Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Total Knee Replacement Brochure PDF
Загружено:
api-260874114Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Total Knee Replacement Brochure PDF
Загружено:
api-260874114Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Total Knee Replacement
http://www.medicinenet.com/total_k
nee_replacement/article.htm
Total Knee Replacement OrthoInfo
http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?t
opic=a00389
An Inside Look
The purpose of this brochure is to
help you become more familiar with
the anatomy of the knee as well as
understand the reasons to have, the
procedure of, and the expectancies
after total knee replacement surgery.
The anatomy of the knee will be
explained briefly, which will lead to a
brief explanation of what total knee
replacement surgery is. A brief list of
reasons to have total knee
replacement surgery will be provided.
Afterwards, the procedure of the
surgery will be described in which
there will be an explanation of what
to expect after surgery is performed.
For more information
about total knee
replacements, please
review the links provided
below.
TOTAL
KNEE
REPLACEMENT
The Process, Reasons for Having It, &
Expectations After Surgery
You are either given general anesthesia (you are put to sleep) or a
regional nerve block anesthesia (you are awake, but numb from
the waist down), and the procedure lasts between 1 to 2 hours. You
will most likely be admitted to the hospital on the day of your
surgery and be hospitalized for several days.
Surgical Procedure:
1. The bone is prepared in which the damaged cartilage
surfaces are removed along with a slim amount of
underlying bone.
2. Metal components are positioned and fitted perfectly to
the shaven surfaces of the bone.
3. Depending on the severity of the damage, the
undersurface of the patella, or kneecap, is also shaved
and resurfaced with a metal component.
4. A plastic spacer is inserted between the metal
components to provide a smooth gliding surface.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kAMuP2MNqUo#t=12
What is to be expected after the surgery?
It is perfectly normal for your knee to not have the same exact
range of motion after surgery; however, it should not prohibit you
from performing daily activities, such as walking, running,
swimming, etc. Swelling and tenderness will also be expected post
(after) surgery.. You will be required to go to physical therapy,
which will assist you in earning back functional range of motion to
return to daily activities.
Reasons for Having Total Knee Replacement
Surgery
There are various reasons for proceeding with total knee replacement
surgery; however, the most common reason is arthritis, which is the
inflammation of a joint-in this case, the knee. There are three types of
arthritis:
Osteoarthritis: Age related, typically found in individuals
50 years and older; when the cartilage (flexible connective
tissue located between the bones) wears away that causes
the bones to rub against one another resulting in pain and
stiffness.
Rheumatoid arthritis: A disease in which the synovial
membrane surrounding the joint becomes inflamed and
thickened; the inflammation may damage the cartilage
resulting in cartilage loss, pain, and stiffness.
Post-traumatic arthritis: A form of arthritis developed
from a serious knee injury, which may involve the tears of
ligaments or fractures of the bone surrounding the joint.
Surgery is recommended when:
- Pain and stiffness of the knee joint interferes with daily
activities
- Moderate or severe pain persists while resting
- Inflammation does not improve with rest or medication
- Knee deformity severe bow-leg or knock-knee condition
Total Knee Replacement Surgery
What is total knee replacement surgery?
Total knee replacement surgery is a surgical procedure in which a
diseased or worn down knee joint is replaced with artificial material.
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
Anatomy of the Knee, TKR Procedure, & Expectations Post-Surgery
Anatomy of the Knee
Total Knee Replacement Procedure
Anatomy of the Knee
The knee joint is a hinge joint made up of the distal portion (lower end) of
the femur (thigh bone), the proximal portion (upper end) of tibia (shin bone)
and the patella (kneecap). The sections of the bones that rest on each other
are protected with articular cartilage, or a smooth surface in which
movement is enabled. Shock absorbers formally known as the menisci,
are C-shaped wedges located between the femur and tibia. Four liaments
(snterior cruciate, posterior cruciate, medial collateral, and lateral collateral)
assist in holding the femur and tibia in place as well as provide stability .
