Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Mole Calculations and Polymerization Reactions
Загружено:
_patmurrayИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Mole Calculations and Polymerization Reactions
Загружено:
_patmurrayАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
GENERAL
mole calculations
PRODUCTION OF MATERIALS
thermal cracking
catalytic cracking
bromine water
test:
cyclohexene
cyclohexane
Polymersation:
ethylene
LDPE
initiation
propagation
termination
(disproportionation)
backbiting
HDPE
vinyl chloride
PVC
styrene PS
condensation
polymerisation of:
3-hydroxybutanoic
acid PHB;
glucose
acid hydrolysis of
cellulose
(breaking -1,4-
glycosidic bonds)
hydrogenation of
ethylene
fermentation
complete
combustion of
ethanol
incomplete
combustion
heat energy
tranfer
addition of water
and ethylene
dehydration of
ethanol
Leclanch cell:
anode
cathode
Button cell:
anode
cathode
producing
transuranic
elements
medical isotope:
Tc-99m
industrial isotope:
Na-24
Recently
discovered
element:
Ununoctium
THE ACIDIC ENVIRONMENT
pH
determining
whether acid or
base
natural acidity of
rain
releasing SO
2
smelting of
sulfide ores
bacterial
fermentation
S-compounds
producing SO
2
form sulfurous
acid
form sulfuric acid
OR
N
2
and O
2
form
nitric oxide with
high temps
form nitrogen
dioxide
form nitricacid
and nitrous acid
nitrous acid forms
nitric acid
natural buffer
system:
H
2
CO
3
/H
2
CO
3
-
-use LCP when
add acid/base
1
photosynthesis
(endergonic
reaction)
Esterification
(forming an ester)
general
making ethyl
butyrate
CHEMICAL MONITORING AND MANAGEMENT
nitrogen oxides
(in traffic from
car engines)
ozone from
photochemical
smog in
troposphere
catalytic
converters in cars
reduce harmful
emissions
Haber process
sources of H
2
removing CO and
CO
2
1
- if acid added,
- if base added
- in both cases, the equilibrium shifts to neutralise the added acid/base
Formation of
ozone
Destruction of
ozone
increased temp at
stratosphere
CFCs in
stratosphere
Chlorine atom in
CFCs make for
catalyst in
destruction of
stratospheric
ozone
catalytic
destruction of O
3
by high-altitude
supersonic aircraft
INDUSTRIAL CHEMISTRY
fertiliser
production
superphosphate
SBR production
Contact process
obtaining SO
2
(1)
smelting
(see AE)
(2)
catalytic oxidation
of SO
2
absorption of SO
3
conversion of
oleum to H
2
SO
4
safety
diluting H
2
SO
4
ionisation
exothermic
S compounds
produce H
2
S
dehyrating agent
secondary process:
why dangerous, not
dehydration
oxidising agent
electrolysis of
NaCl
-molten
anode
cathode
overall
-concentrated
anode
cathode
overall
-dilute
anode
cathode
overall
Mercury cell
anode
cathode
overall
Diaphragm cell
anode
cathode
overall
Membrane cell
anode
cathode
overall
Downs cell
anode
cathode
Saponification
(making soap)
general
glycerol trilaurate
+ NaOH
glycerol + sodium
laurate
glycerol
tristearate +
NaOH glycerol
+ sodium stearate
soap in hardwater
forming scum
(insoluble)
Solvay Process
overall
brine purification
CO
2
formation
ammonia
recovery
carbonic acid
formation
ammonia
saturation
net HCO
3
-
formation
decomposition of
NaHCO
3
Вам также может понравиться
- Contra Wound CoilsДокумент26 страницContra Wound CoilsmiguelteixeiramaОценок пока нет
- TM11 2400 Generators ML 185 A and ML 185 B HydrogenДокумент67 страницTM11 2400 Generators ML 185 A and ML 185 B Hydrogendavid_graves_okstate100% (1)
- Napalm On Screen ChemistryДокумент1 страницаNapalm On Screen ChemistryMohamad HossamОценок пока нет
