Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,497,097 B2
Загружено:
Kasra Golban0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
83 просмотров9 страницPaper
Оригинальное название
Us 7497097
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документPaper
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
83 просмотров9 страницUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,497,097 B2
Загружено:
Kasra GolbanPaper
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 9
US007497097B2
( 1 2) United States Patent ( 1 0) Patent N o . : US 7, 497, 097 B2
Herr ( 45 ) Date o f Patent: Mar. 3 , 2009
( 5 4) SWEAT BLOCKIN G AN D VEN TILATIN G 6, 779, 3 69 B2 * 8/2004 Shepherd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66/1 96
SWEATBAN D FOR HEADWEAR 6, 893 , 695 B2 * 5 /2005 Baychar . . 428/3 61
7, 043 , 767 B2 * 5 /2006 Jaeger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2/87
( 75 ) Inv ento r: Paul Hen. 1 4 E_ Genev a Cir Madiso n, 7, 276, 275 B2 * 1 0/2007 Schindz ielo rz et a1 . . . . . . . . . 428/86
WI ( Us) 5 3 71 7 7, 3 1 4, 840 B2 * 1 /2008 Baychar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 442/3 70
FOREIGN PATEN T DOCUMEN TS
( 73 ) Assignee: Paul Herr, Madiso n, WI ( U S)
EP 0988804 A2 3 /2000
( * ) N o tice: Sub j ect to any disclaim er, the term o f this GB 23 41 784 A 3 /2000
patent is ex tended o r adj usted under 3 5 * Cited b y ex am iner
U. S. C. 1 5 4( b ) b y 5 69 days.
Prim ary Ex am ineriDanny Wo rrell
( 21 ) App1 _ N O; 1 1 /1 47, 297 ( 74) Atto rney, Agent, o r Firm 4Galv in & Palm er; Sheldo n
Palm er
( 22) Filed: Jun. 8, 2005
( 5 7) ABSTRACT
( 65 ) Prio r Pub licatio n Data _ _ _
A spacer- f ab r1 c sWeatb and, f o r, and inco rpo rated into head
US 2006/027795 1 A1 1 3 3 6- 1 4, 2006 Wear Which has an inner, sk in- co ntact f ab ric layer, and an
o uter, headWear- f acing f ab ric layer co nnected b y a m ultiplic
( 5 1 ) Int- Cl- ity o f hydro pho b ic m o no ? lam ent- pile spacing elem ents. The
D04B 1 /24 ( 2006- 01 ) pile spacing elem ents f unctio n lik e tho usands o f m iniature
US. Cl- . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Springs to m aintain the f ab ric layers in Spaced par
( 5 8) Field o f Classi? catio n Search . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66/ 1 69 R, allel relatio n While creating sub stantial, pile- suppo rted air
66/1 70, 1 71 , 1 72 R, 1 95 , 1 96; 2/1 81 , 1 82. 1 , space b etw een the f ab ric layers to f acilitate the m o v em ent o f
2/1 82. 3 , 1 82. 8 v entilating air? o W. The headWear- f acing f ab ric layer is m esh
See applicatio n ? le f o r co m plete search histo ry. lik e f o r enhanced air circulatio n. The sk in- co ntact layer is
( 5 6) Ref erences Cited co m po sed o f so lid sk in- f riendly f ab ric.
U. S. PATEN T DOCUMEN TS
4, 024, 5 86 A * 5 /1 977 Lam b . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2/41 4
4, 274, 1 5 7 A 6/1 981 Bo den
4, 292, 689 A 1 0/1 981 To w nsend, Jr.
5 , 1 01 , 5 1 6 A 4/1 992 Scarnato
5 , 1 5 7, 788 A 1 0/1 992 Schultz
5 , 625 , 901 A 5 /1 997 Healy
5 , 63 0, 23 0 A 5 /1 997 Fuj ino et a1 .
5 , 887, 276 A 3 /1 999 Lee
6, 1 3 8, 280 A 1 0/2000 Bae
The pile segm ents b lo ck sWeat f ro m m igrating f ro m the inner
to the o uter f ab ric layers b y v irtue o f their hydro pho b ic co m
po sitio n. This sWeat- b lo ck ing f unctio n m inim iz es the o ccur
rence o f sWeat stains o n the b o dy o f the headWear and co n
centrates sWeat Within the sk in- co ntact f ab ric layer, f ro m
Which it is sub seq uently sub j ect to ev apo ratio n and co nco m i
tant co o ling b y air ? o Wing thro ugh the pile- suppo rted air
space.
