Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Diract and Indiract
Загружено:
Terry MillerАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Diract and Indiract
Загружено:
Terry MillerАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
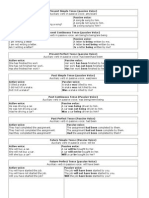
Present - past
"I never understand you," she told me. - She told me she never understood me.
"We are doing exercises," he explained. - He explained that they were doing exercises.
Present perfect - past perfect
"I have broken the window," he admitted. - He admitted that he had broken the window.
"I have been waiting since the morning," he complained. - He complained that he had been
waiting since the morning.
Past - past perfect
"She went to Rome," I thought. - I thought that she had gone to Rome.
"He was thinking of buying a new car," she said. - She said he had been thinking of buying
a new car.
Will - conditional
Will changes into the conditional.
I will come on Sunday," he reminded me. - He reminded me that he would come on
Sunday.
Notes
I shall, we shall usually become would.
"I shall appreciate it," he said. - He said he would appreciate it.
I should, we should usually change into would.
"We should be really glad," she told us. - She told us they would be really glad.
May becomes might.
"I may write to him," she promised. - She promised that she might write to him
Active And Passive Voice Sentences
In last we have shared active and passive voice sentences with
their pronunciation for easy of understanding.
Active Voice And Passive Voice
Active Voice And Passive Voice
Active Voice And Passive Voice
Active Passive Voice Rules
Active Passive Voice Ru PASSIVE VOICE FOR ALL TENSES
RULES
The places of subject and object in sentence are inter-changed in passive voice.
3rd form of verb (past participle) will be used only (as main verb) in passive voice.
Auxiliary verbs for each tense are given below in the table.
Present Simple Tense (passive Voice)
Auxiliary verb in passive voice: am/is/are
Active voice:
He sings a song.
He does not sing a song.Does he sing a song?
Passive voice:
A song is sung by him.
A song is not sung by him.
Is a song sung by him?
Present Continuous Tense (passive Voice)
Auxiliary verb in passive voice: am being/is being/are being
Active voice:
I am writing a letter
I am not writing a letter.
Am I writing a letter?
Passive voice:
A letter is being written by me.
A letter is not being written by me.
Is a letter being written by me?
Present Perfect Tense (passive Voice)
Auxiliary verb in passive voice: has been/have been
Active voice:
She has finished his work
She has not finished her work.
Has she finished her work?
Passive voice:
Her work has been finished by her.
Her work has not been finished by her.
Has her work been finished by her?
Past Simple Tense (passive Voice)
Auxiliary verb in passive voice: was/were
Active voice:
I killed a snake
I did not kill a snake.
Did I kill a snake?
Passive voice:
A snake was killed by me.
A snake was not killed by me.
Was a snake killed by me?
Past Continuous Tense (Passive Voice)
Auxiliary verb in passive voice: was being/were being
Active voice: Passive voice:
He was driving a car.
He was not driving a car.
Was he driving a car?
A car was being driven by him.
A car was not being driven by him.
Was a car being driven by him?
Past Perfect Tense (Passive Voice)
Auxiliary verb in passive voice: had been
Active voice:
They had completed the assignment.
They had not completed the assignment.
Had they completed the assignment?
Passive voice:
The assignment had been completed by them.
The assignment had not been complete by them.
Had the assignment been completed by them?
Future Simple Tense (Passive Voice)
Auxiliary verb in passive voice: will be
Active voice:
She will buy a car.
She will not buy a car.
Will she buy a car?
Passive voice:
A car will be bought by her.
A car will not be bought by her.
Will a car be bought by her?
Future Perfect Tense (passive Voice)
Auxiliary verb in passive voice: will have been
Active voice:
You will have started the job.
You will have not started the job.
Will you have started the job?
Passive voice:
The job will have been started by you.
The job will not have been started by you.
Will the job have been started by you?
Note: The following tenses cannot be changed into passive voice.
1. Present perfect continuous tense
2. Past perfect continuous tense
3. Future continuous tense
4. Future perfect continuous tense
5. Sentence having Intransitive verbs
les
Active Passive Voice Rules
Active Passive Voice Rules
Active voice
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about a grammatical voice. For other uses, see Active voice (disambiguation). For
advice and arguments about the use of active or passive voice, see English passive voice.
Active voice is a grammatical voice common in many of the world's languages. It is
the unmarked voice for clauses featuring a transitive verb in nominativeaccusative languages,
including English and most other Indo-European languages.
