Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Dextrose 10% Injection Description and Usage
Загружено:
Nurul MazniОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Dextrose 10% Injection Description and Usage
Загружено:
Nurul MazniАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
TEVA MEDICAL/DEXTROSE 10% IV INJ ECTION-TPN, 11. 4.
2001
10% Dextrose Injection
(Dextrose in Water) in Plastic Bags.
INTRAVENOUS INJ ECTION / PARENTERAL NUTRIENT
Description
10% Dextrose Injection is a solution of Dextrose 10% in Water. It can be used
either:
(a) As Intravenous solution for fluid replenishment and caloric supply in single
dose container for intravenous administration, or
(b) As parenteral nutrient.
10% Dextrose Injection is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, hypertonic solution. It contains no
antimicrobial or buffering agents.
Composition, osmolarity, pH value and caloric content are as follows:
Composition Dextrose monohydrate 100g/L
Osmolarity 505 mOsm/L
Approximate pH value 4.0
Caloric content 340 Kcal/L
The plastic bag is fabricated from a specially formulated polyvinyl chloride. Water
can permeate from inside the bag into the overwrap in amounts insufficient to affect
the solution significantly. Solutions in contact with the plastic bag can leach out certain
of its chemical components in very small amounts, however, testing was supportive of
the safety of the plastic container materials.
Clinical Pharmacology
10% Dextrose injection has a value as a source of water and calories. it is capable
of inducing diuresis depending on the clinical condition of the patient.
For caloric value see second table above.
Indications
As Intravenous Injection
10% Dextrose Injection is indicated as a source of water and calories.
As Parenteral Nutrient
10% Dextrose Injection is indicated as a caloric component in a parenteral nutrition
regimen. It is used with an appropriate protein (nitrogen) source in the prevention of
nitrogen loss or in the treatment of negative nitrogen balance in patients where:
(1) the alimentary tract cannot or should not be used
(2) gastrointestinal absorption of protein is impaired, or
(3) metabolic requirements for protein are substantially increased, as with
extensive burns.
TEVA MEDICAL/DEXTROSE 10% IV INJ ECTION-TPN , 11. 4. 2001
2
Use in Pregnancy
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Dextrose Injections. It is
also not known whether these solutions can cause fetal harm when administered to a
pregnant woman, or can affect reproduction capacity. Dextrose injections should be
given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Use in Pediatrics
This product should be used with caution in infants of diabetic mothers, except as
may be indicated in hypoglycemic neonates.
Overdosage
In the event of fluid or solute overload during parenteral fluids, reevaluate the
patients condition and institute appropriate corrective treatment.
Storage
Avoid storage at excessive heat. It is recommended that the product be stored at
room temperature (25C); brief exposure up to 40C does not adversely affect the
product.
Registration Number: 14 982 4549
Manufactured By
Teva Medical Ltd.,
P.O. Box 2, Ashdod 77100,
Israel
TEVA MEDICAL/DEXTROSE 10% IV INJ ECTION-TPN , 11. 4. 2001
3
INFORMATION ON 10% DEXTROSE INJECTION WHEN USED
AS INTRAVENOUS INJECTION
Contraindications
None known.
Warnings
10% Dextrose Injection is intended for intravenous administration only. It
should not be administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly.
The administration of Intravenous Injections can cause fluid and/or solute
overloading resulting in dilution of serum electrolyte concentrations, overhydration,
congested states, or pulmonary edema. The risk of dilutional states is inversely
proportional to the electrolyte concentrations of the injections. The risk of solute
overload causing congested states with peripheral and pulmonary edema is directly
proportional to the electrolyte concentrations of the injections.
Excessive administration of dextrose injections may result in significant
hypokalemia.
Administration by central venous catheter should be used only by those familiar with
this technique and its complications.
Dextrose injection should not be administered simultaneously with blood through the
same administration set because of the possibility of pseudoagglutination or
hemolysis.
Adverse Reactions
Reactions which may occur because of the solution or the technique of
administration include febrile response, infection at the site of injection, venous
thrombosis or phlebitis extending from the site of injection, extravasation and
hypervolemia.
Nausea, fever, and flushing of the skin have occurred.
If an adverse reaction does occur, the infusions should be discontinued, the patient
evaluated, appropriate therapeutic countermeasures instituted, and the remainder of
the fluid saved for examination if deemed necessary.
