Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Manual Mantenimiento Mission 40
Загружено:
Daygor Martinez SabucoИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Manual Mantenimiento Mission 40
Загружено:
Daygor Martinez SabucoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Operation and Maintainence Guidelines
DTH HAMMER
Hammer break-out
To avoid damage on the Piston Case, use chain wrench or petol tongs and place it as shown in
the illustration below.
Hammer Type MISSION 40B MISSION 40B
Air Consumption (with optional low
volume tuning ring)
cfm m
3
/min. cfm m
3
/min.
150 psi / 10 bar 180 5.10 151 4.28
250 psi / 18 bar 370 10.48 315 8.92
350 psi / 24 bar 560 15.86 466 13.20
Operating Pressure:150 - 350 psi /10 - 24 bar
Hammer Length:36" / 914mm
Hammer Outside Diameter:3.86" / 98mm
Wrench Flats: 2.56" / 65mm
September 2003
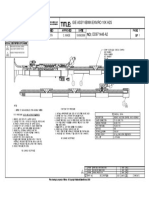
MISSION 40B
MISSION 40BH
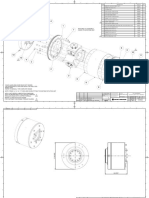
1a. Top Sub with 3 O-Rings, 2-3/8" API Reg. Pin 22 10 33-48001-1/16A
1b. Top Sub with 3 O-Rings, 2-7/8" API Reg. pin 22 10 33-48001-1/11A
2a. O-Ring Top Sub (Spares in Seal Kit)
2b. O-Rings Top Sub (inside) (Spares in Seal Kit)
3. Check Valve Dart 0.6 0.3 25-99001A
4. Check Valve Dart Spring 0.04 0.02 22-99072
5. Check Valve Guide 0.7 0.3 39-48001-1
6. Feed Tube Retainer Pin 0.05 0.03 12-99014
7. Feed Tube with Retainer Pin & Blank Choke, 1.5 0.7 37-48001-1A
7a. Choke Set, Blank
1
/
8
",
3
/
16
", &
1
/
4
" (not shown) 0.25 0.1 29-48017A
8. Tuning Ring for low volume (Not Included) 0.5 0.03 56-48552
9. Piston (for 32-M40B/16 & 32-M40B/11) 15.2 7 36-48081
9a Piston (for 32-M40BH/16) 15.2 7 36-48H01
10. Piston Case with Retainer Ring 33 15 35-48006A
11. Piston Retainer Ring 0.1 0.05 23-99029
12. O-Rings Guide Sleeve & Bit Ret. (3) (Spares in Seal Kit)
13. Guide Sleeve with 2 O-rings (Item #12) 4 1.8 26-48010A
14. Bit Retainer Ring w/O-ring (Item #12) 0.5 0.23 27-48006A
15. Driver Sub (O-ring not required) 7 3.2 34-48006
Not shown
Seal Kit - Includes 1 x item 2a, 2 x item 2b, & 7 x item 12 1 0.45 38-48056
16. Piston Retainer Ring Extractor (Not Included) 0.5 0.23 38-55061
Replacement Parts
Hammer Description Weight Part No.
(lb) (kg)
Mission 40B (2-3/8 API Reg Pin) 83 38 32-M40B/16
Mission 40B (2-7/8 API Reg Pin) 83 38 32-M40B/11
Mission40BH (Horizontal) (2-3/8 API Reg Pin only) 83 38 32-M40BH/16
Rebuild Kit (2-3/8 API Reg Pin) Includes items 1a, 10 & 15 ?? ?? 38-48001/16
Rebuild Kit (2-7/8 API Reg Pin) Includes items 1b, 10 & 15 ?? ?? 38-48001/11
1a or
1b
2a
14
12
12
11
10
2b
15
8
13
12
9
&
9a
3
5
6
4
7
Lubrication
Correct lubrication during drilling
operations is extremely important.
Inadequate lubrication is a major cause
of hammer wear and failure. Excessive
lubrication slows piston and makes
startup difficult.
Use rock drill oil only. Use Figure 1 to
select the correct grade of rock drill
oil.
The recommended amount of rock
drill oil for reliable operation is shown
in Figure 2. An alternative method is
0.15-0.25 quarts/hour per 100 cfm
(0.04 - 0.07 liters/hour per m
3
/min.)
