Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Plant Parts and Functions
Загружено:
Razonable Morales RommelАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Plant Parts and Functions
Загружено:
Razonable Morales RommelАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PLANT PARTS AND FUNCTIONS
Naming Plants
Binomial nomenclature is the scientific system of giving a double name
to plants and animals. The first, or genus name, is followed by a
descriptive or species name. Modern plant classification, or taxonomy,
is based on a system of binomial nomenclature developed by the
Swedish physician Carolus Linnaeus !"#"$!""%&. 'rior to Linnaeus,
people had tried to base classification on leaf shape, plant si(e, flower
color, etc. )one of these systems proved wor*able. Linnaeus+s
revolutionary approach was to base classification on the flowers and,or
reproductive parts of a plant and to give plants a genus and species
name. This has proven to be the best system since flowers are the plant
part least influenced by environmental changes. -or this reason a
*nowledge of the flower and its parts is essential to plant identification.
FLOWERS
The sole function of the flower, which is generally the
showiest part of the plant, is sexual reproduction. .ts
attractiveness and fragrance have not evolved to please
man but to ensure the continuance of the plant species.
-ragrance and color are devices to attract pollinators that
play an important role in the reproductive process.
Parts of the Flower
/s the reproductive part of the plant the flower contains
the male pollen and,or the female ovule plus accessory
parts such as petals, sepals, and nectar glands.
The pistil is the female part of the plant. .t is generally
shaped li*e a bowling pin and located in the center of the
flower. .t consists of the stigma, style, and ovary. The
stigma is located at the top, and is connected to the ovary
by the style. The ovary contains the eggs which reside in
the ovules. /fter the egg is fertili(ed the ovule develops
into a seed.
The stamen is the male reproductive organ. .t consists of
a pollen sac anther& and a long supporting filament. This
filament holds the anther in position so the pollen it
contains may be disbursed by wind or carried to the
stigma by insects, birds or bats.
Sepals are small green, leafli*e structures on the base of
the flower which protect the flower bud. The sepals
collectively are called the calyx.
Petals are highly colored portions of the flower. They may
contain perfume as well as nectar glands. The petals
collectively are called the corolla. The number of petals
on a flower is often used in the identification of plant
families and genera. -lowers of dicots typically have
sepals and,or petals in multiples of four or five. Monocots
typically have these floral parts in multiples of three.
Types of Flowers
.f a flower has a stamen, pistils, petals, and sepals, it is
called a complete flower. .f one of these parts is missing,
the flower is designated incomplete. .f a flower contains
functional stamens and pistils, it is called a perfect flower.
Stamen and pistils are considered the essential parts of a
flower.& .f either of the essential parts is lac*ing, the
flower is imperfect.
Pistillate female& flowers are those which possess a
functional pistils& but lac* stamens. Staminate male&
flowers contain stamens but no pistils. Because cross$
fertili(ation combines different genetic material and
produces stronger seed, cross$pollinated plants are usually
more successful than self$pollinated plants. Conse0uently,
more plants reproduce by cross$pollination than self$
pollination.
/s previously mentioned, there are plants which bear only
male flowers staminate plants& or bear only female
flowers pistillate plants&. Species in which the sexes are
separated into staminate and pistillate plants are called
dioecious. Most holly trees and pistachio trees are
dioecious1 therefore, to obtain berries, it is necessary to
have female and male trees. Monoecious plants are those
which have separate male and female flowers on the same
plant. Corn plants and pecan trees are examples. Some
plants bear only male flowers at the beginning of the
growing season, but later develop flowers of both sexes1
examples are cucumbers and s0uash.
ow Seeds Form
'ollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther to a
stigma. This may occur by wind or by pollinators. 2ind$
pollinated flowers lac* showy floral parts and nectar since
they don3t need to attract a pollinator. -lowers are brightly
colored or patterned and contain a fragrance or nectar
when they must attract insects, animals, or birds. .n the
process of searching for nectar these pollinators will
transfer pollen from flower to flower.
The stigma contains a chemical which stimulates the
pollen, causing it to grow a long tube down the inside of
the style to the ovules inside the ovary. The sperm is
released by the pollen grain and fertili(ation typically
occurs. -ertili(ation is the union of the male sperm
nucleus from the pollen grain& and the female egg in the
ovule&. .f fertili(ation is successful, the ovule will develop
into a seed.
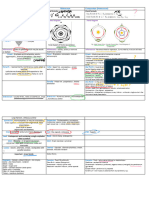
Types of !nflorescences
Some plants bear only one flower per stem and are called
solitary flowers. 4ther plants produce an inflorescence, a
term which refers to a cluster of flowers and how they are
arranged on a floral stem. Most inflorescences may be
classified into two groups, racemes and cymes.
