Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
From This Age in What Patient Group? Start Screening For With Test Frequency
Загружено:
phoenix24601Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
From This Age in What Patient Group? Start Screening For With Test Frequency
Загружено:
phoenix24601Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
1
Preventive Medicine
So to say, we in our life have always been asked to be Pro-active rather than reactive, repeating
up the words Prevention is the best cure. Now is the time to act on it- to our common goal of
Incidence 0% of those diseases that can be prevented. Too many Human Deaths and sufferings
can be prevented and has been shown to be prevented -just by following the recommended screening
strategy as given below in an age chronicle.
A. Patients who have single 1st degree relative with Colorectal Ca diagnosed before the age of 60yrs,
or who have multiple 1st degree relative diagnosed with this cancer - Screening should begin at 40
yrs of age or 10 yrs younger than the age at which the youngest affected relative was diagnosed,
whichever comes 1st.
B. R/F for osteoporosis are
Family history
Smoking
Alcohol
Chronic Steroid use
Low Body weight
C. FOB= Fecal Occult Blood test
D. DRE=Digital Rectal Examination/ PSA=Prostate Specifc Antigen
E. DEXA= Dual-Energy-X-ray-Absorptiometry
For Pap-smear look at Oncology chapter.
From
this Age
In what patient group?
Start screening
for
With test Frequency
18
Female 18-25 of age - who
are sexually active
Chlamydia
Trachomatis
Antigen detection
methods
q 1 yr
20
Only in patient with R/F for
Hyperlipidemia
High cholesterol
Random Total
cholesterol + HDL
At Regular
intervals
35
All Males-
High cholesterol
Random Total
cholesterol + HDL
At Regular
intervals
40
All female Breast Ca Mammography q 1 yr
Patients with R/F for colon
cancer
A
Colon Ca Colonoscopy q 5 yrs
45
All female High cholesterol
Random Total
cholesterol + HDL
At Regular
intervals
All patients-
screening can start earlier if
therere additional R/F
Diabetes
Fasting Blood
glucose
At Regular
intervals
50
All patients Colorectal Ca
FOB
C
q 1yr
Sigmoidoscopy q 5 yrs
Colonoscopy q 10 yrs
Only If patient has clear
family H/O Prostate Ca
Prostate Ca DRE/PSA
D
At Regular
intervals
60
Only In Female patients with
R/F for Osteoporosis
B
Osteoporosis DEXA scan
E
At regular
intervals
65
All female patients Osteoporosis DEXA scan
At regular
intervals
Only in Male patients with
H/O signifcant smoking
Abdominal Aortic
Aneurysm
USG of abdomen
Once is
enough
This is a promotional chapter of the book "I-MED"
Follow the given link to visit the official site of the book
http://sites.google.com/site/imedbooks
2
Preventive Medicine
Preventive management of Lipid Disorders
Atherosclerotic disease is the No. 1 cause of Death in this World. Know that this disease can really be prevented
by well managed care of patients, with the best of all treatment DIET AND LIFESTYLE MODIFICATION-
but sadly it is the Hardest to implement. And as High Cholesterol is a major contributor to the formation of
Atherosclerotic plaques in Arteries, we should be screening all patients for High Cholesterol from an appropriate
age.
If patient has any of the following, then start screening for Hyper-Cholesterolemia from 20 yrs of age
Diabetes Mellitus. 1.
Family H/O hyperlipidemia. 2.
Multiple R/F for Atherosclerotic Vascular disease for e.g. smoking and HTN. 3.
Family H/O 4. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) in a Male relative < 50 yrs or Female relative < 60 yrs
- termed as premature CAD.
If all of the above R/Fs are absent, then regular screening for high cholesterol should be done after 35 yrs in
Male and 45 yrs in Female patients. Screening for high cholesterol should include measurement of Total
Cholesterol and Total HDL. If Random total cholesterol level is Abnormal then NSIM is to do Fasting
cholesterol levels, the levels obtain would dictate the Tx.
Note that Total HDL/ Total cholesterol is a better predictor of risk for Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) than
Total LDL/ Total cholesterol level.
Now what are the management guidelines for High Cholesterol?
