Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
A Sub-Group To Be Formed To Submit The Required Changes To The Third Schedule On The Lines of Schedule VI Companies Act
Загружено:
sj293Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
A Sub-Group To Be Formed To Submit The Required Changes To The Third Schedule On The Lines of Schedule VI Companies Act
Загружено:
sj293Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
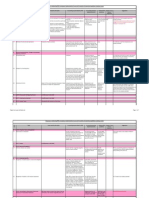
Sub-group on addressing IFRS convergence implementation issues and formulation of operational guidelines relating to banks
Sr. Topic Issues faced by the banks Accounting as prescribed by IFRS Accounting practices Relevant RBI Impact of any Suggestions
No. adopted presently guidelines statute /
legislation
A IAS 1: Presentation of Financial Statements
A.1 Components of financial statements Whether information to be disclosed in the separate A complete set of financial statements Section 29 of the B. R. Act, Forms are set out Companies Act, Form set out in Third schedule needs to be
format? comprises: 1949 prescribes: in Third Schedule 1956 suitably amended.
- Accounting standard does not prescribe a particular i. financial position statement (Balance i. Balance sheet (Form A) of the B.R. Act, A sub-group to be formed to submit the required
format; sheet) ii. Profit and Loss Account 1949 changes to the Third Schedule on the lines of
- Comprehensive statement is requires additional ii. Comprehensive statement (Form B) Schedule VI Companies Act
disclosures not specified in Form B of Third schedule iii. Changes in equity iv. 16 Schedules
of B.R. Act, 1949 iv. Cash flow statement
- The Third schedule does not require banks to v. notes and other explanatory
publish Statement of Changes in Equity in a separate information
statement but are disclosed in separate schedules
"Share Capital" and "Reserves and Surplus"
B IAS 2: Inventories Not Applicable
C IAS 7: Statement of Cash Flows
C.1 Definition of cash and cash equivalents Treatment of bank overdrafts Cash includes cash equivalents with Bank overdrafts are not None AS 3 (Revised): Cash Flow Statements to be
maturities of three months or less from included in cash and cash suitably amended
the date of acquisition and may include equivalents; changes in the
bank overdrafts (IAS 7.8) balances of overdrafts are
classified as financing cash
flows
D IAS 8: Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting
Estimates and Errors
D.1 Extraordinary items Prohibited Defined as events or None AS 5 (Revised): Net Profit or Loss for the Period,
transactions clearly distinct Prior Period Items and Changes in Accounting
from the ordinary activities Policies to be suitably amended
of the entity and are not
expected to recur
frequently and regularly.
The amount is adjusted
against the current profit or
loss.
D.2 Changes in accounting policy Comparatives are restated, unless The effect of change is Master Circular - AS 5 (Revised): Net Profit or Loss for the Period,
specifically exempted; where the effect included in the income Disclosure in Prior Period Items and Changes in Accounting
of periods) not presented is adjusted statement in the period of Financial Policies to be suitably amended
against opening retained earnings change Statements -
Notes to
The Conceptual Framework suggests that Accounts
the itmes which are specifically required
to be stated in the financial statements
cannot be shown only in the Notes.
D.3 Correction of errors Impact of Prior period adjustment disclosed in Notes Comparatives are restated and, if the Restatement is not Master Circular - AS 5 (Revised): Net Profit or Loss for the Period,
to accounts of restate the comparatives? error occurred before the earliest prior required. Reported as a Disclosure in Prior Period Items and Changes in Accounting
period presented, the opening balances prior period adjustment Financial Policies and the Master Circular of RBI which
of assets, liabilities and equity for the separately in the income Statements - requires the impact of prior period adjustments on
earliest prior period presented are statement. Notes to current year's profit or loss to be disclosed in
restated Accounts Notes to accounts to the balance sheet of banks
(Para 4.1)to be suitably amended.