Precautions
Clinical evaluation and periodic laboratory determinations are necessary to monitor
changes in fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and acid-base balance during
prolonged parenteral therapy, or whenever the condition of the patient warrants such
evaluation.
Caution should be exercised in the administration of parenteral fluids, especially
those containing dextrose, to patients receiving corticosteroids or corticotropin.
Caution should be exercised in the administration of these injections to the very
young and to elderly patients.
Administer so that extravasation does not occur. If thrombosis occurs during
administration, stop injection and correct.
Solutions containing dextrose should be used with caution in patients with overt or
subclinical diabetes mellitus, or carbohydrate intolerance.
TEVA MEDICAL/DEXTROSE 10% IV INJ ECTION-TPN , 11. 4. 2001
4
Hyperglycemia and glycosuria may be functions of rate of administration or metabolic
insufficiency. To minimize these conditions, slow the infusion rate, monitor blood and
urine glucose; if necessary, administer insulin.
Vitamin B-complex deficiency may occur with dextrose administration.
Dosage and Administration
Notes: Do not administer unless solution is clear and seal is intact.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and
discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. Use of a
final filter is recommended during administration of all parenteral solutions, where
possible.
The dosage is usually dependent upon the age, weight and clinical condition of the
patient, as well as laboratory determinations. All injections in plastic containers are
intended for intravenous administration using sterile equipment. It is recommended
that intravenous administration apparatus be replaced at least once every 24 hours.
Additives may be incompatible Complete information is not available. Those
additives known to be incompatible should not be used. A pharmacist should be
consulted, if available. If, in the informed judgment of the physician, it is deemed
advisable to introduce additives, aseptic technique should be used. Thorough mixing
should be performed when additives have been introduced.
Solutions containing additives must not be stored.
Directions for Use of Plastic Bags
Warning : Do not use plastic bags in series connections. Such use could result in air
embolism due to residual air being drawn from the primary bag before administration
of the fluid from the secondary bag is completed.
To Open
Do not remove units from overwrap until ready for use. Use all units promptly when
pouch is opened
The overwrap is a moisture barrier. The inner bag maintains the sterility of the
product.
Tear pouch down side at slit and remove solution container. Check for minute leaks
by squeezing inner bag firmly. If leaks are found, discard solution as sterility may be
impaired. If supplemental medication is desired, follow directions below before
preparing for administration.
Preparation for Administration
1. Suspend container from eyelet support.
2. Remove plastic protector from outlet port at bottom of container.
3. Attach administration set. Refer to complete directions accompanying set.
To Add Medication Before Solution Administration
Warning: Additives may be incompatible.
1. Prepare medication site.
2. Using syringe with 19-22 gauge needle, puncture medication port and inject.
3. Mix solution and medication thoroughly. For high density medication such as
potassium chloride, squeeze ports while ports are upright and mix thoroughly.
TEVA MEDICAL/DEXTROSE 10% IV INJ ECTION-TPN , 11. 4. 2001
5
To Add Medication During Solution Administration
1. Close clamp on the set.
2. Prepare medication site.
3. Using syringe with 19-22 gauge needle, puncture resealable medication port and
inject.
4. Remove container from IV pole and/or turn to an upright position.
5. Evacuate both ports by squeezing them while container is in the upright position.
6. Mix solution and medication thoroughly.
7. Return container to in use position and continue administration.
TEVA MEDICAL/DEXTROSE 10% IV INJ ECTION-TPN , 11. 4. 2001
6
INFORMATION ON 10% DEXTROSE INJECTION WHEN USED
AS PARENTERAL NUTRIENT
Contraindications
The infusion of hypertonic dextrose solutions is contraindicated in patients having
intracranial or intraspinal hemorrhage, in patients who are severely dehydrated, in
patients who are anuric, and in patients in hepatic coma.
Warnings
10% Dextrose Injection is intended for intravenous administration only. It
should not be administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly.
Dilute before use to a concentration which will, when administered with an amino
acid (nitrogen) source, result in an appropriate calorie to gram nitrogen ratio, and
which has an osmolarity consistent with the route of administration.
Unless appropriately diluted, the infusion of hypertonic dextrose injections into a
peripheral vein may result in vein irritation, vein damage, and thrombosis. Strongly
hypertonic nutrient solutions should be administered through an indwelling
intravenous catheter with the tip located in a large central vein such as the superior
vena cava.