Active voice is used in a clause whose subject expresses the agent of the main verb. That is, the
subject does the action designated by the verb.
[1]
A sentence whose agent is marked as grammatical
subject is called an active sentence. In contrast, a sentence in which the subject has the role
of patient or theme is named a passive sentence, and its verb is expressed in passive voice. Many
languages have both an active and a passive voice; this allows for greater flexibility in sentence
construction, as either the semantic agent or patient may take the syntactic role of subject.
[2]
Examples[edit]
In the following examples the active and passive voice are illustrated with pairs of sentences using
the same transitive verb.
Language Active voice Passive voice
English The dog bit the postman. The postman was bitten by the dog.
Arabic
. (The dog
bit the postman.)
'e d alklbu sa'ey albryd
. (The
postman was bitten by the dog.)
'eud sa'ey albryd bwasth alklb
French
Brackett a crit ce livre. (Brackett
wrote this book.)
Ce livre a t crit par Brackett. (This book was
written by Brackett.)
German
Der Hund biss den Postboten. (The
dog bit the postman.)
Der Postbote wurde vom Hund gebissen. (The
postman was bitten by the dog.)
Japanese
(A dog bit [someone].)
Inu-ga kanda
(By a dog [I] was bitten.)
Inu-ni kamareta
Spanish
La polica detuvo el trfico. (The police
stopped the traffic.)
El trfico fue detenido por la polica. (The traffic
was stopped by the police.)
Swedish
Tjnaren br vinet. (The servant
carries the wine.)
Vinet brs av tjnaren. (The wine is carried by the
servant.)
Вам также может понравиться
- Passive Voice For All Tenses RulesДокумент2 страницыPassive Voice For All Tenses Rulesapi-322189076100% (3)
- Active and Passive Voice RulesДокумент5 страницActive and Passive Voice RulesLili Min de SanchezОценок пока нет
- Passive Voice For All Tenses RulesДокумент2 страницыPassive Voice For All Tenses RulesUmmahUnityОценок пока нет
- PassiveДокумент2 страницыPassiveShailesh SharmaОценок пока нет
- Active and Passive VoiceДокумент8 страницActive and Passive VoiceHAMID ALI VIRKОценок пока нет
- Passive Voice For All Tenses RulesДокумент3 страницыPassive Voice For All Tenses RulesSth HussainОценок пока нет
- Passive Voice Rule For All Tense RulesДокумент3 страницыPassive Voice Rule For All Tense Ruleskrishankk20080% (1)
- UNIT 7 THE PASSIVE NewДокумент13 страницUNIT 7 THE PASSIVE NewDINDA HUMAIRAОценок пока нет
- Active Passive RulesДокумент8 страницActive Passive Rulesyakshit guptaОценок пока нет
- Passive Voice For All Tenses RulesДокумент3 страницыPassive Voice For All Tenses RulesÁjáý RáñáОценок пока нет
- PPT On Voice 2014Документ17 страницPPT On Voice 2014Kishan KoyaniОценок пока нет
- Passive Voice For All Tenses RulesДокумент2 страницыPassive Voice For All Tenses RulesSyed SalmanОценок пока нет
- Passive Voice For All Tenses RulesДокумент2 страницыPassive Voice For All Tenses RulesjamilОценок пока нет
- Active and Passive VoiceДокумент4 страницыActive and Passive Voicevee propaganda100% (4)
- Active and Passive VoiceДокумент5 страницActive and Passive VoiceSAID LADJEDELОценок пока нет
- Active and Passive Voice For All Tenses RulesДокумент2 страницыActive and Passive Voice For All Tenses RulesLendelx L TsheringОценок пока нет
- Passive Voice For All Tenses RulesДокумент5 страницPassive Voice For All Tenses RulesAyesha S KhakwaniОценок пока нет
- Passive VoiceДокумент4 страницыPassive VoiceJudit Romero PuigОценок пока нет
- The Passive - All Tenses and Modals Known To HumanityДокумент4 страницыThe Passive - All Tenses and Modals Known To HumanityMarinexОценок пока нет