Fig. 1
Rock drill oil chart
Ambient Air Temperature
I
S
O
V
i
s
c
o
s
i
t
y
(
c
S
t
@
4
0
C
)
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
-50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 F
-46 -40 -34 -29 -23 -18 -12 -7 -1 4 10 16 21 27 32 38 43 49 C
220
320
150
100
46
32
- Fig. 2 -
Recommended Oil Lubrication
Air Pressure Flow Rate
psi bar l/hr qt/hr
150 10 0.6 0.6
250 18 1.1 1.1
350 24 1.6 1.6
Use good quality Rock Drill Oil
Piston Retaining Ring Extractor - p/n 38-55061
see next page for more details
Ring Lifter
Ring Puller
10
11
Hammer Maintenance
Piston Case
The piston case (10) is reversible and assembles in either direction. Measure outside diameter regularly.
The piston case life is extended up to 50 percent longer if reversed in a timely manner.
Reversal must be done before wear limit is reached (see Common Procedures section). The best point
to reverse is based on experience in a particular application. Note: The reversal diameter published in
this manual is a recommendation only.
Regularly inspect all parts carefully for burrs, galling or cracks. Replace any parts which are
cracked. Use a file or emery paper to remove any burrs. Any parts which show signs of galling will
also have a mating part with similar damage. If the piston is galled it should be replaced and careful
inspection is required inside the piston case. It is strongly recommended to hone or polish inside the
piston case to smooth the galled surfaces. Look for causes of galling such as poor lubrication or
contamination and take corrective measures to avoid future damage. Neglecting to hone the galled
piston case before installing a new piston will lead to early and repeated piston failures.
Premature thread failure usually results from galling and corrosion and these two problems can be
avoided by using a good quality copper based Thread Grease every time the driver sub is removed
for bit changes. It is also recommended that Thread Grease be applied to the top sub thread every
100 hours or after 10,000 feet (3000 metres) of drilling.
Never grip hammer with any type of tongs over the piston case threads. Gripping with tongs over the
piston case threaded areas makes the threads very difficult to unscrew and can lead to premature
cracking due to jaw marks. Never use excessive force with a steel hammer or apply any weld to the
piston case as this may lead to premature failure and will be denied in the event that a claim is made
for warranty.
Piston Retainer Ring
Only one piston retainer ring is used. The piston retainer ring (11) is the first component to be installed
during hammer assembly. Insert the piston retainer ring into piston case at same end as the driver sub
(15) will be fitted.
Place the piston retainer ring at 90 to its final position and using the bolt on the back of the extractor
tool (16), push the ring so it slides inside the piston case. When it is close to the groove, again use
the bolt to manouever the ring 90 so it snaps into the groove.
To remove the piston retainer ring, simply place the curved side of the extractor tool against the wall
of the piston case, in line with the split in the ring and push forward until the ring lifts out of the groove.
Continue pushing until the ring turns sideways inside the piston case and then pull it out with the
retriever bolt on the back of the extractor tool.
When reversing the piston case, it is strongly recommended to replace the piston retainer ring to
ensure the Gap is maintained between the driver sub and piston case. (see pg.6)
9
Piston
Wipe the piston with rockdrill oil. Install piston (9) into piston
case through top sub end with nose end down (as shown).
Inspect used pistons for galling against piston case, guide sleeve,
or feed tube inside the center air hole. Polish as necessary. Install
used pistons with the piston case horizontal to avoid knocking guide sleeve
out of place.
Regularly inspect the piston striking face and remove any burrs (Peening) with a fine buffing or flap
wheel. DO NOT use a grinding wheel as the rough surface finish will propogate cracks and lead to
premature piston failure.
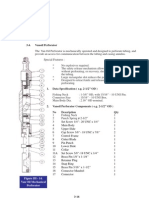
Top Sub Assembly
Oil and assemble parts before installation,
Pull the top sub o-ring (2a) over the top sub threads all the way to its groove,
Insert feed tube o-ring (2b) into the groove inside the top sub,
Assemble dart (3) and spring (4) into the check valve guide (5),
Install desired choke (7a) through feed tube (7) top,
Insert the check valve guide (5), dart (3), and spring (4) into to the feed tube (7)
Carefully line up pin holes,
Install tuning ring (8), if equipped, between the two shoulders on the feed tube (7),
Insert assembly into the top sub until seated, line up retainer pin holes and install feed tube
retainer pin (6),
Make sure the pin does not protrude into threads on either side,
Apply copper based thread grease on threads and install top sub assembly into the piston
case,
Ensure feed tube lines up in the piston center,
Never force assembly, and
Turn clockwise to tighten.
