Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CV 9
Загружено:
Georgie Stephen0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
6 просмотров1 страницаcaer
Оригинальное название
cv9
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документcaer
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
6 просмотров1 страницаCV 9
Загружено:
Georgie Stephencaer
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
The cardiovascular system
In front of the elbow it gives off a large branch, the median
cubital vein, which slants upwards and medially to join
the basilic vein. After crossing the elbow joint the cephalic
vein passes up the lateral aspect of the arm and in front of
the shoulder joint to end in the axillary vein. Throughout
its length it receives blood from the superficial tissues on
the lateral aspects of the hand, forearm and arm.
The basilic vein begins at the back of the hand on the
ulnar aspect. It ascends on the medial side of the forearm
and upper arm then joins the axillary vein. It receives
blood from the medial aspect of the hand, forearm and
arm. There are many small veins which link the cephalic
and basilic veins.
The median vein is a small vein that is not always pres-
ent. It begins at the palmar surface of the hand, ascends
on the front of the forearm and ends in the basilic vein or
the median cubital vein.
The brachiocephalic vein is formed when the subclavian
and internal jugular veins unite. There is one on each
side.
The superior vena cava is formed when the two brachio-
cephalic veins unite. It drains all the venous blood from
the head, neck and upper limbs and terminates in the
escending aorta in the thorax
This part of the aorta is continuous with the arch of the
aorta and begins at the level of the !th thoracic vertebra.
It extends downwards on the anterior surface of the bod-
ies of the thoracic vertebrae "#ig. $.!%& to the level of the
'%th thoracic vertebra, where it passes behind the
diaphragm to become the abdominal aorta.
The descending aorta in the thorax gives off many
paired branches which supply the walls of the thoracic
cavity and the organs within the cavity, including(
bronchial arteries that supply the bronchi and their
branches, connective tissue in the lungs and the
lymph nodes at the root of the lungs
oesophageal arteries that supply the oesophagus
intercostal arteries that run along the inferior border of
the ribs and supply the intercostal muscles, some
muscles of the thorax, the ribs, the skin and its
underlying connective tissues.
Venous return from the thoracic cavity
)ost of the venous blood from the organs in the thoracic
cavity is drained into the azygos vein and the hemiazygos
vein "#ig. $.!*&. +ome of the main veins which join them are right atrium. It is about , cm long and passes
along the right border of the sternum.
downwards
the bronchial, oesophageal and intercostal veins. The a-ygos
103
Right internal
jugular vein----tl
Right
subclavian
vein--t'"t;:<
Left internal
vein
Trachea
rt-----iugular
Right subclavian
artery
Left subclavian
vein
----:
!rachi"ce#halic $--%-%-
artery
RighI
brachi"-
ce#halic
vein
&u#eri"r----:'""'--::()*
vena cava ::++++++::,"--!r"nchus
br"nchial
arteries
an-
&u#eri"r
vena cava
-I;<-+.-*:-%--/e0ia1yg"s
vein
Interc"stal.---23
veins
-4*"""**"""-+i:---Th"racic
a"rta an- its
branches
Right 15th
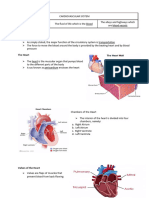
Figure 5.42 The a"rta an- its 0ain branches in the th"ra6* Figure 5.43 The su#eri"r vena cava an- the 0ain veins "f the th"ra6*
Вам также может понравиться
- Java Exclusiava BendusДокумент1 страницаJava Exclusiava BendusGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- Mugloo DbengglarisДокумент2 страницыMugloo DbengglarisGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- Mugloo DinglarisДокумент1 страницаMugloo DinglarisGeorgie GeorgeОценок пока нет
- Near Death Experiences - Pim Van LommelДокумент7 страницNear Death Experiences - Pim Van LommelNASCE_UFMGОценок пока нет
- 10inspiringzapposcustomersupportstories 131028231942 Phpapp01Документ29 страниц10inspiringzapposcustomersupportstories 131028231942 Phpapp01Georgie StephenОценок пока нет
- Leftico MulbarisДокумент1 страницаLeftico MulbarisGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- AfsdghdfДокумент2 страницыAfsdghdfGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- Blacklisted HospitalДокумент72 страницыBlacklisted HospitalGeorgie Stephen100% (1)
- AfsdghdfДокумент2 страницыAfsdghdfGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- Procedural Extensions: Source Common Name Full NameДокумент2 страницыProcedural Extensions: Source Common Name Full NameGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- Design: Relational Model Tuple Calculus Set ListsДокумент1 страницаDesign: Relational Model Tuple Calculus Set ListsGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- 2017 0412 PhocuswrightWebinar WhosWinningInTrafficandConversion JumpshotДокумент35 страниц2017 0412 PhocuswrightWebinar WhosWinningInTrafficandConversion JumpshotGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- Remove Junkware and Malware with JRT ToolДокумент1 страницаRemove Junkware and Malware with JRT ToolGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- Junkware Removal Tool (JRT) by Malwarebytes Version: 8.1.1 (02.11.2017) Operating System: Windows 10 Pro x64Документ1 страницаJunkware Removal Tool (JRT) by Malwarebytes Version: 8.1.1 (02.11.2017) Operating System: Windows 10 Pro x64Georgie StephenОценок пока нет