The remaining surfaces are encased by a thin lining known as a synovial
membrane, which release a fluid that lubricates the cartilage.
Вам также может понравиться
- Osteoarthritis AapmrДокумент5 страницOsteoarthritis AapmrBiandaОценок пока нет
- Emailing Patologi Anatomi GANGGUAN HEMODINAMIK Trombosis DAN SHOCK - Output PDFДокумент38 страницEmailing Patologi Anatomi GANGGUAN HEMODINAMIK Trombosis DAN SHOCK - Output PDFHaykal FathirrahmanОценок пока нет
- BONESДокумент73 страницыBONESsafa_sabaОценок пока нет
- Nur Rachmat Lubis: Divisi Orthopaedi Dept Bedah FK UNSRI/ RS Dr. M. Hoesin PalembangДокумент38 страницNur Rachmat Lubis: Divisi Orthopaedi Dept Bedah FK UNSRI/ RS Dr. M. Hoesin Palembangsoleha09la solehaОценок пока нет
- Lateral Ankel InstabilityДокумент16 страницLateral Ankel InstabilityAleCsss123Оценок пока нет
- Torticollis III BPTДокумент31 страницаTorticollis III BPTKASTURI COLLEGEОценок пока нет
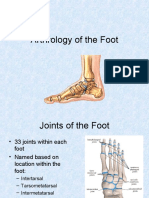
- The ligaments named are:C) Medial collateral ligament D) Lateral collateral ligamentG) Plantar metatarsophalangeal ligamentThe joint named is the first metatarsophalangeal jointДокумент55 страницThe ligaments named are:C) Medial collateral ligament D) Lateral collateral ligamentG) Plantar metatarsophalangeal ligamentThe joint named is the first metatarsophalangeal jointolle3870Оценок пока нет
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer Assessment ToolsДокумент16 страницDiabetic Foot Ulcer Assessment ToolsShity Shita ShituОценок пока нет
- Normal Human LocomotionДокумент16 страницNormal Human LocomotionWendy NgОценок пока нет
- Dr. Arnadi Fraktur & DislokasiДокумент77 страницDr. Arnadi Fraktur & DislokasiPuji Yunisyah RahayuОценок пока нет
- Bone HealingДокумент7 страницBone HealingArfan PrawiragaraОценок пока нет
- Guidelines - Pengkajian Sistem MusculoskeletalДокумент7 страницGuidelines - Pengkajian Sistem MusculoskeletalJoy Harrys PriikitiewwОценок пока нет
- Physical Examination of The SpineДокумент33 страницыPhysical Examination of The SpineyudiОценок пока нет
- Principles of Malunion ManagementДокумент51 страницаPrinciples of Malunion Managementdioz100% (1)
- ArthritisДокумент8 страницArthritissdorji72Оценок пока нет
- Muscles ShoulderДокумент3 страницыMuscles ShoulderGreys SalacupОценок пока нет
- Sistem Otot Muskular 2 (Muscular System)Документ38 страницSistem Otot Muskular 2 (Muscular System)PaRaDoX eLaKSaMaNaОценок пока нет
- Painful Hemiplegic ShoulderДокумент53 страницыPainful Hemiplegic ShoulderpipitОценок пока нет
- Jakarta School of Prosthetics & Orthotics: Upper Limb Prosthetics Course Work Manual 2010Документ84 страницыJakarta School of Prosthetics & Orthotics: Upper Limb Prosthetics Course Work Manual 2010Adinda Dinda100% (1)
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris (Jantung)Документ12 страницMakalah Bahasa Inggris (Jantung)Nia Mldyni100% (1)
- Terapi Latihan Pada Keadaan Immobilisasi Yang Lama (Prolonged Bedrest) "Документ12 страницTerapi Latihan Pada Keadaan Immobilisasi Yang Lama (Prolonged Bedrest) "Tiwi Nur PratiwiОценок пока нет
- Patologi Tulang Dan SendiДокумент79 страницPatologi Tulang Dan SendiDio Reynaldi SusantoОценок пока нет