Patient has following
LDL goal
(target LDL)
Start Lifestyle
and diet modif-
cation
Start Statins
CAD or its Equivalent
1
< 100 mg/dl 100 mg/dl 130 mg/dl
2 or more R/F
2
< 130 mg/dl 130 mg/dl 160 mg/dl
No R/F or just 1 R/F < 160 mg/dl 160 mg/dl 190 mg/dl
MRS lDl, I see
101 in LDL. To
make it easy, use
the number 100
rather than 101.
Now add + 30 to go
downwards and +
30 to go sideways.
This strategy
will be helpful
in remembering
the values and to
construct this table
denovo.
1. So what are the conditions that fall into CAD and its equivalent? They are
Symptomatic Atherosclerotic Diseases- for e.g. Claudication , TIA etc.
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.
DM
Patient diagnosed with Stable Angina MRS. SAD patient
2. R/F that are taken into consideration for management of High cholesterol are, as pertaining to the
above table
Age 45 in males and 55 in females
HyperTenNsive patient
Cigarette smoking.
HDL < 40 mg/dl- (note that HDL > 60 mg/dl removes 1 R/F from this list).
Family H/O premature Coronary Artery disease i.e. CAD occurring at < 55 yrs of age in a Male
relative and < 65 yrs of age in a Female relative.
LDL target is < 70 mg/dl in Patients considered as very high risk. This includes patient with Acute-
coronary syndrome or the combination of stable angina + either DM or tobacco use
This is a promotional chapter of the book "I-MED"
Follow the given link to visit the official site of the book
http://sites.google.com/site/imedbooks
3
Preventive Medicine
LOW HDL management (HDL< 40 mg/dl)
What do we do in this case?
1. The target LDL should always be reached before starting Tx for Low HDL.
2. If theres HDL with TriGlyceride then, correction of TG should be done 1
st
.
3. Only then treat for HDL. The TxOC is Lifestyle modifcation and diet changes. Note
Omega-3 Fatty acid in diet can increase HDL.
4. Then the pharmacological DOC is Fibrate (Gemfbrozil or Clofbrates). Niacin also can be
used, but it causes intense generalized pruritus and Flushing - because Niacin induces release
of Prostaglandins and histamine. Co-Tx with low dose Aspirin will reduce those S/E.
Lets try some CCS, using above-mentioned guidelines
60 y/o Male with H/O intermittent claudication. Total LDL is 100 mg/dl. NSIM start Diet and
lifestyle modifcation. Note that Intermittent claudication is a form of Symptomatic Atherosclerotic
disease.
65 y/o M patient diagnosed with type II DM. Total LDL is 135 mg/dl. NSIM Statin Tx.
65 y/o M diagnosed with HTN. Total LDL is 140 mg/dl. HDL is 65 mg/dl. NSIM Do nothing. This
patient has 2 R/F of age and HTN, but he has HDL > 60 mg/dl. So subtract 1 R/F.
The Statins (Atorvastatin, Simvastatin etc.) are very good drugs to lower LDL levels and they also have
been shown to Stabilize plaques in Acute-coronary Syndrome. Their MOA is inhibition of HMG CoA
reductase, which is the Rate-limiting enzyme for Bio-synthesis of cholesterol. Their Major S/E are Myo-
pathy (S/S of muscle generalized pain with in serum CreatineKinase), and Hepatotoxicity (ALT/
AST). Theres increased incidence of Myopathy with associated Conditions like Hypothryroidism and
Co-administration of Fibrates. If Myopathy develops then NSIMstop Statin (or else his condition may
worsen).
This is a promotional chapter of the book "I-MED"
Follow the given link to visit the official site of the book
http://sites.google.com/site/imedbooks
4
Preventive Medicine
ADULT VACCINATION
When is not prevention better than cure anyway? All patients should specifc vaccination when it is required
and recommended. It is our duty and imperative to do so.
1
st
step in determining when and what vaccine should be given to the patient - is all about whether the patient
is Immuno-compromised or not.
Does the patient have H/O of any of the following?
