Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Collision Tectonics Through Paleozoic Era
Загружено:
Ahmed Magdy Beshr0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
59 просмотров2 страницыCollision Tectonics Through Paleozoic Era
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документCollision Tectonics Through Paleozoic Era
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
59 просмотров2 страницыCollision Tectonics Through Paleozoic Era
Загружено:
Ahmed Magdy BeshrCollision Tectonics Through Paleozoic Era
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Collision Tectonics Through Paleozoic Era
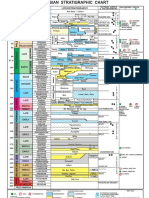
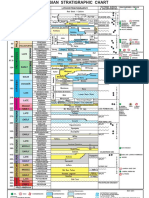
Six major Paleozoic continents are recognized after Rodinia breakup:
1. Gondwana: Southern continents, India.
Mozambique ocean separated East and West Gondwana
2. Laurentia: North America, Greenland, part Great Britain.
3. Baltica: Northern Europe.
4. Siberia: Most of Northern Asia.
5. Kazakhstania: part Central Asia.
6. China: All of Southeast Asia and Southeast China.
Events of the Paleozoic Era
Tectonics
Ordovician Tectonic orogeny Avalonia collides with Laurentia.
Silurian Caledonian orogeny Laurentia collides with Baltica, forming
Laurasia.
Devonian Acadian orogeny Southern Avalonia collides with
Laurentia.
Mississippian Ouachita orogeny South America collides with Laurasia.
Pennsylvanian Hercynian orogeny - Laurasia collides with Gondwana,
forming the Western half of Pangea.
- Siberia Collides with Kazakhstania,
forming the Altai mountains.
Permian Pangea complete Kazakhstania collides with Baltica,
forming the Ural mountains.
1. Pre-Cambrian:
- The supercontinent Rodinia was formed about 1100 million years ago, and
was located about the South Pole.
2. Cambrian:
- Rodinia broke into smaller continents about 750 million years ago, opening
the Iapetus ocean.
- The continents were flooded by shallow seas.
- Gondwana was formed and was located near the South Pole.
3. Ordovician:
- Gondwana moved to the South Pole location, so glaciers were found (Late
Ordovician tillites).
- Avalonia (Microcontinent and Island Arcs) was collided with Laurentia
(led to Taconic Orogeny), narrowing Iapetus.
- Ordovician is called Ice age, as in which most of Gondwana was covered
with ice.
4. Silurian:
- Laurentia collided with Baltica (led to Caledonian Orogeny), closing the
northern branch of the Iapetus Ocean and forming Laurasia (Old Red
Sandstone continent).
5. Devonian:
- Southern Avalonia collided with Laurentia (led to Acadian Orogeny),
closing the southern branch of the Iapetus Ocean.
- After closing of the ocean, remaining saltwater were vaporized, forming
salt domes.
6. Carboniferous:
a) Early Carboniferous (Mississippian):
- Paleozoic ocean between Euramerica (Laurasia) and Gondwana began to
close, forming the Appalachian and Variscan mountains.
- Gondwana moved toward the north, so an ice cap grew at the South Pole
and forests consist of ferns plants grew at the Equator.
b) Late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian):
- Laurasia collided with Gondwana (led to Hercynian Orogeny), forming
the Western half of Pangea.
- Siberia Collides with Kazakhstania, forming the Altai mountains.
- Melting of the ice cap at the South Pole, leading to transgression of seas
on the ferns forests at the Equator, forming coal deposits in Europe and
North America.
7. Permian:
- Kazakhstania collided with Baltica, forming the Ural mountains.
- The supercontinent Pangea was formed, and was surrounded by Panthalassa
ocean.
