Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
307 311maths X
Загружено:
api-259591583Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
307 311maths X
Загружено:
api-259591583Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
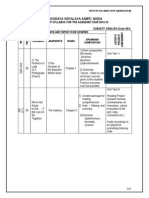
SPLIT UP SYLLABUS 2014-15(MATHEMATICS-X)
307
NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA SAMITI-NOIDA
SPLITUP OF SYLLABUS FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2014-15
CLASS: X SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS
TERM I
UNIT NAME OF UNIT MARKS
I NUMBER SYSTEM 11
II ALGEBRA 23
III GEOMETRY 17
IV TRIGONOMETRY 22
V STASTISTICS 17
M
O
N
T
H
N
O
.
O
F
D
A
Y
S
UNITS/SUB UNITS TO BE COVERED
ACTIVITIES/
ASSESSMENT
(FA/Assignment/pr
ojects etc.)
A
P
R
I
L
/
J
U
N
E
25 ALGEBRA
i)Polynomials:
Zeros of a polynomial. Relationship between zeros and
coefficients of quadratic polynomials. Statement and simple
problems on division algorithm for polynomials with real
coefficients
ii)Pair of linear equations in two variables:
Pair of linear equations in two variables. Geometric
representation of different possibilities of solutions
inconsistency. Algebraic conditions for number of solutions.
Solution of pair of linear equations in two variables algebraically
by substitution, by elimination must be included. Simple
problems on equations reducible to linear equations may be
included
Activity-1&2
Assignment-1
J
U
L
Y
27 NUMBER SYSTEM:
Real Numbers:
Euclid division lemma, Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
statements after reviewing work done earlier and after
illustrating and motivating through examples, Proofs of results
irrationality of , , decimal expansions of rational
numbers in terms of terminating / non-terminating recurring
decimals
STATISTICS:
Mean, median and mode of grouped data (bimodal situation to
be avoided). Cumulative frequency graph.
Activities-3&4
Project-1
FA-1
SPLIT UP SYLLABUS 2014-15(MATHEMATICS-X)
308
A
U
G
U
S
T
25 GEOMETRY:
Triangles: Similar triangles:
Definitions, examples, counter examples of similar triangles.
(i)(prove) If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to
intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two
sides are divided in the same ratio.
(ii) (motivate) If a line divides two sides of a triangle in the same
ratio, the line is parallel to the third side.
(iii) (motivate) If in two triangles, the corresponding angles are
equal, their corresponding sides are proportional and the
triangles are similar.
(iv) (motivate) If the corresponding sides of two angles are
proportional their corresponding angles are equal and the two
triangles are similar.
(v) (motivate) If one angle of a triangle is equal to one angle of
another triangle and the sides including these angles are
proportional, the two triangles are similar.
(vi) (motivate) If a perpendicular is drawn from the vertex of right
angle of a right triangle to the hypotenuse, the triangles on each
side of the perpendicular are similar to the whole triangle and to
each other.
(vii)(prove) The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal
to the ratio of the squares on their corresponding sides.
(viii)(prove) In a right triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is
equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
(ix)(prove) In a triangle, If the square on one side is equal to
sum of the squares on the other two sides, the angle opposite to
the first side is a right angle.
Activities 5&6
Assignment-II
Activities-7&8
S
E
P
T
E
M
B
E
R
24 TRIGONOMETRY: Introduction to Trigonometry. Trigonometric
ratios of an acute angle of a right-angled triangle. Proof of their
existence (well defined); motivate the ratios, whichever are
defined at 0
0
and 90
0
values (with proofs) of the trigonometric
ratios of 30
0
, 45
0
and 60
0
. Relationships between the ratios.
Trigonometric identities:
Proof and applications of the identity Sin
2
A + Cos
2
A = 1. Only
simple identities to be given. Trigonometric ratios of
complementary angles.