HIV
steroid use
organ transplant
Diabetes Mellitus
Alcoholism
cancer
any form of chronic liver, kidney or lung disease? (For e.g. Cystic fbrosis, Chronic Renal Fail-
ure, Cirrhosis of liver, COPD, Bronchiectasis etc.).
If YES, then the patient should get these two preventive vaccinations regardless of age, they are-
The Flu vaccine thats usually given IM on a yearly basis. If the patient is allergic to eggs, then this IM
Flu vaccine isnt given, as this vaccine contains egg antigens. Another formulation of vaccine is given
which is commercially available in Intra-nasal form, in which egg isnt used for the manufacturing
process.
Strep vaccine (pneumovax) One Booster doses of this vaccine should be given after 5 years of the 1
st
dose.
Well if the patient doesnt have any of those above conditions, only then take into consideration our patients
age
If patients age is >50 years then, start yearly Flu vaccine shot. MRS Flu Fifty
Then as our patient reaches 65 years of age, we give one-time-shot of Pneumovax and no boosters of
Strep pneumovax are required in Immunocompetent patients. MRS strep sixty fve
Remember that all patients regardless of age should get Diptheria and Tetanus (DT) vaccine every 10 years.
This is a promotional chapter of the book "I-MED"
Follow the given link to visit the official site of the book
http://sites.google.com/site/imedbooks
5
Preventive Medicine
Miscellaneous
Now lets try some CCS using above mentioned Guidelines
A 25 y/o man with Cystic fbrosis came to your clinic for regular checkup and his last checkup was 10
years ago. He hasnt received Booster dose of Pneumovax.
Ans: He gets all of the above vaccinations i.e. DT q10 years, Flu q1year and one booster dose of Pneumovax.
A 35 y/o man with Diabetes Mellitus came to your clinic. His last checkup was 6 years ago - All his vac-
cinations are up-to-date. He has already received one booster dose of Pneumovax.
Ans: He gets the Flu shot (q1yr).
A 47 y/o female with HTN or Hypercholesterolemia or H/O of MI. Her last checkup was 7 years ago and
all her vaccinations are up-to-date.
Ans: She will get no vaccination. Remember the differences between DM and HTN or other chronic metabolic
disease i.e. the latter ones arent considered as high risk or in other words Immuno-compromised.
A perfectly healthy 70 y/o female came for her routine checkup. Her last visit to a doctor was 15 years
ago.
Ans: she should get the DT Booster dose, Flu shot, Strep pneumovax single shot.
Remember another two specifc situation of (1) surgical Splenectomy and (2) Autosplenectomy cases
in Sickle cell anemia. These group of patients should get the following vaccinations designed for
encapsulated organism
1. N. meningitis one shot.
2. Strep Pneumomia - two shot pneumovax within a period of 5yrs.
All HIV +ve patients, if Asymptomatic and not severly Immunocompromised, should Receive MMR
vaccination even though its a live Vaccine.
Patients who are allergic to eggs should not get IM inFluenza vaccine and MMR and Yellow fever
vaccine.MRS FRY Eggs
is the patent
immuncompromised?
Give IM fu (q1yr)
Pneumovax (q5yr)
DT (q10yr)
YES NO
then look at the
patents age
<50 y/o
DT (q10yrs)
>50 y/o
IMfu (q1yr)
DT (q10yrs)
>65 y/o
Pneumovax (justonetme)
Give IM fu (q1yr)
DT (10yrs)
This is a promotional chapter of the book "I-MED"
Follow the given link to visit the official site of the book
http://sites.google.com/site/imedbooks
6
Preventive Medicine
Rabies Prophylaxis
Tetanus prevention
The most imp question to answer is, does our patient get both active and passive immunization or neither of
them? The vaccination shouldnt be given if theres no need for that, i.e. when we are sure that the animal
doesnt have Rabies.
CCS- H/O Domestic animal bite - then see if the animal has any signs of rabies virus infection (i.e. exces-
sive salivation and violent aggressive behavior). If yes, then kill the animal and then send for pathology
examination of the brain. If pathology report is +ve for rabies then our patient should be vaccinated with
both Active and Passive immunization.