1 8 Claim s, 3 Draw ing Sheets
US. Patent Mar. 3 2009 Sheet 1 o f 3
US. Patent Mar. 3 , 2009 Sheet 2 o f 3 US 7, 497, 097 B2
US. Patent Mar. 3 , 2009 Sheet 3 o f 3 US 7, 497, 097 B2
US 7, 497, 097 B2
1
SWEAT BLOCKIN G AN D VEN TILATIN G
SWEATBAN D FOR HEADWEAR
CROSS- REFEREN CE TO RELATED
APPLICATION S
N o ne
BACKGROUN D OF THE IN VEN TION
1 . Field o f the Inv entio n
The present inv entio n relates to inside hat b ands Which are
so m etim es also ref erred to as sWeatb ands, and m o re particu
larly to a hat b and that pro v ides co m f o rt, v entilatio n, co o ling
and sWeat- stain- b lo ck ing f unctio ns.
2. Descriptio n o f the Related Art
HeadWear is o f ten Wo rn in Warm co nditio ns in o rder to
pro tect the head f ro m sunlight and/o r physical inj ury ( f o r
ex am ple, cycle, spo rt, em ergency perso nnel, co nstructio n and
m ilitary helm ets) , o r sim ply f o r esthetic reaso ns. The head is
also o ne o f the hum an b o dys prim ary heat radiato rs, o r heat
lo ss sites. Thus, placing headWear o v er the head in a Warm
env iro nm ent q uick ly leads to o v erheating and pro f use sWeat
ing. In co nv entio nal headWear, sWeat is ab so rb ed b y the
sWeatb and- po rtio n o f the headWear and o f ten m igrates b y
capillary actio n f ro m the sWeatb and into the b o dy o f the
headWear itself , pro ducing unsightly ex terio r sWeat stains
that are dif ? cult o r im po ssib le to rem o v e. Many o f these
sWeat- stained hats and caps are either discarded o r linger
unWo m in clo sets. The sk in- co ntact po rtio n o f the headb and
also creates an unco m f o rtab le ho t- spo t o n the users head.
As is Well k no w n to tho se sk illed in the art, a sWeatb and f o r
headWear is a b and lining the inside edge o f a hat o r cap to
pro tect it against the sWeat f ro m the Wearers head and pro
v ide a co m f o rtab le ? t f o r the Wearer.
There are disclo sed in the prio r art v ario us m eans f o r pro
v iding a v entilating space to separate the sk in- co ntact surf ace
o f the sWeatb and f ro m the m ain b o dy o f the headWear b y
using spacing elem ents, and thereb y pro v ide a v entilating and
co o ling ef f ect to the Wearer. N o ne o f these v entilating sWeat
b and designs also sim ultaneo usly b lo ck sWeat- stains. The
sWeatb and designs pro po sed in the prio r art hav e b een either
co stly o r inco nv enient to m ak e, im practical to use, unco m
f o rtab le, no n- esthetic, o r dif ? cult to inco rpo rate into ex isting
headWear designs. U. S. Pat. N o . 5 , 1 5 7, 788 disclo ses a v enti
lating spacing elem ent f o rm ed o f m o lded plastic. A sWeat
b and design co ntaining a plastic insert such as this Wo uld
lik ely b e unco m f o rtab le to Wear and di? icult to inco rpo rate
into ex isting headWear b ecause o f the di? iculty o f co nf o rm
ing sem i- rigid plastic to the co m plex shapes o f headWear.
U. S. Pat. N o . 5 , 1 01 , 5 1 6 describ es spacing elem ents co m
po sed o f ab so rb ent spo nge b alls. Multi- elem ent designs o f
this so rt are co stly and inco nv enient to m anuf acture. Using
spo nge, o r o ther hydro philic m aterials, as spacing elem ents
Wo uld no t pro v ide a sWeat- stain- b lo ck ing f unctio n. Rather,
the spo nge o r o ther hydro philic m aterial Wo uld ab so rb and
transm it the m o isture. U. S. Pat. N o . 4, 274, 1 5 7 describ es
spacing elem ents co m po sed o f tub es o f ? ex ib le m aterial.
Designs such as this, With o nly a sm all num b er o f spacing
elem ents, Wo uld b e unco m f o rtab le to Wear b ecause o f pres
sure- po ints at the lo catio ns o f the spacing- elem ent attach
m ent and Wo uld no t pro v ide co nsistent spacing o f the sWeat
b and f ro m the headWear b ecause o f the lim ited num b er o f
pro po sed spacing elem ents. U. S. Pat. N o . 5 , 625 , 901
describ es spacing elem ents f o rm ed o f a plurality o f ? ex ib le
? ngers co m po sed o f inj ectio n- m o lded therm o plastic m ate
rial. Designs such as this, Where stif f , plastic, spacing- ele
20
25
3 0
3 5
40
45
5 0
5 5
60
65
2
m ents co m e in direct co ntact With the users head create
unco m f o rtab le pressure po ints and leav e indentatio ns in the
sk in surf ace if Wo rn f o r any signi? cant perio d o f tim e. U. S.