E IAS 10: Events after the Reporting Period No differences in the GAAP
F IAS 11: Construction Contracts No differences in the GAAP
G IAS 12: Income Taxes Discussed by the Income tax Core Group
Report on issues for Banks.xls Page 1 of 7
Sub-group on addressing IFRS convergence implementation issues and formulation of operational guidelines relating to banks
Sr. Topic Issues faced by the banks Accounting as prescribed by IFRS Accounting practices Relevant RBI Impact of any Suggestions
No. adopted presently guidelines statute /
legislation
H IAS 16: Property, Plant and Equipment
H.1 Depreciation on Computers An item of property, plant and All commercial banks Circular DBOD The circular needs to be suitably withdrawn/
equipment should be depreciated over excluding RRBs and LABs No.BP.BC.37/21. amended
its estimated useful life, and the are required to charge 04.018/2000
depreciation charge must be recognized depreciation on computers dated October
as an expense unless it has to be on Straight line Basis at the 20,2000
included in the carrying amount of rate of 33.33 % p.a
another asset
I IAS 17: Leases No differences in the GAAP
J IAS 18: Revenue Recognition
J.1 Effective Interest rate method Interest shall be recognized using the Interest is recorded without The RBI RBI has issued Draft guidelines on Valuation of
effective interest method any adjustments pertaining guidelines are Investments which shall be looked by another
to effective interest silent on the group working on AS 30/31/32
method method of
interest income
recognition.
K IAS 19: Employee Benefits
K.1 Recognition of liability based on constructive obligation Under IFRS, post-employment benefits Unlike IFRS, read with AS - - -
include all benefits payable after 29, it also does not seem to
employment (before or during allow recognition of
retirement) e.g., pensions, medical termination benefits based
benefits after employment and severance on constructive obligation.
payments. Post-employment benefit
plans include both formal arrangements
and informal arrangements that give rise
to constructive obligations. All post-
employment benefits are accounted for
under a single set of requirements.
K.2 Recognition of liability in the financial statements Under IFRS, actuarial gains and losses of The AS15 does not allow - - AS 15 needs to be suitably amended
defined benefit plans are recognized corridor approach to
either in profit or loss, or immediately recognizing actuarial gains
directly in equity. Amounts recognized and losses – these should be
directly in equity are not recycled to recognized immediately in
profit or loss. The corridor is 10 percent the profit and loss account.
of the greater of the obligation and the
fair value of plan assets at the beginning
of the period.
L IAS 20: Accounting for Government Grants and RBI issues various circulars from time to time on Exposure Draft on AS UBD.PCB.Cir.No. No conclusion was reached
Disclosure of Government Assistance subvention, loan waivers (forgivable loans), etc 12(Revised). Last date to 58/13.05.000/2
comment 31.07.2008 007-08 dated
June 20, 2008
M IAS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange
Rates
M.1 Recording and reporting of FC transactions - concept Can functional cuurency be different from local An entity measures its assets, liabilities, There is no concept of - - -
of functional currency currency? revenues and expenses in its functional functional currency under
currency, which is the currency that best Indian GAAP. Enterprises in
reflects the economic substance of the India have to prepare their
underlying events and circumstances general purpose financial
relevant to the entity, i.e. the currency statements in Indian
of the primary economic environment in rupees. (Schedule VI part I
which the entity operates. Functional note (b) and Part II of the
currency of an entity may be different Companies Act, 1956)
from the local currency. (IAS 21.8-13)
Report on issues for Banks.xls Page 2 of 7
Sub-group on addressing IFRS convergence implementation issues and formulation of operational guidelines relating to banks
Sr. Topic Issues faced by the banks Accounting as prescribed by IFRS Accounting practices Relevant RBI Impact of any Suggestions
No. adopted presently guidelines statute /
legislation
M.2 Integral and Non integral operations Whether foreign branches of Indian Banks and Off The financial statements of foreign There is a distinction As per the RBI - On implementation of IFRS, the RBI circular on
shore banking units should be classified as ‘non – operations are translated as follows: between integral and non- circular on compliance with AS 11 (R) would have to be
integral foreign operation’. Representative offices assets and liabilities at the closing rate, integral foreign operations. compliance with withdrawn
would be classified as ‘Integral foreign operations’? revenues and expenses at actual rates or The reporting currency of AS – 11 (R) –
appropriate averages, and equity even an integral foreign
components at historic rates. operation will be different
from the reporting currency
of the reporting entity,
thereby necessitating
translation.
M.3 Presentation of transactions An entity may present supplementary No guidance available under - - -
financial information in a currency other Indian GAAP.
than its presentation currency if certain
disclosures are made.
