Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
11 Particles of Which Substances Are Made
Загружено:
api-2352694010 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
36 просмотров16 страницОригинальное название
11 particles of which substances are made
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
36 просмотров16 страниц11 Particles of Which Substances Are Made
Загружено:
api-235269401Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 16
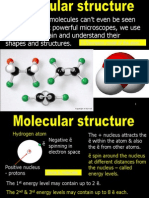
Elements & Atoms:
All substances are made up of the most simple of
particles atoms.
All elements are made up of individual atoms, with all
the atoms of a particular element having the same
structure. They cant be broken into simpler substances.
The noble gases are the only substances that exist as
single, separate atoms in nature. All other atoms are
joined to other atoms of the same kind or of a
different kind. Noble gases: He, Ne, Ar, Kr Xe, Rn
Atoms
1
Compounds:
When atoms of different elements combine in a
chemical reaction, compounds are formed consisting
of 2 or more atoms from different elements.
Compounds consist of a group of 2 or more different
atoms, attached together by strong forces or bonds in
definite, specific ratios.
Compounds may be broken down into simpler
substances by chemical means.
Particles of compounds exist as molecules or ions
depending upon the types of bonds formed.
Atoms, elements, molecules and compounds
2
Types of compounds
There are 2 types of compounds:
Molecular compounds in which the particles are
individual molecules often held together by
intermolecular forces or bonds.
Examples: H
2
O, SO
2
, CH
4
, CO
2
Ionic compounds when hundreds of + & - ions are
held together in a large crystal lattice.
Examples: NaCl, CuSO
4
, PbNO
3
, KMnO
4
Ionic & molecular compounds
3
Covalent Bonding sharing of pairs
Mostly between non-metals. Often diatomic
molecules are formed. eg H
2
O, Cl
2
Ionic Bonding transfer of ions formed
Between metals and non-metals. Positive
and negative ions are formed. eg NaCl, KF
Metallic Bonding + ions in sea of
Within metals. eg Na, Cu
Type of bonds determine physical & chemical properties
Ionic & covalent bonding
Covalent bond
4
H
2
molecule H
2
O
2
N
2
single double triple
covalent bonds sharing pairs
Other molecules containing covalent bonds:
Water H
2
O carbon dioxide CO
2
methane CH
4
molecules
These are
compounds
Elements
I
2
Shapes of molecules
5
When metals lose their outer (s) to non-metals, + & -
ions are formed. These ions hold together with
electrostatic (Coulomb) forces of attraction called ionic
bonds. These bonds are strong bonds & many ions are
held together in a giant crystal lattice.
Na
+
are cations, & Cl
-
are anions, NaCl formula unit
Ionic bond
6
Consider copper wire:
= dislodged
= + Cu ions
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ +
+
+
+ +
+
+
Metallic bonding is set up between the + Cu
ions and the dislodged in the wire.
Metallic bond
7
Metallic bonding
8
Forces between atoms within molecules are called
chemical bonds eg ionic & covalent bonds.
These kinds of bonds (within molecules) are called
intramolecular forces.
Examples: Covalent, ionic & metallic
Forces between molecules are called intermolecular
forces.
Examples: hydrogen bonds
& van der Waals forces
van der Waal's forces
9
O
H
H
O
H
H
_
_
+
+
Intramolecular force
(covalent bond strong)
Intermolecular force
(weaker) called
hydrogen bond
These respective forces and shapes explain why
water is a dipole and how it is possible to float a pin
on water even though its density is greater.
H
2
O molecules
in water
Hydrogen bonds
H bonding in water
10
Allotropes are merely atoms of the same element,
combined in different ways/ratios and this gives
rise to different properties.
Diamonds and graphite are allotropes of carbon.
Diamonds are hard, non-conductors of electricity
Graphite is soft & conducts electricity by means of
free .
These are called covalent network structures &
also apply to quartz & sulphur.
Allotropes of C
11
Diamonds are made of carbon atoms that have
been covalently bonded in a very large, strong
crystal lattice, in which each atom is bonded to 4
others.
The resulting structure
makes it the hardest
material of all.
The pattern gives rise to
the sparkling facets.
Since there are no lose it
does not conduct
electricity.
Diamond & graphite
12
Like diamonds, graphite is also composed of carbon
atoms. Here each C atom is covalently bonded to 3
others in a plate-like structure.