Dextrose injection should not be administered simultaneously with blood through
the same infusion set because of the possibility of pseudoagglutination.
Adverse Reactions
Too rapid infusion of a hypertonic dextrose solution may result in diuresis,
hyperglycemia, glycosuria, and hyperosmolar coma. Continual clinical monitoring of
the patient is necessary in order to identify and initiate measures for these clinical
conditions.
Reactions which may occur because of the solution or the technique of
administration include febrile response, infection at the site of injection, venous
thrombosis or phlebitis extending from the site of injection, extravasation and
hypervolemia. If an adverse reaction does occur, the infusion should be discontinued,
the patient evaluated, appropriate therapeutic countermeasures instituted, and the
remainder of the fluid saved for examination if deemed necessary.
Precautions
Administration of hypertonic dextrose (nutrient or solution) and amino acid solutions
via central venous catheter may be associated with complications which can be
prevented or minimized by careful attention to all aspects of the procedure. This
includes attention to solution preparation, administration, and patient monitoring.
It is essential that a carefully prepared protocol, based upon current medical
practice, be followed, preferably by an experienced team. The package insert of
the protein (nitrogen) source should be consulted for dosage and all precautionary
information.
During the prolonged parenteral therapy or whenever the condition of the patient
warrants evaluation, clinical evaluation and periodic laboratory determinations are
necessary to monitor changes in fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and acid-
base balance. Interruption or rapid cessation of hypertonic dextrose therapy may
result in a hypoglycemic reaction. It is suggested that the patient be titrated with a
dilute dextrose solution until the patient has reached glucose equilibrium.
Special care must be taken when giving hypertonic glucose to patients with overt or
subclinical diabetes mellitus.
It has been suggested that glucose solutions should not be used after acute
ischemic strokes as hyperglycemia has been implicated in increasing cerebral
ischemic brain damage and in impairing recovery.
TEVA MEDICAL/DEXTROSE 10% IV INJ ECTION-TPN , 11. 4. 2001
7
Care should be taken to avoid circulatory overload, particularly in patients with
cardiac insufficiency.
Caution must be exercised in the administration of these injections to patients
receiving corticosteroids or corticotropin.
Dosage and Administration
Notes: Do not administer unless solution is clear and seal is intact.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and
discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. Use of a
final filter is recommended during administration of all parenteral solutions, where
possible.
Injection of the solution should be made slowly.
The maximum rate at which dextrose can be infused without producing glycosuria is
0.5 g/kg body weight/hour. About 95% of the dextrose is retained when infused at a
rate of 0.8 g/kg/hour.
The dose of 10% Dextrose Injection is dependent upon the age, weight and clinical
condition of the patient, as well as laboratory determinations.
When it is used as a caloric source in parenteral nutrition therapy, the package
insert of the protein (nitrogen) source should be consulted for the correct carbohydrate
dosage.
Additives may be incompatible. Complete information is not available. Those
additives known to be incompatible should not be used. A pharmacist should be
consulted, if available. If, in the informed judgment of the physician, it is deemed
advisable to introduce additives, aseptic technique should be used.
Thorough and careful mixing should be performed when additives have been
introduced.
Solutions containing additives must not be stored.
These admixed injections in plastic bags are intended for intravenous administration
using sterile equipment.
Exposure of pharmaceutical products to heat should be minimized. Excessive heat
should be avoided. It is recommended that products be stored at room temperature
(25C). Brief exposure up to 40C does not adversely affect the product.
Note: It is recommended that all intravenous administration apparatus,
including the needle, be replaced at least once every 24 hours.
Directions for Use of Plastic Bags
Warning : Do not use plastic bags in series connections. Such use could result in air
embolism due to residual air being drawn from the primary bag before administration
of the fluid from the secondary bag is completed.
Preparation for Administration
1. Suspend bag.
2. Remove plastic bag from outlet port at bottom of bag.
3. Attach administration set. Refer to complete directions accompanying set.
To Add Medication
Using syringe.
1. Prepare medication site.
2. Using a 20-22 gauge needle, puncture resealable rubber plug at target area
and inject. Multiple additions may be made in this manner.
3. Mix solution and medication thoroughly. For high density medications such as
potassium chloride, squeeze ports while ports are upright, and mix thoroughly.
