Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
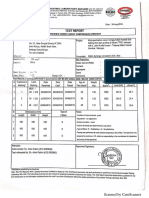
Standard Proctor
Загружено:
Fendi RoonАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Standard Proctor
Загружено:
Fendi RoonАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Soil Lab Experiment: Standard Proctor
Introduction
The Proctor compaction test is a laboratory method of experimentally determining
the optimal moisture content at which a given soil type will become most dense and
achieve its maximum dry density. The term Proctor is in honour of R. R. Proctor, who
in 1933 showed that the dry density of a soil for a given compactive effort depends
on the amount of water the soil contains during soil compaction.
Theory of Soil compaction
Compaction is the process by which the bulk density of an aggregate of matter is
increased by driving out air. For any soil, for a given amount of compactive effort, the
density obtained depends on the moisture content. At very high moisture contents,
the maximum dry density is achieved when the soil is compacted to nearly
saturation, where (almost) all the air is driven out. At low moisture contents, the soil
particles interfere with each other; addition of some moisture will allow greater bulk
densities, with a peak density where this effect begins to be counteracted by the
saturation of the soil.
Objective
1. Increasing the bearing capacity of foundations
2. Decreasing the undesirable settlement of structures
3. Control undesirable volume changes
4. Reduction in hydraulic conductivity
5. Increasing the stability of slopes
Equipment and apparatus
1. Mould
2. Rammer
3. Manual Rammer
4. Balance
5. Mixing pan
6. Trowel
7. Straight edge
8. Hammer
9. Lids
10. Drying oven
11. Steel ruler
12. Soil
Procedure
1. Lumpy soils are pulverized to small sizes by using a rammer and 3 kg of the
soil is weighted
2. The weight of the soil sample as well as the weight of the compaction mould
with its base (without the collar) is determined by using the balance and
record the weights.
3. Compute the amount of initial water to add by the following method
a) Assume water content to be at 8 percent
b) Compute water to add from the following equation
Water to add in ml =
Where water to add and the soil mass are in grams
4. The water is the measure out, the water is added to the soil, and the soil is
then mixed thoroughly using the trowel until the soil gets a uniform colour
5. The compaction based is then assembled to the mould, some soil is placed in
the mould and the soil is compacted in the three of equal layers specified by
the type of compaction method employed .27 of drops of the rammer per layer
is applied to the soil .The drops should be applied at a uniform rate not
exceeding around 1.5 seconds per drop, and the rammer should provide
uniform coverage of the specimen surface
6. The soil should completely fill the cylinder and the last compacted
7. Layer must extend slightly above the collar joint. If the soil is below the collar
joint at the completion of the drops, the test point must be repeated.
8. The collar and trim off is carefully removed from the compacted soil so that it
is completely even with the top of the mould using the trowel. The top layer of
the soil is trimmed by using steel ruler
9. The compacted soil is weighted while its in the mould and to the base, and
the mass is recorded. The wet mass of the soil is determined by subtracting
the weight of the mould and base.
10. The soil from the mould is removed by using hammer and straight edge is
used to take some wet soil and is placed in the weighted lid and placed it in
the drying oven.
11. The dried soil is then weighted and the water content is determined.
12. Step 1-11 is repeated buy using different soil and different amount of water.
Analysis
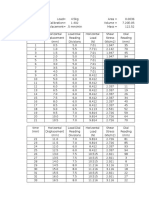
1) Calculate the moisture content of each compacted soil specimen by using the
average of the two water contents.
2) Compute the wet density in grams per cm3 of the compacted soil sample by
dividing the wet mass by the volume of the mould used.
3) Compute the dry density using the wet density and the water content
determined in step 1. By using the following formula:
4) Plot the dry density values on the y-axis and the moisture contents on the x-
axis. Draw a smooth curve connecting the plotted points.
5) On the same graph draw a curve of complete saturation or zero air voids
curve. The values of dry density and corresponding moisture contents for
plotting the curve can be computed from the following equation:
6) Identify and report the optimum moisture content and the maximum dry
density. We have recorded the method of compaction used on data sheet.