M.4 Accounting for foreign exchange contracts At present there is a conflict relating to accounting IAS 21 does not deal with forward The treatment prescribed At present # Convergence with IAS 39 is prescribed in AS 30
of forward exchange contracts as per AS -11 or AS -30 exchange contracts as the entire gamut under AS -11 of accounting NACAS suitable modifications will have to be made to
(recommendatory) of foreign exchange derivative is covered for forward exchange mandates reduce the scope of forward exchange contracts
by IAS 39. (IAS 21 Para 3(a), 4 and 5) contracts is different than standards till from AS 11
that under IAS 39. (AS 11.36- AS 29 # NACAS will need to incorporate AS–30/31 and
39) future IFRS as mandatory standards for a banking
company
N IAS 23: Borrowing Costs The revised IAS 23 removes the option The AS-16 did not have None - -
to expense borrowing costs and is the option of expensing
applicable from 01.01.2009 borrowing costs.
Capitalization was
required.
O IAS 24: Related Party Disclosures
O.1 Definition of Related party transactions The control definition is different from the one Determined by the level of direct or Based on legal form rather None - Need to suitably amend the control definition
prescribed in IFRS as a result less number of entities indirect control, joint control or than substance
are covered under related party as per Indian GAAP significant influence of one party over
another or common control of an entity
P IAS 27: Consolidated and Separate Financial
Statements
P.1 Definition of Control The control definition is different from the one Control is the power to govern the Control is defined as None Companies Act, Need to suitably amend the control definition
prescribed in IFRS financial and operating policies of an ownership of more than half 1956
entity so as to obtain economic benefits of the voting rights or
from its activities control of composition of
the board of directors or
governing body so as to
obtain economic benefits
from its activities
P.2 Special Purpose Entity (SPE) The consolidation of SPEs is not covered Consolidated where substance of the No specific guidance - - Need to issue an interpretation on the lines of SIC-
relationship indicates control 12
All the SIC/ IFRIC will be the part of the standards
on convergence with IFRS
Q IAS 28: Investments in Associates No differences in the GAAP
R IAS 29: Financial Reporting in Hyperinflationary Need guidance Hyperinflation is indicated by No specific guidance - - The ASB should issue a standard in this regard
Economies characteristics of economic for banks having branches in such economies;
environment of country, which include: e.g. Zimbabwe and need to consolidated the
population's attitude towards local accounts
currency and prices linked to price The standard will be issued very soon
index; if cumulative inflation rate over
3 years is approaching or exceeds 100%
S IAS 31: Interests in Joint Ventures
Report on issues for Banks.xls Page 3 of 7
Sub-group on addressing IFRS convergence implementation issues and formulation of operational guidelines relating to banks
Sr. Topic Issues faced by the banks Accounting as prescribed by IFRS Accounting practices Relevant RBI Impact of any Suggestions
No. adopted presently guidelines statute /
legislation
S.1 Contractual arrangement whereby two or more parties Presentation of jointly controlled entities (joint In Consolidated financials: both In Consolidated financials: None - The AS 27 needs to be suitably amended to be in
undertake an economic activity, which is subject to ventures) proportional consolidation and equity proportional consolidation line with IFRS
joint control. method permitted is used
In standalone financials: at cost or fair In standalone financials: at
value as per IAS 39 cost less impairment
Report on issues for Banks.xls Page 4 of 7
Sub-group on addressing IFRS convergence implementation issues and formulation of operational guidelines relating to banks
Sr. Topic Issues faced by the banks Accounting as prescribed by IFRS Accounting practices Relevant RBI Impact of any Suggestions
No. adopted presently guidelines statute /
legislation
T IAS 32: Financial Instruments- Presentation Discussed in a seaprate sheet
U IAS 33: Earnings per share No differences in the GAAP
V IAS 34: Interim Financial Reporting No differences in the GAAP
W IAS 36: Impairment of Assets No differences in the GAAP
X IAS 37: Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and No differences in the GAAP
Contingent Assets
Y IAS 38: Intangible Assets
Y.1 Acquired intangible assets Whether to amortise over useful life or 10 years Capitalized if recognition criteria are Capitalized if recognition
irrespective of useful life less/more than 10 years? met; amortized over useful life. criteria are met; all
Intangibles assigned an indefinite useful intangibles are amortized
life are not amortized but reviewed at over the useful life with a
least annually for impairment. rebuttable presumption of
Revaluations are permitted not exceeding 10 years.