CCS H/O domestic animal bite and the animal doesnt show any signs of rabies. Here we can observe
the dog for 10 days, to see if the dog develops any signs of rabies or not. If the signs develop then kill the
animal and send for pathology examination and henceforth manage according to the pathology report. But
if the animal doesnt develop any signs of rabies for the period of 10 observed days, then dont have to do
anything - just reassure the patient.
CCS- H/O animal bite in the face or neck region dont wait for anything. NSIM is immediately vac-
cinate patient - no time for evaluation.
CCS- H/O wild animal bite - then immediately vaccinate with both active and passive immunization,
because usually the wild animals cant be caught and hence their brains cant pried open to see if there are
signs of rabies infection or not.
Remember that all bite-injuries for e.g. human, dog, cat or raccoon bite should get Px for Pasteurella
Multicoda - DOC is Amoxicillin + Clavulanate combination.
H/O tetanus immunization
>1cm deep wounds or wound > 6 hr
ago
1
, or Dirty wounds for e.g. wounds
due to burn or crush injuries
Wounds that dont fall into the
previous category for e.g. Clean
wound < 6 hr ago.
never vaccinated or
< 3 doses of vaccine in the past
TT + TIG TT
3 doses of vaccine TT, only if last dose is > 5 yrs ago
TT only if last dose > 10 yrs
ago
1. 6 hrs is the average time for Lag stage in bacterial growth sigmoidal curve, after 6 hrs the bacteria are
multiplying like hell and their population growth is exponential, hence increased risk.
TT- Tetanus Toxoid- Active vaccination
TIG- Tetanus ImmunoGlobulin- Passive vaccination
This is a promotional chapter of the book "I-MED"
Follow the given link to visit the official site of the book
http://sites.google.com/site/imedbooks
7
Preventive Medicine
TRAVEL AND VACCINE
All travelers to the developed world for e.g. to North America and European countries usually
require no travel Vaccinations.
All travelers to the developing world should get Hepatitis A Vaccine - One dose of Active vaccination
will induce immunity within 4 weeks. So if the patient is travelling within 2 weeks then both Active and
Passive immunization is given. If the patient is travelling after 2 weeks then only the Active vaccination
is given
To simplify the cases for travel medicine, lets remember the two projections or the two big peninsulas
in the world map, they are (1) the Sub-Saharan African continent and (2) the Sub-Himalayan Indo-Nepal
territory. Two important points when patients are travelling to these 2 territories
1. Chloroquine resistant regions Hence Mefoquine (DOC) or Doxycycline is given for Malaria
prophylaxis (Px). If the patient is pregnant then Atovaquone Proguanil is given as Mefoquine
and Doxycyline is C/I in pregnancy. MRS- we become MAD when malaria is resistant to
chloroquine.
2. Get N. Meningitidis Prophylaxis with either Ciprofoxacin or Rifampin
And remember the Latin American region- another big peninsula in the world map. They are Chloroquine
sensitive region, so Travellers to this region are given Chloroquine for Malaria Px.
Note that patients travelling to make the Hajj to Mecca in Saudi Arabia are legally mandated to have N.
Meningitidis vaccination.
Other vaccines like vaccines for Yellow fever, Typhoid, Cholera, Rabies - it all depends upon where our
patient is going? What kind of disease are endemic in that area? What are their travel schedule and pur-
poses? That information should be researched properly before sending the patient to travel.