Pat. N o . 4, 292, 689 describ es a spacing elem ent co m po sed o f
a sinuso idal f o am b and. This type o f design, Where f o am
spacing elem ents co m e in direct sk in co ntact, create pressure
po ints and unco m f o rtab le ho t- spo ts at the po ints o f sk in co n
tact.
Fab ric- type spacing elem ents hav e also b een pro po sed.
U. S. Pat. N o s. 5 , 63 0, 23 0 and 5 , 887, 276 describ e spacing
elem ents co nsisting o f hydro philic, no n Wo v en, Water- ab so r
b ent pads. These pads are designed to b e hydrated b ef o re use
b y plunging the headWear into a b ath o f Water. Designs that
need to b e hydrated b ef o re use are no t a practical so lutio n f o r
m any headWear applicatio ns. Designs With hydro philic pads
Wo uld ab so rb and transm it sWeat and theref o re Wo uld no t
pro v ide a sWeat- b lo ck ing f unctio n.
There are relativ ely f eW disclo sures in the prio r art o f
designs that pro v ide sWeat- stain- b lo ck ing f unctio ns. U. S.
Pat. N o . 6, 1 3 8, 280 describ es a lam inated sWeatb and structure
co m po sed o f b o th sWeat ab so rb ing and sWeat b lo ck ing no n
Wo v en f ab ric layers. The no n- ab so rb ent, sWeat- b lo ck ing
layer is a no n- Wo v en f ab ric strip co ated With a hydro pho b ic
synthetic resin. The no n- ab so rb ent layer is intended to k eep
sWeat f ro m reaching and Wetting the cro Wn o f the hat o r cap.
This sWeatb and design is describ ed as ab le to ef f ect b lo ck ing
o f Wetting, b ut do es no t purpo rt to sim ultaneo usly pro v ide
v entilatio n o r co o ling.
Additio nal relev ant prio r art includes U. S. Pat. N o . 6, 75 5 ,
05 2, Which disclo ses a k nitted stretch spacer m aterial and
m etho d o f m ak ing it; U. S. Pat. N o . 6, 644, 070 Which disclo ses
a three- dim ensio nal f ab ric f o r a seat; U. S. Pat. N o . 5 , 896, 75 8
Which disclo ses a three- dim ensio nal k nit spacer f ab ric f o r
f o o tWear and b ack pack s; U. S. Pat. N o . 5 , 81 7, 3 91 Which dis
clo ses a three- dim ensio nal k nit spacer f ab ric f o r b ed pads;
U. S. Pat. N o . 5 , 746, 01 3 Which disclo ses a sho e hav ing an
air- co o led b reathab le sho e liner; and U. S. Pat. N o . 6, 1 05 , 401
Which disclo ses a k nitted tex tile structure With do ub le sk in
and adj ustab le b inding threads. Finally, there is a co m m er
cially av ailab le dev ice describ ed in UK Patent 2, 3 41 , 784;
U. S. Pat. N o . 6, 1 99, 21 4 and Euro pean Patent Applicatio n 99
3 07 488. 9. This dev ice is intended to b e added to caps to
im pro v e their v entilating and sWeat b lo ck ing f unctio ns.
BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE IN VEN TION
Spacer f ab rics hav e b een inco rpo rated into in a v ariety o f
co nsum er pro ducts in recent years in applicatio ns Where co m
f o rt and heat and m o isture- elim inatio n are desirab le. Spacer
f ab rics can b e f o und in pro ducts such as sho es, f o undatio n
garm ents, o ther articles o f Wearing apparel, b ack pack s,
glo v es, m edical suppo rts and Wraps, athletic Wraps and
b races, etc. , Wo rn o n the b o dy.
The present inv entio n inco rpo rates a spacer f ab ric into
articles o f headWear, said spacer f ab ric f unctio ning as a
sWeatb and. The spacer f ab ric used in this inv entio n is so
co n? gured as to m inim iz e headWear sWeat- staining While
sim ultaneo usly enhancing v entilatio n, ev apo rativ e co o ling
and co m f o rt. These pro perties o r f unctio ns, especially When
co nsidered in co nnectio n With spo rt o r ex ercise apparel are
so m etim es ref erred to b y the term m o isture m anagem ent.
