Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
ANT Tutorial: Ashley J.S Mills
Загружено:
Srikanth Madasu0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
30 просмотров13 страницAnt tutorial
Оригинальное название
Ant
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документAnt tutorial
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
30 просмотров13 страницANT Tutorial: Ashley J.S Mills
Загружено:
Srikanth MadasuAnt tutorial
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 13
ANT Tutorial
Ashley J.S Mills
<ug55axm@cs.bham.ac.uk>
Copyright 2002 The University Of Birmingham
Table of Contents
1. Introduction ................................................................................................................................................. 1
2. Ant Installation ............................................................................................................................................. 1
3. Ant Basics ................................................................................................................................................... 1
4. ATypical Project .......................................................................................................................................... 3
5. ABit About FileSets ..................................................................................................................................... 8
6. AdvancedTopics .......................................................................................................................................... 10
6.1. FlowOf Control ................................................................................................................................. 10
7. References ................................................................................................................................................... 13
1. Introduction
Imagine that you are working on a large project. The project is a Java project and consists of many .java files. It consists of
classes that are dependent on other classes and classes which are stubs or drivers, they are situated in multiple directories and the
output files must go into multiple directories too, you have various project build routes for different applications and at the mo-
ment are coordinating all of this manually or using some other build utility which doesn't do what you want it to so many hours are
spent changing directories compiling individual files and so on... Now, imagine if their was a tool that could alleviate the stress
and hassle you are experiencing, OK, enough of the rhetoric, this tool exists, it is called ANT. For a nice definition of what Ant is,
see http://jakarta.apache.org/ant/.
Ant (originally an acronym for Another Neat Tool), is a build tool with special support for the Java programming language but can
be used for just about everything. Ant is platform-independent; it is written purely in Java. Ant is particularly good at automating
complicated repetitive tasks and thus is well suited for automating standardised build processes. Ant accepts instructions in the
form of XML documents thus is extensible and easy to maintain.
2. Ant Installation
The documentation for the installation is written under the assumption that the reader has some experience of installing software
on computers and knows how to change the operating environment of the particular operating system they are using. The docu-
ments entitled Configuring A Windows Working Environment [../winenvars/winenvarshome.html] and Configuring A Unix Work-
ing Environment [../unixenvars/unixenvarshome.html] are of use to people who need to know more.
1. Download the binaries from http://jakarta.apache.org/ant/index.html, unzip them to a suitable directory.
2. Append /path/to/ant/bin to the PATH environment variable.
3. Append the .jar files in /path/to/ant/lib/ to the CLASSPATH environment variable. Set JAVA_HOME to point to the lo-
cation of the JDK installation on the machine that the software is being installed on. Append /path/to/jdk/lib/* to the
CLASSPATH environment variable.
The installation instructions provided with the Ant software installation download are clear enough to warrant abstaining from
writing any more about the installation here. Refer to /path/to/ant/docs/manual/install.html.
3. Ant Basics
An Ant build file comes in the form of an XML document, all that is required is a simple text editor to edit the build file(s). An ed-
itor that provides XML syntax highlighting is preferable. The Ant installation comes with a JAXP-Compliant XML parser, this
means that the installation of an external XML parser is not necessary.
A simple Ant example is shown below followed by a set of instructions indicating how to use Ant. It is recommended that the
reader follow these instructions to gain some experience in using Ant.
1
Example 1. Basic build.xml Example
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<project name="test" default="compile" basedir=".">
<property name="src" value="."/>
<property name="build" value="build"/>
<target name="init">
<mkdir dir="${build}"/>
</target>
<target name="compile" depends="init">
<!- - Compile the java code - ->
<javac srcdir="${src}" destdir="${build}"/>
</target>
</project>
<?xml version="1.0"?>
Since Ant build files are XML files the document begins with an XML declaration which specifies which version of XML is
in use, this is to allow for the possibility of automatic version recognition should it become necessary.
<project name="test" default="compile" basedir=".">
The root element of an Ant build file is the project element, it has three attributes.
name: The name of the project, it can be any combination of alphanumeric characters that constitute valid XML.
default: The default target to use when no target is specified, out of these three attributes default is the only required at-
tribute.
basedir: The base directory from which any relative directories used within the Ant build file are referenced from. If this
is omitted the parent directory of the build file will be used.
<property name="src" value="."/>
<property name="build" value="build"/>
The property element allows the declaration of properties which are like user-definable variables available for use within an
Ant build file. The name attribute specifies the name of the property and the value attribute specifies the desired value of the
property. The name and value values are subject to standard XML constraints. In the markup shown above src has been as-
signed the value ".".
In order to reference a property defined in this manner one specifies the name between ${ and }, for example, to reference the
value of src one uses ${ src }. In the example, src is used later on to specify the location of the .java files to be processed.
<target name="init">
<mkdir dir="${build}"/>
</target>
The target element is used as a wrapper for a sequences of actions. A target has a name, so that it can be referenced from
elsewhere, either externally from the command line, or internally via the depends keyword, or through a direct call. The tar-
get in the example is called "init" (initiate), it makes a directory using the mkdir element with the name specified by the
build property defined in three.
The target element has a number of possible attributes, unless otherwise specified, these are optional:
name: The name of the target is used to reference it from elsewhere, it is subject to the constraints of XML well formed-
ness. This is the only required attribute for the target element.
depends: This is a comma separated list of all the targets on which this target depends, for example, number 5 illustrates
how compile depends on init, in other words, depends contains the list of the targets that must be executed prior to exe-
cuting this target.