The flat sheets are weakly bonded to one another & can
easily be rubbed off as in the case of pencils.
plate
Weak
forces
between
plates
Graphite & diamonds
13
Here 60 carbon atoms are joined with each atom
bonded to 3 other carbon atom to form a shape
like a soccer ball.
Buckyball
14
Particles
Small, strong
covalent bonds,
weak attraction,
easily vaporised
Strong bonds in
giant structure
Properties
Low M.P. & B.P.
Dont conduct
heat or
electricity.
High M.P. & B.P.,
hard, graphite
conducts electricity
others not
Example
H
2
N
2
I
2
Diamond (carbon)
Graphite (carbon)
Metals, limestane
Simple
molecules
Giant
molecules
Giant molecule
15
These are usually solids, often in crystal form with
high melting points as a result of the strong ionic
bonds that need to be broken in order to melt.
They are brittle & can be made finer by crushing.
M.P. = 800
0
C
B.P. = 1413
0
C
- As a result of strong
ionic bonds between
ions
Properties of ionic compounds
16
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Katara Towers Bms Schematic Diagram 06may2021Документ20 страницKatara Towers Bms Schematic Diagram 06may2021Elektrikal InhinyeroОценок пока нет
- Design of Structural Steel Pipe Racks PDFДокумент12 страницDesign of Structural Steel Pipe Racks PDFmobin1978100% (3)
- Pavement Engineering Notes 2012Документ77 страницPavement Engineering Notes 2012Mohamed Wehliye90% (10)
- Lingual Braces 693Документ2 страницыLingual Braces 693api-235269401Оценок пока нет
- Ceramic Braces 809Документ2 страницыCeramic Braces 809api-235269401Оценок пока нет
- Invisalign 947Документ3 страницыInvisalign 947api-235269401Оценок пока нет
- Inman Aligners 781Документ3 страницыInman Aligners 781api-235269401Оценок пока нет
- Metal Braces 1072Документ3 страницыMetal Braces 1072api-235269401Оценок пока нет
- Braces Introduction 244Документ2 страницыBraces Introduction 244api-235269401Оценок пока нет
- Backward PlanningДокумент18 страницBackward Planningapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g12m Finance Growth DecayДокумент28 страницg12m Finance Growth Decayapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g12m TrigonometryДокумент33 страницыg12m Trigonometryapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- How To Use A Student PlannerДокумент35 страницHow To Use A Student Plannerapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g12m Patterns Sequences SeriesДокумент48 страницg12m Patterns Sequences Seriesapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g12m FunctionsДокумент34 страницыg12m Functionsapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g12m StatisticsДокумент25 страницg12m Statisticsapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g12m Euclidean GeometryДокумент25 страницg12m Euclidean Geometryapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g12m Differential CalculusДокумент66 страницg12m Differential Calculusapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g11 3 Numbers PatternsДокумент21 страницаg11 3 Numbers Patternsapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g12m Analytical GeometryДокумент28 страницg12m Analytical Geometryapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g11 7 MeasurementДокумент20 страницg11 7 Measurementapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g12m Counting ProbabilityДокумент31 страницаg12m Counting Probabilityapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g11 9 Finance Growth and DecayДокумент25 страницg11 9 Finance Growth and Decayapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g11 10 StatisticsДокумент49 страницg11 10 Statisticsapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g11 6 TrigonometryДокумент73 страницыg11 6 Trigonometryapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g11m Analytical GeometryДокумент18 страницg11m Analytical Geometryapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g11 5 FunctionsДокумент76 страницg11 5 Functionsapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g11 1 Exponents and SurdsДокумент31 страницаg11 1 Exponents and Surdsapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- g11m Equations