Вам также может понравиться
- 5% Dextrose: R OnlyДокумент4 страницы5% Dextrose: R OnlyJeannette Richelle DacilloОценок пока нет
- 1105 PDFДокумент1 страница1105 PDFAgapa Yagamo GamikaОценок пока нет
- Dextrose 50 InjectionДокумент6 страницDextrose 50 InjectionLip StickОценок пока нет
- DEXTROSE AND SODIUM CHLORIDE-dextros e and S Odium Chloride Injection, S Olution Baxter Healthcare CorporationДокумент30 страницDEXTROSE AND SODIUM CHLORIDE-dextros e and S Odium Chloride Injection, S Olution Baxter Healthcare CorporationSulistiaОценок пока нет
- Ceftriaxoneinj DEVAДокумент11 страницCeftriaxoneinj DEVAMuhammad AwaisОценок пока нет
- 9% Sodium Chloride Solution MSDSДокумент14 страниц9% Sodium Chloride Solution MSDSbidangОценок пока нет
- Dextrose Injection IV Solution PDFДокумент0 страницDextrose Injection IV Solution PDFChip AmigoОценок пока нет
- Solu CortefДокумент4 страницыSolu CortefOliver BagarinaoОценок пока нет
- 5% Dextrose Inj AVIVA PI 30july2014 enДокумент8 страниц5% Dextrose Inj AVIVA PI 30july2014 ensoniaZDОценок пока нет
- Makalah Can JadiДокумент13 страницMakalah Can JadiTaufiks RohmansОценок пока нет
- Fluimucil 300mg / 3mlДокумент3 страницыFluimucil 300mg / 3mlRezti PratiwiОценок пока нет
- Label PDFДокумент8 страницLabel PDFfarmasi ulmОценок пока нет
- EtopexДокумент11 страницEtopexMohammed HaiderОценок пока нет
- Managing Medical and Pharmacological CareДокумент33 страницыManaging Medical and Pharmacological CareZNEROLОценок пока нет
- CeftriaxoneaftinjДокумент18 страницCeftriaxoneaftinjbarbawurakОценок пока нет
- Gastrointestinal System (Total Parenteral NutritionДокумент8 страницGastrointestinal System (Total Parenteral NutritionFritz MirandaОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент14 страницDrug StudyKatrina EstoconingОценок пока нет
- Flixonase-Nasule-Drops Pi 004 04 Draft-CleanДокумент10 страницFlixonase-Nasule-Drops Pi 004 04 Draft-CleanNisrin SaadОценок пока нет
- 0.9% NaCl or Plain NSSДокумент13 страниц0.9% NaCl or Plain NSSJeannette Richelle DacilloОценок пока нет
- Guidelines For The Adminstration of Drugs Via Enteral Feeding TubesДокумент13 страницGuidelines For The Adminstration of Drugs Via Enteral Feeding TubesDamodara Kumaran100% (3)
- Beta Karoten: (BAY Ta KARE Oh Teen)Документ9 страницBeta Karoten: (BAY Ta KARE Oh Teen)Nisa'ul KhoiriyahОценок пока нет
- Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride (Benadryl) 50mg/1mlДокумент6 страницDiphenhydramine Hydrochloride (Benadryl) 50mg/1ml'SheenMarkReal'Оценок пока нет
- Total Parenteral NutritionДокумент8 страницTotal Parenteral NutritionSrishti Bajaj100% (1)
- Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыDrug StudyCheriz LukbanОценок пока нет
- D BL Promethazine Hydrochloride in JДокумент10 страницD BL Promethazine Hydrochloride in JarthurbaidoodouglasОценок пока нет
- Nursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboДокумент7 страницNursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboAlexa Abidin Oldenborg100% (8)
- Gelofusine Guide for Medical ProfessionalsДокумент9 страницGelofusine Guide for Medical ProfessionalsRoxana CalderonОценок пока нет
- 5pct10pct Dextrose Injections USP in Viaflex Plastic Container ENДокумент12 страниц5pct10pct Dextrose Injections USP in Viaflex Plastic Container ENSolhaОценок пока нет
- SurvantaДокумент2 страницыSurvantasyafiraОценок пока нет
- Drug Safety Monitoring GuidelinesДокумент6 страницDrug Safety Monitoring GuidelinesShivam Malik100% (1)
- Prescribing Information for Kenalog-10 InjectionДокумент8 страницPrescribing Information for Kenalog-10 InjectionArlette DerizkaОценок пока нет