ANT Tutorial
2
if: This is a useful attribute which allows one to add a conditional attribute to a target based on the value of a property ,
for example, if="gui-ready" could be used to only execute the encapsulating target's instructions if the property gui-ready
was is (to any value).
unless: This is the converse of if, for example, unless="gui-ready" could be used to conditionally execute the contents of
the encapsulating target. The targets' contents will be executed unless the the property gui-ready is set (to any value).
description: This is a short description of the target.
<target name="compile" depends="init">
<!- - Compile the java code - ->
<javac srcdir="${src}" destdir="${build}"/>
</target>
As explained in four, depends allows one to specify other targets that must be executed prior to the execution of this target.
In the listing above depends="init" is used to indicate that the compile target requires that the target named init be executed
prior to executing the body of compile.
<target name="compile" depends="init">
<!- - Compile the java code - ->
<javac srcdir="${src}" destdir="${build}"/>
</target>
The javac element, as used above, is a task, tasks are performed in the body of a target, in this case, the source directory is
specified by referencing the src property and the destination directory is specified by referencing the build property. The ex-
ample above causes javac to be executed, compiling all the .java files in the directory specified by the src property and
placing the resultant .class files in the directory specified by the build property.
Copy the source code in the example into a text editor and save the file as build.xml. Create a test directory and place the file in
it. Create some arbitrary .java file and place it in the same directory as build.xml. For convenience, here is an example .java
file: test.java. Place the java file in the same directory as build.xml.
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
Type the following at the commandline in the test directory:
ant -v
This will create a directory called build, compile test.java and place the .class file created in the build directory. The -v
directs ant to be verbose. This verbosity causes the command to echo lots of information, information that is not really necessary
for most normal purposes. Execute the command sequence again. An example output message is shown below:
[javac] test.java omitted as /path/to/temp/build/test.class is up todate
A nice feature of Ant is that by default, only those .java input files that have a more recent timestamp than their corresponding
.class output files will be compiled.
4. A Typical Project
This section intends to provide and describe a typical Ant buildfile, such that, the example given could be easily modified to suit
ones personal needs.
When starting a project it is a good idea to follow the suggestion in the Ant documentation of using three directories:
1. src : For project source files.
2. build : For compiled/output files produced (by Ant).
3. lib : For class libraries and dependency files.
Create a test directory and from within this, create the three directories described above.
A simple Java program will be used to illustrate the use of Ant. Copy the following program into a file called UKLights.java
and place it in the src directory:
ANT Tutorial
3
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class UKLights extends JFrame {
public UKLights() {
super("UKLights");
ImageIcon icon = new ImageIcon("uklights.jpeg");
getContentPane().add(new JLabel(icon));
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setSize(new Dimension(315,244));
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
new UKLights();
}
}
Alternatively, download the file from here: UKLights.java [files/uklights/UKLights.java]. The program imports the auxilliary Java
classes and defines two methods. The first method is the constructor for the class which extends JFrame. The constructor calls su-
per to initiate a JFrame with the title "UKLights". An ImageIcon is created containing the image uklights.jpeg. uk-
lights.jpeg can be downloaded here: uklights.jpeg [files/uklights/uklights.jpeg].
Readers of the print version of this tutorial should use some other jpeg or gif and make the necessary adjustments to the program
source. After the ImageIcon is created it is added to the a new JLabel which is then added to the JFrame. The default close opera-
tion for the JFrame is set, the size set to that of the ImageIcon, and the frame made visible. The second method is the main method
which is called when executing the program like this:
java UKLights
The program displays the specified image in a JFrame. Change into the base directory that the directories src, build, and lib
were created from. Create a file called build.xml.
The first thing that the build file must contain is a standard XML declaration:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
This provides a way for any tools that may process the file to find out the version of XML in use. Next, add the standard Ant root
XML element, project:
<project name="UKLights" default="all" basedir=".">
</project>
The rest of the Ant buildfile is contained within this element. Three attributes have been specified for the project. The first is
name; the name given to this project. The second is default; the default target to build, in this case all. The third is basedir which
specifies the directory to use as the base directory, in this case, the current directory is used as indicated by '.'. The base directory
is relative to the build file.
The rest of the code snippets in this section shouold be placed inside the project element in the sequence in which they are intro-
duced. Add these property definitions:
<property name="src" value="src"/>
<property name="build" value="build"/>
<property name="lib" value="lib"/>
These property definitions define properties of which the values can be accessed within the buildfile by enclosing the property
name within braces and prefixing it with a dollar sign. To reference the property src use ${src}. In this example, properties speci-
fying the location of the source, build, and library directories described earlier have been created. This may seem unnecessary
since, in this case, it takes longer to reference the property names than to type the actual values. However, referencing these direc-
tories via properties allows one to change the locations of these directories without having to change every reference to them. If
Ant is ran on this buildfile the following error message is produced:
Buildfile: build.xml
BUILD FAILED
Target `all' does not exist in this project.