Revaluations are not
permitted
Y.2 Definition of an intangible asset An intangible asset is recognized An intangible asset is Section 15(1) of - Section 15 needs to suitably exclude certain
separately from goodwill if it represents recognized in the B.R.Act, 1949 intangibles
contractual or legal rights and is capable amalgamations accounted restricts payment
of being separated or divided and sold, under the purchase method of dividend by
transferred, licensed, rented or using the fair value, if it is Indian banks
exchanged. Acquired in process research probable that the future until all
and development (R&D) is recognized as economic benefits that are intangibles are
a separate intangible asset if it meets the attributable to the asset completely
definition of an intangible asset and its will flow to the enterprise written off.
fair value can be measured reliably. Non and the cost of the asset
identifiable intangible assets are will be measured reliably.
subsumed within goodwill. However the fair value of
For an item to be recognized as an the intangible asset with no
intangible asset it must be an active market is reduced to
identifiable non-monetary asset without the extent of capital
physical substance. (IAS 38.8-17, BC.4-5) reserve, if any, arising from
the amalgamation.
An intangible asset is an
identifiable non-monetary
asset without physical
substance held for use in
the production or supply of
goods or services, for rental
to others or for
administrative purposes. AS
26.6
Y.3 Recognition and amortization of intangible assets # Rebuttable presumption of 10 years Intangible assets with finite useful lives There is a rebuttable Section 15(1) of - RBI vide circular DBOD No. BP.BC.
# Review of residual value at minimum each financial are amortized over their expected useful presumption that the useful the B.R.Act, 1949 82/21.04.018/2003 – 04 has issued guidance on
year lives. There is no presumption under IAS life of an intangible asset restricts payment compliance of AS 26 by banks. RBI has stated that
# Revaluation is not permitted under Indian GAAP 38 as regards useful life of an intangible will not exceed 10 years. of dividend by banks in India will have to seek exemption from
unlike IFRS asset. (IAS 38.7) (AS 26.63) Indian banks section 15(1) of the B.R.Act, 1949 from the
until all government. Else, the B.R.Act, 1949 needs to be
The residual value of an intangible asset The residual value is intangibles are amended to that effect.
with a finite useful life is reviewed at estimated using prices completely
least at each financial year end/ prevailing at the date of written off.
reporting year end. (IAS 38.102) acquisition of the asset.
The residual value is not
Intangible assets may be revalued to fair subsequently increased for
value only if there is an active market. changes in price or value.
(AS 26.77)
Revaluation of intangible
assets not permitted.
Report on issues for Banks.xls Page 5 of 7
Sub-group on addressing IFRS convergence implementation issues and formulation of operational guidelines relating to banks
Sr. Topic Issues faced by the banks Accounting as prescribed by IFRS Accounting practices Relevant RBI Impact of any Suggestions
No. adopted presently guidelines statute /
legislation
Z IAS 39:Financial Instruments - Recognition and Discussed in separate sheet
Measurement
AA IAS 40: Investment Property
AA.1 Time period of acquisition of Investment property by Section 9 of the B.R.Act, 1949 states that assets in Investment Property are disclosed under At present investment in Schedule 8 Many Real Estate Venture Funds & Investors are
banks. Further, no specific head is mentioned about the nature of Investment Property can be acquired Non Current Assets the form of property is not "Investments" locking in capital in Investment Properties where
the disclosure requirements for Investment Property for period of 7 years and for further 5 years with the very prevalent in the Indian under the Third they are getting Rental Returns of 9 % to 12 % p.a
under Third Schedule of the B.R.Act, 1949 special extension from the RBI Banking Scenario. Schedule Schedule to the on Investment and the possibility of Capital
8 "Investments" under the Banking Appreciation. Further Real Estate Mutual Funds
Third Schedule to the Regulation Act, are on the anvil. Hence we suggest:
B.R.Act, 1949 classifies 1949. # Suitable amendment to B.R.Act, 1949 to permit
Investment under : Banks to invest in these type of Investment
1) Government Securities Properties
2) Other Approved # The disclosure norms in the Schedule 8 under
Securities Third Schedule must be specific
3)Shares
4)Debentures and Bonds
5)Subsidiaries and/or Joint
Ventures
6) Others (to be specified)
AB IAS 41: Agriculture Not applicable to banks
AC IFRS 1: First-Time Adoption of International Financial Not addressed by Indian GAAP No specific guidance
Reporting Standards
AD IFRS 2: Share-based Payment
AD.1 Measurement and recognition Fair value or intrinsic value? Share-based employee payments should Share-based employee - - -
be measured with reference to fair payments can be accounted
value. (IFRS 2.11) for either by the fair value
Goods or services received in a SBT are method or the intrinsic
measured at fair value. value method. However, an
An intrinsic value approach is permitted entity using the intrinsic
only when the FV of the equity value method is required to
instruments cannot be estimated make extensive fair value
reliably. disclosures. (Guidance Note
Para 10 to 39 and 48)
AD.2 Measurement of goods and services No guidance on measurement of goods Goods should be recognized when they No guidance is available in - - -
are obtained and services recognized respect of the goods.
over the period that they are received. Employee services are
(IFRS 2.Para 13-15) recognized over the period
that they are received.