2a
2b
(Inside)
4
5
7a
3
8
(optional)
7
6
Guide Sleeve
Install two O-rings (12) on guide sleeve (13). These O-rings are critical for proper hammer align-
ment and for holding guide sleeve in place when changing bits.
The guide sleeve will install correctly into the piston case only in one direction. Coat the guide
sleeve with oil and insert with the shoulder that fits against the piston retaining ring.
Use the shank of a discarded MIssion Bit to push the guide sleeve into piston case. Continue to
push the guide sleeve until it will go no
further and then it is in the correct position.
To remove guide sleeve, stand piston case
vertically with guide sleeve nearest the
ground.
From the top sub end, insert a wooden or
aluminium bar which is the same length as
the piston case and 1/4 (6mm) smaller in
diameter than the piston and tap against
the guide sleeve until it can be remove
from the driver sub end of the piston case.
Carefully inspect guide sleeve inside where it
seals against the piston nose. Polish if
surface is galled. Replace if cracked or
otherwise damaged.
Driver Sub
Install driver sub (15) using only copper-based
thread grease on its threads. During storage, the bit retainer ring (14), made up of two half rings
plus an O-ring (12), may be inserted without a drill bit installed.
When assembling the hammer without a drill bit, use a cover to prevent contamination from
entering hammer.
Inspect used driver subs for nicks or burrs in the thread. Polish as needed.
Inspect interior spline for wear. Replace driver sub if spline is at one third or less of original
width.
Check the driver sub's remaining outside diameter and discard if appropriate. Most of the time,
the driver sub will wear more rapidly than other hammer components; two spare driver subs are
typically used per piston case. Never install a used driver sub on a new piston case.
Sometimes vertical channels are eroded adjacent to drill bit flushing groves. When replacing the
bit, always index the driver sub to alleviate this problem. Some operators rebuild driver subs by
adding weld material. This is not recommended as it may cause warping or cracking. Welding,
as described herein, cancels any remaining driver sub or piston case thread warranty.
The Gap
When the Driver Sub has been screwed into the Piston Case with the Guide Sleeve and Bit Re-
tainer Rings installed, a gap must be visible where the Piston Case and Driver Sub join. The
dimension of this gap is not critical, but it should not be less than 0.020 (0.5mm) and not more
than 0.040 (1.00mm). When this gap is no longer visible, the Piston Retainer Ring should be
replaced. If hammer operation continues with no visible gap, there is a high risk of component
failure. Warranty claims for broken parts may be denied in this situation.
15
14
13
12
Common Procedures
Start-up
The MISSION hammer line has a large contact surface between the piston and the inside of the
piston case. This improves lubrication and increases wear life. It also requires attention during new
hammer and cold hammer start-up. Before starting a brand new hammer or a used hammer which
has not been used for more than 2 days, flush hammer thoroughly with clean, lubricated air from
the compressor before attempting to drill. This will warm the hammer and remove any oil buildup
that has migrated down from the drill pipe. This procedure is essential in cold climates with tight
hammer clearances and thick oil.
Wear Limits and Case Reversal
Piston Case Outside Diameter (New).................................................................... 3.86 (98mm)
Piston Case Outside Diameter (Recommended Time to Reverse).......................3.62" (92mm)
Piston Case Outside Diameter (Time to Replace)..................................................3.39" (86mm)
Piston Case Inside Diameter Wear Limit......................................................3.0595" (77.711mm)
Piston Diameter Wear Limit.........................................................................3.0465" (77.381mm)
Maximum Piston Case/Piston Clearance..........................................................0.013" (0.33mm)
Driver sub length (Recommended Time to Replace or Rebuild).......................2.380 (60.4mm)
Minimum Used Bit Diameter....................................................................................3.78 (96mm)
Rotation Speed
Rotational speed is largely determined by drilling conditions, typically 20-60 RPM for a 4-inch
hammer. As a result of its higher piston frequency and penetration rate, the MISSION 40B should
have a higher rotation speed than conventional hammers. Depending on the rock type and
conditions, it may be necessary to increase rotation speed 10-15 percent to achieve the smoothest
and most efficient drilling.