FA-2
S
E
P
T
/
O
C
T
REVISION -SA 1
SPLIT UP SYLLABUS 2014-15(MATHEMATICS-X)
309
TERM-II
UNIT NAME OF UNIT MARKS
II ALGEBRA(Contd.) 23
III GEOMETRY(Contd.) 17
IV TRIGONOMETRY (Contd.) 08
V PROBABILITY 22
VI CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY 11
VII MENSURATION 23
M
O
N
T
H
P
E
R
I
O
D
S
UNITS/SUB UNITS TO BE COVERED
ACTIVITIES/
ASSESSMENT
(FA/Assignment/projects
etc.)
O
C
T
O
B
E
R
&
N
O
V
E
M
B
E
R
38 ALGEBRA:
i)Quadratic Equations:
Standard form of a quadratic equation ax
2
+bx+c=0, (a0).
Solution of the quadratic equations (only real roots) by
factorization by completing the square, and by using
quadratic formula. Relationship between discriminant and
nature of roots.
Problems related to day to day activities to be incorporated.
ii)Arithmetic Progressions:
Motivation for studying A.P. Derivation of standard results
of finding the n
th
term and sum of first n terms and their
application in solving daily life problems.
GEOMETRY:
i)Circles:
Tangents to a circle motivated by chords drawn from points
coming closer and closer to the point.
(i) (prove) the tangent at any point of a circle is
perpendicular to the radius through the point to
contact.
(ii) (prove) The lengths of tangents drawn from an
external point to circle are equal
ii)Constructions:
(i) Division of a line segment in a given ratio
(internally)
(ii) Tangent to a circle from a point outside it.
(iii) Construction of a triangle similar to a given
triangle
Activity-9&10
Assignment-III
SPLIT UP SYLLABUS 2014-15(MATHEMATICS-X)
310
D
E
C
E
M
B
E
R
25 PROBABILITY:
Classical definition of probability.
Connection with probability as given in Class IX. Simple
problems on single events, not using set notation
TRIGONOMETRY
Heights and Distances:
Simple and believable problems on heights and distances.
Problems should not involve more than two right triangles.
Angles of elevation/depression should be only 30
0
, 45
0
,
60
0
.
CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY:
Lines (In two dimension)- Reviews the concepts of co-
ordinate geometry done in earlier including graphs of linear
equations, Awareness of geometrical representation of
quadratic polynomials. Distance between two points and
section formula (internal). Area of triangle
Activities 11&12
Project-2
FA-3
J
A
N
U
A
R
Y
27 MENSURATION:
I)Area related to circle:
Areas of plane figures- Motivation- Relating its needs in
day to day life. The area of a circle; are of sectors and
segments of a circle. Problems based on areas and
perimeter / circumference of the above said plane figures
(In calculating area of segment of a circle, problems should
be restricted to central angle of 60, 90 & 120 degrees only.
Plane figures involving triangles, simple quadrilaterals and
circle should be taken.)
Activities-13&14
Assignment-IV
F
E
B
R
U
A
R
Y
24 ii)Surface areas and Volumes:
i) Problems on finding surface areas and
volumes of combinations of any two of the
following: cubes, cuboids, spheres, hemi-
spheres and right circular cylinders / cones.
Frustum of a cone.
ii) Problems involving converting one type of
metallic solid into another and other mixed
problems. (Problems with combination of not
more than two different solids be taken).
FA-4/ PSA
M
A
R
C
H
REVISION-SA 2
SOME OF THE SUGGESTED LAB ACTIVITIES
To obtain the conditions for consistency of system of linear equation in two variables by
graphical method.
SPLIT UP SYLLABUS 2014-15(MATHEMATICS-X)
311
To verify the basic proportionality theorem using parallel line board and triangles cut out.
To verify the Pythagoras theorem by method of paper folding cutting and pasting
To find the mean, median, mode of mathematics marks of UT of class X, draw the OGIVE.
To verify the ratio of the area of two similar triangles is equal to ratio of corresponding side
square.