Example Calculations
Gs= 2.7(assumed)
w=1.0 g/cm3
Assumed w sat% Calculated Pd (g/cm3)
9 2.17
12 2.04
6 2.32
15 1.92
18 1.82
Discussions
The optimum water content is the water content that results in the greatest density
for a specified compactive effort. Compacting at water contents higher than (wet of )
the optimum water content results in a relatively dispersed soil structure (parallel
particle orientation ns) that is weaker , more ductile, less pervious, softer, more
susceptible to shrinking, and less susceptible to swelling than soil compacted dry of
optimum to the same density. The soil compacted lower than (dry of) the optimum
water content typically results in a flocculated soil structure (random particle
orientations) that has the opposite characteristics of the soil compacted wet of the
optimum water content to the same density.
Reference
http://www.uic.edu/classes/cemm/cemmlab/Experiment%209-Compaction.pdf
Appendix
Вам также может понравиться
- Report Standard Compaction TestДокумент14 страницReport Standard Compaction TestLuqman Yusof100% (1)
- Proctor Compaction TestДокумент5 страницProctor Compaction Testsanduni89% (27)
- Falling Head Permeability Test Lab ReportДокумент7 страницFalling Head Permeability Test Lab ReportHaziq ZuhaimiОценок пока нет
- Falling Head Permeability TestДокумент8 страницFalling Head Permeability Testdwivediashish2100% (2)
- Standard Proctor Compaction TestДокумент3 страницыStandard Proctor Compaction TestSami Sami80% (5)
- Discussin and Conclusion Geotechnical Falling HeadДокумент2 страницыDiscussin and Conclusion Geotechnical Falling HeadAzizi YahyaОценок пока нет
- Sand Replacement MethodДокумент8 страницSand Replacement MethodMudin DinОценок пока нет
- Constant Falling Head Permeability Test Lab ReportДокумент12 страницConstant Falling Head Permeability Test Lab ReportHaziq Zuhaimi100% (3)
- Falling Head Permeability TestДокумент9 страницFalling Head Permeability TestFaeez Zain83% (6)
- Sand ReplacementДокумент4 страницыSand ReplacementHidayah MuzaimilОценок пока нет
- Proctor Standard Soil CompactionДокумент11 страницProctor Standard Soil CompactionAmin Saufi100% (3)
- Civil Engineering Center Consolidation TestДокумент4 страницыCivil Engineering Center Consolidation TestrbhavishОценок пока нет
- Lab Sheet - Atterberg LimitsДокумент6 страницLab Sheet - Atterberg LimitsLuqman YusofОценок пока нет
- Falling Head PermeabilityДокумент13 страницFalling Head PermeabilitySitiОценок пока нет
- 3.0 Determination of Liquid Limit Using The Cone PenetrometerДокумент10 страниц3.0 Determination of Liquid Limit Using The Cone PenetrometerasОценок пока нет
- Liquid Limit, Plastic Limit and Plasticity Index TestingДокумент3 страницыLiquid Limit, Plastic Limit and Plasticity Index TestingShiaz Syed IsmailОценок пока нет
- Sieve analysis soil sample Sonoma ranchДокумент8 страницSieve analysis soil sample Sonoma ranchr6Yamaha100% (5)
- Lab Report-Permeability TestДокумент11 страницLab Report-Permeability TestOchini Chandrasena83% (18)
- Free Swell IndexДокумент3 страницыFree Swell IndexGanesh ÇkmОценок пока нет
- Atterburg Limit TestДокумент16 страницAtterburg Limit TestJanith ChamilkaОценок пока нет
- Speed Spot Study Lab ReportДокумент9 страницSpeed Spot Study Lab ReportXamen50% (4)
- Outflow MeterДокумент5 страницOutflow MeterFirash ImranОценок пока нет
- Determining Soil Permeability Using Falling Head MethodДокумент5 страницDetermining Soil Permeability Using Falling Head MethodSaleem Anas100% (3)
- Constant N Permeability ReportДокумент24 страницыConstant N Permeability Reportilasensei50% (2)
- 17-Stream Water Quality Analysis - F11Документ12 страниц17-Stream Water Quality Analysis - F11Michelle de Jesus100% (1)
- Atterberg Limit Tests for Cohesive SoilДокумент7 страницAtterberg Limit Tests for Cohesive SoilAnip EsanОценок пока нет