(Guidance Note Para 10 to
12)
AD.3 Settlement in redeemable shares No guidnace in the Indian GAAP A Share-based transaction settled in No guidance available - - -
redeemable shares is classified as cash-
settled.
AD.4 Treatment of awards with graded vesting Option to treat as separate Share-based arrangement Awards with graded vesting are Awards with graded vesting - - -
or on straight line basis accounted for as separate Share-based may be accounted for as
payment arrangements. separate Share-based
arrangement or on a
straight-line basis over the
total service period of the
award. However, the cost
recognized at any date
must at least equal the FV
of the vested portion of the
award at that date.
Report on issues for Banks.xls Page 6 of 7
Sub-group on addressing IFRS convergence implementation issues and formulation of operational guidelines relating to banks
Sr. Topic Issues faced by the banks Accounting as prescribed by IFRS Accounting practices Relevant RBI Impact of any Suggestions
No. adopted presently guidelines statute /
legislation
AD.5 Share based payments to non employees No guidance in the Indian GAAP Share-based payments to non-employees No guidance is available - - -
generally are measured based on the fair
value of the goods or services received.
(IFRS 2.13)
AE IFRS 3: Business Combinations Will be discussed in Phase 2
AF IFRS 4: Insurance Contracts Not applicable to banks
AG IFRS 5: Non-Current Assets Held for Sale and
Discontinued Operations
AG.1 Definition The definition as per AS-24 does not cover Operations and cash flows that can be A component that DBOD No. -
subsidiaries acquired exclusively with a view to resell clearly distinguished operationally and represents a separate major BP.BC.82/21.04.
for financial reporting and represent a line of business or 018/2003-04
separate major line of business or geographical area of Merger/ closure
geographical area of operations, or are operations and can be of branches of
subsidiaries acquired exclusively with a distinguished operationally banks by
view to resale and for financial reporting transferring the
purposes assets/ liabilities
to the other
branches of the
same bank may
not be deemed
as a
discontinuing
operation
AG.2 Discontinued operations - envisaged timescale No timescale specified in the AS/ Circular for Completed within a year with limited No timeframe specified. Circular DBOD The AS/ Circular to be amended suitably
completion exceptions Standard envisages several No.
months or longer but BP.BC.82/21.04.
emphasise on a single 018/2003-04
coordinated plan
AG.3 Measurement Measurement requirements of discontinued Lower of carrying value or fair value less Apply other relevant Circular DBOD No guidance in the Circular
operations not there in AS-24 costs to sell accounting standards, e.g. No.
by applying AS on BP.BC.82/21.04.
impairment, provisions, etc 018/2003-04
AH IFRS 6: Exploration for and Evaluation of Mineral Not applicable to banks
Resources
AI IFRS 7: Financial Instruments - Disclosures Discussed in separate sheet
AJ IFRS 8: Operating Segments
Whether to report the uniform segments as per RBI Operating segments are identified based on AS 17: Segment Reporting needs to DBOD.No.BP.BC.81/21.04.0 RBI circular needs to be suitably amended
circular or decide on operating segments based on the management reporting system which meet the revised 18/2006-07 dated April 18,
flowchart? majority of aggregation criteria and the quantitative 2007
thresholds
AK IFRIC/ SIC Will be discussed in Phase 2
Report on issues for Banks.xls Page 7 of 7
Вам также может понравиться
- D6a - D8a PDFДокумент168 страницD6a - D8a PDFduongpn63% (8)
- Planas V Comelec - FinalДокумент2 страницыPlanas V Comelec - FinalEdwino Nudo Barbosa Jr.100% (1)
- Commonly Found Non-Compliances of SCH II&III of Companies Act - CA - Akshat BahetiДокумент37 страницCommonly Found Non-Compliances of SCH II&III of Companies Act - CA - Akshat BahetiCIBIL CHURUОценок пока нет