- Kinesiology ElbowДокумент53 страницыKinesiology Elbowsingle_ladyОценок пока нет
- Precautions Following Hemiarthoplasty PDFДокумент8 страницPrecautions Following Hemiarthoplasty PDFdrprashantmb1012Оценок пока нет
- PCL's Avulsion FractureДокумент22 страницыPCL's Avulsion FractureNey da OnneyОценок пока нет
- 11.sitoskeleton Dan Pergerakan Sel-Dr - IsraДокумент40 страниц11.sitoskeleton Dan Pergerakan Sel-Dr - IsraTa RaОценок пока нет
- Alians Proximal Humerus: Innovation Means MotionДокумент8 страницAlians Proximal Humerus: Innovation Means MotionDaniel G. A. C.Оценок пока нет
- Healing of Bone and Cartilage FracturesДокумент36 страницHealing of Bone and Cartilage Fracturescatharinam100% (1)
- Rotator Cuff SyndromeДокумент14 страницRotator Cuff SyndromeRatu Suci Angraini HasibuanОценок пока нет
- Rehabilitation of LeprosyДокумент72 страницыRehabilitation of LeprosyNur OctavianiОценок пока нет
- Hip Replacement GuideДокумент28 страницHip Replacement GuideZulaika NaisОценок пока нет
- Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) Stretching Techniques Hold-Relax HR ALLДокумент8 страницProprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) Stretching Techniques Hold-Relax HR ALLKiné Therapeut-manuelle Masseur GabiОценок пока нет
- Perioperative Management 1203114432600412 4Документ53 страницыPerioperative Management 1203114432600412 4polushkyОценок пока нет
- Alat Untuk Mengukur Kedalaman AnestesiДокумент3 страницыAlat Untuk Mengukur Kedalaman AnestesiditaОценок пока нет
- CS-Abdominal and Extremity Compartment SyndromeДокумент17 страницCS-Abdominal and Extremity Compartment SyndromeBudiono Gunawan SutantoОценок пока нет
- Biodata Parestesi Juli 2011 Edit IpoДокумент56 страницBiodata Parestesi Juli 2011 Edit Iporahmat feryadiОценок пока нет
- Short Wave Diathermy Is Defined As The Clinical Application of High Frequency Alternating Current, at A Frequency of 27.12Mhz and Wavelength of 11.06 MeterДокумент1 страницаShort Wave Diathermy Is Defined As The Clinical Application of High Frequency Alternating Current, at A Frequency of 27.12Mhz and Wavelength of 11.06 MeterMohd AsadОценок пока нет
- Scapular Winging PDFДокумент11 страницScapular Winging PDFzwecker4458Оценок пока нет
- Teknik Anamnesis & Pemeriksaan Fisik Umum (Dr. Rini Bachtiar, SP - PD)Документ79 страницTeknik Anamnesis & Pemeriksaan Fisik Umum (Dr. Rini Bachtiar, SP - PD)nurfatrianiОценок пока нет
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Fraktur: Oleh Johansen HutajuluДокумент51 страницаAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Fraktur: Oleh Johansen HutajuluLaris ManikОценок пока нет
- Lect 8 Lower Extremity Fracture 2Документ22 страницыLect 8 Lower Extremity Fracture 220-221 Crisny Novika Yely Br. HutagaolОценок пока нет
- GAIT EXAMINATIONДокумент32 страницыGAIT EXAMINATIONAsry WahidОценок пока нет
- Fraktur VertebraeДокумент41 страницаFraktur VertebraeTomy WiknaОценок пока нет
- Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisДокумент15 страницAmyotrophic Lateral SclerosisYakan AbdulrahmanОценок пока нет
- Bio Mechanics and Pathomechanics of Ankle JointДокумент35 страницBio Mechanics and Pathomechanics of Ankle Joint56 Vignesh j 079Оценок пока нет