- Guidelines For The Administration of Drugs Through Enteral Feeding Tubes AnonДокумент24 страницыGuidelines For The Administration of Drugs Through Enteral Feeding Tubes AnonChen Boon TeyОценок пока нет
- Annex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsДокумент194 страницыAnnex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsKarthik YadaОценок пока нет
- Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate InjectionДокумент10 страницDexamethasone Sodium Phosphate InjectionRobiansyahОценок пока нет
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolДокумент26 страницGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolAnna Joy Antone100% (1)
- CeftriaxoneДокумент60 страницCeftriaxoneKazamatsu RyoОценок пока нет
- Targocid PI - NewДокумент4 страницыTargocid PI - NewDR JAMAL WARISОценок пока нет
- Taketomo 2019Документ328 страницTaketomo 2019Oscar AguileraОценок пока нет
- Pocket Card Parenteral Nutrition February 2021Документ5 страницPocket Card Parenteral Nutrition February 2021Kouba MarciminiОценок пока нет
- Description: Nutriflex Peri: Each Litre Contains Amino Acids (15 Different Laevorotatory Amino Acids andДокумент5 страницDescription: Nutriflex Peri: Each Litre Contains Amino Acids (15 Different Laevorotatory Amino Acids andgregory johnОценок пока нет
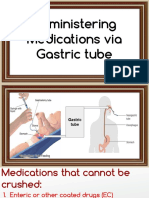
- Administering Medication Via Gastric TubeДокумент20 страницAdministering Medication Via Gastric TubeDwight Kristian CruzОценок пока нет
- Reference ID: 3109129: WWW - Fda.gov/medwatchДокумент22 страницыReference ID: 3109129: WWW - Fda.gov/medwatchGabriel MataОценок пока нет
- CIPROFLOXACIN AND DEXAMETHASONE-ciprofloxacin and Dexamethasone Suspension/ Drops Sandoz IncДокумент22 страницыCIPROFLOXACIN AND DEXAMETHASONE-ciprofloxacin and Dexamethasone Suspension/ Drops Sandoz IncnnОценок пока нет
- DextroseДокумент1 страницаDextroseamaliea234Оценок пока нет
- Parenteral nutrition guideДокумент3 страницыParenteral nutrition guideDarren RossОценок пока нет
- Case StudyДокумент16 страницCase StudyRaidis PangilinanОценок пока нет
- HYDROCORTISONE-hydrocortis One Cream HYDROCORTISONE - Hydrocortis One Ointment Perrigo New York IncДокумент8 страницHYDROCORTISONE-hydrocortis One Cream HYDROCORTISONE - Hydrocortis One Ointment Perrigo New York IncHardiyanti banduОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент10 страницDrug StudyFritzie Beatrice NomusОценок пока нет
- Hydroxyzine Orifarm Film-Coated Tablet ENG SMPC - 09001bee807a397dДокумент11 страницHydroxyzine Orifarm Film-Coated Tablet ENG SMPC - 09001bee807a397dmaroxgamingОценок пока нет
- Drug Study DMДокумент5 страницDrug Study DMKimsha ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- Nasogastric Tube InsertionДокумент12 страницNasogastric Tube Insertionmemon_bilqeesОценок пока нет
- Care of The Patient Receiving Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)Документ29 страницCare of The Patient Receiving Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)majd100% (1)
- Inotrope (Vasoactive Medication) Administration in The Paediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU)Документ6 страницInotrope (Vasoactive Medication) Administration in The Paediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU)Κατερίνα ΣιάλουОценок пока нет
- Amoxicillin Patient Drug ProfileДокумент4 страницыAmoxicillin Patient Drug ProfileKaren T. Celetaria75% (12)
- Drug Study AGEДокумент9 страницDrug Study AGECherry Jani OlmedoОценок пока нет
- 07 - SMPC - Lactated Ringers Injection USP - V1Документ10 страниц07 - SMPC - Lactated Ringers Injection USP - V1Andrianna NastasyaОценок пока нет
- Hernia Medical ManagementДокумент5 страницHernia Medical ManagementCherilyn MedalleОценок пока нет