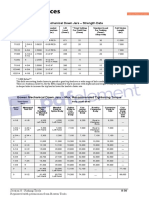
Choice of Choke
180 206 239 284
370 412 464 538
560 618 690 791
5.10 5.83 6.77 8.04
10.48 11.67 13.14 15.23
15.86 17.50 19.54 22.40
151 177 210 255
315 357 409 483
466 524 596 697
4.28 5.01 5.95 7.22
8.92 10.11 11.58 13.68
13.20 14.84 16.88 19.74
Blank 1/8 3/16 1/4
HAMMER FL HAMMER FL HAMMER FL HAMMER FL HAMMER FLO OO OOW RA W RA W RA W RA W RATES TES TES TES TES WITH WITH WITH WITH WITH V VV VVARIOUS CHOKE ARIOUS CHOKE ARIOUS CHOKE ARIOUS CHOKE ARIOUS CHOKE
HIGH VOLUME - Without Tuning Ring (Donut) in Top Sub
LOW VOLUME - With Tuning Ring (Donut) in Top Sub
Blank 1/8 3/16 1/4
150 psi
250 psi
350 psi
10 bar
18 bar
24 bar
150 psi
250 psi
350 psi
10 bar
18 bar
24 bar
Weight on Bit
For efficient drilling it is important that the buttons on the face of the bit are in close con-
tact with the rock at all times. Drilling feed weight on bit must be sufficient to keep the bit
closed against the driver sub allowing the maximum amount of piston energy to be transferred
to the rock.
If drilling feed weight is insufficient, the rock breaking energy stays within the hammer and
will cause premature component failure.
Several problems can occur if drilling feed weight is excessive. The buttons will penetrate
too deep into the rock resulting in bit face damaged, the rotation torque will increase, flushing
will be reduced in softer ground and in some conditions, hole deviation could occur.
The optimum weight on bit will vary according to many conditions, such as the type of
rock, bit design, rotation speed. The optimum weight on bit is best determined by the driller,
but below is a guide for weights at various operating pressures.
Minimum recommended weight on bit.
DRILTECH MISSION, LLC
1300 HERITAGE PARKWAY MANSFIELD, TEXAS 76063 USA Tel + 1 817 453 2600 Telefax +1 817 453 2389
Registered Trademarks US Patent Nos. 1467904 1345598 348800 3450099 34500443 6131672 other patents pending
P/N M40B, 3/03 2001 DRILTECH MISSION, LLC
Website Address :- www.driltechmission.sandvik.com
WARRANTY NOTICE
If the Mission40 hammer is operated at pressures above 350 psi (24 bar), greatly increased productivity can be
achieved, but Driltech Mission will not be held responsible for component failure or premature wear.
The warranty against faulty workmanship and materials on the
Mission40 Hammer and Bits is only valid
for operating pressures up to 350 psi (24 bar) only.