- Active To Passive: Hussain K. Neama (Mr. Daniel)Документ4 страницыActive To Passive: Hussain K. Neama (Mr. Daniel)Hussain K .NeamaОценок пока нет
- Active and Passive VoiceДокумент11 страницActive and Passive VoiceNandana Khan0% (1)
- Activeandpassivevoicerules 140514031042 Phpapp02Документ5 страницActiveandpassivevoicerules 140514031042 Phpapp02Jaam Awais HayatОценок пока нет
- Active Passive VoiceДокумент18 страницActive Passive VoiceBilal AliОценок пока нет
- Active and Passive VoiceДокумент16 страницActive and Passive VoiceChristine Joy ManlangitОценок пока нет
- Active VoiceДокумент9 страницActive VoicehamzaОценок пока нет
- Passive Voice 2023Документ58 страницPassive Voice 2023mudaneabdiwali157Оценок пока нет
- Active Passive VoiceДокумент7 страницActive Passive VoiceS. Kathirvelu System AdministratorОценок пока нет
- Passive VoiceДокумент2 страницыPassive Voice에반살사Оценок пока нет
- TotonitowДокумент3 страницыTotonitowkhyatishetty8Оценок пока нет
- Unit 2-Tech - EngДокумент23 страницыUnit 2-Tech - EngkarrisuryaadityaОценок пока нет
- Summary of German Verb TensesДокумент5 страницSummary of German Verb Tensesteddygun80100% (2)
- Class Note HU101 (Module - 1 Grammar - Voice and Narration)Документ19 страницClass Note HU101 (Module - 1 Grammar - Voice and Narration)nkprince0% (1)
- 1 - Class Notes-HU 101 - (Module 1-Grammar)Документ15 страниц1 - Class Notes-HU 101 - (Module 1-Grammar)Sukhwinder SinghОценок пока нет
- For Active and PassiveДокумент19 страницFor Active and PassiveJang YoungОценок пока нет
- Passive and ActiveДокумент7 страницPassive and ActiveZainabОценок пока нет
- Active Passive Voice (Notes)Документ12 страницActive Passive Voice (Notes)khushbooОценок пока нет
- Active Passive Voice For The BeginnresДокумент18 страницActive Passive Voice For The BeginnresWaqas AhmedОценок пока нет
- Bismilllaaah Senjata Untuk EAPДокумент166 страницBismilllaaah Senjata Untuk EAPFathimah KurniawatiОценок пока нет
- Passive VoiceДокумент2 страницыPassive VoiceRaul Wal SchОценок пока нет
- General English Module 2Документ39 страницGeneral English Module 2shambhavi sinhaОценок пока нет
- Active and Passive Voice Tense Wise RulesДокумент31 страницаActive and Passive Voice Tense Wise RulesMdMehediHasan100% (5)
- German TensesДокумент6 страницGerman TenseswcgokulОценок пока нет
- English GrammarДокумент11 страницEnglish Grammaralifiaar100% (1)
- Passive VoiceДокумент3 страницыPassive VoiceNatalia SimascoОценок пока нет
- Grammar - Voice and NarrationДокумент19 страницGrammar - Voice and NarrationMEDU AZADОценок пока нет
- Active Passive Voice PDFДокумент14 страницActive Passive Voice PDFKomal DhaliwalОценок пока нет
- Passive Voice and Narration ArticalДокумент69 страницPassive Voice and Narration ArticalSyed AlamОценок пока нет
- Active & PASSIVE VOICE GRADE 8Документ5 страницActive & PASSIVE VOICE GRADE 8fathima sarahОценок пока нет
- Passive Voice (Theory IMANOL)Документ5 страницPassive Voice (Theory IMANOL)Aitor Soto RuizОценок пока нет
- Passive and ActiveДокумент7 страницPassive and Activeapi-304729893Оценок пока нет
- NotesДокумент7 страницNotesnur nashirahОценок пока нет
- Passive VoiceДокумент11 страницPassive VoiceOmar AchirОценок пока нет
- Passive VoiceДокумент13 страницPassive VoiceTianbestdionZaiОценок пока нет
- Passive Voice Rule For All Tense RulesДокумент2 страницыPassive Voice Rule For All Tense Rulesgub123Оценок пока нет
- Active Passive VoiceДокумент6 страницActive Passive VoiceSandeep SinghОценок пока нет
- Passive Voice Rules For All Tenses - With ExamplesДокумент2 страницыPassive Voice Rules For All Tenses - With ExamplesDard TongОценок пока нет
- 9 Passive Voice PDFДокумент2 страницы9 Passive Voice PDFIna SestacovschiОценок пока нет