In o rder to ef f ectuate the o b j ects o f this inv entio n, it sho uld
b e no ted that o nly a specialiZ ed sub set o f spacer f ab rics po s
sess the physical pro perties needed to sim ultaneo usly pro v ide
co m f o rt, ? ex ib ility, m o isture- b lo ck ing, and v entilatio n. An
aspect o f the inv entio n is theref o re the caref ul selectio n o f pile
yarn co m po sitio n ( it m ust b e hydro pho b ic) , pile yarn type
US 7, 497, 097 B2
3
( m o no ? lam ent) , pile thick ness ( 3 - 1 2 m m ) , aperture diam eter
( 1 - 1 2 m m ) and aggregate aperture area as great as is practi
cab le f o r the headWear f acing o uter f ab ric layer, b ut pref er
ab ly greater than 5 0%. A seco nd aspect o f the inv entio n is the
m o de o f attachm ent. If the sWeatb and is irrev ersib ly co m
pressed b y the attachm ent pro cess, f o r ex am ple b y stitching it
into the headWear using standard seWing eq uipm ent, its m o is
ture- b lo ck ing pro perty Will b e def eated. It is theref o re im po r
tant that the spacer f ab ric sWeatb and b e attached in an unco m
pressed state, f o r ex am ple, b y gluing it into the headWear
using either a dry o r Wet adhesiv e, and in the f o rm er case, b y
inserting a dry adhesiv e strip b etWeen the headWear and the
sWeatb and, and then heating to the po int o f m elting the adhe
siv e. Attaching the spacer f ab ric in the unco m pressed state
also m ax im iz es v entilatio n and ev apo rativ e- co o ling pro per
ties o f the m aterial b y m aintaining o pen ro utes o f ingress and
egress f o r air? o W. A third aspect o f the inv entio n, pref erab le
b ut no t necessary, is the inclusio n, in so m e applicatio ns such
as b aseb all caps, o f caref ully placed v ents in the cro Wn o f the
hat that co rrespo nd to the lo catio n o f the spacer f ab ric sWeat
b and. Such v ents Wo rk synergistically With the apertures in
the headWear- f acing surf ace o f the spacer- f ab ric sWeatb and
to direct air? o W to the sk in- co ntact o r inner surf ace o f the
spacer f ab ric sWeatb and Where ev apo rativ e co o ling o ccurs.
The spacing elem ents acco rding to the present inv entio n,
unlik e tho se in the prio r art, co m prise tho usands o f thin,
? ex ib le, hydro pho b ic, m o no ? lam ent pile ? b ers arrayed at
precise interv als inside a specially- designed spacer f ab ric.
The pile spacing elem ents are an integral part o f spacer f ab
rics and are inco rpo rated into them during the k nitting pro
cess b y Which they are m ade. The m o no ? lam ent pile spacing
elem ents f unctio n to m aintain a precise degree o f separatio n
b etWeen the tWo layers f o rm ing the spacer f ab ric, i. e. , an
inner, o r sk in f acing layer and an o uter, o r headWear f acing
layer, thereb y creating a pile- suppo rted airspace that b o th
b lo ck s sWeat m igratio n and pro v ides a m ax im um o f v entilat
ing airspace. The thin, ? ex ib le and spring- lik e nature o f the
m o no ? lam ent spacing elem ents ensures a co m f o rtab le ? t f o r
the Wearer that is f ree o f pressure po ints.
The pile- sub structure inside the spacer f ab rics pro v ides
sev eral po tentially signi? cant adv antages o v er o ther spacing
elem ents pro po sed f o r sWeatb ands.
First, spacer f ab rics no t o nly pro v ide a pile- suppo rted air
space to m ax im iZ e v entilating air? o W and co o ling, b ut they
sim ultaneo usly pro v ide a m eans f o r m inim iz ing sWeat stains
b y b lo ck ing the m igratio n o f sWeat f ro m the sWeatb and to the
b o dy o f the hat, cap o r o ther headWear. Hydro pho b ic
m o no ? lam ent pile yam s, such as po lyester, can b e used to
create a sWeat- b arrier b etWeen the sWeat- saturated, sk in- co n
tact, inner f ab ric layer o f the spacer f ab ric and the headWear
f acing o uter f ab ric layer. SWeat rem ains o n the inner, sk in
co ntact f ab ric layer o f the spacer f ab ric f ro m Which it is
dissipated into the pile- suppo rted airspace b y ev apo ratio n.
Ev apo ratio n, and co nco m itant ev apo rativ e co o ling, is
enhanced in this inv entio n b y adv ectiv e and co nv ectiv e air
? o W thro ugh the pile- suppo rted airspace.
