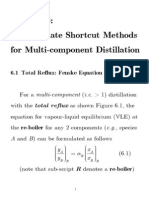
Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Packed Bed
Загружено:
Naveen Kumar0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
235 просмотров3 страницыpacked bed assignment
Оригинальное название
packed bed
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документpacked bed assignment
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
235 просмотров3 страницыPacked Bed
Загружено:
Naveen Kumarpacked bed assignment
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
APPLICATIONS OF PACKED BED
BY
E.GIRIDHAR DEV
ROLL-UG116215
CLASS-(II/IV) B.TECH
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
INTRODUCTION
In chemical processing, a packed bed is a hollow tube, pipe, or other vessel that is filled
with a packing material. The packing can be randomly filled with small objects likeRaschig
rings or else it can be a specifically designed structured packing. Packed beds may also
contain catalyst particles or adsorbents such as zeolite pellets, granular activated carbon,
etc.
The purpose of a packed bed is typically to improve contact between two phases in a
chemical or similar process. Packed beds can be used in a chemical reactor, a
distillation process, or a scrubber, but packed beds have also been used to store heat in
chemical plants.
APPLICATIONS:
Packed Column
In industry, a packed column is a type of packed bed used to perform separation
processes, such as absorption, stripping, and distillation. A packed column is a pressure
vessel that has a packed section.
[1]
Columns used in certain types of chromatography consisting of a tube filled with packing
material can also be called packed columns and their structure has similarities to packed
beds.
Column Structure: Random and Stacked packed columns
The column can be filled with random dumped packing (creating a random packed column)
or with structured packing sections, which are arranged or stacked (creating a stacked
packed column). In the column, liquids tend to wet the surface of the packing and the
vapours pass across this wetted surface, where mass transfer takes place. Packing offers
the advantage of a lower pressure drop across the column (when compared to plates or
trays), which is beneficial while operating under vacuum. Differently shaped packing
materials have different surface areas and void space between the packing. Both of these
factors affect packing performance.
Liquid and Vapour Distribution (vapour to liquid ratio)
Another factor in performance, in addition to the packing shape and surface area, is the
liquid and vapor distribution that enters the packed bed. The number of theoretical
stages required to make a given separation is calculated using a specific vapor to liquid
ratio. If the liquid and vapor are not evenly distributed across the superficial tower area as it
enters the packed bed, the liquid to vapor ratio will not be correct and the required
separation will not be achieved.
[1]
Packed bed reactors
Packed bed reactors can be used in chemical reaction. These reactors are tubular and are
filled with solid
catalyst particles,
most often used to
catalyze gas
reactions.
[2]
The
chemical reaction
takes place on the
surface of
the catalyst. The
advantage of using a
packed bed reactor is
the higher conversion
per weight of catalyst
than other catalytic
reactors. The reaction
rate is based on the
amount of the solid catalyst rather than the volume of the reactor.
Column Chromatography
Column chromatography is a separation technique in which the stationary bed is within a
tube. The particles of the solid stationary phase or the support coated with a liquid stationary
phase may fill the whole inside volume of the tube (packed column) or be concentrated on or
along the inside tube wall leaving an open, unrestricted path for the mobile phase in the
middle part of the tube (open tubular column). Differences in rates of movement through the
medium are calculated to different retention times of the sample.
[1]
In expanded bed
adsorption, a fluidized bed is used, rather than a solid phase made by a packed bed. This
allows omission of initial clearing steps such as centrifugation and filtration, for culture broths
or slurries of broken cells
Packed Bed Scrubbers
or Packed Tower, is designed to remove gaseous or vaporous pollutants from an
air stream. The process is accomplished by contacting the contaminated air
stream with scrubbing liquor that absorbs or chemically reacts with the
pollutants. Some vapours can be simply removed by condensation through the
cooling effect of the circulating liquid. The cleaned air is then discharged to the
atmosphere and the contaminated scrubbing liquor is either disposed of in an
approved manner or chemically treated and recycled. In some cases, the
collected contaminants can be recovered and reused in the original or other
processes.