This is a promotional chapter of the book "I-MED"
Follow the given link to visit the official site of the book
http://sites.google.com/site/imedbooks
Вам также может понравиться
- Objectives IMДокумент104 страницыObjectives IMlaraОценок пока нет
- HY ObgynДокумент32 страницыHY ObgynAndreiSaffiotiОценок пока нет
- Syncope Mnemonic WOMAN 3-2-1 PEДокумент3 страницыSyncope Mnemonic WOMAN 3-2-1 PEanishdОценок пока нет
- DermatologyДокумент29 страницDermatologymariana yllanesОценок пока нет
- Uw Step 2 CK Im H OДокумент67 страницUw Step 2 CK Im H OAilyn MОценок пока нет
- USMLE Step 3 ER PDFДокумент12 страницUSMLE Step 3 ER PDFlalaОценок пока нет
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) Recommendations - Stats - Medbullets Step 2 - 3Документ5 страницU.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) Recommendations - Stats - Medbullets Step 2 - 3mtataОценок пока нет
- Michael W, COMAT FMДокумент4 страницыMichael W, COMAT FMSeanОценок пока нет
- MTB Cardiology NotesДокумент11 страницMTB Cardiology Noteskabal321Оценок пока нет
- Master the Boards: USMLE Step 2 CK UpdatesДокумент4 страницыMaster the Boards: USMLE Step 2 CK Updatesultimate knowledgezoneОценок пока нет
- SoCal's UW Step 2 CK EOs (UTD 10 Nov)Документ292 страницыSoCal's UW Step 2 CK EOs (UTD 10 Nov)JJ0% (1)
- Nbme 7 Block 2 Answerr+ExplanationsДокумент24 страницыNbme 7 Block 2 Answerr+ExplanationsShauki AliОценок пока нет
- Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Is The Diagnostic Study of Choice When A Patient Presents With Acute Alkali Ingestion. 2Документ2 страницыUpper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Is The Diagnostic Study of Choice When A Patient Presents With Acute Alkali Ingestion. 2Mariam MohamedОценок пока нет
- Uworld BiostatisticsДокумент2 страницыUworld BiostatisticsКостянтин РоманівОценок пока нет
- IMG EPIDEMIOLOGY STUDY GROUPДокумент8 страницIMG EPIDEMIOLOGY STUDY GROUPManivanh AvalosОценок пока нет
- USPSTF RecommendationsДокумент3 страницыUSPSTF RecommendationsKevinMathewОценок пока нет
- DeVirglio NotesДокумент77 страницDeVirglio NotesAlvand SehatОценок пока нет
- 2019AdultPreventiveHealthGuidelines PDFДокумент7 страниц2019AdultPreventiveHealthGuidelines PDFvesvОценок пока нет
- CardiologyДокумент8 страницCardiologykhalidzubairiОценок пока нет
- Top 25 Microorganisms for USMLE Step 1Документ29 страницTop 25 Microorganisms for USMLE Step 1Ramanpreet Kaur MaanОценок пока нет
- Epi Cheatsheet PDFДокумент4 страницыEpi Cheatsheet PDFDrbee10Оценок пока нет
- Form 1Документ108 страницForm 1Asim MohamedОценок пока нет
- Nephrotic and Nephritic Syndrome GuideДокумент3 страницыNephrotic and Nephritic Syndrome Guidewinston1234Оценок пока нет
- Third-Year OSCE Manual 2019-2020Документ17 страницThird-Year OSCE Manual 2019-2020Agleema AhmedОценок пока нет
- Shelf IM Video SlidesДокумент69 страницShelf IM Video SlidesRuth SanmooganОценок пока нет
- Brunner Step 2 CK Study PlanДокумент2 страницыBrunner Step 2 CK Study PlanhellayeahОценок пока нет
- Bio Chem 1Документ5 страницBio Chem 1Reynaldo RiveraОценок пока нет
- Emma Holliday Surgery Notes - Cornell StyleДокумент299 страницEmma Holliday Surgery Notes - Cornell StyleBanana MuffinОценок пока нет
- ASD: Presents with FIXED SPLIT S2 as a systolic ejection murmurДокумент17 страницASD: Presents with FIXED SPLIT S2 as a systolic ejection murmurSeanОценок пока нет