- GFR I PDFДокумент267 страницGFR I PDFvijayОценок пока нет
- GF ARules Rajasthan Part 1Документ258 страницGF ARules Rajasthan Part 1apОценок пока нет
- CA Journal - Article On Schedule IIIДокумент6 страницCA Journal - Article On Schedule IIISIDDHARTH MANDELIAОценок пока нет
- Ifrs, Their Interpretations and Us Gaaps - An OverviewДокумент9 страницIfrs, Their Interpretations and Us Gaaps - An OverviewNmОценок пока нет
- GF & AR Part-IДокумент255 страницGF & AR Part-IAbdul Rashid QureshiОценок пока нет
- Cfas Q2Документ12 страницCfas Q2dorothynicole.resurreccion.acctОценок пока нет
- Final Accounts of Companies NotesДокумент23 страницыFinal Accounts of Companies NotesRajesh NangaliaОценок пока нет
- SL NO Principles Name of IAS Details About IAS Principles Status of ACI With IAS Complied Not CompliedДокумент6 страницSL NO Principles Name of IAS Details About IAS Principles Status of ACI With IAS Complied Not CompliedNaimmul FahimОценок пока нет
- Assignment Financial Accounting & Analysis: Answer 1. Sr. No Point of Differentiation Indian GAAP Ifrs Ind ASДокумент3 страницыAssignment Financial Accounting & Analysis: Answer 1. Sr. No Point of Differentiation Indian GAAP Ifrs Ind ASRASHMIОценок пока нет
- Amendments in Schedule III of Companies Act, W.E.F. 1st April 2021Документ16 страницAmendments in Schedule III of Companies Act, W.E.F. 1st April 2021Selvi balanОценок пока нет
- Government of RajasthanДокумент209 страницGovernment of RajasthanEr Kamal SinghОценок пока нет
- Australian GAAP Vs IFRSДокумент25 страницAustralian GAAP Vs IFRSMichael ZhangОценок пока нет
- IFRS Illustrative Financial Statements (Dec 2021)Документ292 страницыIFRS Illustrative Financial Statements (Dec 2021)bacha436Оценок пока нет
- Compilation of Material Findings On 2019 Afs Reviewed by The CommissionДокумент10 страницCompilation of Material Findings On 2019 Afs Reviewed by The CommissionAllyssa Camille ArcangelОценок пока нет
- ICAI RTP November 2020Документ55 страницICAI RTP November 2020Purva WakadeОценок пока нет
- © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaДокумент56 страниц© The Institute of Chartered Accountants of Indianandish pnОценок пока нет
- CAROДокумент9 страницCAROSai Lakshmi PОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 6 Comparative Study of Indian Gaap, Ifrs & Ind AsДокумент88 страницChapter - 6 Comparative Study of Indian Gaap, Ifrs & Ind AsSaurabh GargОценок пока нет
- International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) : An OverviewДокумент10 страницInternational Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) : An Overviewsanjay guptaОценок пока нет
- 74931bos60524 m1 AnnexureДокумент38 страниц74931bos60524 m1 AnnexureBala Guru Prasad TadikamallaОценок пока нет
- Audited FS IllustrationДокумент123 страницыAudited FS IllustrationEphraim MandalОценок пока нет
- IASB Documents Published To Accompany IFRS 3Документ38 страницIASB Documents Published To Accompany IFRS 3KenОценок пока нет
- Difference BTW As IFRS and INDДокумент5 страницDifference BTW As IFRS and INDrahul jambagiОценок пока нет
- Companies Act, 2013 PDFДокумент25 страницCompanies Act, 2013 PDFshivam vermaОценок пока нет
- Add Accounts RTP May 2017Документ49 страницAdd Accounts RTP May 2017VinayОценок пока нет
- 3.4 Presentation of Financial Statements: Adaptation For The Public Sector ContextДокумент133 страницы3.4 Presentation of Financial Statements: Adaptation For The Public Sector ContextTung NguyenОценок пока нет
- 05 Acctg Ed 1 - Statement of Financial Position PDFДокумент8 страниц05 Acctg Ed 1 - Statement of Financial Position PDFGian Christian Magno BuenaОценок пока нет
- © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaДокумент176 страниц© The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaNaziya TamboliОценок пока нет