- 100 DAY PLAN WorksheetДокумент2 страницы100 DAY PLAN WorksheetGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- Yes&noДокумент1 страницаYes&noGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- STRTДокумент1 страницаSTRTGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- JPRTДокумент1 страницаJPRTGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- LFS2006 - 2 Industry CodesДокумент23 страницыLFS2006 - 2 Industry CodesGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- GiiiiiiiiДокумент1 страницаGiiiiiiiiGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- JRTДокумент1 страницаJRTGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- HohДокумент1 страницаHohGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- Tourist StatiДокумент203 страницыTourist StatiGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- A1Документ4 страницыA1Georgie StephenОценок пока нет
- Tourism 09Документ25 страницTourism 09gramamukhyaОценок пока нет
- Building A Team ExerciseДокумент3 страницыBuilding A Team ExerciseGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- Keyword Planner 2015-11-05 at 00-47-30Документ4 страницыKeyword Planner 2015-11-05 at 00-47-30Georgie StephenОценок пока нет
- Flair Business PlanДокумент31 страницаFlair Business PlanGeorgie StephenОценок пока нет
- Grammar For Academic Writing Ism PDFДокумент94 страницыGrammar For Academic Writing Ism PDFsarnai dandarОценок пока нет
- Simple Guide To PunctuationДокумент2 страницыSimple Guide To PunctuationBrian RogersОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Nursing Care of Children with Cardiovascular DisordersДокумент11 страницNursing Care of Children with Cardiovascular DisordersJœnríčk AzueloОценок пока нет
- Tetralogy of Fallot.......Документ7 страницTetralogy of Fallot.......Sam AlipioОценок пока нет
- cardiomyopathy types and causesДокумент39 страницcardiomyopathy types and causesأبوأحمد الحكيمОценок пока нет
- Ecg Made EasyДокумент45 страницEcg Made Easyfisiopop100% (4)
- Vital Signs ProcedureДокумент10 страницVital Signs ProcedureJojebelle Kate Iyog-cabanlet100% (3)
- (Case Based Discussion) A-55 Years Old Woman With Chest PainДокумент56 страниц(Case Based Discussion) A-55 Years Old Woman With Chest PainEnErin AnindithaОценок пока нет
- Appendix A: Doppler Ultrasound and Ankle-Brachial Pressure IndexДокумент26 страницAppendix A: Doppler Ultrasound and Ankle-Brachial Pressure IndexabigailОценок пока нет
- Circulation of the Pulp MicrocirculationДокумент3 страницыCirculation of the Pulp MicrocirculationKarina HernandezОценок пока нет
- Atheroma: 2 History of ResearchДокумент7 страницAtheroma: 2 History of ResearchZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Hipertensi EmergencyДокумент31 страницаHipertensi Emergencysar tikaОценок пока нет
- Thorax Card Final ExaminationДокумент3 страницыThorax Card Final ExaminationAbdul QuaiyumОценок пока нет
- Hypertension GuidelinesДокумент33 страницыHypertension GuidelinesErlinda NRAОценок пока нет
- European Heart Journal Supplements (2019) - SeptemberДокумент82 страницыEuropean Heart Journal Supplements (2019) - SeptemberBeard BeardОценок пока нет
- Week 2 - Ms1 Course Task - Cu 2Документ3 страницыWeek 2 - Ms1 Course Task - Cu 2jaira magbanuaОценок пока нет
- Interpreting ECGs A Practical Approach 1st EdДокумент769 страницInterpreting ECGs A Practical Approach 1st EdArtem Trunov100% (2)
- Acute Treatment of Pulmonary EmbolismДокумент2 страницыAcute Treatment of Pulmonary EmbolismМихаил НеболеевОценок пока нет
- Lymphatic SystemДокумент10 страницLymphatic SystemTsegaye HailuОценок пока нет
- Cor Pulmonale PresentationДокумент17 страницCor Pulmonale Presentationandi reskifaisОценок пока нет
- Ccu Survival GuideДокумент10 страницCcu Survival Guideomegasauron0gmailcom100% (1)
- L3 Anatomy and Physiology Learner Workbook 1A Mar12Документ84 страницыL3 Anatomy and Physiology Learner Workbook 1A Mar12markОценок пока нет
- External Anatomy of The HeartДокумент2 страницыExternal Anatomy of The HeartAndres LarrottaОценок пока нет
- A Pocket Guide To Blood Pressure Measurement in ChildrenДокумент4 страницыA Pocket Guide To Blood Pressure Measurement in ChildrenKira23406Оценок пока нет
- Pencegahan Dan Pengobatan Hipertensi Pada Penderita Usia DewasaДокумент7 страницPencegahan Dan Pengobatan Hipertensi Pada Penderita Usia DewasaGladys SariowanОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular SystemДокумент6 страницCardiovascular Systemjamielsomera120Оценок пока нет
- Fphys 07 00653 PDFДокумент10 страницFphys 07 00653 PDFvirnaОценок пока нет
- NEJM Defibrilation Strategies For Refractory VFДокумент10 страницNEJM Defibrilation Strategies For Refractory VFScience BrasilОценок пока нет
- 1circulatory SystemДокумент26 страниц1circulatory SystemElisa EstebanОценок пока нет
- 56 MediastinumДокумент6 страниц56 MediastinumRahmi Dwi AzkiahОценок пока нет
- DR - Shetty Advices For Heart CareДокумент19 страницDR - Shetty Advices For Heart CarekintelboyОценок пока нет
- FPH 101 Module on Non-Communicable DiseasesДокумент36 страницFPH 101 Module on Non-Communicable DiseasesNathaniel OrtegaОценок пока нет