Total time: 1 second
This specifies that the target all has not been defined yet, add it:
<target name="all" depends="UKLights"
description="Builds the whole project">
<echo>Doing all</echo>
ANT Tutorial
4
</target>
The all target depends on the target "UKLights", meaning that "UKLights" will be called prior to executing the body of all. The
description defined will be used by Ant's projecthelp option. Add the "UKLights" target that all depends on:
<target name="UKLights"
description="Builds the main UKLights project">
<echo>Doing UKLights</echo>
</target>
This target has a name and a description. The target descriptions are used by Ant's projecthelp option to display information
about the available targets. If one executes the following command sequence:
ant -projecthelp
The output produced is:
Buildfile: build.xml
Main targets:
UKLights Builds the main UKLights project
all Builds the whole project
Default target: all
One executes the build file by typing ant in the base directory, the output produced is:
Buildfile: build.xml
UKLights:
[echo] Doing UKLights
all:
[echo] Doing all
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
Total time: 1 second
Notice that "UKLights" was called before "all" because "all" depended on it. Both targets have simple tasks, they both echo a mes-
sage to the screen indicating that they have been called. The target should compile the Java file so add the line:
<javac srcdir="${src}" destdir="${build}"/>
Ant has built in support for the Java oriented commands java and javac. The javac element compiles all the java files in the direc-
tory specified by the srcdir attribute and places them in the directory specified by the destdir attribute. Ant will only compile those
source files with more recent timestamps than their corresponding output .class files. This behaviour is present in certain other
Ant tasks, where it is not present, one must add the desired functionality manually. The output produced when Ant is ran on the
modified build file is shown below:
Buildfile: build.xml
UKLights:
[echo] Doing UKLights
[javac] Compiling 1 source file to \blah\blah\blah\build
all:
[echo] Doing all
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
Total time: 2 seconds
There are various options that may be supplied to the javac task by setting their respective attributes in the task call. Options avail-
able include, listfiles - to list the files to be compiled, failonerror - to cause the build to fail if compilation errors are encountered,
and verbose to specify that java be verbose. To set an attribute, set it's value to "true". If ant is ran on the buildfile again without
modifying anything it produces the output:
Buildfile: build.xml
UKLights:
[echo] Doing UKLights
all:
[echo] Doing all
ANT Tutorial
5
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
Total time: 1 second
Which illustrates that no compilation was done this time round. Change into the build directory and execute UKLights.class.
No picture is available because it was not copied into the build directory, add this line before the javac task:
<copy file="${src}/UKLights.jpeg" tofile="${build}/UKLights.jpeg"/>
Running ant on the modified build file produces identical output to last time with the addition of the line:
[copy] Copying 1 file to C:\docbook\docproj\src\items\ant\files\build
By default, Ant will only copy the file if it is more recent than the target file or the target file does not exist. To override this be-
haviour so that Ant always copies the file(s) specified, set the overwrite attribute to "true".
Another source file will be added to the program. Change the constructor of UKLights.java to:
public UKLights() {
super("UKLights");
ImageIcon icon = new ImageIcon("uklights.jpeg");
JButton exitButton = new JButton("Exit");
exitButton.addActionListener(new ExitControl());
JButton aboutButton = new JButton("About");
aboutButton.addActionListener(new AboutControl());
getContentPane().setLayout(new FlowLayout());
getContentPane().add(new JLabel(icon));
getContentPane().add(aboutButton);
getContentPane().add(exitButton);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setSize(new Dimension(315,294));
setVisible(true);
}
An exit button has been added and an about button, the layout has been set to FlowLayout, and the size of the JFrameincreased to
accommodate the buttons. The ExitControl to handle events from exitButton:
import java.awt.event.*;
public class ExitControl implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
}
Save this in a file called ExitControl.java, or download it here: ExitControl.java [files/uklights/ExitControl.java]. Put the file
in the src directory. ExitControl causes the program to terminate when the user clicks on the exit button. An about button is cre-
ated to display information about the picture loaded, events from this button are handled by AboutControl:
import java.awt.event.*;
public class AboutControl implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
new AboutPopup();
}
}
Save this in a file called AboutControl.java, or download it here: AboutControl.java [files/uklights/AboutControl.java]. Put
the file in the src directory. AboutControl.java creates a new AboutPopup:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class AboutPopup extends JFrame {
public AboutPopup() {
super("About");
String message = "\n";
message+="This image of Earth's city lights was created with data ";
message+="from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program ";
message+="(DMSP) Operational Linescan System (OLS). ";
message+="Originally designed to view clouds by moonlight, ";
message+="the OLS is also used to map the locations of permanent ";
message+="lights on the Earth's surface.\n\n";
message+="The image has been modified by Ashley Mills to only include ";
message+="the UK, the original image and further description can be ";
message+="found at:\n\n";
message+="http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/viewrecord?5826\n\n";
message+="This is also where the description was taken from.";
ANT Tutorial
6
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
setSize(new Dimension(315,294));
JTextPane messagePane = new JTextPane();
messagePane.setBackground(Color.BLACK);
messagePane.setForeground(Color.GRAY);
messagePane.setEditable(false);
messagePane.setText(message);
getContentPane().add(messagePane);
setResizable(false);
setVisible(true);
}
}
Save this in a file called AboutPopup.java or download it here: AboutPopup.java [files/uklights/AboutPopup.java]. Put the file
in the src directory. AboutPopup.java extends JFrame hence when instantiated will create a new frame so super is called with
the string that will be the title of the JFrame. A message is defined. The default close operation for the JFrame is set. The size of
the JFrameis set. A JTextPane is created, it's colours are setup and it's is made non-editable. It's message is set. It is added to the
JFrame. The JFrame is made non-resizable and made visible.
Modify the "UKLights" target in build.xml:
<target name="UKLights" depends="AboutControl,ExitControl"
description="Builds the main UKLights project">
<echo>Doing UKLights</echo>
<copy file="${src}/UKLights.jpeg" tofile="${build}/UKLights.jpeg"/>
<javac srcdir="${src}" destdir="${build}" includes="UKLights.java"/>
</target>
The "UKLights" target now depends on the "AboutControl" and "ExitControl" targets. The javac line has been modified so that
only UKLights.java is compiled by this target, the includes attribute, which can accept a list of files, is used to acheive this.