- Gf&ar RajasthanДокумент258 страницGf&ar RajasthanNishant ThapaОценок пока нет
- Adv Accounting RTPДокумент59 страницAdv Accounting RTPRushin FuriaОценок пока нет
- Modelos de Demonstrações Financeiras Observações E Ligação Às NCRFДокумент13 страницModelos de Demonstrações Financeiras Observações E Ligação Às NCRFFátimaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 2023Документ9 страницChapter 1 2023Diễm QuỳnhОценок пока нет
- International Accounting StandardsДокумент6 страницInternational Accounting StandardsReza Al SaadОценок пока нет
- Ias Accounting StandardДокумент2 страницыIas Accounting StandardJoyce CabacangОценок пока нет
- P1 1 PDFДокумент40 страницP1 1 PDFSravan NareshОценок пока нет
- IAAG 1 Jan 2017 FinalДокумент46 страницIAAG 1 Jan 2017 FinalKryztel BranzuelaОценок пока нет
- Amendments To Finance Act 2006 A Focus On Form 3cdДокумент8 страницAmendments To Finance Act 2006 A Focus On Form 3cdSURYA SОценок пока нет
- Ey Applying Ifrs Leases Transitions Disclsosures November2018Документ43 страницыEy Applying Ifrs Leases Transitions Disclsosures November2018BT EveraОценок пока нет
- IFRS Illustrative Financial Statements (Dec 2023)Документ286 страницIFRS Illustrative Financial Statements (Dec 2023)Vamsi Krishna GaragaОценок пока нет
- Acc Cap1 PresentationДокумент30 страницAcc Cap1 PresentationtafsirmhinОценок пока нет
- Presentationof Financial Statements Pas 1Документ7 страницPresentationof Financial Statements Pas 1Amber AgustinОценок пока нет
- IAS1 Presentation of FSДокумент6 страницIAS1 Presentation of FSIrishLove Alonzo BalladaresОценок пока нет
- 2-Share Based PaymentДокумент42 страницы2-Share Based PaymentChelsea Anne VidalloОценок пока нет
- Rev SCH III - Sent PDFДокумент18 страницRev SCH III - Sent PDFAjay DesaleОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 Preparation of Final Accounts of A Company: ObjectiveДокумент20 страницUnit 4 Preparation of Final Accounts of A Company: ObjectiveWajid AhmedОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Components and General Features of Financial Statements (3114AFE)Документ19 страниц2.1 Components and General Features of Financial Statements (3114AFE)WilsonОценок пока нет
- Adv Acc RTP PDFДокумент47 страницAdv Acc RTP PDFkomal bhosaleОценок пока нет
- AU Section 411Документ7 страницAU Section 411Indf CBPSMОценок пока нет
- MODULE 19 Assessment TaskДокумент117 страницMODULE 19 Assessment TaskMichelleОценок пока нет
- Presentation BCIC Session On Companies Act April 23, 2021Документ56 страницPresentation BCIC Session On Companies Act April 23, 2021NEHA NAYAKОценок пока нет
- Amendments To PAS 1 - PrefaceДокумент20 страницAmendments To PAS 1 - PrefaceMarc John IlanoОценок пока нет
- Group 3 - ReportДокумент104 страницыGroup 3 - ReportRenelle HabacОценок пока нет
- 10-TaclobanCity2018 Part3-Status of PY's RecommДокумент13 страниц10-TaclobanCity2018 Part3-Status of PY's Recommrobert lachicaОценок пока нет
- Financial Statement Presentation. Theory of Accounts GuideДокумент20 страницFinancial Statement Presentation. Theory of Accounts GuideCykee Hanna Quizo LumongsodОценок пока нет
- TOAMOD2 Financial Statement PresentationДокумент20 страницTOAMOD2 Financial Statement PresentationCukeeОценок пока нет
- 17 - Indian Gaap Vs IfrsДокумент20 страниц17 - Indian Gaap Vs IfrsrchhapariaОценок пока нет
- Wiley GAAP for Governments 2018: Interpretation and Application of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles for State and Local GovernmentsОт EverandWiley GAAP for Governments 2018: Interpretation and Application of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles for State and Local GovernmentsОценок пока нет
- Wiley GAAP for Governments 2017: Interpretation and Application of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles for State and Local GovernmentsОт EverandWiley GAAP for Governments 2017: Interpretation and Application of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles for State and Local GovernmentsОценок пока нет