- Anic Chemistry ReviewДокумент59 страницAnic Chemistry ReviewEnrica GaОценок пока нет
- Travenol's Finest - 1981 Hays Kansas Employee CookbookДокумент109 страницTravenol's Finest - 1981 Hays Kansas Employee CookbookBeau DealyОценок пока нет
- Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary SAR ManualДокумент134 страницыCanadian Coast Guard Auxiliary SAR ManualAnjaana PrashantОценок пока нет
- How To Make A Robot WalkДокумент15 страницHow To Make A Robot Walkadmer100% (1)
- Seamanship Reference Manual For TowingДокумент56 страницSeamanship Reference Manual For TowingAdnan MohamedОценок пока нет
- VOL 5 Pulse GeneratorsДокумент755 страницVOL 5 Pulse Generatorsgorods5rtОценок пока нет
- Carlton Chaisaw Chain ManualДокумент35 страницCarlton Chaisaw Chain ManualstarkopeteОценок пока нет
- USCG LightList V7 2018 PDFДокумент256 страницUSCG LightList V7 2018 PDFBrian BrohlОценок пока нет
- Fresh PerspectiveДокумент96 страницFresh PerspectiveKhanh Dam100% (1)
- TM11-2405 Meteorological Balloons, 1944Документ51 страницаTM11-2405 Meteorological Balloons, 1944david_graves_okstateОценок пока нет
- 1 Tan Your Own Hide PDFДокумент13 страниц1 Tan Your Own Hide PDFTanya Michaela Kneidinger0% (3)
- Fourteenacre Catalogue October 2018Документ28 страницFourteenacre Catalogue October 2018spaceОценок пока нет
- Ce 1983 01 PDFДокумент140 страницCe 1983 01 PDFJose Cedillo ElBuenoОценок пока нет
- 7.P-Block Elements (Group 15 To 18) KCET PYQsДокумент2 страницы7.P-Block Elements (Group 15 To 18) KCET PYQsPunith kumarОценок пока нет
- Cable Fault PrototypeДокумент124 страницыCable Fault PrototypearnenylundОценок пока нет
- Svnthesis of Tartaric AcidДокумент7 страницSvnthesis of Tartaric Acidsergey sergeev100% (1)
- Electrochemistry Lab ReportДокумент7 страницElectrochemistry Lab ReportMatt ParkОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Catalysis-Chapter 7 (Part 1)Документ22 страницыEnzyme Catalysis-Chapter 7 (Part 1)OmSilence2651Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry Module F5Документ209 страницChemistry Module F5rabbitОценок пока нет
- EICO 324 Signal Generator User ManualДокумент15 страницEICO 324 Signal Generator User ManualJShearer83% (6)
- Gold Leaching Using ThioureaДокумент6 страницGold Leaching Using Thioureanlinaresg19100% (1)
- Electronics Today 1979 11Документ90 страницElectronics Today 1979 11cornel_24Оценок пока нет
- 01 Jan1962 73 Mag PDFДокумент100 страниц01 Jan1962 73 Mag PDFBravo KiloОценок пока нет
- Pork Cut Guide: Loin Cuts Under 40 CharactersДокумент2 страницыPork Cut Guide: Loin Cuts Under 40 CharacterstimhorkinОценок пока нет
- TM11-2410 Pilot Baloon TablesДокумент127 страницTM11-2410 Pilot Baloon Tablesdavid_graves_okstateОценок пока нет
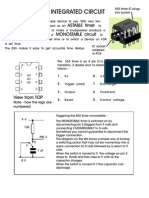
- 555 TimerДокумент7 страниц555 TimerHERMAWAN100% (1)
- Iso 12643-4-2010Документ58 страницIso 12643-4-2010Thuý AnОценок пока нет
- Scout Regen v1.2.1Документ47 страницScout Regen v1.2.1vimaru88Оценок пока нет
- Production of Sodium Chlorite PDFДокумент13 страницProduction of Sodium Chlorite PDFangelofgloryОценок пока нет
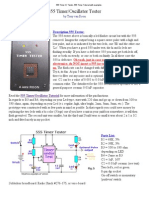
- 555 Timer IC Tester, 555 Timer Tutorial With ExamplesДокумент2 страницы555 Timer IC Tester, 555 Timer Tutorial With ExamplesfgaluppoОценок пока нет
- TransistorsДокумент3 страницыTransistorsSohaib AhmedОценок пока нет
- Mini Circuits ProductsДокумент164 страницыMini Circuits ProductsewnatalОценок пока нет