Вам также может понравиться
- Regional-Residual Separation 1Документ1 страницаRegional-Residual Separation 1Ahmed Magdy BeshrОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Exercise : Profile Coordinate (M) G (Gu)Документ1 страницаExercise : Profile Coordinate (M) G (Gu)Ahmed Magdy BeshrОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Regional-Residual Separation 2Документ1 страницаRegional-Residual Separation 2Ahmed Magdy BeshrОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Gravity Map 4Документ1 страницаGravity Map 4Ahmed Magdy BeshrОценок пока нет
- Gravity Data Correction 5Документ1 страницаGravity Data Correction 5Ahmed Magdy BeshrОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Exercise : Answer The FollowingДокумент1 страницаExercise : Answer The FollowingAhmed Magdy BeshrОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- "Station-0" Represents A Base Station (BS) - "Dist. (M) " Is The Station Location, MeasuredДокумент1 страница"Station-0" Represents A Base Station (BS) - "Dist. (M) " Is The Station Location, MeasuredAhmed Magdy BeshrОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Exercise : You Are Asked ToДокумент1 страницаExercise : You Are Asked ToAhmed Magdy BeshrОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- "G-Obs (G.u.) " Is The Measured Gravity Value. Ask The FollowingДокумент1 страница"G-Obs (G.u.) " Is The Measured Gravity Value. Ask The FollowingAhmed Magdy BeshrОценок пока нет
- On Your Answer. On Your Answer.: Student Name: Student NameДокумент1 страницаOn Your Answer. On Your Answer.: Student Name: Student NameAhmed Magdy BeshrОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Exercise : You Are Requested ToДокумент1 страницаExercise : You Are Requested ToAhmed Magdy BeshrОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Exercise : You Are Asked ToДокумент1 страницаExercise : You Are Asked ToAhmed Magdy BeshrОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- ExercisesДокумент13 страницExercisesAhmed Magdy Beshr100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Western University - Department of Earth Sciences ES3372A: Introduction To Petroleum Systems Fall 2013Документ5 страницWestern University - Department of Earth Sciences ES3372A: Introduction To Petroleum Systems Fall 2013Ahmed Magdy BeshrОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- TOPSAR Deburst and MergeДокумент2 страницыTOPSAR Deburst and MergeAhmed Magdy BeshrОценок пока нет
- StratigraphicДокумент1 страницаStratigraphicMohamed SahnounОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Earth's History (Grade 7) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingДокумент2 страницыEarth's History (Grade 7) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingnick21070Оценок пока нет
- Periods of The Paleozoic Era: Cambrian PeriodДокумент8 страницPeriods of The Paleozoic Era: Cambrian PeriodChinatsu HayashidaОценок пока нет
- Mapa Geologico HuacaretaДокумент1 страницаMapa Geologico Huacaretavanesa100% (1)
- Geologic Time ScaleДокумент2 страницыGeologic Time ScaleVinze AgarcioОценок пока нет
- Geologic TimeДокумент7 страницGeologic TimeAnar AliyevОценок пока нет
- Cráton Do São FranciscoДокумент4 страницыCráton Do São FranciscoKelly NatalyОценок пока нет
- Scara StratigraficaДокумент1 страницаScara Stratigraficaaborigin06Оценок пока нет
- KahliДокумент8 страницKahliMarilyn GenoveОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
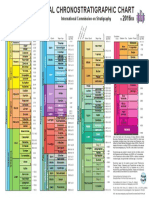
- International Chronostratigraphic Chart 2016Документ1 страницаInternational Chronostratigraphic Chart 2016Diego Ardila100% (1)
- Proterozoic Eon: ArcheanДокумент3 страницыProterozoic Eon: ArcheanDick Jefferson Ocampo PatingОценок пока нет
- Geo Time ScaleДокумент5 страницGeo Time ScalealkanosОценок пока нет
- Geologic History of EarthДокумент4 страницыGeologic History of EarthRoy VeseyОценок пока нет
- Geologic Time Scale REVIEWERДокумент11 страницGeologic Time Scale REVIEWERasdfghjkl100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Geological Time-ScaleДокумент9 страницGeological Time-ScaleNothing100% (1)
- Geological Time ScaleДокумент7 страницGeological Time ScaleAnandhu AnilОценок пока нет
- Geologic Time ScaleДокумент20 страницGeologic Time ScaleMaria Cielo Lucino100% (4)
- Geologic Time Scale ActivityДокумент10 страницGeologic Time Scale Activityno thankyouОценок пока нет
- DinosaursДокумент2 страницыDinosaursDerdy JanliОценок пока нет
- Earth Science FinalДокумент5 страницEarth Science Finaldave lucasОценок пока нет
- ChronostratChart2017 02Документ1 страницаChronostratChart2017 02ross182Оценок пока нет
- ScienceДокумент32 страницыScienceJustin Solis EvangelioОценок пока нет
- International Stratigraphic Chart PDFДокумент1 страницаInternational Stratigraphic Chart PDFCamilo Pedroza BarbosaОценок пока нет
- Serie Age Formation Top OH M DJHN-3 0 Continental IntercalaireДокумент12 страницSerie Age Formation Top OH M DJHN-3 0 Continental IntercalaireAlexander KlmОценок пока нет
- International Chronosgraphic Trat Chart PDFДокумент1 страницаInternational Chronosgraphic Trat Chart PDFLara CitlalliОценок пока нет
- Budowa Geologiczna Regionu KrakowaДокумент7 страницBudowa Geologiczna Regionu KrakowaAnton VSОценок пока нет
- Deep History of Life On Earth HHMI LabДокумент2 страницыDeep History of Life On Earth HHMI LabNoemmy Okhman0% (1)
- Paleozoic Early PDFДокумент219 страницPaleozoic Early PDFmarcos15121986100% (2)
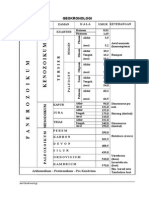
- GeokronologiДокумент4 страницыGeokronologiTamzy AguanteОценок пока нет
- Stratigraphic PDFДокумент1 страницаStratigraphic PDFsami NaОценок пока нет