Usually one would just use a single javac task to compile all the classes by ommiting the includes attribute. Add the AboutControl
target:
<target name="AboutControl" depends="AboutPopup"
description="Builds AboutControl">
<echo>Doing AboutControl</echo>
<javac srcdir="${src}" destdir="${build}" includes="AboutControl.java"/>
</target>
This compiles AboutControl.java and depends on the "AboutPopup" target. Add the "AboutPopup" target:
<target name="AboutPopup" description="Builds AboutPopup">
<echo>Doing AboutPopup</echo>
<javac srcdir="${src}" destdir="${build}" includes="AboutPopup.java"/>
</target>
This compiles AboutPopup.java. Add the "ExitControl" target:
<target name="ExitControl" description="Builds ExitControl">
<echo>Doing ExitControl</echo>
<javac srcdir="${src}" destdir="${build}" includes="ExitControl.java"/>
</target>
This compiles ExitControl.java. One more target, "Clean", will be added. "Clean"'s purpose is to delete the contents of the
build directory.
<target name="Clean" description="Removes previous build">
<delete verbose="true">
<fileset dir="${build}"/>
</delete>
</target>
This deletes the contents of the build directory, this is achieved by specifying a fileset with the dir attribute set to the directory to
delete the contents of. To delete the directory as well as the contents of the directory, set theincludeEmptyDirs attribute to "true".
The verbose attribute on delete is set to "true" so that Ant will list each file being deleted.
The completed build.xml can be downloaded here: build.xml [files/uklights/build.xml]. The completed UKLights.java can be
downloaded here: UKLights.java [files/uklights/UKLights.java].
The project is complete; testing can commence. Execute the "Clean" target to remove the old build:
ant Clean
This produces output similar to:
Buildfile: build.xml
ANT Tutorial
7
Clean:
[delete] Deleting 2 files from \blah\blah\build
[delete] Deleting \blah\blah\blah\build\UKLights.class
[delete] Deleting \blah\blah\blah\build\uklights.jpeg
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
Total time: 1 second
Run Ant with no arguments so it executes the default target, "all", by typing ant at the command line in the base directory, the out-
put produced is:
Buildfile: build.xml
AboutPopup:
[echo] Doing AboutPopup
[javac] Compiling 1 source file to \blah\blah\blah\build
AboutControl:
[echo] Doing AboutControl
[javac] Compiling 1 source file to \blah\blah\blah\build
ExitControl:
[echo] Doing ExitControl
[javac] Compiling 1 source file to \blah\blah\blah\build
UKLights:
[echo] Doing UKLights
[copy] Copying 1 file to \blah\blah\blah\build
[javac] Compiling 1 source file to \blah\blah\blah\build
all:
[echo] Doing all
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
Total time: 4 seconds
Notice the order that the targets are executed, first "AboutPopup", then "AboutControl", then "ExitControl" then "UKLights", then
finally, "all". This is because the dependencies of a target are exectuted before the target itself. The build was successful as indi-
cated by "BUILD SUCCESSFUL", UKLights.class was created, execute UKLights.class and enjoy the image. The reader
should now be able to use Ant in a simple project.
5. A Bit About FileSets
A FileSet is a filter which uses one or more patterns to specify which files are desired. A FileList is a list of desired files. FileSets
use PatternSets and Patterns to define their actions.
? is used to match any character.
* is used to match zero or more characters.
** is used to match zero or more directories.
A FileSet must specify a base directory from which all other path calculations are made, this is supplied via the dir attribute. A
FileSet has the basic form:
<fileset dir="BASEDIR"/>
Or:
<fileset dir="BASEDIR">
</fileset>
Since both of these FileSets contain no patterns, they match the default; every file in the base directory and all it's subdirectories,
recursively, apart from the files which match the following patterns:
**/*~
**/#*#
**/.#*
**/%*%
**/._*
**/CVS
**/CVS/**
**/.cvsignore
ANT Tutorial
8
**/SCCS
**/SCCS/**
**/vssver.scc
**/.svn
**/.svn/**
Notice that the sequence "**" is used above to denote zero or more directories, for example, the first pattern matches any file in
the base directory or any of it's directories that end with the '~' character, which some common tools use to denote scratch or
backup files. The other patterns are excluded for similar reasons.
Note
If one desires to delete any of these defaultly excluded files, for example, to delete all scratch files that vim (a text editor)
made, recursively, one has to set defaultexcludes="no" so that the defaults are not excluded and then one could use some-
thing like:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<project name="Scratch Cleaner" default="clean" basedir=".">
<target name="clean">
<echo>Removing temporary files...</echo>
<delete verbose="true"> <!- - Remove all *~ files - ->
<fileset dir="${basedir}" defaultexcludes="no">
<include name="**/*~"/>
</fileset>
</delete>
</target>
</project>
<fileset dir="." includes="**/*.blah **/*.bleh"
Includes all files ending in the extensions "blah" and "bleh" in the base directory and all subdirectories, the pattern is applied re-
cursively in the subdirectories.
<fileset dir=".">
<include name="**/*bl*"/>
<exclude name="**/blah/*"/>
</fileset>
Includes all files that contain the string "bl" in the base directory and all sub directories, recursively. Excludes any files in any di-
rectory called "blah", whether it occurs in the current directory or any of the sub directories, recursively. Notice that the syntax is
slightly different, in that, include and name are used instead of includes and exclude and name are used instead of excludes.
Note
In the context of the sentences above, the word "recursively" means that the pattern is applied to each of the sub-
directories as well as the base directory hence it is then applied to the sub-directories of the sub-directories and so on. The
pattern is applied to all directories under the base directory.