- Equity Research: Indian Broking IndustryДокумент32 страницыEquity Research: Indian Broking Industrysj293Оценок пока нет
- Ar 2008 2009Документ75 страницAr 2008 2009sj293Оценок пока нет
- Annual Report Jklaxmi 7 8Документ60 страницAnnual Report Jklaxmi 7 8sj293Оценок пока нет
- SEBI Guidelines On Employees Stock Purchase SchemeДокумент6 страницSEBI Guidelines On Employees Stock Purchase Schemesj293Оценок пока нет
- A Sub-Group To Be Formed To Submit The Required Changes To The Third Schedule On The Lines of Schedule VI Companies ActДокумент7 страницA Sub-Group To Be Formed To Submit The Required Changes To The Third Schedule On The Lines of Schedule VI Companies Actsj293Оценок пока нет
- Land Degradetion NarmДокумент15 страницLand Degradetion NarmAbdikafar Adan AbdullahiОценок пока нет
- 254 AssignmentДокумент3 страницы254 AssignmentSavera Mizan ShuptiОценок пока нет
- Business Occupancy ChecklistДокумент5 страницBusiness Occupancy ChecklistRozel Laigo ReyesОценок пока нет
- Https Code - Jquery.com Jquery-3.3.1.js PDFДокумент160 страницHttps Code - Jquery.com Jquery-3.3.1.js PDFMark Gabrielle Recoco CayОценок пока нет
- Bondoc Vs PinedaДокумент3 страницыBondoc Vs PinedaMa Gabriellen Quijada-TabuñagОценок пока нет
- Bench VortexДокумент3 страницыBench VortexRio FebriantoОценок пока нет
- QP 4Документ4 страницыQP 4Yusra RaoufОценок пока нет
- ProAim InstructionsДокумент1 страницаProAim Instructionsfeli24arias06Оценок пока нет
- CNS Manual Vol III Version 2.0Документ54 страницыCNS Manual Vol III Version 2.0rono9796Оценок пока нет
- Scheme Bidirectional DC-DC ConverterДокумент16 страницScheme Bidirectional DC-DC ConverterNguyễn Quang KhoaОценок пока нет
- Module 5 - Multimedia Storage DevicesДокумент10 страницModule 5 - Multimedia Storage Devicesjussan roaringОценок пока нет
- Tan Vs GumbaДокумент2 страницыTan Vs GumbakjsitjarОценок пока нет
- Perpetual InjunctionsДокумент28 страницPerpetual InjunctionsShubh MahalwarОценок пока нет
- Irrig in AfricaДокумент64 страницыIrrig in Africaer viОценок пока нет
- DevelopmentPermission Handbook T&CPДокумент43 страницыDevelopmentPermission Handbook T&CPShanmukha KattaОценок пока нет
- Appleyard ResúmenДокумент3 страницыAppleyard ResúmenTomás J DCОценок пока нет
- NCR Minimum WageДокумент2 страницыNCR Minimum WageJohnBataraОценок пока нет
- Bharat Heavy Electricals LimitedДокумент483 страницыBharat Heavy Electricals LimitedRahul NagarОценок пока нет
- Shares and Share CapitalДокумент50 страницShares and Share CapitalSteve Nteful100% (1)
- Well Stimulation TechniquesДокумент165 страницWell Stimulation TechniquesRafael MorenoОценок пока нет
- Oops in PythonДокумент64 страницыOops in PythonSyed SalmanОценок пока нет
- Marshall Baillieu: Ian Marshall Baillieu (Born 6 June 1937) Is A Former AustralianДокумент3 страницыMarshall Baillieu: Ian Marshall Baillieu (Born 6 June 1937) Is A Former AustralianValenVidelaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Hospital and Clinical Pharmacy Choplete PDF Notes D.Pharma 2nd Notes PDF NoteskartsДокумент7 страницChapter 1 Hospital and Clinical Pharmacy Choplete PDF Notes D.Pharma 2nd Notes PDF NoteskartsDrx Brajendra LodhiОценок пока нет
- Theories of Economic Growth ReportДокумент5 страницTheories of Economic Growth ReportAubry BautistaОценок пока нет
- A Case On Product/brand Failure:: Kellogg's in IndiaДокумент6 страницA Case On Product/brand Failure:: Kellogg's in IndiaVicky AkhilОценок пока нет
- Ewellery Ndustry: Presentation OnДокумент26 страницEwellery Ndustry: Presentation Onharishgnr0% (1)
- Singapore Electricity MarketДокумент25 страницSingapore Electricity MarketTonia GlennОценок пока нет
- ESK-Balcony Air-AДокумент2 страницыESK-Balcony Air-AJUANKI PОценок пока нет