.n the racemose group, the florets, which are individual
flowers in an inflorescence, bloom from the bottom of the
stem and progress toward the top. Some examples of
racemose inflorescence include spi*e, raceme, corymb,
umbel, and head. / spi*e is an inflorescence in which
many stemless florets are attached to an elongated flower
stem or peduncle, an example being gladiolus. / raceme is
similar to a spi*e except the florets are borne on small
stems attached to the peduncle. /n example of a raceme
inflorescence is the snapdragon. / corymb is made up of
florets whose stal*s and pedicels are arranged at random
along the peduncle in such a way that the florets create a
flat, round top. 5arrow has a corymb inflorescence. /n
umbel is similar except that the pedicels all arise from one
point on the peduncle. 6ill has an umbel inflorescence. /
head or composite inflorescence is made up of numerous
stemless florets which is characteristic of daisy
inflorescence.
.n the cyme group, the top floret opens first and blooms
downward along the peduncle. / dischasium cyme has
florets opposite each other along the peduncle. Baby+s
breath inflorescence is an example. / helicoid cyme is one
in which the lower florets are all on the same side of the
peduncle, examples being freesia and statice
inflorescences. / scorpioid cyme is one in which the
florets are alternate to each other along the peduncle.
7xamples are tomato and potato inflorescences.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Farm Plan and BudgetДокумент8 страницFarm Plan and BudgetMaria Angela Somera Naval0% (1)
- UNIT 2A - Plant AnatomyДокумент48 страницUNIT 2A - Plant AnatomyMyreal Venice CrudaОценок пока нет
- ECCD Checklist Skills for 5-Year-OldДокумент2 страницыECCD Checklist Skills for 5-Year-OldRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- GerryДокумент8 страницGerryRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- 01 Implementing Active Directory Domain ServicesДокумент37 страниц01 Implementing Active Directory Domain ServicesRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- 15 Motion Media and Information 170927073911Документ29 страниц15 Motion Media and Information 170927073911Razonable Morales Rommel50% (2)
- Tea and Coffee EquipmentДокумент7 страницTea and Coffee EquipmentRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- National Assessment - PPT GerryДокумент27 страницNational Assessment - PPT GerryRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- Syllabus Computer OrganizationДокумент3 страницыSyllabus Computer OrganizationRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- Qualification: Computer System Servicing NC II Unit of Competency: Install and Configure Computer SystemsДокумент2 страницыQualification: Computer System Servicing NC II Unit of Competency: Install and Configure Computer SystemsRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- Word 2007 Screen PartsДокумент3 страницыWord 2007 Screen PartsapolsoftОценок пока нет
- Report of Printing Press UnitДокумент29 страницReport of Printing Press Unitsmartwayrcp100% (3)
- Trainee Characteristics Gathering InstrumentДокумент7 страницTrainee Characteristics Gathering InstrumentRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- Steve Volleyball Lay-OutДокумент2 страницыSteve Volleyball Lay-OutRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- Utilize Electronic Media 2 2012Документ153 страницыUtilize Electronic Media 2 2012veronica_celestialОценок пока нет
- Supervising Work-Based LearningДокумент11 страницSupervising Work-Based LearningRazonable Morales Rommel100% (1)
- Tick The ColumnДокумент9 страницTick The ColumnRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- The Normal Abilities of StudentДокумент17 страницThe Normal Abilities of StudentRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- Developmental Biology Is The Study of The Process by Which Organs Grow and DevelopДокумент2 страницыDevelopmental Biology Is The Study of The Process by Which Organs Grow and DevelopRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- Why The Sky Is HighДокумент1 страницаWhy The Sky Is HighRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- CHS NC II Exam GuideДокумент10 страницCHS NC II Exam GuideKristine CapaoОценок пока нет
- Certification for transfer of Pantawid Pamilya Pilipino Program benefits of Mrs. Perla S. CortezДокумент1 страницаCertification for transfer of Pantawid Pamilya Pilipino Program benefits of Mrs. Perla S. CortezRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- A Community-Based Mothers and Infants CenterДокумент10 страницA Community-Based Mothers and Infants CenterRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- Animal FunctionsДокумент2 страницыAnimal FunctionsRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- The Teaching ProcessДокумент19 страницThe Teaching ProcessRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- Developmental Biology Is The Study of The Process by Which Organs Grow and DevelopДокумент2 страницыDevelopmental