Patterns can be 'saved' for future use by encapsulating them within a patternset element:
<fileset dir=".">
<patternset id="blah">
<include name="**/*bl*"/>
<exclude name="**/blah/*"/>
</patternset>
</fileset>
This pattern could be referenced by any other element that supports this kind of referencing:
<fileset dir=">
<patterset refid="blah"/>
</fileset>
One can also use the if and unless attributes with include and exclude to provide conditional inclusions or exclusions:
<fileset dir=".">
<include name="**/extensions/*.java" if="version.professional"/>
</fileset>
Which includes all the java files within any sub-directories called "extensions", from the base directory, only if some property
called "version.professional" is set.
<fileset dir=".">
<exclude name="chinese.lang" unless="language.chinese"/>
ANT Tutorial
9
</fileset>
Which excludes the chinese language module unless the property "language.chinese" is set. If one finds that a lot of include or ex-
clude elements are being used, it can be useful to define the include and exclude elements in an external file. The external file can
then be referenced from within a build file with includesfile or excludesfile respectively. The referenced file is treated as having
one include or exclude element per line:
<fileset dir=".">
<includesfile name="some.file"/>
</fileset>
some.file would look like:
bl?h.bl?h
*.java
Notice, that each line contains the value that would be assigned to each of the include statements' name attribute. Similarly, an
exludesfile could be specified:
<fileset dir=".">
<excludesfile name="some.file"/>
</fileset>
some.file would look like:
Test.java
**/extensions/*
build.xml
cool.file
if and unless can be used with includesfile and excludesfile. FileLists specify a list of files and do not support wildcards. The dir
attribute specifies the base directory. The files attribute specifies a comma or space separated list of files and the id attribute is op-
tional:
<filelist id="blah" dir="."
files="blah.blah bleh.bleh"/>
ids may be referenced from another filelists:
<filelist refid="blah"/>
I know of no way arbitrarily exclude or include a filelist, for this behaviour use a fileset, patternset or dirset.
6. Advanced Topics
6.1. Flow Of Control
Since Ant does not contain any real control structures like if..then..else, one has to manipulate Ant's ability to call internal targets
that support conditional execution to emulate the desired control structures. Consider the control sequence:
if( condition ) {
if( inner-condition ) {
A
} else {
B
}
} else {
C
}
There are three possible routes that the program could take, designated by the actions A, B and C. This can be expressed in Ant as:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<project name="Flow.Of.Control" default="nested-if" basedir=".">
<target name="nested-if">
<condition property="condition">
<available file="fileone"/>
</condition>
<antcall target="then"/>
<antcall target="else"/>
</target>
<target name="then" if="condition">
<echo>THEN BODY EXECUTED</echo>
<condition property="inner-condition">
<available file="filetwo"/>
ANT Tutorial
10
</condition>
<antcall target="inner.then"/>
<antcall target="inner.else"/>
</target>
<target name="inner.then" if="inner-condition">
<echo>INNER THEN BODY EXECUTED</echo>
</target>
<target name="inner.else" unless="inner-condition">
<echo>INNER ELSE BODY EXECUTED</echo>
</target>
<target name="else" unless="condition">
<echo>ELSE BODY EXECUTED</echo>
</target>
</project>
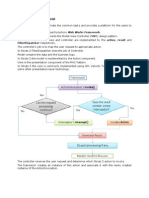
It can be downloaded here: build.xml [files/build.xml]. A diagram which attempts to clarify the location of the various compo-
nents of the control structure is shown below:
Figure 1. Nested If..Then..Else In Ant
Assuming the case where the first file, fileone, and the second file, filetwo are not available. The initial condition checks if
the file fileone available, if it is, the property condition is set. Calls to the targets then and else follow. The execution of then is
conditional, dictated by (if="condition"). Since the assumption is fileone is not available, condition will not be set and the body
of then will not be executed. The next target, else, will be called. The execution of else is conditional, dictated by condi-
(unless="tion") which means that the body will be executed unlesscondition is set. Since condition has not been set, the body of
else will be executed. The output from simulating this by running ant on the build file with the files fileone and filetwo not
available is shown below:
Figure 2. Output produced when ant is ran when fileone and filetwo are not available
ANT Tutorial
11
Assuming the case where the first file, fileone, is present, and the second file, filetwo is not. The initial condition will be set
because fileone is available so the call to then will be successful. The body of then contains another condition which checks for
the existence of the file filetwo, if it is available, the property, inner-condition is set. Since the assumption is that filetwo is
not available, the property inner-condition will not be set. Calls to the targets inner.then and inner.else follow. The execution of
inner.then is conditional, dictated by (if="inner-condition") so the body of inner.then will not be executed. The execution of in-
ner.else is conditional, dictated by (unless="inner-condition") so the body of inner.else will be executed since the only thing that
would stop the execution of it would be if inner-condition was set. The output from simulating this by running ant on the build
file with the file fileone available and the file filetwo not available is shown below:
Figure 3. Output produced when ant is ran with fileone available and filetwo not available
Upon exiting the call to then, the target else will be called but the body will not be executed because the condition condi-
(unless="tion"), specifies that if condition is set, the target should not be executed.