Draw tree factorization of a given number.
Factorization of polynomial by activity kit.
Verification of the trigonometric identities.
To verify the given sequence is an arithmetic progression by paper cutting and pasting method.
To verify that sum of the first n natural numbers is n(n+1)/2 by graphical method.
To verify using the method of paper cutting, pasting and folding that
i) The angles in semi circle is a right angle.
ii) The angles in a major segment is acute.
iii) The angle is in a minor segment is obtuse.
To verify by the method of paper cutting pasting the length of tangent drawn from an external
point are equal.
To make right circular cylinder of given height, circumference of the base.
To obtain the formula for the lateral surface area of right circular cylinder in terms of the radius
r, of its base and height h.
To make a cone of given slant height 1 and base circumference 2r
To give a suggestive demonstration of the formula for the lateral surface area of a cone.
To get familiar with the idea of probability of an event through double color card experiment.
To make a clinometers and use it to measure the height of an object.
To verify the sum of first n odd natural numbers is n2 by an activity
To verify the sum of areas of 3 sectors of the same radius r found at any triangle is r
2
/2 using
paper cutting and pasting
NOTE: Please refer CBSE Curriculum 2014-15 for clarification, if any.
*****
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- KPMG Numerical Test 3 SolutionДокумент11 страницKPMG Numerical Test 3 SolutionEmmanuel100% (1)
- Siop Lesson PlanДокумент2 страницыSiop Lesson Planapi-445759289Оценок пока нет
- Hypotenuse Leg Theorem Worksheet and Activity PDFДокумент9 страницHypotenuse Leg Theorem Worksheet and Activity PDFRoniAmОценок пока нет
- Book 4Документ16 страницBook 4api-259591583Оценок пока нет
- Book 3Документ14 страницBook 3api-259591583Оценок пока нет
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya Prabhat Pattan Class-Xib: TERM TEST - II - (SESSION 2014-15)Документ2 страницыJawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya Prabhat Pattan Class-Xib: TERM TEST - II - (SESSION 2014-15)api-259591583Оценок пока нет
- ViibДокумент4 страницыViibapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- Book 1Документ14 страницBook 1api-259591583Оценок пока нет
- ViiaДокумент4 страницыViiaapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- Desm S ChemistryДокумент13 страницDesm S Chemistryapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- Book 2Документ16 страницBook 2api-259591583Оценок пока нет
- MehndiДокумент4 страницыMehndiapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- Desm S ChemistryДокумент13 страницDesm S Chemistryapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- VIII AДокумент4 страницыVIII Aapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- VIII BДокумент4 страницыVIII Bapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 271 275science IxДокумент5 страниц271 275science Ixapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 260 265englis IxДокумент6 страниц260 265englis Ixapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 312 316science XДокумент5 страниц312 316science Xapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 297 306english XДокумент10 страниц297 306english Xapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 382 383geography XiДокумент2 страницы382 383geography Xiapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 266 270maths IxДокумент5 страниц266 270maths Ixapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 366 369economics XiДокумент4 страницы366 369economics Xiapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 380 381history XiДокумент2 страницы380 381history Xiapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 349 353physics XiДокумент5 страниц349 353physics Xiapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 338 343english XiДокумент6 страниц338 343english Xiapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 438 440economics XiiДокумент4 страницы438 