Вам также может понравиться
- Fluid Mixing II: A Symposium Organised by the Yorkshire Branch and the Fluid Mixing Processes Subject Group of the Institution of Chemical Engineers and Held at Bradford University, 3-5 April 1984От EverandFluid Mixing II: A Symposium Organised by the Yorkshire Branch and the Fluid Mixing Processes Subject Group of the Institution of Chemical Engineers and Held at Bradford University, 3-5 April 1984Оценок пока нет
- R1 Chemical Absorption in Packed BedДокумент12 страницR1 Chemical Absorption in Packed BedSzeQiLungОценок пока нет
- Oxidation of Organic Compounds: Medium Effects in Radical ReactionsОт EverandOxidation of Organic Compounds: Medium Effects in Radical ReactionsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Production of Ammonia: Department of Chemical Engineering A Report OnДокумент29 страницProduction of Ammonia: Department of Chemical Engineering A Report OnDr.AhmedОценок пока нет
- Design Project 2013Документ154 страницыDesign Project 2013Fahad HussainОценок пока нет
- Design of Packed Column 3q Sy2010 11Документ65 страницDesign of Packed Column 3q Sy2010 11abderrahimnОценок пока нет
- Kinetics of Surface ReactionsДокумент24 страницыKinetics of Surface ReactionsShehRoz KhanОценок пока нет
- SharpCookie PDFДокумент346 страницSharpCookie PDFhinjmmmmОценок пока нет
- Diff Equation 2 2011-Fall TheoryДокумент48 страницDiff Equation 2 2011-Fall TheoryAna CristacheОценок пока нет
- (How To) Design A Scrubber (Packed Column) - Pharma EngineeringДокумент8 страниц(How To) Design A Scrubber (Packed Column) - Pharma EngineeringpratikОценок пока нет
- Catalytic Oxidation of Ammonia To NitrogenДокумент139 страницCatalytic Oxidation of Ammonia To Nitrogenagnotts09Оценок пока нет
- Nitric Acid Chematur WheaterlyДокумент4 страницыNitric Acid Chematur WheaterlyAnonymous 1XHScfCI100% (1)
- Mat3110 2019 20 Tutorial Sheet 1 Power Series Euler and SystemsДокумент2 страницыMat3110 2019 20 Tutorial Sheet 1 Power Series Euler and SystemsChaka MbeweОценок пока нет
- Synthesis AmmoniaДокумент9 страницSynthesis AmmoniaNaufal AzrizalОценок пока нет
- Production of Ammonium NitrateДокумент3 страницыProduction of Ammonium NitrateSk jahidul IslamОценок пока нет
- Supercritical Fluid ExtractionДокумент12 страницSupercritical Fluid ExtractionSata AjjamОценок пока нет
- Final ProjectДокумент73 страницыFinal ProjectKedar Yadav100% (2)
- Appendix F - SteamTable SmithДокумент76 страницAppendix F - SteamTable SmithNIXОценок пока нет
- Chemical Reactor Design - NotesДокумент4 страницыChemical Reactor Design - NotesJanaki Devi ParratОценок пока нет
- Nitric Acid Production ReportДокумент34 страницыNitric Acid Production ReportNellai GtrОценок пока нет
- CO2 Capture Over K2CO3 MgO Al2O3 Dry Sorbent in A Fluidized BedДокумент8 страницCO2 Capture Over K2CO3 MgO Al2O3 Dry Sorbent in A Fluidized BedFarah Talib Al-sudaniОценок пока нет
- Industrial MetabolismДокумент3 страницыIndustrial MetabolismtbeedleОценок пока нет
- Modeling and Simulation of A Spray Column For NOx AbsorptionДокумент15 страницModeling and Simulation of A Spray Column For NOx AbsorptionAnel MamaniОценок пока нет
- Fluid Dispersion-Generalization and Comparison of Mathematical Models-I Generalization of ModelsДокумент11 страницFluid Dispersion-Generalization and Comparison of Mathematical Models-I Generalization of ModelsJesus Moreno CastilloОценок пока нет
- Ammonium Nitrate: 1 FertilizerДокумент5 страницAmmonium Nitrate: 1 FertilizerPeyman KhОценок пока нет
- Two-Step Production of 13-Butadiene From EthanolДокумент197 страницTwo-Step Production of 13-Butadiene From EthanolSanchez JorgeОценок пока нет
- CLEMENTS 2002 Granular Activated Carbon Management at A Water Treatment Plant PDFДокумент187 страницCLEMENTS 2002 Granular Activated Carbon Management at A Water Treatment Plant PDFjambrong8850% (2)
- Introduction To Mass TransferДокумент44 страницыIntroduction To Mass TransferDeb Datta100% (1)
- 06 Approximate Methods For Multi-Component DistillationДокумент61 страница06 Approximate Methods For Multi-Component DistillationNagwa Mansy100% (1)
- Energy Engineering Lab Manual (WEC)Документ74 страницыEnergy Engineering Lab Manual (WEC)haseebОценок пока нет
- Role of Catalysis in Sustainable Development4thДокумент59 страницRole of Catalysis in Sustainable Development4thSwamiОценок пока нет
- Fayaz Report On Challenges Associated With Sepn of Hcl-Water Azeotrope 04.08Документ27 страницFayaz Report On Challenges Associated With Sepn of Hcl-Water Azeotrope 04.08fayaz5uin1234Оценок пока нет