Assuming the case where the first file, fileone, and the second file, filetwo are both available. The outer condition will cause
the property condition to be set because fileone is available, so when the target then is called, the body will be executed. The
condition within then will cause the property inner-condition to be set because filetwo is available. This means that the call to
inner.then will be successful. Upon exiting inner.then, inner.else will be called but the body will not be executed because inner-
condition is set. Upon exiting then, else will be called but the body will not be executed because condition is set. The output from
simulating this by running ant on the build file with the files, fileone and filetwo, available is shown below:
Figure 4. Output produced when ant is ran with fileone and filetwo both available
ANT Tutorial
12
7. References
http://jakarta.apache.org/ant/resources.html
Apache Ant Resource Homepage
http://jakarta.apache.org/ant/manual/index.html [http://jakarta.apache.org/ant/manual/index.html]
Apache Ant 1.5 Manual
http://www.iseran.com/Java/ant/tutorial/ant_tutorial.html
A beginners guide to Ant Steve Loughran 2001-04-30
ANT Tutorial
13
Вам также может понравиться
- Ant ScriptДокумент12 страницAnt ScriptmyappsanandОценок пока нет
- ANT Tutorial: Ashley J.S MillsДокумент13 страницANT Tutorial: Ashley J.S Millsamit.vyas.in3221Оценок пока нет
- JAVASCRIPT FRONT END PROGRAMMING: Crafting Dynamic and Interactive User Interfaces with JavaScript (2024 Guide for Beginners)От EverandJAVASCRIPT FRONT END PROGRAMMING: Crafting Dynamic and Interactive User Interfaces with JavaScript (2024 Guide for Beginners)Оценок пока нет
- Apache Ant: K. M. Fazle Azim BabuДокумент31 страницаApache Ant: K. M. Fazle Azim BabuazimbabuОценок пока нет
- DevOps. How to build pipelines with Jenkins, Docker container, AWS ECS, JDK 11, git and maven 3?От EverandDevOps. How to build pipelines with Jenkins, Docker container, AWS ECS, JDK 11, git and maven 3?Оценок пока нет
- Yet Another Ant TutorialДокумент6 страницYet Another Ant TutorialvidurindaОценок пока нет
- Getting started with Spring Framework: A Hands-on Guide to Begin Developing Applications Using Spring FrameworkОт EverandGetting started with Spring Framework: A Hands-on Guide to Begin Developing Applications Using Spring FrameworkРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- ANT Interview Questions and Answers: Ques:1 Give Example How We Can Deploy File On Server Using Ant? AnsДокумент10 страницANT Interview Questions and Answers: Ques:1 Give Example How We Can Deploy File On Server Using Ant? AnsajhiredОценок пока нет
- Using Apache Ant for Enterprise DevelopmentДокумент17 страницUsing Apache Ant for Enterprise DevelopmentSabapathy KannappanОценок пока нет
- Ant Quick GuideДокумент22 страницыAnt Quick Guideid047Оценок пока нет
- Oracle Database Transactions and Locking Revealed: Building High Performance Through ConcurrencyОт EverandOracle Database Transactions and Locking Revealed: Building High Performance Through ConcurrencyОценок пока нет
- Tutorials Point, Simply Easy Learning: Apache ANT TutorialДокумент15 страницTutorials Point, Simply Easy Learning: Apache ANT TutorialajsamsamОценок пока нет
- Build and Test Tools Ant - PrintДокумент25 страницBuild and Test Tools Ant - PrintpughazhenthybОценок пока нет
- Spring Boot Intermediate Microservices: Resilient Microservices with Spring Boot 2 and Spring CloudОт EverandSpring Boot Intermediate Microservices: Resilient Microservices with Spring Boot 2 and Spring CloudОценок пока нет
- Ant: Another Nice Tool: Ali Beyad October 1, 2003Документ19 страницAnt: Another Nice Tool: Ali Beyad October 1, 2003sambitmohapatraОценок пока нет
- 01 - Basics of Apache ANTДокумент17 страниц01 - Basics of Apache ANTamitfegade121Оценок пока нет
- SCM/Build & Release Management: Chiranjeevi PatelДокумент14 страницSCM/Build & Release Management: Chiranjeevi PatelpsushmithОценок пока нет
- Sample Ant Build File - JARДокумент6 страницSample Ant Build File - JARShailesh KhuneОценок пока нет
- SCM Introduction BuildAutomationДокумент16 страницSCM Introduction BuildAutomationkasimОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Ant build toolДокумент43 страницыIntroduction to Ant build toolBhaskar GunduОценок пока нет
- Apacheant 120721102820 Phpapp02Документ28 страницApacheant 120721102820 Phpapp02amitfegade121Оценок пока нет
- Using Open Source in Java ProjectsДокумент127 страницUsing Open Source in Java Projectsapi-3827215100% (1)
- Fire Framework Installation StepsДокумент23 страницыFire Framework Installation Stepsaj iseОценок пока нет
- What Is Ant?: 2. Why Do You Call It Ant?Документ9 страницWhat Is Ant?: 2. Why Do You Call It Ant?avinashkakarlaОценок пока нет
- How To Setup A Basic Struts Project Using Eclipse IDE - Apache StrutsДокумент26 страницHow To Setup A Basic Struts Project Using Eclipse IDE - Apache StrutsKalyan CheediОценок пока нет
- Build ToolДокумент11 страницBuild ToolSabari NathanОценок пока нет
- Ejb3, Step by Step by Example: (Pick The Date)Документ9 страницEjb3, Step by Step by Example: (Pick The Date)martin nadОценок пока нет
- Spring Quick Start TutorialДокумент45 страницSpring Quick Start Tutorialanon-156973100% (9)
- Environment Setup JDK, Ant and Junit: Case Study 3Документ16 страницEnvironment Setup JDK, Ant and Junit: Case Study 3Joker JrОценок пока нет