- Financial Statement Analysis (Hinopak Motors LTD,.)Документ55 страницFinancial Statement Analysis (Hinopak Motors LTD,.)Terry Miller100% (1)
- Title Page of Financial AddddnalysisДокумент3 страницыTitle Page of Financial AddddnalysisTerry MillerОценок пока нет
- TABLE OF CONTENT Plat Form Palt SR.# Description Page #Документ1 страницаTABLE OF CONTENT Plat Form Palt SR.# Description Page #Terry MillerОценок пока нет
- Table of Content SR.# Description Page #Документ1 страницаTable of Content SR.# Description Page #Terry MillerОценок пока нет
- Subject-Verb Agreement (English)Документ2 страницыSubject-Verb Agreement (English)Kelly CalingasanОценок пока нет
- Grammar B2+ - 3 Passive VoiceДокумент9 страницGrammar B2+ - 3 Passive VoiceТатьяна РадионоваОценок пока нет
- English Short Stories FreeДокумент4 страницыEnglish Short Stories FreeJesus RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Grammar Recap - 35 Hi Freq PointsДокумент6 страницGrammar Recap - 35 Hi Freq PointsShristi SinghОценок пока нет
- Detailed Lesson PlanДокумент3 страницыDetailed Lesson PlanMarianne Hilario91% (23)
- Phonetic Tongue TwistersДокумент7 страницPhonetic Tongue Twistersdaljmer100% (1)
- Quiz AlfalinkДокумент4 страницыQuiz AlfalinkAfifah Putri Amanda AnwarОценок пока нет
- Bahasa Inggris Kelas XДокумент18 страницBahasa Inggris Kelas XArdi SiladorkОценок пока нет
- How To Make A ComplaintДокумент1 страницаHow To Make A ComplaintMagdaleno Cruz MedinaОценок пока нет
- Tips Upsr Section AДокумент18 страницTips Upsr Section AShaqeel O'neelОценок пока нет
- Task 3 - Online English TestДокумент7 страницTask 3 - Online English TestDidier Armando Pardo LeytonОценок пока нет
- Kannada Kali - 1 NKДокумент4 страницыKannada Kali - 1 NKShivu GowdaОценок пока нет
- Form Present SimpleДокумент4 страницыForm Present SimpleLaura GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Basics of English Gramm Ar: by Manm Ohan Sing H Sidhu Class-10 U Roll No - 3 0Документ13 страницBasics of English Gramm Ar: by Manm Ohan Sing H Sidhu Class-10 U Roll No - 3 0Manmohan Singh SidhuОценок пока нет
- American Speakout-Intermediate-Student S BookДокумент95 страницAmerican Speakout-Intermediate-Student S BookFernandaRoxanaPeralta100% (1)
- Learning English Classroom Materials May AdvancedДокумент4 страницыLearning English Classroom Materials May AdvancedThe GuardianОценок пока нет
- Collocations With Phrasal VerbsДокумент26 страницCollocations With Phrasal VerbsDejan Spasic100% (1)
- 1.1 Parts of Speech and Simple Present 3CCДокумент5 страниц1.1 Parts of Speech and Simple Present 3CCGabriel PR100% (1)
- Parts of Speech ExamplesДокумент9 страницParts of Speech ExamplesMj Sebastian GuadalupeОценок пока нет
- The Natural LenguageДокумент14 страницThe Natural LenguageAndrea Laguado EspinozaОценок пока нет
- Swahili Tense AspectДокумент326 страницSwahili Tense Aspectnikolakr8526Оценок пока нет
- STRESSДокумент20 страницSTRESSDini AuliaОценок пока нет
- Banker's Wife's Blues: Does Live LivesДокумент44 страницыBanker's Wife's Blues: Does Live LivesLorena PinedoОценок пока нет
- Pidgin: Language, Is A Grammatically LimitedДокумент25 страницPidgin: Language, Is A Grammatically LimitedAnkit RaoОценок пока нет
- OC Lecturenotes French Lesson 2 PDFДокумент25 страницOC Lecturenotes French Lesson 2 PDFB. Samuel100% (1)
- Er Present Tense VerbsДокумент12 страницEr Present Tense VerbsChandan DasОценок пока нет
- Relative Clauses Grammar ReferenceДокумент2 страницыRelative Clauses Grammar ReferencemariecbaОценок пока нет
- Verbs! Verb Forms Review of TensesДокумент22 страницыVerbs! Verb Forms Review of TensesangeloОценок пока нет
- Past Simple (Regular/Irregular Verbs)Документ8 страницPast Simple (Regular/Irregular Verbs)Pavle PopovicОценок пока нет