- DLSU-CE-Geotech Lab 2 Unconfined Compression Test ReportДокумент5 страницDLSU-CE-Geotech Lab 2 Unconfined Compression Test ReportAbigail Lorico100% (2)
- Aggregate Impact ValueДокумент7 страницAggregate Impact ValueAisyah Ibrahim84% (25)
- Determination of Field Density by Core Cutter MethodДокумент3 страницыDetermination of Field Density by Core Cutter MethodYogendra Patil100% (1)
- Mohammad Yunus Salehi I11007770 Experiment 4: Unconfined Compression TestДокумент6 страницMohammad Yunus Salehi I11007770 Experiment 4: Unconfined Compression TestMohammad Yunus Salehi75% (4)
- Consolidation TestДокумент16 страницConsolidation Test1man1bookОценок пока нет
- UCTДокумент10 страницUCTMohd Syafiq AkmalОценок пока нет
- Constant HEAD ExperimentДокумент7 страницConstant HEAD ExperimentSayed Mahdi Hazheer100% (1)
- Lab 3: Atterberg Limits CE 340Документ8 страницLab 3: Atterberg Limits CE 340satyam agarwal100% (1)
- Sand ReplacementДокумент14 страницSand ReplacementMuniey Aziz75% (8)
- Falling Head Permeability Lab TestДокумент6 страницFalling Head Permeability Lab TestHamierul MohamadОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 (Sandy Lean Clay)Документ17 страницChapter 1 (Sandy Lean Clay)John Raymund TanugaОценок пока нет
- Plastic LimitДокумент9 страницPlastic LimitPoovan Rajaratnam100% (1)
- O.E.Lab - Docx For Direct Shear TestДокумент14 страницO.E.Lab - Docx For Direct Shear TestAmirah SyakiraОценок пока нет
- Unconfined Compression TestДокумент8 страницUnconfined Compression TestMohdIkrami100% (1)
- PenetrationДокумент14 страницPenetrationTarmidzi Mohd Zailani100% (1)
- Compaction ReportДокумент6 страницCompaction ReportharinderОценок пока нет
- Lab 4 - Hydrometer Testnvxjkcvbcxckvbckjvjkvknvck.Документ6 страницLab 4 - Hydrometer Testnvxjkcvbcxckvbckjvjkvknvck.Amirah ShafeeraОценок пока нет
- Civil Engineering Lab Report Softening Point TestДокумент52 страницыCivil Engineering Lab Report Softening Point TestAzllina AnuarОценок пока нет
- Lab Soil-Hydrometer TestДокумент6 страницLab Soil-Hydrometer TestSyed Zulfaizzuan AljufriОценок пока нет
- Proba MackintoshДокумент18 страницProba Mackintoshnazlie170750% (2)
- Determining Permeability of Sands Using Constant Head TestДокумент12 страницDetermining Permeability of Sands Using Constant Head TestArisan Iqma100% (2)
- Discussion UctДокумент2 страницыDiscussion UctMohd YusriОценок пока нет
- Constant Head Permeability TestДокумент6 страницConstant Head Permeability TestSalih MohayaddinОценок пока нет
- Compaction Test PDFДокумент6 страницCompaction Test PDFACTION plusОценок пока нет
- Moisture Content-Unit Weight Relationship (Compaction Test: Soil Mechanics Laboratory Tests Experiment No. 7Документ6 страницMoisture Content-Unit Weight Relationship (Compaction Test: Soil Mechanics Laboratory Tests Experiment No. 7Mohamad DuhokiОценок пока нет
- Compaction LabДокумент10 страницCompaction LabKarl Todd100% (5)
- Lab 1 - CompactionДокумент5 страницLab 1 - CompactionPrantik MaityОценок пока нет
- Compaction Test ReportДокумент5 страницCompaction Test ReportMahmoud Khalifa91% (22)
- تقرير تحديد الكثافة والحدل للتربةДокумент16 страницتقرير تحديد الكثافة والحدل للتربةEng.AhmedShamkhiОценок пока нет
- Exp 6Документ3 страницыExp 6Leah RiveraОценок пока нет
- Soil Compaction LabДокумент12 страницSoil Compaction LabSaif SulemanОценок пока нет
- Standard Proctor Test ResultsДокумент4 страницыStandard Proctor Test Resultsmira asyafОценок пока нет
- Proctor Standard Comp Action TestДокумент9 страницProctor Standard Comp Action TestlipasemasОценок пока нет