- 04 Very BasicДокумент7 страниц04 Very Basicamitfegade121Оценок пока нет
- Ant Step by StepДокумент22 страницыAnt Step by StepGuru KallamОценок пока нет
- Spring Boot NitДокумент572 страницыSpring Boot Nitsonam80% (30)
- Spring Interview QuestionsДокумент17 страницSpring Interview QuestionsPRABHU SORTURОценок пока нет
- Jenkins ThefinalДокумент14 страницJenkins ThefinalVijay DhanakodiОценок пока нет
- Build Bar File WMBДокумент5 страницBuild Bar File WMBSandeepNayakОценок пока нет
- Company Based Interview AnswersДокумент178 страницCompany Based Interview Answersshabbir_ahmed5023Оценок пока нет
- Trend Micro Soap ExampleДокумент6 страницTrend Micro Soap ExampleAlzheimer B. BoonthОценок пока нет
- Struts 1 - How To Setup A Basic Struts Project Using Eclipse IDEДокумент18 страницStruts 1 - How To Setup A Basic Struts Project Using Eclipse IDEchandukaturiОценок пока нет
- Zend Installation Creating Controllers Creating Views Database Connectivity Naming Conventions Creating Models Rest API CallsДокумент13 страницZend Installation Creating Controllers Creating Views Database Connectivity Naming Conventions Creating Models Rest API Callspass123wordОценок пока нет
- Folder Path "C:/apache-AntДокумент2 страницыFolder Path "C:/apache-Antdba_123Оценок пока нет
- 3 Jndi NotesДокумент14 страниц3 Jndi NotesSomesh SumanОценок пока нет
- AEM HandbookДокумент5 страницAEM HandbookckjОценок пока нет
- Hibernate: Simple - Example: Part One - The Example StepsДокумент5 страницHibernate: Simple - Example: Part One - The Example StepsDinesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Building s2 ApplicationsДокумент62 страницыBuilding s2 Applicationsapi-3698136Оценок пока нет
- Spring Boot Reference 400Документ266 страницSpring Boot Reference 400wmarasigan2610Оценок пока нет
- The Power of Xdoclet Cis 764 - Database System DesignДокумент9 страницThe Power of Xdoclet Cis 764 - Database System DesignDoi Gio HuОценок пока нет
- Hibernate PracticalsДокумент49 страницHibernate PracticalsTamil kutty videosОценок пока нет
- Spring Rest APIДокумент45 страницSpring Rest APIMohamed HaydarОценок пока нет
- How To Create JCA Using NetbeansДокумент1 страницаHow To Create JCA Using Netbeansmohamed shaheenОценок пока нет
- InstallShield 2010, InstallScript, Directory Properties and Windows Environment VariablesДокумент16 страницInstallShield 2010, InstallScript, Directory Properties and Windows Environment VariablesPauloОценок пока нет
- SE Tools and Practices Lab 5Документ6 страницSE Tools and Practices Lab 5Habtamu FantahunОценок пока нет
- Spring Step by StepДокумент58 страницSpring Step by Stepthithithi2143Оценок пока нет
- Struts 2 Framework Tutorial: Filterdispatcher RespectivelyДокумент26 страницStruts 2 Framework Tutorial: Filterdispatcher RespectivelyChandan Kumar KhuntiaОценок пока нет
- SCJPДокумент2 страницыSCJPSrikanth MadasuОценок пока нет
- JSTL Quick Reference GuideДокумент13 страницJSTL Quick Reference GuideShiva DixitОценок пока нет
- JSTL Quick Reference GuideДокумент13 страницJSTL Quick Reference GuideShiva DixitОценок пока нет
- JSTL Quick Reference GuideДокумент13 страницJSTL Quick Reference GuideShiva DixitОценок пока нет
- Oculus Mobile v0.5.0 SDK DocumentationДокумент84 страницыOculus Mobile v0.5.0 SDK DocumentationjuanОценок пока нет
- Documentum Composer Quick Start GuideДокумент12 страницDocumentum Composer Quick Start GuideValentin BragaruОценок пока нет
- Java Means Durga Soft: DURGA SOFTWARE SOLUTIONS, 202 HUDA Maitrivanam, Ameerpet, Hyd. PH: 040-64512786Документ19 страницJava Means Durga Soft: DURGA SOFTWARE SOLUTIONS, 202 HUDA Maitrivanam, Ameerpet, Hyd. PH: 040-64512786amitfegade121Оценок пока нет
- Salesforce Migration GuideДокумент47 страницSalesforce Migration GuidePratip DuttaОценок пока нет
- Module 1 Introduction To Java TechnologyДокумент62 страницыModule 1 Introduction To Java TechnologyStefano EdicОценок пока нет
- DevOps-IIB BuildAndDeploy Automation v1.2Документ44 страницыDevOps-IIB BuildAndDeploy Automation v1.2Diacamo MankungiОценок пока нет
- Deepa Deshpande: Professional ProfileДокумент9 страницDeepa Deshpande: Professional ProfileAnkit ButiyaОценок пока нет
- Gradle User GuideДокумент436 страницGradle User GuideunIimitedОценок пока нет
- JMonkey Documentation Chapter 1Документ68 страницJMonkey Documentation Chapter 1Marthinus A. BothaОценок пока нет
- PLATFORM BASICS INITIALIZATION AND UPDATE PROCESSДокумент18 страницPLATFORM BASICS INITIALIZATION AND UPDATE PROCESSIshika KumarОценок пока нет
- FireAnt TutorialДокумент16 страницFireAnt TutorialMaytri SahaОценок пока нет
- AntGuide1 8 1Документ670 страницAntGuide1 8 1Mahesh BabuОценок пока нет
- ONTAP - TRACNGHIEM - ADP (AutoRecovered)Документ25 страницONTAP - TRACNGHIEM - ADP (AutoRecovered)TRAN ANH QUANОценок пока нет
- JasperReports Server CP Upgrade GuideДокумент36 страницJasperReports Server CP Upgrade GuideJhoel Rincon GelvezОценок пока нет
- Amitesh Raj - TechnofunctionalДокумент3 страницыAmitesh Raj - Technofunctionalapi-19789524Оценок пока нет
- 4 Hybris Install PDFДокумент10 страниц4 Hybris Install PDFravikanchuОценок пока нет
- Jgraph and Jgraph Layout Pro User ManualДокумент148 страницJgraph and Jgraph Layout Pro User Manualkowens0826742Оценок пока нет