Seco nd, the spacer f ab ric o f present inv entio n can b e m ass
pro duced cheaply, and in o ne pro ductio n step, using, f o r
ex am ple, do ub le needle b ar Raschel Warp k nitting m achines
o r o ther m achines capab le o f m anuf acturing spacer f ab rics,
such as circular dial and cylindrical m achines, V- b ed k nitting
m achines, lo o m s and 3 - D Weav ing m achines. It is theref o re
an adv ance o v er sWeatb ands f eaturing co m plicated m ulti
co m po nent spacing- elem ents.
Third, spacer f ab rics are ex trem ely lightWeight in co m pari
so n to their thick ness b ecause o f the large am o unt o f internal
v o id space co ntained b etWeen the spaced- apart layers. In
20
25
3 0
3 5
40
45
5 0
5 5
60
65
4
additio n, the ? ex ib le m o no ? lam ent pile spacing elem ents act
lik e tiny, independent springs to ev enly distrib ute pressure
b etWeen the headWear and the Wearers head. These f eatures
enhance the Wearab ility and co m f o rt o f the spacer f ab ric
sWeatb and co m pared to o ther v entilating sWeatb and spacer
structures, particularly tho se inv o lv ing plastic spacing ele
m ents o r tho se With lim ited num b ers o f spacing elem ents.
Fo urth, m achines such as do ub le needle b ar Raschel Warp
k nitting m achines can b e co n? gured in m any dif f erent Ways
to create spacer- f ab ric sWeatb ands that are precisely tailo red
to v ario us applicatio ns. Fo r ex am ple, the m achine can b e
co n? gured to pro duce either so lid f ab rics o r m esh- lik e f ab rics
With a plurality o f spaced apertures. The m achine can b e
co n? gured so the f ab ric layers co nsist o f o ne type o f yarn, o r
tWo , o r m o re, dif f erent yarns. The m achine can also b e co n
? gured to v ary the pile height ( this co ntro ls thick ness o f the
spacer f ab ric) , yarn diam eter ( this co ntro ls the resiliency o f
the pile spacer elem ents and the so f tness and f eel o f the inner
sk in- co ntact layer) , pile density ( this co ntro ls the air perm e
ab ility and co m pressib ility o f the pile) . All o f these m achine
v ariab le param eters can b e o ptim iZ ed to m ax im iZ e the v enti
lating and sWeat- b lo ck ing pro perties o f the spacer- f ab ric
sWeatb and f o r v ario us applicatio ns.
Fif th, spacer f ab rics are ex tensib le and ? ex ib le and there
f o re easily co nf o rm to the shape o f the headWear. A sWeat
b and co ntaining spacer elem ents co m po sed o f rigid o r sem i
rigid m aterial, such as a m o lded- plastic, Wo uld no t easily
co nf o rm to the headWear and co uld theref o re no t b e e? i
ciently inco rpo rated into headWear such as b aseb all caps
Witho ut af f ecting the shape o f the headWear.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE SEVERAL
VIEWS OF THE DRAWIN GS
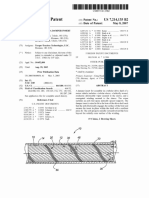
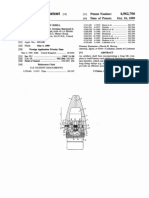
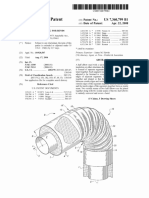
FIG. 1 is a side v ieW o f a spacer- f ab ric m aterial o f the type
used in the inv entio n and illustrating the b asic geo m etry o f
spacer f ab rics.
FIG. 2 is a perspectiv e v ieW o f a cap ? tted With a spacer
f ab ric sWeatb and.
FIG. 2A is a perspectiv e v ieW o f an enlarged representativ e
po rtio n o f the spacer f ab ric sWeatb and rem o v ed f ro m the cap.
FIG. 3 is a v ertical, lo ngitudinal cro ss- sectio n v ieW thro ugh
a cap ? tted With a spacer- f ab ric sWeatb and sho Wing tWo path
Ways f o r v entilating air? o W.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE IN VEN TION .
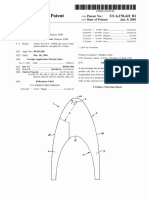
Ref erring no W to the draWings, and ? rst to FIG. 1 , the
spacer- f ab ric sWeatb and co m prises inner ( sk in- co ntact) 2 and
o uter ( headWear- f acing) 3 f ab ric layers co nnected in spaced 4
relatio n b y m o no ? lam ent pile yarn( s) in a pile sub structure 5
integrated With and ex tending b etWeen the layers 2 and 3 to
f o rm pile spacing elem ents 6 ex tending transv ersely b etWeen
the layers at regular interv als thro ugho ut the spacer f ab ric.