psi 150 200 250 300 350
lbs 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500
bar 10 14 17 20 24
kgs 680 910 1140 1360 1590
Вам также может понравиться
- Sinodrills DTH Hammer Bits, DTH Hammer, DTH Bits, DTH Drill Rods, ODEX, SymmetirxДокумент26 страницSinodrills DTH Hammer Bits, DTH Hammer, DTH Bits, DTH Drill Rods, ODEX, SymmetirxJackChanОценок пока нет
- FSH ToolДокумент9 страницFSH ToolArcenio Jimenez Morgan100% (1)
- HQ Heavy Duty ChuckДокумент2 страницыHQ Heavy Duty ChuckPDLОценок пока нет
- Rotary CuttersДокумент3 страницыRotary CuttersISPОценок пока нет
- RollerLatch UndergroundHeadAssembly Brochure EnglishДокумент4 страницыRollerLatch UndergroundHeadAssembly Brochure EnglishCarlos Antonio Chavez EgoavilОценок пока нет
- Super Maxbit Hammer Bit BrochureДокумент6 страницSuper Maxbit Hammer Bit BrochurezapspazОценок пока нет
- Secoroc RotaryДокумент84 страницыSecoroc RotaryElgi Zacky ZachryОценок пока нет
- CDSEZ RC2.23mtr AustraliaДокумент33 страницыCDSEZ RC2.23mtr AustraliaElgi Zacky ZachryОценок пока нет
- Core BarrelsДокумент20 страницCore BarrelsEmerson PasquarelliОценок пока нет
- Sandvik Rock Drill Steels 259 Eng. March 2003Документ12 страницSandvik Rock Drill Steels 259 Eng. March 2003Alejandro Arrieta C100% (1)
- 9851 2962 01b - Robbins 34RH C - Technical Specification - EnglishДокумент8 страниц9851 2962 01b - Robbins 34RH C - Technical Specification - EnglishJulio Acevedo MartinezОценок пока нет
- Titan Energetics Spectra2 Coiled Tubing Cutters Flyer3Документ2 страницыTitan Energetics Spectra2 Coiled Tubing Cutters Flyer3faiz bugtiОценок пока нет
- Hawkjaw Sr. Manual M100K-2GSR Serial Numbers 201 To 370Документ215 страницHawkjaw Sr. Manual M100K-2GSR Serial Numbers 201 To 370sitaОценок пока нет
- Sandvik Wireline Catalogue 2007 PDFДокумент31 страницаSandvik Wireline Catalogue 2007 PDFGeorge BoafoОценок пока нет
- Atlas Copco Brand Identity Manual For DistributorsДокумент20 страницAtlas Copco Brand Identity Manual For DistributorsAndré ZanutoОценок пока нет
- Cubex Mining Products 2006Документ10 страницCubex Mining Products 2006Diogo Cordova100% (1)
- Roller Cone Design ApplicationДокумент60 страницRoller Cone Design Applicationamin peyvandОценок пока нет
- 146 Pusherlegs and StopersДокумент1 страница146 Pusherlegs and StopersKenny CasillaОценок пока нет
- Manual Del PerforistaДокумент2 страницыManual Del PerforistaJuan Carlos Negro Martinez RojasОценок пока нет
- Please Specify Tubing Diameter and Weight When Ordering.: R o T A R o F R e P H C N U P G N I B U T e N I L e R I W E C PДокумент1 страницаPlease Specify Tubing Diameter and Weight When Ordering.: R o T A R o F R e P H C N U P G N I B U T e N I L e R I W E C PSLK SPVОценок пока нет
- 42mm NQ DST Permeability Testing Inflatable PackersДокумент2 страницы42mm NQ DST Permeability Testing Inflatable PackersRipe PackersОценок пока нет
- 118 Secoroc Rock ToolsДокумент13 страниц118 Secoroc Rock ToolsKenny CasillaОценок пока нет
- Bowen Mechanical Jar DownДокумент1 страницаBowen Mechanical Jar Downnasr yassinОценок пока нет
- 6991 1450 01b Overhauling Instructions For Rotation Unit Diamec U4 PHCДокумент35 страниц6991 1450 01b Overhauling Instructions For Rotation Unit Diamec U4 PHCMoises Fernando Quijada ContrerasОценок пока нет
- Spooler De710 Parts Be00002544852Документ1 страницаSpooler De710 Parts Be00002544852Morgan DunnОценок пока нет
- Redress Kit For N Test ToolДокумент1 страницаRedress Kit For N Test Toolsong Li100% (1)
- Chap 03-Rotary Percussive Drilling Accessories PDFДокумент12 страницChap 03-Rotary Percussive Drilling Accessories PDFpnakurОценок пока нет
- PCE WL Releasable OvershotДокумент2 страницыPCE WL Releasable OvershotFabio ParceroОценок пока нет