- Packed Column Design - Flow Through A Packed BedДокумент10 страницPacked Column Design - Flow Through A Packed BedWONG TSОценок пока нет
- Fluidized Bed Reactor DesignДокумент22 страницыFluidized Bed Reactor Designs barmanОценок пока нет
- Addis Ababa University Institute of Technology: School of Civil and Environmental EngineeringДокумент13 страницAddis Ababa University Institute of Technology: School of Civil and Environmental Engineeringashe zinabОценок пока нет
- Flow Through Fluidised BedsДокумент27 страницFlow Through Fluidised Bedsa_so8535Оценок пока нет
- Sample Problem #5Документ5 страницSample Problem #5DozdiОценок пока нет
- Gas Separation by Adsorption ProcessesДокумент10 страницGas Separation by Adsorption ProcessesSanti SanchezОценок пока нет
- 1 - SO2 and NOx PDFДокумент13 страниц1 - SO2 and NOx PDFAaron David ReidОценок пока нет
- Chl407 Study MaterialДокумент104 страницыChl407 Study MaterialNana kwadwoОценок пока нет
- Synthesis GasДокумент8 страницSynthesis GasTotok IswantoОценок пока нет
- Bayer Process PDFДокумент2 страницыBayer Process PDFFrandi CahyaОценок пока нет
- Bio Degradation of PlasticsДокумент24 страницыBio Degradation of PlasticsArchit Gupta100% (1)
- Armfield Rising Film EvaporatorДокумент2 страницыArmfield Rising Film EvaporatorEvy Citra Ayu NegariОценок пока нет
- Anaerobic Digestion of Cow Dung For Biogas Production: Baba Shehu Umar Ibn Abubakar and Nasir IsmailДокумент4 страницыAnaerobic Digestion of Cow Dung For Biogas Production: Baba Shehu Umar Ibn Abubakar and Nasir IsmailanantriОценок пока нет
- A Review of Oxy-Fuel Combustion in Fluidized Bed ReactorsДокумент25 страницA Review of Oxy-Fuel Combustion in Fluidized Bed ReactorsIlyan Tik NantaОценок пока нет
- Methanol From GlycerinДокумент5 страницMethanol From GlycerinaudreysosoОценок пока нет
- Activity CoefficientДокумент45 страницActivity CoefficientAlexander MintsОценок пока нет
- Ammonia Process InformationДокумент4 страницыAmmonia Process InformationRishikesh AwaleОценок пока нет
- Heat Exchange in A Prilling TowerДокумент6 страницHeat Exchange in A Prilling TowerSean KimОценок пока нет
- Mass Transfer QuizzesДокумент10 страницMass Transfer QuizzesNate JamesОценок пока нет
- A Platinum-Rhodium Catalyst Used in Nitric AcidДокумент2 страницыA Platinum-Rhodium Catalyst Used in Nitric AcidAlaa MagdyОценок пока нет
- Kunii e Levenspiel (1997)Документ12 страницKunii e Levenspiel (1997)Elson Teti100% (1)
- ThermolysisДокумент5 страницThermolysisJoao MinhoОценок пока нет
- 24 Ijecsmay PDFДокумент11 страниц24 Ijecsmay PDFHarshaОценок пока нет
- Flash Point TutorialДокумент8 страницFlash Point TutorialS. GreenОценок пока нет
- Hydro CarbonДокумент6 страницHydro CarbonAlpesh PatelОценок пока нет
- Appendices Meeting 11 Sept 2019Документ176 страницAppendices Meeting 11 Sept 2019aseОценок пока нет
- Disaster Risk Reduction and Climate Change AdaptationДокумент69 страницDisaster Risk Reduction and Climate Change AdaptationBryan MayoralgoОценок пока нет
- Nicks Four Roses Family Restaurant - PrintInspectionДокумент3 страницыNicks Four Roses Family Restaurant - PrintInspectionLiz ShepardОценок пока нет
- Boat and StreamДокумент4 страницыBoat and StreamAllin 1Оценок пока нет
- Heat Treating Titanium and Its AlloysДокумент8 страницHeat Treating Titanium and Its Alloysm5416Оценок пока нет
- Power Production Based On Osmotic Pressure.: Øystein S. Skråmestø, Stein Erik Skilhagen, Werner Kofod NielsenДокумент10 страницPower Production Based On Osmotic Pressure.: Øystein S. Skråmestø, Stein Erik Skilhagen, Werner Kofod NielsenShrishti ChaurasiaОценок пока нет
- Leaflet I-LIFE SlimДокумент16 страницLeaflet I-LIFE Slimjose luisОценок пока нет
- Week 4 Review Questions 2022Документ13 страницWeek 4 Review Questions 2022Asfin HaqueОценок пока нет
- ElepahatShield BrocureДокумент11 страницElepahatShield BrocureBinoy KaladiОценок пока нет
- Article 5 Normal Baseline: I. BaselinesДокумент7 страницArticle 5 Normal Baseline: I. BaselinesKing BangngayОценок пока нет
- M4 M6 Q Series ManualДокумент26 страницM4 M6 Q Series ManualAhmet MetinОценок пока нет
- Sponge ColoringДокумент3 страницыSponge Coloringapi-282203693Оценок пока нет
- Water PoliticsДокумент16 страницWater PoliticsanamakramОценок пока нет
- Carbon Dioxide Absorption - lw08Документ13 страницCarbon Dioxide Absorption - lw08javilapiedraОценок пока нет