- The Chemistry of Soils - Including Information on Acidity, Nitrification, Lime Requirements and Many Other Aspects of Soil ChemistryОт EverandThe Chemistry of Soils - Including Information on Acidity, Nitrification, Lime Requirements and Many Other Aspects of Soil ChemistryРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Weekly ReportДокумент3 страницыWeekly ReportFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Weekly Report: Monday (8/10/19) ActivityДокумент1 страницаWeekly Report: Monday (8/10/19) ActivityFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Weekly Report: Monday (8/10/19) ActivityДокумент1 страницаWeekly Report: Monday (8/10/19) ActivityFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Facility Floor Layout PDFДокумент1 страницаFacility Floor Layout PDFFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- PPorg GenIV WCs ReadmeДокумент1 страницаPPorg GenIV WCs ReadmeFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- JKR Gombak Project Monitoring StatusДокумент1 страницаJKR Gombak Project Monitoring StatusFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Batch 2 (Intake: Feb 2019) : Pusb Graduate TraineeДокумент1 страницаBatch 2 (Intake: Feb 2019) : Pusb Graduate TraineeFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Daily ReportДокумент1 страницаDaily ReportFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Daily ReportДокумент1 страницаDaily ReportFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Result 28hari 406.9Документ1 страницаResult 28hari 406.9Fendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ5 страницChapter 1Fendi RoonОценок пока нет
- 11D Ramirez 02 26 10 PDFДокумент12 страниц11D Ramirez 02 26 10 PDFFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ14 страницChapter 3Fendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Bms 201 Engineering Statistics 201409Документ8 страницBms 201 Engineering Statistics 201409Fendi RoonОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Excel WorksheetДокумент15 страницNew Microsoft Excel WorksheetFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Filter Design CurveДокумент1 страницаFilter Design CurveFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1 Warming UpДокумент13 страницAssignment 1 Warming UpFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Structure Lab-Strut BucklingДокумент7 страницStructure Lab-Strut BucklingFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Badminton PaperДокумент17 страницBadminton PaperFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- MPU 3273/ LANG 2128/ BLC 221: Professional CommunicationДокумент33 страницыMPU 3273/ LANG 2128/ BLC 221: Professional CommunicationFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Measuring BanksДокумент6 страницMeasuring BanksFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- MPU 3273/ LANG 2128/ BLC 221: Professional CommunicationДокумент17 страницMPU 3273/ LANG 2128/ BLC 221: Professional CommunicationFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1 Warming UpДокумент13 страницAssignment 1 Warming UpFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- BBM205 Assignment - Business Plan for EngineersДокумент1 страницаBBM205 Assignment - Business Plan for EngineersFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Print AUTOLine Dealership WordДокумент4 страницыPrint AUTOLine Dealership WordFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Structure Lab-Three Hinge ArcДокумент13 страницStructure Lab-Three Hinge ArcFendi Roon100% (1)
- Print AUTOLine Dealership WordДокумент4 страницыPrint AUTOLine Dealership WordFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Print AUTOLine PresentationДокумент21 страницаPrint AUTOLine PresentationFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- Lab Report TemplateДокумент2 страницыLab Report TemplateFendi RoonОценок пока нет
- (Version 3.0) Effectiveness of Banana (Musa Paradisiaca) Peel As An Alternative Floor WaxДокумент2 страницы(Version 3.0) Effectiveness of Banana (Musa Paradisiaca) Peel As An Alternative Floor WaxAlexis Barquilla0% (1)