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesОт EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Methods 508Документ2 страницыMethods 508Nurul MazniОценок пока нет
- I-PSS Prostate Symptom ScoreДокумент2 страницыI-PSS Prostate Symptom ScoreFrida AnggaОценок пока нет
- Standards For Maternal and Neonatal Care - WHOДокумент72 страницыStandards For Maternal and Neonatal Care - WHODharmendra PanwarОценок пока нет
- ArtCVP MonitoringДокумент18 страницArtCVP MonitoringKarine SouzaОценок пока нет
- NG3 Guidance (Updated) 20151202Документ65 страницNG3 Guidance (Updated) 20151202Nurul MazniОценок пока нет
- Staff duty rosterДокумент7 страницStaff duty rosterNurul MazniОценок пока нет
- Hahahaha 1Документ2 страницыHahahaha 1Nurul MazniОценок пока нет
- BF Guide 1 PDFДокумент6 страницBF Guide 1 PDFNurul MazniОценок пока нет
- Consensus Guidelines On The Management of Epilepsy 2010Документ94 страницыConsensus Guidelines On The Management of Epilepsy 2010alivestyledОценок пока нет
- TBI Clinicians Factsheet-AДокумент2 страницыTBI Clinicians Factsheet-Aleonjunchan_66965707Оценок пока нет
- NRP Guidelines Flyer English FINALДокумент2 страницыNRP Guidelines Flyer English FINALJeremiah HiiОценок пока нет
- CPG Management of Hypertension (4th Edition)Документ98 страницCPG Management of Hypertension (4th Edition)ssfdsОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Lecture Notes: Control of Microbes by Physical and Chemical AgentsДокумент5 страницChapter 7 Lecture Notes: Control of Microbes by Physical and Chemical AgentsMaureen DireroОценок пока нет
- Efelid ReferenceДокумент3 страницыEfelid ReferenceNurul MazniОценок пока нет
- Antibiotics as First-Line Therapy for Acute Appendicitis: A Population-Based StudyДокумент24 страницыAntibiotics as First-Line Therapy for Acute Appendicitis: A Population-Based StudyNurul MazniОценок пока нет
- 23Документ1 страница23Nurul MazniОценок пока нет
- Jadual Jaga Malam Koass Bedah (4/11/2013 - 11/1/2014) : Raissa (Yuli)Документ1 страницаJadual Jaga Malam Koass Bedah (4/11/2013 - 11/1/2014) : Raissa (Yuli)Nurul MazniОценок пока нет
- DyspepsiaДокумент25 страницDyspepsiaCynthia StefanusОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Lecture Notes: Control of Microbes by Physical and Chemical AgentsДокумент5 страницChapter 7 Lecture Notes: Control of Microbes by Physical and Chemical AgentsMaureen DireroОценок пока нет
- Jurnal Ocular HypertensionДокумент22 страницыJurnal Ocular HypertensionNurul MazniОценок пока нет
- Psychiatry Clinical Clerkship Assessment Sheet UKRIDA Jakarta Medical SchoolДокумент1 страницаPsychiatry Clinical Clerkship Assessment Sheet UKRIDA Jakarta Medical SchoolNurul MazniОценок пока нет
- Eye Exam GuideДокумент41 страницаEye Exam GuideNurul MazniОценок пока нет
- Adult Hypoglycemia Management ProtocolДокумент4 страницыAdult Hypoglycemia Management ProtocolNurul MazniОценок пока нет
- 23Документ1 страница23Nurul MazniОценок пока нет
- Anogenitalfindings OnexaminationДокумент1 страницаAnogenitalfindings OnexaminationNurul MazniОценок пока нет
- Wa0010.Документ9 страницWa0010.WaseemОценок пока нет
- Lead poisoning case studies highlight risks of old lead paintДокумент8 страницLead poisoning case studies highlight risks of old lead paintAle Escamilla Anaya100% (1)
- Human Sexuality-A Psycho Social R LopaterДокумент767 страницHuman Sexuality-A Psycho Social R LopaterBrian Bros100% (1)
- Quality of Life After Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients With Chronic RhinosinusitisДокумент15 страницQuality of Life After Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients With Chronic RhinosinusitisNarendraОценок пока нет
