mark QuestionsPreethi SharmiОценок пока нет
- TOM Question BankДокумент10 страницTOM Question BankMadhan Kumar GovindarajuОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of Machinary April 2021Документ2 страницыKinematics of Machinary April 2021mighty statusОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological UniversityДокумент3 страницыGujarat Technological UniversityKRISHI JANIОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of Machinery May2004 Rr222105 Nr220304Документ9 страницKinematics of Machinery May2004 Rr222105 Nr220304Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryОценок пока нет
- Time: 3 Hours Total Marks: 70: Printed Pages: Sub Code: Paper Id: Roll NoДокумент3 страницыTime: 3 Hours Total Marks: 70: Printed Pages: Sub Code: Paper Id: Roll NoAwanish SinghОценок пока нет
- 2017 Winter Question PaperДокумент4 страницы2017 Winter Question PaperRocky JОценок пока нет
- KDMДокумент3 страницыKDMDeep RavalОценок пока нет
- Fifth Semester B.Tech Degree Regular and Supplementary Examination December 2020Документ2 страницыFifth Semester B.Tech Degree Regular and Supplementary Examination December 2020Nandagopan GОценок пока нет
- Kom Assignment QuestionДокумент8 страницKom Assignment QuestionrajapratyОценок пока нет
- Sample Question Paper Kinematics of MachinesДокумент3 страницыSample Question Paper Kinematics of MachinesAnonymous utfuIcnОценок пока нет
- O in I and - Lled in y U: Foll W G Paper LL Roll No Tobefi o R Answer Book) Roll NoДокумент6 страницO in I and - Lled in y U: Foll W G Paper LL Roll No Tobefi o R Answer Book) Roll NoMohd. QadriОценок пока нет
- Kom 208Документ2 страницыKom 208Muzaffar AlamОценок пока нет
- Question Bank KomДокумент11 страницQuestion Bank KomStar SathishОценок пока нет
- Test No 01: Subject: - Theory of Machines Max Marks 100 Time 3 HourДокумент4 страницыTest No 01: Subject: - Theory of Machines Max Marks 100 Time 3 Hourvithal082Оценок пока нет
- Kinematics of MachinesДокумент2 страницыKinematics of Machinessameer_m_daniОценок пока нет
- Analysis OF Mechanisms GTU IMPДокумент5 страницAnalysis OF Mechanisms GTU IMPSwastik PanchalОценок пока нет
- 07a4ec04 Kinematics of MachineryДокумент8 страниц07a4ec04 Kinematics of Machineryaditya56Оценок пока нет
- Robot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlОт EverandRobot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlОценок пока нет
- Design and Implementation of Large-Range Compliant Micropositioning SystemsОт EverandDesign and Implementation of Large-Range Compliant Micropositioning SystemsОценок пока нет
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkОт EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkОценок пока нет
- Lect 3.1Документ18 страницLect 3.1Sri RОценок пока нет
- Internal Combustion EnginesДокумент27 страницInternal Combustion EnginesSri RОценок пока нет
- Unit IV MisraДокумент101 страницаUnit IV MisraSri RОценок пока нет
- Mechanical R-15 SyllabusДокумент95 страницMechanical R-15 SyllabusSri RОценок пока нет
- Chalapathi Institute of Engineering & Technology Chalapathi Nagar, Lam, Guntur - 34Документ3 страницыChalapathi Institute of Engineering & Technology Chalapathi Nagar, Lam, Guntur - 34Sri RОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mechanics Lab ManualДокумент36 страницEngineering Mechanics Lab ManualSri RОценок пока нет
- Genichi Taguchi: Incorrect He Is A Quality GuruДокумент3 страницыGenichi Taguchi: Incorrect He Is A Quality GuruSri RОценок пока нет
- Dyvasasanam by MadanbabuДокумент48 страницDyvasasanam by MadanbabuSri R100% (2)
- Unit IДокумент10 страницUnit ISri RОценок пока нет
- Jagtial Arya Vyshya CommunityДокумент2 страницыJagtial Arya Vyshya CommunitySri RОценок пока нет