- Farmakologi Penyakit-Penyakit Degenerasi Tulang Dan SendiДокумент19 страницFarmakologi Penyakit-Penyakit Degenerasi Tulang Dan SendiCici MastaОценок пока нет
- Otot-Otot Hip: Sari Tri Yulianti, S.FT., M.BiomedДокумент39 страницOtot-Otot Hip: Sari Tri Yulianti, S.FT., M.Biomedkim mingyuОценок пока нет
- Unit 1: Introduction To Kinesiology and Sports BiomechanicsДокумент70 страницUnit 1: Introduction To Kinesiology and Sports BiomechanicsGOLDEN FIZZIK GYM100% (1)
- Tinpus HNPДокумент34 страницыTinpus HNPDimas JanuarОценок пока нет
- Exercise 2 Activity 3 Muscle SummationДокумент13 страницExercise 2 Activity 3 Muscle SummationElvira BasilioОценок пока нет
- Lecture 11aДокумент40 страницLecture 11aElliya Rosyida67% (3)
- CTEV TreatmentДокумент22 страницыCTEV TreatmentDavin Silalahi100% (1)
- Tuberculosis of Knee: Presented By: DR Dipendra Maharjan 2 Yr Resident, MS Orthopaedics NAMS, Bir HospitalДокумент25 страницTuberculosis of Knee: Presented By: DR Dipendra Maharjan 2 Yr Resident, MS Orthopaedics NAMS, Bir HospitalshravaniОценок пока нет
- Achilles TendonДокумент30 страницAchilles TendonMeldianaОценок пока нет
- Preventable Death: Dco: DR Thit Lwin School of Medicine UMSДокумент56 страницPreventable Death: Dco: DR Thit Lwin School of Medicine UMSStar CruiseОценок пока нет
- Knee Replacement / Arthroplasty: Current PositionДокумент20 страницKnee Replacement / Arthroplasty: Current PositionFerdiriva HamzahОценок пока нет
- Total Knee ReplacementДокумент14 страницTotal Knee ReplacementJuanRuizОценок пока нет
- Understanding ACL Injuries and SurgeryДокумент38 страницUnderstanding ACL Injuries and SurgerySzilvia MartonosОценок пока нет
- Knee Replacement Surgery: Everything You May Like To Know AboutДокумент16 страницKnee Replacement Surgery: Everything You May Like To Know AboutansfaridОценок пока нет
- Knee Joint ThesisДокумент5 страницKnee Joint Thesisamywashingtonpittsburgh100% (2)
- A Tertiary Health Care Centre Experience of The Impact of COVID On The Case Load in The Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology at MGM Hospital, AurangabadДокумент4 страницыA Tertiary Health Care Centre Experience of The Impact of COVID On The Case Load in The Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology at MGM Hospital, AurangabadInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Ncp-Ineffective Breathing PatternДокумент4 страницыNcp-Ineffective Breathing PatternRoxanne Ganayo Claver100% (1)
- EMT Training at Mansion Mandiri HotelДокумент4 страницыEMT Training at Mansion Mandiri Hotelyuna triazОценок пока нет
- Eclampsia Guidelines FINAL Ratified MCYP SG Sept20 15Документ20 страницEclampsia Guidelines FINAL Ratified MCYP SG Sept20 15Grigore PopaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Epidemiology of Infection Diseases PDFДокумент17 страницIntroduction To Epidemiology of Infection Diseases PDFRovaidKhanОценок пока нет
- Typhoid Management Guideline 2022-Jun-22 - 221107 - 103145Документ15 страницTyphoid Management Guideline 2022-Jun-22 - 221107 - 103145Shanza AmaanОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Acidosis: Prepared By: Riezel Umaming Kathleen Testado Hazel AlarillaДокумент16 страницRespiratory Acidosis: Prepared By: Riezel Umaming Kathleen Testado Hazel AlarillaDareRaymond100% (2)