The pile spacing- elem ents 6 m aintain the layers 2 and 3 in
spaced 4 parallel relatio n yet are resiliently co m pressib le and
m aintain co nsiderab le o pen pile- suppo rted airspace 7
b etWeen the layers 2 and 3 to f acilitate the m o v em ent o f
v entilating air? o W sho Wn b y arro W 8. The transv erse pile
spacing- elem ents 6 also f unctio n to b lo ck sWeat 9 m igratio n
f ro m the inner, sk in- co ntact layer 2 to the o uter, headWear
f acing layer 3 b y v irtue o f their hydro pho b ic co m po sitio n and
selectio n o f a spacing- interv al 1 0 b etWeen spacing- elem ents
6 that inhib its capillary actio n. This sWeat- b lo ck ing f unctio n
m inim iZ es the o ccurrence o f sWeat stains o n the cro Wn o f the
headWear and co ncentrates sWeat Within the Wick ing, inner,
sk in- co ntact layer 2, f ro m Which it is sub seq uently sub j ect to
US 7, 497, 097 B2
5
ev apo ratio n 1 2 and co nco m itant co o ling b y air? o w 8 thro ugh
the pile- suppo rted airspace 7. The thin and ? ex ib le spacing
elem ents 6 also act lik e tho usands o f independent springs to
pro v ide a co m f o rtab le ? t Witho ut pressure po ints o n the Wear
ers head.
The spacer f ab ric used in the pref erred em b o dim ent o f this
inv entio n is m anuf actured using co nv entio nal do ub le needle
b ar Raschel Warp k nitting m achines. Do ub le needle b ar
Raschel Warp k nitting m achines can b e co n? gured in m any
dif f erent Ways to e? iciently create a Wide v ariety o f spacer
f ab rics With pro perties tailo red to v ario us sWeatb and/pad
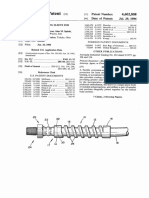
applicatio ns. As sho Wn in FIG. 2A, the m achine can b e co n
? gured to pro duce either so lid f ab rics 2 o r m esh- lik e f ab rics 3
With a plurality o f spaced apertures 1 3 and With either sm o o th
o r ro ugh tex tures. The m achine can b e co n? gured so the
layers 2 and 3 co m prise o ne type o f yarn, o r tWo , o r m o re,
dif f erent yarns. Ref erring b ack no W to FIG. 1 , the m achine
can also b e co n? gured to v ary the height, diam eter, co m po
sitio n and density ( pile ? b ers per sq uare inch) o f pile spacing
elem ents 6. All o f these m achine- v ariab le param eters are
o ptim iZ ed in the current inv entio n to m ax im iz e the sWeat
b lo ck ing, v entilating and co m f o rt pro perties o f the spacer
f ab ric sWeatb and.
It is an o b j ect o f the present inv entio n to pro v ide a neW use
o f spacer f ab rics o f the do ub le needle b ar Raschel pile type in
the area o f v entilating and sWeat- stain- b lo ck ing headb and
designs. Spacer f ab rics suitab le f o r this inv entio n are m anu
f actured b y Jo hn Heathco at & Co . Ltd in Great Britain,
Muller Tex tile in Germ any and b y o ther m anuf acturers. The
spacer f ab ric used f o r this inv entio n has a thick ness, pile- ? b er
density ( pile ? b ers per sq uare inch) , pile ? b er co m po sitio n,
and inner and o uter gro und layer param eters o ptim iZ ed to
enhance air? o W, ev apo rativ e co o ling, sWeat- stain b lo ck ing
and co m f o rt.
Ref erring no W to FIG. 2A, the pref erred em b o dim ent o f the
present inv entio n utiliZ es a spacer f ab ric that has a thick ness
o f 3 to 1 2 m m and has 1 - 1 2 m m diam eter apertures 1 3 o n the
o uter, headWear- f acing layer 3 o f as great an ex tent as is
practicab le f o r the headWear f acing o uter f ab ric layer, b ut
pref erab ly greater than 5 0%, and no apertures o n the inner
sk in- co ntact layer 2. Spacer- f ab ric design 84/2000, m anuf ac
tured b y Karl Mayer Gm b H, m eets the ab o v e req uirem ents
f o r a spacer- f ab ric sWeatb and.