- Abrupta Placenta - 4 Pt presents with vaginal bleeding, ABDOMINAL PAIN, and uterine tendernessДокумент211 страницAbrupta Placenta - 4 Pt presents with vaginal bleeding, ABDOMINAL PAIN, and uterine tendernessroad2successОценок пока нет
- Step1 Journey-To 271Документ7 страницStep1 Journey-To 271Nilay BhattОценок пока нет
- USMLE WORLD QUESTIONS QuizletДокумент87 страницUSMLE WORLD QUESTIONS QuizletPatricio AlexanderОценок пока нет
- HY Cardio - 2Документ36 страницHY Cardio - 2oopsseОценок пока нет
- Immuno Micro VirologyДокумент15 страницImmuno Micro VirologyReynaldo RiveraОценок пока нет
- Step 1 UW Objectives Subjectwise 2022Документ474 страницыStep 1 UW Objectives Subjectwise 2022saranya sankarОценок пока нет
- PFT Interpretation AlgorithmДокумент4 страницыPFT Interpretation AlgorithmJason Steel50% (2)
- Dr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKДокумент29 страницDr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKmarina shawkyОценок пока нет
- Uworld CK Questions NotesДокумент2 страницыUworld CK Questions NotesPierreОценок пока нет
- Goljan Transcripts - Nts MODIFIED With SLIDES 5Документ91 страницаGoljan Transcripts - Nts MODIFIED With SLIDES 5Divya KondaveetiОценок пока нет
- Internal Medicine Table SummaryДокумент31 страницаInternal Medicine Table SummaryShazaan Nadeem100% (1)
- Grand Rounds - Pulmonary EmbolismДокумент25 страницGrand Rounds - Pulmonary EmbolismAdrian CastroОценок пока нет
- March 21 2014Документ48 страницMarch 21 2014fijitimescanadaОценок пока нет
- 3 Comments SHELF Practice Questions Surgery USMLE Step 2 HomeДокумент8 страниц3 Comments SHELF Practice Questions Surgery USMLE Step 2 HomeIndy PhangurehОценок пока нет
- USMLE Step 2 Practice TestДокумент986 страницUSMLE Step 2 Practice Testgirlygirl10100% (4)
- HY ObgynДокумент52 страницыHY ObgynteapalmtreeОценок пока нет
- Mehlmanmedical Hy PulmonaryДокумент31 страницаMehlmanmedical Hy PulmonaryJennifer Ross-ComptisОценок пока нет
- High Yield Step 2ckДокумент4 страницыHigh Yield Step 2ckCesar_Palana_3832Оценок пока нет
- Step 2 CKДокумент92 страницыStep 2 CKazankhan99Оценок пока нет
- Ethics Uworld NotesДокумент3 страницыEthics Uworld NotesActeen MyoseenОценок пока нет
- Dr. Waqas Ayubian Notes For Step 3Документ772 страницыDr. Waqas Ayubian Notes For Step 3Muhammad HammadОценок пока нет
- OME Peds NotesДокумент11 страницOME Peds Notessmian08Оценок пока нет
- Goljan Transcribed NotesДокумент59 страницGoljan Transcribed NotesJiyeon JeonОценок пока нет
- Cephalosporins and FriendsДокумент4 страницыCephalosporins and FriendsErika De JesusОценок пока нет
- SABER IM PrometricДокумент71 страницаSABER IM Prometricisra zaidОценок пока нет
- International Medical Graduate and the United States Medical Residency Application: A Guide to Achieving SuccessОт EverandInternational Medical Graduate and the United States Medical Residency Application: A Guide to Achieving SuccessRaghav GovindarajanОценок пока нет
- Rommel CPCДокумент89 страницRommel CPCphoenix24601Оценок пока нет
- Cardio IEДокумент39 страницCardio IEphoenix24601Оценок пока нет
- USMLE Step 3 CCS NotesДокумент20 страницUSMLE Step 3 CCS Notesaustinhitz96% (25)
- Arlete S Notes PDFДокумент28 страницArlete S Notes PDFjrabeОценок пока нет
- Kahveci: OzkanДокумент2 страницыKahveci: OzkanVictor SmithОценок пока нет
- Embryo If Embryonic Period PDFДокумент12 страницEmbryo If Embryonic Period PDFRyna Miguel MasaОценок пока нет
- What is zone refining processДокумент1 страницаWhat is zone refining processKeshav MadanОценок пока нет
- AVANTIZ 2021 LNR125 (B927) EngineДокумент16 страницAVANTIZ 2021 LNR125 (B927) EngineNg Chor TeckОценок пока нет