- Massage & Massage & Massage: Reyes Spa Reyes Spa Reyes SpaДокумент2 страницыMassage & Massage & Massage: Reyes Spa Reyes Spa Reyes SpaEloisa ReyesОценок пока нет
- REVALIDA EXAM 200 Answers With RationaleДокумент17 страницREVALIDA EXAM 200 Answers With Rationalexaileenx100% (1)
- Autistic Adult Perspectives On Occupational Therapy For Autistic Children and YouthДокумент8 страницAutistic Adult Perspectives On Occupational Therapy For Autistic Children and YouthNataliaОценок пока нет
- LIST OF REGISTERED DRUGS DECEMBER 2012Документ18 страницLIST OF REGISTERED DRUGS DECEMBER 2012Benjamin Tantiansu100% (1)
- The How and Why of The Movement System As The Identity of Physical TherapyДокумент8 страницThe How and Why of The Movement System As The Identity of Physical TherapyValeria Javalera BatОценок пока нет
- Dr. Az Rifki, Span - Kic Departemen Anestesiologi Dan Reanimasi Rsi Siti Rahmah/Fk-Fkg Universitas Baiturrahmah PadangДокумент62 страницыDr. Az Rifki, Span - Kic Departemen Anestesiologi Dan Reanimasi Rsi Siti Rahmah/Fk-Fkg Universitas Baiturrahmah PadangKamelia MarcshendaОценок пока нет
- The Discomfort of Labor: Pailz and and BirthДокумент11 страницThe Discomfort of Labor: Pailz and and BirthIhwan ZoffonОценок пока нет
- Significant Events in The Development of The Counseling ProfessionДокумент3 страницыSignificant Events in The Development of The Counseling ProfessionWendy Joy CuyuganОценок пока нет
- Peptic Ulcer PrintДокумент6 страницPeptic Ulcer PrintSyazmin KhairuddinОценок пока нет
- Outcomes of Masking and Habituation Therapy With The Implementation of A New Sound Therapy ProtocolДокумент7 страницOutcomes of Masking and Habituation Therapy With The Implementation of A New Sound Therapy ProtocolGöksel TurhalОценок пока нет
- Meden-Inmed Hydrotherapy & Balneotherapy Catalogue 2020Документ32 страницыMeden-Inmed Hydrotherapy & Balneotherapy Catalogue 2020Xuan NguyenОценок пока нет
- Niacin Chemical Forms, Bioavailability, and Health EffectsДокумент10 страницNiacin Chemical Forms, Bioavailability, and Health EffectsNutri_InfoОценок пока нет
- PaxilДокумент5 страницPaxilSandro AlcobaçaОценок пока нет
- PerdevДокумент33 страницыPerdevBatchie Bugs StuartОценок пока нет
- Music Therapy Depression CochReviewДокумент22 страницыMusic Therapy Depression CochReviewselviaharumОценок пока нет
- 5 Health As A Social InstitutionДокумент34 страницы5 Health As A Social InstitutionSze Yinn PikaaОценок пока нет
- Maquet Servo 900c - User ManualДокумент105 страницMaquet Servo 900c - User Manualpaola_96Оценок пока нет
- Hallucinations and Hearing VoicesДокумент5 страницHallucinations and Hearing VoicesdevОценок пока нет
- Goodman and Gilman39s Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics Latest EditionДокумент3 страницыGoodman and Gilman39s Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics Latest EditionLinda0% (1)
- Mu 089Документ4 страницыMu 089Rahul RaiОценок пока нет
- Evaluation of Psychiatric Disorders: Key ConceptsДокумент12 страницEvaluation of Psychiatric Disorders: Key ConceptsraniОценок пока нет
- Narrative ReportДокумент11 страницNarrative Reportwhatss upОценок пока нет
- How To Critically Appraise A PaperДокумент6 страницHow To Critically Appraise A PaperAmbar RahmanОценок пока нет
- Pancreatic Cancer - Clinical Management - S. Srivastava (Intech, 2012) WW PDFДокумент324 страницыPancreatic Cancer - Clinical Management - S. Srivastava (Intech, 2012) WW PDFpouiftfvoОценок пока нет
- The Stages of Adlerian TherapyДокумент3 страницыThe Stages of Adlerian TherapyRirika MomobamiОценок пока нет
- Opioid Induced HyperalgesiaДокумент39 страницOpioid Induced HyperalgesiaAnonymous XEbh4UxfОценок пока нет