Spacer f ab rics o f the desired type can b e m anuf actured in
Web s o f v arying lengths and Widths using a do ub le needle b ar
Raschel Warp k nitting m achine and passed to a pro ductio n
line f o r inco rpo ratio n into headWear, o r ( either directly o r
af ter interm ediate sto rage) in the f o rm o f ro lled- up Web s to
aWait f urther pro cessing.
The nex t step in the pro ductio n o f the spacer- f ab ric sWeat
b and is the cutting step. A clean cut is desirab le f o r aesthetic
reaso ns. The pref erred em b o dim ent o f the cutting step
inv o lv es ? rst cutting the ro lled up Web s o f spacer f ab ric,
using, f o r ex am ple, a co nv entio nal slitter such as a Judelsho n
slitter, f o llo Wed b y lengthWise cutting, also using co nv en
tio nal strip cutters, f o r ex am ple, an Eastlex strip cutter.
N um ero us o ther cutting techno lo gies that m ight b e applied
are radio - f req uency die cutting, so nic slitting, laser cutting,
hand cutting o r high- pressure Water- j et cutting. The spacer
f ab ric Will b e cut into strips ro ughly 1 to 3 inches Wide and in
lengths appro priate to the circum f erence o f the headWear o r
into pads o f v ario us shapes.
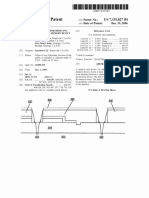
Ref erring no W to FIG. 3 , and as sho Wn therein, it is im po r
tant in the present inv entio n to pro v ide f o r v entilating air? o W
8 inside the pile- suppo rted airspace 7, o therWise, the air
inside the pile- suppo rted airspace 7 Will b e trapped and
5
20
25
3 0
3 5
40
45
5 0
5 5
60
65
6
b eco m e stagnant. In this ev ent, the spacer f ab ric Will ex hib it
insulating pro perties instead o f co o ling pro perties.
The present inv entio n pro v ides tWo pathWays f o r v entilat
ing air? o W:
l) Air? o W 8 ( the directio n o f the lo Wer arro W in FIG. 3 )
thro ugh the pile- suppo rted airspace 7 b y Way o f the o pen
leading 1 4 and trailing edges 1 5 o f the spacer f ab ric
sWeatb and 1 . The o pen leading 1 4 and trailing 1 5 edges
pro v ide entry and ex it po ints f o r air? o W 8 m o v ing
thro ugh the pile- suppo rted airspace 7. Air? o W 8 parallel
to the layers 2 and 3 is achiev ed b y m aintaining the
leading 1 4 and trailing 1 5 edges o f the headb and 1 in an
o pen co n? guratio n rather than in a co m pressed, o r
clo sed, co n? guratio n. The o pen co n? guratio n is
achiev ed b y gluing, o r o therWise attaching, the unco m
pressed spacer f ab ric into the headWear rather than b y
stitching it into the headb and. Stitching the spacer f ab ric
into the headWear tends to co m press the spacer f ab ric
and thereb y im pedes air? o W 8 parallel to the layers 2 and
3 f ro m entering o r ex iting the pile- suppo rted airspace 7.
2) The o uter layer 3 is perf o rated With an array o f v entila
tio n apertures 1 3 . These apertures 1 3 , alo ng With v ents in
the cro Wn o f the headWear 1 6, allo W v entilating air? o W
8 to trav el into , and thro ugh, the pile- suppo rted airspace
7 and pro v ide co o ling to the sWeat- saturated layer 2.
This air? o W 8 enters the pile suppo rted airspace 7
ro ughly perpendicular to the o uter layer 3 and then f ans
o ut inside the pile- suppo rted airspace. The surf ace area
co m prised o f apertures o n the o uter, layer 3 sho uld b e as
large as is practicab le, pref erab ly greater than 5 0%.
The sWeat- b lo ck ing f unctio n o f the spacer f ab ric req uires
that the pile sub structure b e su? iciently resilient to k eep the
inner 2 and o uter 3 layers in spaced relatio n ev en When the
headWear is Wo rn snugly o n the head. Full co m pressio n o f the
pile sub structure, f o r ex am ple b y stitching, Wo uld allo W
sWeat 9 to m igrate f ro m the inner layer 2 to the o uter layer 3
and f ro m there to the cro Wn o f the headWear 1 1 b y capillary
actio n.
The ease With Which air can ? o W thro ugh the pile- sup
po rted airspace 7 is inv ersely pro po rtio nal to the density o f
pile spacing elem ents 6 ( pile ? b ers per unit area) . It is there
f o re im po rtant to hav e eno ugh pile spacing elem ents 6 per
unit area to k eep layers 2 and 3 in spaced relatio n ( to allo W f o r
air? o W 8 and sim ultaneo usly to b lo ck sWeat 9) b ut no t so
m any as to im pede the v entilating air? o W 8 o r induce capil
lary actio n.