- Java Web Services Using Apache Axis2Документ24 страницыJava Web Services Using Apache Axis2kdorairajsgОценок пока нет
- Financial Accounting TutorialДокумент14 страницFinancial Accounting TutorialDiman IonutОценок пока нет
- Google Android - A Comprehensive: Technical Report: TUB-DAI 03/09-01Документ31 страницаGoogle Android - A Comprehensive: Technical Report: TUB-DAI 03/09-01Deniisa BalutaОценок пока нет
- IBM Websphere WebservicesДокумент816 страницIBM Websphere WebservicesSubramanyamОценок пока нет
- GDPR 2 LogsДокумент5 212 страницGDPR 2 LogsSaloni MalhotraОценок пока нет
- Axis2-Geronimo Online BankДокумент27 страницAxis2-Geronimo Online BankHenk HeriyantoОценок пока нет
- Kuldeep MalhotraДокумент8 страницKuldeep Malhotraapi-3750978Оценок пока нет
- The tIDE Java IDE Manual: Draft Version, Not Yet CompleteДокумент45 страницThe tIDE Java IDE Manual: Draft Version, Not Yet CompleteMario Ayil HuicabОценок пока нет
- Java Card Development Kit User GuideДокумент257 страницJava Card Development Kit User GuideAbiy MulugetaОценок пока нет
- ResumeДокумент2 страницыResumeRustam KhashimkhodjaevОценок пока нет
- Openbravo Eclipse Devel SetupДокумент37 страницOpenbravo Eclipse Devel SetupJack PremuОценок пока нет
- Shyam RamathДокумент9 страницShyam RamathrajujonnyОценок пока нет
- Building OSMF & OSMF-based ProjectsДокумент12 страницBuilding OSMF & OSMF-based ProjectsGozo GargicОценок пока нет
- Learn Python Programming for Beginners: Best Step-by-Step Guide for Coding with Python, Great for Kids and Adults. Includes Practical Exercises on Data Analysis, Machine Learning and More.От EverandLearn Python Programming for Beginners: Best Step-by-Step Guide for Coding with Python, Great for Kids and Adults. Includes Practical Exercises on Data Analysis, Machine Learning and More.Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (34)
- Software Engineering at Google: Lessons Learned from Programming Over TimeОт EverandSoftware Engineering at Google: Lessons Learned from Programming Over TimeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (11)
- What Algorithms Want: Imagination in the Age of ComputingОт EverandWhat Algorithms Want: Imagination in the Age of ComputingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (41)
- Introducing Python: Modern Computing in Simple Packages, 2nd EditionОт EverandIntroducing Python: Modern Computing in Simple Packages, 2nd EditionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (7)
- The Advanced Roblox Coding Book: An Unofficial Guide, Updated Edition: Learn How to Script Games, Code Objects and Settings, and Create Your Own World!От EverandThe Advanced Roblox Coding Book: An Unofficial Guide, Updated Edition: Learn How to Script Games, Code Objects and Settings, and Create Your Own World!Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Excel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceОт EverandExcel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceОценок пока нет
- Nine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersОт EverandNine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (7)
- Linux: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learn Linux Operating System, Command Line and Linux Programming Step by StepОт EverandLinux: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learn Linux Operating System, Command Line and Linux Programming Step by StepРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (9)
- Generative Art: A practical guide using ProcessingОт EverandGenerative Art: A practical guide using ProcessingРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- Unit Testing Principles, Practices, and PatternsОт EverandUnit Testing Principles, Practices, and PatternsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (3)
- Clean Code: A Handbook of Agile Software CraftsmanshipОт EverandClean Code: A Handbook of Agile Software CraftsmanshipРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (13)
- Python Programming : How to Code Python Fast In Just 24 Hours With 7 Simple StepsОт EverandPython Programming : How to Code Python Fast In Just 24 Hours With 7 Simple StepsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (54)
- CODING FOR ABSOLUTE BEGINNERS: How to Keep Your Data Safe from Hackers by Mastering the Basic Functions of Python, Java, and C++ (2022 Guide for Newbies)От EverandCODING FOR ABSOLUTE BEGINNERS: How to Keep Your Data Safe from Hackers by Mastering the Basic Functions of Python, Java, and C++ (2022 Guide for Newbies)Оценок пока нет
- GROKKING ALGORITHMS: Simple and Effective Methods to Grokking Deep Learning and Machine LearningОт EverandGROKKING ALGORITHMS: Simple and Effective Methods to Grokking Deep Learning and Machine LearningОценок пока нет
- Python: For Beginners A Crash Course Guide To Learn Python in 1 WeekОт EverandPython: For Beginners A Crash Course Guide To Learn Python in 1 WeekРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (23)
- Excel 2016: A Comprehensive Beginner’s Guide to Microsoft Excel 2016От EverandExcel 2016: A Comprehensive Beginner’s Guide to Microsoft Excel 2016Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Data Analytics with Python: Data Analytics in Python Using PandasОт EverandData Analytics with Python: Data Analytics in Python Using PandasРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)