Biology Is The Study of The Process by Which Organs Grow and DevelopRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- PMC 4 Report Gender M&E and C&a 90-138Документ49 страницPMC 4 Report Gender M&E and C&a 90-138Razonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- BotanyДокумент5 страницBotanyRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- Maintain Session PlanДокумент5 страницMaintain Session PlanRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- Social JusticeДокумент32 страницыSocial JusticeRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- Configure Computer System and Networks: Evidence PlanДокумент2 страницыConfigure Computer System and Networks: Evidence PlanRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- Conferinta - USDC - 2019 Expression of Some Genes Implicated in Antioxidative Defense System in PDFДокумент200 страницConferinta - USDC - 2019 Expression of Some Genes Implicated in Antioxidative Defense System in PDFAna CalmîșОценок пока нет
- Monograph of Andira (Legimnosae-Papilionoideae)Документ144 страницыMonograph of Andira (Legimnosae-Papilionoideae)MauriciofigueiraОценок пока нет
- 1PUCBIOLOGY RlsДокумент5 страниц1PUCBIOLOGY Rlsmyp148940Оценок пока нет
- Flowers: Sexual Reproduction in AngiospermsДокумент106 страницFlowers: Sexual Reproduction in AngiospermsAlfonso PlantillaОценок пока нет
- The Chilean Calceolaria Integrifolia Ehrhart2005Документ30 страницThe Chilean Calceolaria Integrifolia Ehrhart2005Evaldo PapeОценок пока нет
- Curry Leaf ProductionДокумент58 страницCurry Leaf ProductionJebewathani SundaravelОценок пока нет
- Botany I (EM) BLM 2021-22Документ61 страницаBotany I (EM) BLM 2021-22Tanzeela Hashmi0% (1)
- Hydrangea Bulletin HiДокумент16 страницHydrangea Bulletin HiDan Danut100% (1)
- Guatemalan Flora: MyrtaceaeДокумент152 страницыGuatemalan Flora: MyrtaceaeMajo TorallaОценок пока нет
- Bearing Habits of Fruit CropsДокумент38 страницBearing Habits of Fruit CropsFlori rs R nagar, Hyd100% (5)
- Key To LAMIACEAE of Colorado - Mint FamilyДокумент6 страницKey To LAMIACEAE of Colorado - Mint FamilyColorado Native Plant SocietyОценок пока нет
- F Y B SC Botany (Revised) - 19.062020Документ12 страницF Y B SC Botany (Revised) - 19.062020Pooja SaryawanshiОценок пока нет
- Flora Mesoamericana - Rosaceae PDFДокумент61 страницаFlora Mesoamericana - Rosaceae PDFGerardo Morales CarreonОценок пока нет
- Pseudocentrumglabrum-J S MorenoP A HardingДокумент6 страницPseudocentrumglabrum-J S MorenoP A HardingAlexander DamiánОценок пока нет
- American Society of Plant Taxonomists Systematic BotanyДокумент20 страницAmerican Society of Plant Taxonomists Systematic BotanyMaikel GaitkoskiОценок пока нет
- Practical Plant IdentificationДокумент370 страницPractical Plant IdentificationHaider Imad93% (15)
- Dioscorea L. (PROSEA) - PlantUse English PDFДокумент8 страницDioscorea L. (PROSEA) - PlantUse English PDFfortuna_dОценок пока нет
- Medicinal and Aromatic Plants-Industrial ProfilesДокумент157 страницMedicinal and Aromatic Plants-Industrial ProfilesEmmanuel GleveauОценок пока нет
- Bamboo ClasificationДокумент12 страницBamboo ClasificationFernando Bambu de XalОценок пока нет
- Learn Inflorescence Types & Flower Evolution in 40 CharactersДокумент19 страницLearn Inflorescence Types & Flower Evolution in 40 CharactersThivya RamanОценок пока нет
- Families NewДокумент2 страницыFamilies New78x8qcpdq40% (1)
- (23279834 - HortScience) The Effect of Temperature On Leaf and Flower Development and Flower Longevity of Zygopetalum Redvale 'Fire Kiss' OrchidДокумент5 страниц(23279834 - HortScience) The Effect of Temperature On Leaf and Flower Development and Flower Longevity of Zygopetalum Redvale 'Fire Kiss' OrchidTesfamariam Setargew MesfinОценок пока нет
- Brijesh Kumar (Author) - Surabhi Tiwari (Author) - Vikas Bajpai (A - Phytochemistry of Plants of Genus Piper (2020, CRC Press) (10.1201 - 9781003014874) - Libgen - LiДокумент89 страницBrijesh Kumar (Author) - Surabhi Tiwari (Author) - Vikas Bajpai (A - Phytochemistry of Plants of Genus Piper (2020, CRC Press) (10.1201 - 9781003014874) - Libgen - LiAggelis EleandrosОценок пока нет
- Studies On Hanguana For Sunda II - Five New Forest Species From Peninsular Malaysia and Recircumscription of Hanguana Malayana - (Willdenowia 40 (2), 205-219) - Nurfazilah Et Al., 2010Документ15 страницStudies On Hanguana For Sunda II - Five New Forest Species From Peninsular Malaysia and Recircumscription of Hanguana Malayana - (Willdenowia 40 (2), 205-219) - Nurfazilah Et Al., 2010Peter BoyceОценок пока нет
- A Taxonomic Revision of The Western South American Genus Presliophytum (Loasaceae)Документ19 страницA Taxonomic Revision of The Western South American Genus Presliophytum (Loasaceae)Jimmy Christian Quinaya GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Mango BreedingДокумент82 страницыMango Breedingsuprita HulipalledОценок пока нет
- 02-Plant Morphology (Exercise)Документ5 страниц02-Plant Morphology (Exercise)varshavishuОценок пока нет
- PoaceaeДокумент7 страницPoaceaeping32Оценок пока нет