- WhatsoldДокумент141 страницаWhatsoldLuciana KarajalloОценок пока нет
- Driving Continuous Improvement by Developing and Leveraging Lean Key Performance IndicatorsДокумент10 страницDriving Continuous Improvement by Developing and Leveraging Lean Key Performance IndicatorskellendadОценок пока нет
- Second Law of EntrophyДокумент22 страницыSecond Law of EntrophyMia Betia BalmacedaОценок пока нет
- Singer NM37 57manualДокумент266 страницSinger NM37 57manualpaulkoby100% (2)
- Board 2Документ1 страницаBoard 2kristine_nilsen_2Оценок пока нет
- Creatures Since Possible Tanks Regarding Dengue Transmission A Planned Out ReviewjnspeДокумент1 страницаCreatures Since Possible Tanks Regarding Dengue Transmission A Planned Out Reviewjnspeclientsunday82Оценок пока нет
- Ana White - PLANS - A Murphy Bed YOU Can Build, and Afford To Build - 2011-03-03Документ20 страницAna White - PLANS - A Murphy Bed YOU Can Build, and Afford To Build - 2011-03-03Ahmad KamilОценок пока нет
- Living Nonliving DeadДокумент11 страницLiving Nonliving DeadArun AcharyaОценок пока нет
- Lanegan (Greg Prato)Документ254 страницыLanegan (Greg Prato)Maria LuisaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To OpmДокумент30 страницIntroduction To OpmNaeem Ul HassanОценок пока нет
- Product CycleДокумент2 страницыProduct CycleoldinaОценок пока нет
- PREMIUM BINS, CARDS & STUFFДокумент4 страницыPREMIUM BINS, CARDS & STUFFSubodh Ghule100% (1)
- Inventarisasi Data Kondisi Jalan Ke Dalam Aplikasi Sistem Informasi Geografis (Sig)Документ10 страницInventarisasi Data Kondisi Jalan Ke Dalam Aplikasi Sistem Informasi Geografis (Sig)Wiro SablengОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2 Mathematics Curriculum in The Intermediate GradesДокумент15 страницLesson 2 Mathematics Curriculum in The Intermediate GradesRose Angel Manaog100% (1)
- ĐỀ SỐ 3Документ5 страницĐỀ SỐ 3Thanhh TrúcОценок пока нет
- Programming Manual Magic 308/616-CLI Quick ReferenceДокумент16 страницProgramming Manual Magic 308/616-CLI Quick ReferencekrishnamarajublrОценок пока нет
- Trading Course DetailsДокумент9 страницTrading Course DetailsAnonymous O6q0dCOW6Оценок пока нет
- Course Tutorial ASP - Net TrainingДокумент67 страницCourse Tutorial ASP - Net Traininglanka.rkОценок пока нет
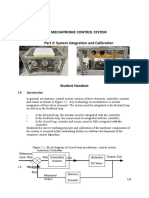
- Calibration Motion Control System-Part2 PDFДокумент6 страницCalibration Motion Control System-Part2 PDFnurhazwaniОценок пока нет
- 2019-10 Best Practices For Ovirt Backup and Recovery PDFДокумент33 страницы2019-10 Best Practices For Ovirt Backup and Recovery PDFAntonius SonyОценок пока нет
- Department of Education: Weekly Home Learning Plan Grade Ii Fourth Quarter Week 8Документ8 страницDepartment of Education: Weekly Home Learning Plan Grade Ii Fourth Quarter Week 8Evelyn DEL ROSARIOОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - International Banking Meaning: Banking Transactions Crossing National Boundaries Are CalledДокумент6 страницUnit 1 - International Banking Meaning: Banking Transactions Crossing National Boundaries Are CalledGanesh medisettiОценок пока нет
- S2 Retake Practice Exam PDFДокумент3 страницыS2 Retake Practice Exam PDFWinnie MeiОценок пока нет
- Drafting TechnologyДокумент80 страницDrafting Technologyong0625Оценок пока нет
- SQL Server 2008 Failover ClusteringДокумент176 страницSQL Server 2008 Failover ClusteringbiplobusaОценок пока нет
- Diemberger CV 2015Документ6 страницDiemberger CV 2015TimОценок пока нет