440economics Xiiapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 360 365biology XiДокумент6 страниц360 365biology Xiapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 438 440economics XiiДокумент4 страницы438 440economics Xiiapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 421 425physics XiiДокумент5 страниц421 425physics Xiiapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 344 348maths XiДокумент5 страниц344 348maths Xiapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 447-448history XiiДокумент2 страницы447-448history Xiiapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- 413-416english Core-XiiДокумент4 страницы413-416english Core-Xiiapi-259591583Оценок пока нет
- ENGG MATH 1 – Trigonometry ReviewДокумент3 страницыENGG MATH 1 – Trigonometry ReviewJan Leynard ParraОценок пока нет
- Pre Board MATHEMATICS September 2019 Practice Test SolutionsДокумент20 страницPre Board MATHEMATICS September 2019 Practice Test SolutionsVener Sandoval ManlapatОценок пока нет
- QB - Differentiation and Its ApplicationsДокумент4 страницыQB - Differentiation and Its ApplicationsfgfgfОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus BreakdownДокумент4 страницыCBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus Breakdownराहुल रविराजОценок пока нет
- World Math Championship Intermediate SolutionsДокумент13 страницWorld Math Championship Intermediate SolutionsMinh NgôОценок пока нет
- VisMath-Volume12 No3 2o1o-Origami PDFДокумент13 страницVisMath-Volume12 No3 2o1o-Origami PDFhugoОценок пока нет
- Q4 G9 QuizДокумент2 страницыQ4 G9 QuizEmelie HernandezОценок пока нет
- The Guivy Zaldastanishvili American Academy in Tbilisi: DURATION: 90 MinutesДокумент6 страницThe Guivy Zaldastanishvili American Academy in Tbilisi: DURATION: 90 MinutesMzeo MariamiОценок пока нет
- Pythagorean Theorem in BusinessДокумент4 страницыPythagorean Theorem in BusinessDeelanshiОценок пока нет
- Maths in OrigamiДокумент31 страницаMaths in OrigamiLuis Eduardo Lara HenriquezОценок пока нет
- Class 10 Maths Term-Wise Syllabus 2021-22Документ5 страницClass 10 Maths Term-Wise Syllabus 2021-22Lakshay JainОценок пока нет
- 2014 Intermediate Individual Solutions (English) PDFДокумент8 страниц2014 Intermediate Individual Solutions (English) PDFalex jobogОценок пока нет
- Math RevДокумент4 страницыMath RevEdmond BajadoОценок пока нет
- The Triangle and Its Properties: MADE BY Arpit Agrawal Class 7 A Roll Number 33Документ9 страницThe Triangle and Its Properties: MADE BY Arpit Agrawal Class 7 A Roll Number 33safsdfОценок пока нет
- Mathematics: (Simplified)Документ271 страницаMathematics: (Simplified)faizan khalilОценок пока нет
- 4 6 Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницы4 6 Lesson Planapi-194153634Оценок пока нет
- Imo Problem Solution 1959 2009Документ342 страницыImo Problem Solution 1959 2009Immanuel Rukun Sitepu100% (2)
- Pythagorean Theorem Lesson PlanДокумент8 страницPythagorean Theorem Lesson PlanChikahantayo TVОценок пока нет
- HP Calculators: HP 10s Powers and RootsДокумент4 страницыHP Calculators: HP 10s Powers and RootsromenegonОценок пока нет
- General Education PRCДокумент30 страницGeneral Education PRCherma joyce colomaОценок пока нет
- For Print 1Документ30 страницFor Print 1davidrferrerОценок пока нет
- Maths Class X Periodic Test II 40 Marks Sample Paper 03 PDFДокумент3 страницыMaths Class X Periodic Test II 40 Marks Sample Paper 03 PDFK VaralakshmiОценок пока нет
- 2017 MK Sample Questions NEW PDFДокумент12 страниц2017 MK Sample Questions NEW PDFnimitj1968Оценок пока нет
- MATH10-QUARTER2-MODULE6-Applying The Distance Formula To Prove Some Geometric PropertiesДокумент21 страницаMATH10-QUARTER2-MODULE6-Applying The Distance Formula To Prove Some Geometric PropertiesDreyzen Ganotisi100% (1)
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 8Документ22 страницыMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 8Nylinam100% (1)
- M9GE IVb C 1Документ30 страницM9GE IVb C 1Saharah PundugОценок пока нет
- 3RD QUARTER EXAM Grade 9Документ3 страницы3RD QUARTER EXAM Grade 9Sarah Sarael0% (1)