- Narrative Report World Toilet DayДокумент2 страницыNarrative Report World Toilet DayBithao Daisy84% (19)
- (ODLAB) Catalogue (Eng)Документ20 страниц(ODLAB) Catalogue (Eng)vateloki7Оценок пока нет
- Physiological - Morphological and Behavioural Adaptations of Namib Desert Lizard Aporosaura AnchietaeДокумент19 страницPhysiological - Morphological and Behavioural Adaptations of Namib Desert Lizard Aporosaura AnchietaeraviОценок пока нет
- Literature Review On RiversДокумент8 страницLiterature Review On Riversl1wot1j1fon3100% (1)
- Waste Seg EngДокумент2 страницыWaste Seg Enganiya syoОценок пока нет
- Roman Baths OriginДокумент25 страницRoman Baths OriginNitescu DorinОценок пока нет
- Thermal Oxidizer BasicsДокумент8 страницThermal Oxidizer BasicsDiego1980b100% (1)
- Chanel ConnectivityДокумент15 страницChanel ConnectivityAlfian AminОценок пока нет
- Hydropower Slide 2Документ46 страницHydropower Slide 2Shankar ShaudОценок пока нет
- Umpp Greener Future121015 PDFДокумент68 страницUmpp Greener Future121015 PDFMohan KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Disaster Management: (Unit-1)Документ11 страницDisaster Management: (Unit-1)Milan Subhashchandra ShahОценок пока нет
- NM Methane Advisory Panel Draft Technical ReportДокумент301 страницаNM Methane Advisory Panel Draft Technical ReportNM Transparency InitiativeОценок пока нет
- Brochure RIBASIM 2009 DeltaresДокумент4 страницыBrochure RIBASIM 2009 DeltaresHydroCoОценок пока нет
- Manual final-FWG10-1Документ36 страницManual final-FWG10-1Leonid LeonovОценок пока нет
- CO2 Heat Pumps PotentialДокумент3 страницыCO2 Heat Pumps PotentialAnonymous ub0Yzv1PCОценок пока нет
- Kitchenuhmaykoosib Inninuwug P: RotocolsДокумент37 страницKitchenuhmaykoosib Inninuwug P: Rotocolsdavid_soneОценок пока нет
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldОт EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (58)
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellОт EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (82)
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonОт EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (103)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincОт EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (137)
- Permaculture for the Rest of Us: Abundant Living on Less than an AcreОт EverandPermaculture for the Rest of Us: Abundant Living on Less than an AcreРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (33)
- When the Heavens Went on Sale: The Misfits and Geniuses Racing to Put Space Within ReachОт EverandWhen the Heavens Went on Sale: The Misfits and Geniuses Racing to Put Space Within ReachРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (6)
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarОт EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (19)
- Dirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureОт EverandDirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (125)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldОт EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Four Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceОт EverandFour Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- The Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaОт EverandThe Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaОценок пока нет
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyОт EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyОценок пока нет
- Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceОт EverandPale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (588)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationОт EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (46)
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsОт EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (242)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindОт EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindОценок пока нет
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestОт EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (28)
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerОт EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (54)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastОт EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (31)
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyОт EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (24)