- Report Bka PDFДокумент20 страницReport Bka PDFFatin Nadia DieyaОценок пока нет
- Norma Astm d543-95Документ7 страницNorma Astm d543-95Gabriel Aristizabal100% (1)
- Module 1 Ability To Absorb WaterДокумент36 страницModule 1 Ability To Absorb WaterNerissa BaricauaОценок пока нет
- The Chemical Accidents (Emergency Planning, Preparedness and Response) Rules, 1996Документ44 страницыThe Chemical Accidents (Emergency Planning, Preparedness and Response) Rules, 1996erbhaveshparmarОценок пока нет
- 11.2 - Ingliskeelne NimekiriДокумент37 страниц11.2 - Ingliskeelne NimekiriMichael MacDonaldОценок пока нет
- Coo Seg Cat CDC Eqf 0002 0Документ182 страницыCoo Seg Cat CDC Eqf 0002 0Ricardo VerdugoОценок пока нет
- Basement Take-OffДокумент11 страницBasement Take-OffRightie CubeОценок пока нет
- Creep Damage and Expected Creep LifeДокумент9 страницCreep Damage and Expected Creep LifeTrương Ngọc SơnОценок пока нет
- Blasia 32Документ1 страницаBlasia 32Marcelo Ferreira MeloОценок пока нет
- IOGCA 2019 Conference Proceedings PDFДокумент295 страницIOGCA 2019 Conference Proceedings PDFadityamduttaОценок пока нет
- 1-Classification of Monomers and PolyreactionsДокумент19 страниц1-Classification of Monomers and PolyreactionsMohanraj ShanmugamОценок пока нет
- L4047-2016-08 Raspador Martin PDFДокумент16 страницL4047-2016-08 Raspador Martin PDFEduardoОценок пока нет
- Schmidthammer: Elektrokohle GMBHДокумент20 страницSchmidthammer: Elektrokohle GMBHudhayОценок пока нет
- Moehle 1Документ6 страницMoehle 1trabajosicОценок пока нет
- Inspection Procedure Giudelines (Vertical Projects) 08 - 15 - 18Документ51 страницаInspection Procedure Giudelines (Vertical Projects) 08 - 15 - 18Jjammppong AcostaОценок пока нет
- Review Article: Harvesting Ambient Environmental Energy For Wireless Sensor Networks: A SurveyДокумент21 страницаReview Article: Harvesting Ambient Environmental Energy For Wireless Sensor Networks: A Surveymarc estebanОценок пока нет
- Air Conditioner Installation Manual FriedrichДокумент42 страницыAir Conditioner Installation Manual FriedrichDavid GarciaОценок пока нет
- 2010-F3-CHEM Final Exam Paper ReviewДокумент39 страниц2010-F3-CHEM Final Exam Paper Review2E (04) Ho Hong Tat AdamОценок пока нет
- SPE 121182 Selective Water Shutoff in Gas Well Turns A Liability Into An Asset: A Successful Case History From East Kalimantan, IndonesiaДокумент7 страницSPE 121182 Selective Water Shutoff in Gas Well Turns A Liability Into An Asset: A Successful Case History From East Kalimantan, Indonesiahade wantoОценок пока нет
- Preformulation drug optimizationДокумент49 страницPreformulation drug optimizationShaimaa AlsamarraiОценок пока нет
- Thermal Science and Engineering ProgressДокумент10 страницThermal Science and Engineering ProgressAmirОценок пока нет
- Wrought Nickel-Iron Soft Magnetic Alloys (UNS K94490, K94840, N14076, N14080)Документ6 страницWrought Nickel-Iron Soft Magnetic Alloys (UNS K94490, K94840, N14076, N14080)Tomy lee youngОценок пока нет
- Install HDPE Pipelines Safely and EffectivelyДокумент20 страницInstall HDPE Pipelines Safely and EffectivelyAvaan IvaanОценок пока нет
- Thilaga Sonu. SureshДокумент16 страницThilaga Sonu. SureshMageshwarОценок пока нет
- Irrigation Canal Estimation Munji ExampleДокумент31 страницаIrrigation Canal Estimation Munji ExampleAbdul Manan AsadzaiОценок пока нет
- PART-6 Road Construction MethodsДокумент5 страницPART-6 Road Construction MethodsNasibullahОценок пока нет
- Analysis and Experimental Test of Electrical Characteristics On Bonding WireДокумент21 страницаAnalysis and Experimental Test of Electrical Characteristics On Bonding WireCristian RoblesОценок пока нет
- VTU SyllabusДокумент164 страницыVTU SyllabusChethan KSОценок пока нет
- 2505-013 014 015 0803Документ2 страницы2505-013 014 015 0803Sri PupОценок пока нет