- 4-06 Tandem Side Loading Stripper PackerДокумент14 страниц4-06 Tandem Side Loading Stripper PackerDEATH ASSASSIN GAMERОценок пока нет
- Global Product Catalogue: Reverse Circulation ToolsДокумент20 страницGlobal Product Catalogue: Reverse Circulation Toolsengelberth22Оценок пока нет
- 6-24 Tandem Pump Assembly Front Drive Pump Housing, Valves and PlugsДокумент4 страницы6-24 Tandem Pump Assembly Front Drive Pump Housing, Valves and PlugsPaull SalasОценок пока нет
- 6991 1820 01 - Diamec Smart 8 Technical Specification - EnglishДокумент8 страниц6991 1820 01 - Diamec Smart 8 Technical Specification - EnglishPABLOОценок пока нет
- Geothermal & Waterwell DrillingДокумент4 страницыGeothermal & Waterwell DrillingGogot Pantja ParijogoОценок пока нет
- 96 64000e Tesco Power CatwalkДокумент4 страницы96 64000e Tesco Power CatwalkSoufiane HazelОценок пока нет
- CS4002 U-Deck Recommended SparesДокумент5 страницCS4002 U-Deck Recommended SparesedwinОценок пока нет
- Drilling Depth Guidelines: Fluid Filled Metric U.S. Drill Rod/Core Barrel Hole Depth (Meters) Hole Depth (Feet)Документ10 страницDrilling Depth Guidelines: Fluid Filled Metric U.S. Drill Rod/Core Barrel Hole Depth (Meters) Hole Depth (Feet)Peter Leano100% (1)
- DTH Tools PDFДокумент48 страницDTH Tools PDFengineerg165285Оценок пока нет
- Cluster Drill Holte PDFДокумент7 страницCluster Drill Holte PDFmevice63Оценок пока нет
- 9852 2423 01 Boom Overhaul Kit But 28Документ39 страниц9852 2423 01 Boom Overhaul Kit But 28Jorge B100% (1)
- Vanoil PerforatorДокумент3 страницыVanoil PerforatorFrans TongaОценок пока нет
- Atlas Copco Secoroc: Reverse Circulation EquipmentДокумент12 страницAtlas Copco Secoroc: Reverse Circulation EquipmentSergio Perez100% (1)
- Hydraulic Oil JarДокумент3 страницыHydraulic Oil JarYermi ParabangОценок пока нет
- Raise Boring Product Catalogue 2007Документ16 страницRaise Boring Product Catalogue 2007Alexandre Moreira100% (1)
- LF 230 Core Drill: Technical Data SheetДокумент7 страницLF 230 Core Drill: Technical Data SheetLuis Aparcana100% (1)
- Baker PDFДокумент6 страницBaker PDFanthony silvaОценок пока нет
- Wireline Retriever: Instruction Manual 8820Документ5 страницWireline Retriever: Instruction Manual 8820GОценок пока нет
- Presentation ON Aggregate and Concrete Production: Kanhu Charan Nayak (1654006) Shantanu Kumar Behera (1654012)Документ92 страницыPresentation ON Aggregate and Concrete Production: Kanhu Charan Nayak (1654006) Shantanu Kumar Behera (1654012)PritamОценок пока нет
- RH550MMДокумент30 страницRH550MMAmber SmithОценок пока нет
- Fishing EquipmentДокумент8 страницFishing EquipmentRizwan FaridОценок пока нет
- Sandvik De880 Multi-Purpose Surface DrillДокумент4 страницыSandvik De880 Multi-Purpose Surface DrillAhmed Ghoneim100% (2)
- Roller Cone Bit DesignДокумент17 страницRoller Cone Bit Designknn52unnОценок пока нет
- JointДокумент2 страницыJointJohnОценок пока нет
- Self-Drilling Anchor System: Nut PlateДокумент1 страницаSelf-Drilling Anchor System: Nut PlateJackChanОценок пока нет
- Hawkjaw Iron Roughneck 65K-950JR Operations Maintenance Parts ManualДокумент155 страницHawkjaw Iron Roughneck 65K-950JR Operations Maintenance Parts ManualFranklin Jose Almera AcostaОценок пока нет
- Sec Roc Drill Pipe and AdaptersДокумент16 страницSec Roc Drill Pipe and AdaptersSerkanAl50% (2)
- 1 DD971446 - GihДокумент1 страница1 DD971446 - GihAbhinav KumarОценок пока нет
- DR900 U Specifications: Depth Rating Wireline Hoist AssemblyДокумент1 страницаDR900 U Specifications: Depth Rating Wireline Hoist AssemblyJhonattan GonzalezОценок пока нет
- 12 Lubrication SystemДокумент5 страниц12 Lubrication SystemAnderson L RoncerosОценок пока нет