- Fever and Rash: Dr. Karwan Hawez Sulaiman MBCHB, Ficms, FM Family Medicine Specialist College of MedicineДокумент20 страницFever and Rash: Dr. Karwan Hawez Sulaiman MBCHB, Ficms, FM Family Medicine Specialist College of MedicinesamiОценок пока нет
- HYDRONEPHROSISДокумент43 страницыHYDRONEPHROSISEureka RathinamОценок пока нет
- Rubrics Normal DeliveryДокумент3 страницыRubrics Normal DeliveryKYLE MITZIE SENGCOОценок пока нет
- Slavin 1996Документ6 страницSlavin 1996jahdsdjad asffdhsajhajdkОценок пока нет
- Hepato-Biliary System 26.4.2016Документ59 страницHepato-Biliary System 26.4.2016S B SayedОценок пока нет
- Primary Chest Wall Hydatid Cyst - A Rare Case Report: - PresenterДокумент8 страницPrimary Chest Wall Hydatid Cyst - A Rare Case Report: - PresenterEdison Varghese VadakkencheryОценок пока нет
- Staph Lecture MicrococcusДокумент30 страницStaph Lecture Micrococcussophia salibaОценок пока нет
- Presented by DR Rahul D AgrawalДокумент64 страницыPresented by DR Rahul D AgrawalRahul AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Hip Resurfacing Expectations and LimitationsДокумент4 страницыHip Resurfacing Expectations and LimitationsCristian BenayОценок пока нет
- Gram Positive CocciДокумент11 страницGram Positive CocciUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Congenital Anatomic AnomaliesДокумент12 страницCongenital Anatomic Anomaliesmahparah_mumtazОценок пока нет
- Attesta™ DR Mri Surescan™ Atdr01: Dual Chamber Rate Responsive Pacemaker (DDDR)Документ42 страницыAttesta™ DR Mri Surescan™ Atdr01: Dual Chamber Rate Responsive Pacemaker (DDDR)mytake100Оценок пока нет
- Minimally Invasive Spine SurgeryДокумент510 страницMinimally Invasive Spine SurgeryLuis RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Upper Extremity Venous Doppler Ultrasound PDFДокумент12 страницUpper Extremity Venous Doppler Ultrasound PDFLayla Salomão0% (1)
- Hematologic Reference Ranges: MSD Manual Veterinary ManualДокумент3 страницыHematologic Reference Ranges: MSD Manual Veterinary ManualShiva KarthikОценок пока нет
- FNDRC Vol 2 AppendicesДокумент43 страницыFNDRC Vol 2 AppendicesJohn Michael Macabenta100% (1)
- Treatment of Endometriosis in Women Desiring FertilityДокумент23 страницыTreatment of Endometriosis in Women Desiring FertilityVaisnavi Muthoovaloo67% (3)
- 2015parathyroid Carcinoma Challenges in Diagnosis and TreatmentДокумент9 страниц2015parathyroid Carcinoma Challenges in Diagnosis and TreatmentCharley WangОценок пока нет
- Winkler - Chapter 8. Khalid AlshareefДокумент4 страницыWinkler - Chapter 8. Khalid AlshareefKhalid Bin FaisalОценок пока нет
- Voice and Speech DisordersДокумент2 страницыVoice and Speech DisordersVishal Gaurav100% (1)
- Anomalies of ConvergenceДокумент12 страницAnomalies of ConvergenceDaniDenzongpaSulaemanОценок пока нет
- Dialysis Inspection Tool 2014Документ11 страницDialysis Inspection Tool 2014Maek100% (1)
- Rearrange The Jumble Letters: 10 1 10Документ4 страницыRearrange The Jumble Letters: 10 1 10Shafee ArafatОценок пока нет