- The Reaction Between Sulfur and Calcium Hydroxide PDFДокумент4 страницыThe Reaction Between Sulfur and Calcium Hydroxide PDFJavier Aviles100% (1)
- BR 1938 PDFДокумент4 страницыBR 1938 PDFashok KumarОценок пока нет
- The History of Using Solar EnergyДокумент8 страницThe History of Using Solar Energyarnika33Оценок пока нет
- A, Krohn, Bohn - 1972 - Electrodeposition and Surface TreatmentДокумент13 страницA, Krohn, Bohn - 1972 - Electrodeposition and Surface TreatmentDhanapal PalОценок пока нет
- 41C NavegationДокумент57 страниц41C NavegationjorgenunopereiraОценок пока нет
- Agreed Statement of Facts: Her Majesty The Queen V Benjamin LevinДокумент11 страницAgreed Statement of Facts: Her Majesty The Queen V Benjamin LevinJohn Laws100% (1)
- Installation Ac UnitДокумент75 страницInstallation Ac Unitkaliman2010Оценок пока нет
- DRO-550 Construction GuideДокумент23 страницыDRO-550 Construction GuidePeterОценок пока нет
- BEOPLAY V1 TV DETAILSДокумент10 страницBEOPLAY V1 TV DETAILSkg_selvarajОценок пока нет
- The Sproutie MK II HF Regen Receiver FiltersДокумент81 страницаThe Sproutie MK II HF Regen Receiver Filtersdetroit_me25530% (1)
- Ferrocement A Versatile Construction Material Use in Asia 1976Документ113 страницFerrocement A Versatile Construction Material Use in Asia 1976David Sachs100% (1)
- LED LIGHT BRICK PROJECT GUIDEДокумент10 страницLED LIGHT BRICK PROJECT GUIDEDumitrescu Leonard CezarОценок пока нет
- Completion Design Review With Focus On Well Integrity and ProductivityДокумент105 страницCompletion Design Review With Focus On Well Integrity and ProductivityarbakleОценок пока нет
- Eico 753 schematic and parts list in one page and three piecesДокумент32 страницыEico 753 schematic and parts list in one page and three piecesQuinn GoldenОценок пока нет
- Chemc1000v2 Manual SampleДокумент9 страницChemc1000v2 Manual Sampleankara271828Оценок пока нет
- Radio Electronics December 1989 PDFДокумент100 страницRadio Electronics December 1989 PDFManny De GuzmanJrОценок пока нет
- Advanced Ceramic Components - Materials, Fabrication, and Applications PDFДокумент32 страницыAdvanced Ceramic Components - Materials, Fabrication, and Applications PDFDaxel Val100% (1)
- Monitoring Times 1997 06Документ124 страницыMonitoring Times 1997 06Benjamin DoverОценок пока нет
- Hobbywing WP 1040Документ2 страницыHobbywing WP 1040andresОценок пока нет
- Digital Microscope User ManualДокумент19 страницDigital Microscope User ManualZaegorОценок пока нет
- S9407 Ab HBK 010 - Rev2Документ276 страницS9407 Ab HBK 010 - Rev2Emily StewartОценок пока нет
- Eico 1963 CatalogДокумент28 страницEico 1963 CatalogbhaidriОценок пока нет
- ClockДокумент4 страницыClockSanjay ChandrasekarОценок пока нет
- Black Powder Definitions FINALДокумент5 страницBlack Powder Definitions FINALErwin VermeerschОценок пока нет
- SPDIF WhitepaperДокумент14 страницSPDIF Whitepaperapi-3760834100% (1)
- Signal Engineering GilbertДокумент144 страницыSignal Engineering Gilbertbdavid2012Оценок пока нет
- Homemade Nixie TubesДокумент6 страницHomemade Nixie TubesRulo VillanoОценок пока нет
- Simple Kitchin Regenerative Receiver ProjectsДокумент5 страницSimple Kitchin Regenerative Receiver Projectsrik206Оценок пока нет
- British Special Quality Valves and Electron Tube Devices Data Annual 1964–65От EverandBritish Special Quality Valves and Electron Tube Devices Data Annual 1964–65Оценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент10 страницUntitledGhh FyjОценок пока нет