- Yugavatharam Katha TeluguДокумент99 страницYugavatharam Katha TeluguSri RОценок пока нет
- HvpeДокумент3 страницыHvpeSri RОценок пока нет
- Mid Descriptive Questionpaper FormatДокумент2 страницыMid Descriptive Questionpaper FormatSri RОценок пока нет
- All Accounts Balance DetailsДокумент1 страницаAll Accounts Balance DetailsSri RОценок пока нет
- College Physics EOC Questions Chapter 8Документ9 страницCollege Physics EOC Questions Chapter 8Sri RОценок пока нет
- All About Robotics: LPI Contribution Number 1454Документ1 страницаAll About Robotics: LPI Contribution Number 1454Sri RОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Engineering R13 II Year Draft Syllabus Jntu9.inДокумент38 страницMechanical Engineering R13 II Year Draft Syllabus Jntu9.inSri RОценок пока нет
- 1 VДокумент3 страницы1 VSri RОценок пока нет
- ME PAPER 2sdadfasfДокумент72 страницыME PAPER 2sdadfasfRanga SriОценок пока нет
- Proceedings of Spie: Design and Simulation Analysis of A Magnetic Shielding Box For Ring Laser GyroscopeДокумент9 страницProceedings of Spie: Design and Simulation Analysis of A Magnetic Shielding Box For Ring Laser GyroscopeTanzil ZaidiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7: Magnetostatic FieldsДокумент39 страницChapter 7: Magnetostatic FieldsᄆᄉᄒОценок пока нет
- LensesДокумент13 страницLenseshelmi_tarmiziОценок пока нет
- Power Divider, Combiner and CouplerДокумент60 страницPower Divider, Combiner and Couplergaurav_juneja_4Оценок пока нет
- AngularДокумент57 страницAngularThomas Edoche EdocheОценок пока нет
- Chapter 16 - Solubility and Complex Ion EquilibriaДокумент17 страницChapter 16 - Solubility and Complex Ion Equilibriar1meshb1lla1969Оценок пока нет
- EC312 Lesson 15 Antenna Fundamentals-StudentsДокумент14 страницEC312 Lesson 15 Antenna Fundamentals-StudentsDonnОценок пока нет
- Lidocaine - HPLCДокумент3 страницыLidocaine - HPLCRoger (Sisfarma)Оценок пока нет
- Instruction ManualДокумент140 страницInstruction ManualJerryChenОценок пока нет
- Absolute Asymmetric SynthesisДокумент21 страницаAbsolute Asymmetric SynthesisJC Jane BarnesОценок пока нет
- Ansys Report 2Документ7 страницAnsys Report 2thilipkumarОценок пока нет
- Classical Field TheoryДокумент35 страницClassical Field TheorySagar JCОценок пока нет
- 11N90Документ7 страниц11N90rudra_1Оценок пока нет
- 08 - Chapter 2 PDFДокумент44 страницы08 - Chapter 2 PDFthegubesОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Cheat SheetДокумент1 страницаFinal Exam Cheat SheetDanielle GuindonОценок пока нет
- Academic Year 2020 - 2021 - ODD Semester PH8151 - Engineering Physics Unit-V Crystal PhysicsДокумент10 страницAcademic Year 2020 - 2021 - ODD Semester PH8151 - Engineering Physics Unit-V Crystal PhysicsBala NandaОценок пока нет
- KIE3004 Chapter 2 Plane WavesДокумент79 страницKIE3004 Chapter 2 Plane WavesKoay HV0% (1)
- EM 3000 Conzerv MeterДокумент4 страницыEM 3000 Conzerv Metersbhatta73Оценок пока нет
- Boundary Conditions in Fluid MechanicsДокумент6 страницBoundary Conditions in Fluid MechanicsnickolasnaimОценок пока нет
- Geometric Shapes and TransformationsДокумент10 страницGeometric Shapes and TransformationsisidroОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics by S K MondalДокумент179 страницFluid Mechanics by S K MondalAghu AkzОценок пока нет
- Convolution: 8.1. Linear Translation Invariant (LTI or LSI) OperatorsДокумент9 страницConvolution: 8.1. Linear Translation Invariant (LTI or LSI) OperatorsAnonymous OOeTGKMAdDОценок пока нет
- SalidaДокумент47 страницSalidaAriadna Sánchez CastilloОценок пока нет
- Crystal StructureДокумент16 страницCrystal StructurejyotiblossomsОценок пока нет
- Mini Projek Meriam BuluhДокумент6 страницMini Projek Meriam BuluheizharОценок пока нет