- TDRДокумент1 страницаTDRJones LakerОценок пока нет
- M-S-215 Static Cone PenetrometerДокумент4 страницыM-S-215 Static Cone PenetrometerJunpieter GultomОценок пока нет
- Everything About WoolДокумент31 страницаEverything About Woolletuongthuy2000Оценок пока нет
- A Beautiful Mine - UpgradedДокумент19 страницA Beautiful Mine - UpgradedalОценок пока нет
- Smokey EyesДокумент107 страницSmokey EyesSangita SarmaОценок пока нет
- Risk Assessment No. 35 USING GRINDER Rev 0Документ2 страницыRisk Assessment No. 35 USING GRINDER Rev 0Lalit ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- Muster List & Boarding Sequences 20.03.2023Документ2 страницыMuster List & Boarding Sequences 20.03.2023SenpaiОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 (Home Sweet Home) : Book (Page 25)Документ7 страницUnit 3 (Home Sweet Home) : Book (Page 25)Athirah FadzilОценок пока нет
- Word ClassificationДокумент43 страницыWord ClassificationlekinhthangОценок пока нет
- 1) Count Variation: 2) Unevenness or Irregularity: 3) Frequently Occurring FaultsДокумент40 страниц1) Count Variation: 2) Unevenness or Irregularity: 3) Frequently Occurring FaultsshaifaliОценок пока нет
- Brand KeyДокумент39 страницBrand KeyHaree MCBОценок пока нет
- The Elements and Principles of Design With ExamplesДокумент74 страницыThe Elements and Principles of Design With ExamplesAr Abhinav SrivastavОценок пока нет
- Shiftee: Shirts To Shift ToДокумент23 страницыShiftee: Shirts To Shift ToSheila SerranoОценок пока нет
- Massai TribeДокумент1 страницаMassai TribeYishu MalhotraОценок пока нет
- Promageddon Waiver 2014 WordДокумент1 страницаPromageddon Waiver 2014 Wordapi-245697299Оценок пока нет
- Art AppreciationДокумент13 страницArt AppreciationCha AcuezaОценок пока нет
- Supplemental Guidelines On The Delinquency Report System: (Strengthening The Disciplinary Authority of Chief of Office)Документ26 страницSupplemental Guidelines On The Delinquency Report System: (Strengthening The Disciplinary Authority of Chief of Office)Einno SnowОценок пока нет
- Filipino Musical InstrumentsДокумент9 страницFilipino Musical InstrumentsralphОценок пока нет
- Magna Bend SopДокумент1 страницаMagna Bend Sopvasu_suvaОценок пока нет
- Diagnostic Study Report of Readymade Garment Cluster - BangaloreДокумент46 страницDiagnostic Study Report of Readymade Garment Cluster - BangalorevenkateshdaveyОценок пока нет
- Pashmina Vs Cashmere - What Is The Difference - Which Is BetterДокумент15 страницPashmina Vs Cashmere - What Is The Difference - Which Is BetterSJVN CIVIL DESIGN100% (1)
- Bahasa Inggris LatihanДокумент91 страницаBahasa Inggris LatihanYudiSuhendarОценок пока нет
- DfaДокумент4 страницыDfaElla Dia HebronОценок пока нет
- A Study of Iconic WomenДокумент28 страницA Study of Iconic WomenKay100% (2)
- Guideline For Green HotelДокумент66 страницGuideline For Green HotelsufijinnОценок пока нет
- I'Ll Go Home Then, It's Warm and Has Chairs - David ThorneДокумент195 страницI'Ll Go Home Then, It's Warm and Has Chairs - David ThorneStelian Subotin100% (1)
- Egyptian Arabic-English SentencesДокумент15 страницEgyptian Arabic-English Sentencesgodsent7Оценок пока нет
- Fingersmith EssayДокумент2 страницыFingersmith EssaydpagoffsОценок пока нет
- Bikol Dictionary PDFДокумент333 страницыBikol Dictionary PDFJovito AseradoОценок пока нет
- Jray CVДокумент7 страницJray CVapi-283057640Оценок пока нет
- Fushiguro TДокумент332 страницыFushiguro Tangelaagbonze82Оценок пока нет
- Grey's Anatomy - 03x01 - Time Has Come Today - Uncut DVDRipДокумент53 страницыGrey's Anatomy - 03x01 - Time Has Come Today - Uncut DVDRipNabila Exa TalitaОценок пока нет