- All Chemical Reactions 2023Документ29 страницAll Chemical Reactions 2023Aryan MishraОценок пока нет
- Humidity Cells - ASTM-D5744Документ13 страницHumidity Cells - ASTM-D5744shiagigiОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Model Exam QuestionsДокумент16 страницChemistry Model Exam QuestionsSajeevОценок пока нет
- Science Class X SyllabusДокумент172 страницыScience Class X SyllabusVishnu DuttОценок пока нет
- Hsslive Xii Chemistry Term 2 Dec 2022 Key Anil KumarДокумент5 страницHsslive Xii Chemistry Term 2 Dec 2022 Key Anil Kumaradithaj.2006220Оценок пока нет
- Chapter Seventeen Electrochemistry: For ReviewДокумент51 страницаChapter Seventeen Electrochemistry: For ReviewSimon FarbmanОценок пока нет
- Elektrohemijska Sinteza Metal Organskih JedinjenjaДокумент10 страницElektrohemijska Sinteza Metal Organskih JedinjenjaJelena ZdravkovicОценок пока нет
- 04 - Metode ElektrogravimetriДокумент19 страниц04 - Metode ElektrogravimetriNurul Aulia HusainОценок пока нет
- INDIAN EXCELLENT Pvt. SCHOOL HOLIDAY HOMEWORKДокумент20 страницINDIAN EXCELLENT Pvt. SCHOOL HOLIDAY HOMEWORKssssОценок пока нет
- 6433 Topper 21 129 510 2 43 Electrochemistry Up201612091847 1481289429 3Документ44 страницы6433 Topper 21 129 510 2 43 Electrochemistry Up201612091847 1481289429 3Rishab PurkayasthaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry IAДокумент4 страницыChemistry IARebecca KuaОценок пока нет
- Test 34 - Redox Reactions - Middle of PyramidДокумент6 страницTest 34 - Redox Reactions - Middle of PyramidJay PatelОценок пока нет
- 2018 (Fleischmann, S.) Hybridization of Electrochemical Energy Storage Nanohybrid Materials and Hybrid Cell Architectures (Alemanha)Документ165 страниц2018 (Fleischmann, S.) Hybridization of Electrochemical Energy Storage Nanohybrid Materials and Hybrid Cell Architectures (Alemanha)KaíqueОценок пока нет
- 9th Class Chemistry Guess PapersДокумент11 страниц9th Class Chemistry Guess PapersMarkpiciОценок пока нет
- Nitric Acid 70% MSDSДокумент6 страницNitric Acid 70% MSDSyayax_619Оценок пока нет
- Oxidation-Reduction (Exercise 1 - 4) Module-1Документ19 страницOxidation-Reduction (Exercise 1 - 4) Module-1Raju SinghОценок пока нет
- Reactions in Aqueous Solution Student VersionДокумент74 страницыReactions in Aqueous Solution Student VersionNabila Hanim100% (1)
- Bylkas 1997Документ5 страницBylkas 1997Catarina SabinoОценок пока нет
- Graphene-Based Materials Supported Advanced Oxidation Processes For Water and Wastewater Treatment: A ReviewДокумент23 страницыGraphene-Based Materials Supported Advanced Oxidation Processes For Water and Wastewater Treatment: A Reviewnidia LouvianaОценок пока нет
- 6.2 - Standard Electrode Potentials - Chemistry LibreTextsДокумент19 страниц6.2 - Standard Electrode Potentials - Chemistry LibreTextsMildred Mae RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry Answer KeyДокумент6 страницElectrochemistry Answer KeyAriesMascarhenasОценок пока нет
- Oxidation-Reduction Reactions ExplainedДокумент5 страницOxidation-Reduction Reactions ExplainedMatthew BeekhooОценок пока нет
- BOD and COD Removal Using Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 - USP TechnologiesДокумент3 страницыBOD and COD Removal Using Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 - USP TechnologiesAshish PhadnisОценок пока нет
- S3749rev HemcoSanJoseReviewReport13082020Документ32 страницыS3749rev HemcoSanJoseReviewReport130820201394203031Оценок пока нет
- Prateek 1Документ12 страницPrateek 1Hayato ffОценок пока нет