and InequalitiesДокумент38 страницg11m Equations and Inequalitiesapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- 12 Chemistry of WaterДокумент8 страниц12 Chemistry of Waterapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- 07 CH Chemical Bonds and Shapes of MoleculesДокумент13 страниц07 CH Chemical Bonds and Shapes of Moleculesapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- 09 CH Electronegativity and Polar MoleculesДокумент12 страниц09 CH Electronegativity and Polar Moleculesapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- 14 Snells LawДокумент8 страниц14 Snells Lawapi-235269401Оценок пока нет
- Forces Between Atoms and MoleculesДокумент13 страницForces Between Atoms and MoleculesDoc_CrocОценок пока нет
- Single Core Unarmoured LV CablesДокумент1 страницаSingle Core Unarmoured LV CablesPrashanth ShastryОценок пока нет
- Ross 2015Документ11 страницRoss 2015mohanpusОценок пока нет
- User Manual: Product Type: Switching Power Supply Model Name: HG2, HP2, PSM, PSLДокумент17 страницUser Manual: Product Type: Switching Power Supply Model Name: HG2, HP2, PSM, PSLotrupon melliОценок пока нет
- GROUP 2 - General Physics II Microwave RadiationДокумент9 страницGROUP 2 - General Physics II Microwave RadiationRheyven JuanОценок пока нет
- B Tech21911R07 PDFДокумент52 страницыB Tech21911R07 PDFRajeev BujjiОценок пока нет
- Time-of-Flight (Ultrasonic Displacement Sensor)Документ23 страницыTime-of-Flight (Ultrasonic Displacement Sensor)igoy saputraОценок пока нет
- NTC ThermistorДокумент3 страницыNTC ThermistorPablo AllosiaОценок пока нет
- Pressure Seal Bonnet Design: Dedication To DeliveryДокумент44 страницыPressure Seal Bonnet Design: Dedication To DeliverylutОценок пока нет
- Overload Clutches For Index Drives (Type D-Sa, Adjustable) : Operating PrincipleДокумент4 страницыOverload Clutches For Index Drives (Type D-Sa, Adjustable) : Operating PrincipleSuhas KODREОценок пока нет
- Rooftex BrochureДокумент2 страницыRooftex BrochureTRAG ProjectsОценок пока нет
- AR 303 Vol 1 DДокумент968 страницAR 303 Vol 1 DAnonymous gM6RZL5lYdОценок пока нет
- Word File PDFДокумент4 страницыWord File PDFanusha kОценок пока нет
- Iei Epitome: in This IssueДокумент27 страницIei Epitome: in This Issueabarna kamОценок пока нет
- 4051 Manuscript 10825 1 10 20220331Документ12 страниц4051 Manuscript 10825 1 10 20220331Chandra MouliОценок пока нет
- 6 - Mass, Weight and C.GДокумент17 страниц6 - Mass, Weight and C.GRafayОценок пока нет
- I. Melc.: Perpetual Succour Academy, Inc. National Rd. Poblacion Dos, Malabuyoc, Cebu Science 10Документ4 страницыI. Melc.: Perpetual Succour Academy, Inc. National Rd. Poblacion Dos, Malabuyoc, Cebu Science 10Cry BeroОценок пока нет
- Electric Potential: Arranged By: Group 1Документ27 страницElectric Potential: Arranged By: Group 1Lasmaenita SiahaanОценок пока нет
- D38999/24WD35S N D38999/20WB35S N D38999/24WB35S N D38999/26WB35P N D38999/26WC35P NДокумент49 страницD38999/24WD35S N D38999/20WB35S N D38999/24WB35S N D38999/26WB35P N D38999/26WC35P NsdfsdfОценок пока нет
- W2manual42 Part2 Theory Rev1Документ256 страницW2manual42 Part2 Theory Rev1Maria Camila Valencia CárdenasОценок пока нет
- Fully Automatic Current and Voltage Transformer Test SetДокумент8 страницFully Automatic Current and Voltage Transformer Test SetMuhammad ShahidОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Calculus 2021 Second BatchДокумент2 страницыFinal Exam Calculus 2021 Second BatchOliric NabcihОценок пока нет
- Form 2 Math Chapter 10Документ4 страницыForm 2 Math Chapter 10velavanОценок пока нет
- Projet RockyДокумент19 страницProjet RockyCassella AdrianoОценок пока нет
- Lesson 8 Shear or Diagonal Tension in RC BeamsДокумент8 страницLesson 8 Shear or Diagonal Tension in RC BeamsJoshua John JulioОценок пока нет
- Huygens' Principle, Maxwell's Displacement CurrentДокумент7 страницHuygens' Principle, Maxwell's Displacement CurrentGalleta Galleta MetralletaОценок пока нет
- Airflow Sensors AWM5000 Series High Flow Mass Airflow/AmplifiedДокумент4 страницыAirflow Sensors AWM5000 Series High Flow Mass Airflow/AmplifiedwidsonmeloОценок пока нет