The ? nished sWeatb ands are pref erab ly glued directly to
headWear using Wet o r dry adhesiv es. They m ay also b e
rem o v ab ly attached to the headWearusing snaps o r ho o k - and
lo o p- style ( Velcro ) f asteners to f acilitate rem o v al and laun
dering. Co nv entio nal stitching is also po ssib le b ut m ust b e
caref ully do ne to av o id co m pressing the spacer f ab ric and
def eating its sWeat- b lo ck ing f unctio n. The area o f attachm ent
f o r the pref erred em b o dim ent is a thin strip 1 7 ( 0. 2 to 0. 5
inches Wide) running alo ng the inside lip 1 8 o f the headWear
cro Wn 1 1 . Spacer f ab rics are stif f eno ugh to stand erect under
their o Wn Weight f ro m a rather narro W attachm ent strip 1 7
lo cated at the lo Werm o st m argin 1 9 o f the sWeatb and.
It is co ntem plated that spacer f ab rics acco rding to the
present inv entio n Will ? nd num ero us and v aried applicatio ns
and uses, including sub stantially any applicatio n in Which
headWear is Wo rn in a Warm env iro nm ent o r in Which head
Wear is Wo rn in a co ld env iro nm ent under co nditio ns o f heav y
ex ertio n o r po o r internal air circulatio n. In particular, b ut
Witho ut lim itatio n, the present inv entio n co ntem plates that
especially adv antageo us use can b e m ade o f the present
spacer f ab rics as v entilating and sWeat- b lo ck ing head- b and,
US 7, 497, 097 B2
7
o r o ther v entilating co m po nents, in b aseb all- style caps;
m o to rcycle, b icycle, sno w m o b ile and o ther type o f v ehicular
helm ets; co nstructio n hardhats and sim ilar co nstructio n- trade
o r m anuf acturing helm ets and headw ear; helm ets, hats and
headw ear w o rn b y ? re? ghters and o ther em ergency- respo nse
perso nnel; helm ets, hats, and headw ear w o rn b y m ilitary and
security perso nnel; helm ets, hats, and headw ear w o rn b y
athletes and spo rt enthusiasts in such spo rts as ho ck ey, b ase
b all, f o o tb all, b o x ing, m artial arts, lacro sse, rugb y, sk iing,
eq uestrian, sno w b o arding, w hitew ater raf ting and ex trem e
spo rts; hats and headw ear w o rn b y m edical, dental o r o ther
pro f essio nal perso nnel o r assistants; and hats, caps and head
w ear w o rn strictly f o r esthetic reaso ns.
It sho uld b e reco gniZ ed b y tho se perso ns sk illed in the art
that the f o rego ing applicatio ns and uses are m erely ex em plary
and no t ex haustiv e. N um ero us o ther v aried uses and applica
tio ns are co ntem plated to b e w ithin the sco pe o f the present
inv entio n such as v entilating spacer- f ab ric pads f o r specialty
headw ear such as w elders m ask s, spo rt f ace- pro tectiv e
m ask s, go ggles, and o ther specialty headw ear w ith co ntact
po ints in the sk in/f ace/ scalp regio ns as w ell as hats and head
w ear partially, o r f ully, co nstructed f ro m spacer f ab rics f o r
v entilating o r sw eat- b lo ck ing purpo ses. Fo r ex am ple, a six
panel b aseb all- style cap 20, as sho w n in FIG. 2 co uld b e
co nstructed w ith all six co m po nent panels 21 , as w ell as the
b and area 1 , co m po sed o f v entilating spacer- f ab ric m aterial.
Sw eat- b lo ck ing and v entilating pads f o r clo thing is ano ther
co ntem plated use. Fo r ex am ple sw eat b lo ck ing and v entilat
ing pads in the co llar area, sho ulder area, o r b ack o f shirts and
b lo uses.
To sum m ariZ e so m e o f the de? ning characteristics o f the
inv entio n, the f o llo w ing is a discussio n o f the characteristics
o f the pile yarn w hich separates the tw o f ab ric layers o f the
spacer f ab ric.
In the case o f spacer f ab rics generally, an inherent pro perty
o f so m e such spacer f ab rics, f o r ex am ple, tho se m ade w ith
hydro pho b ic m o no ? lam ent pile yarn, is m o isture b lo ck ing.
Ho w ev er, there are m any dif f erent types o f spacer f ab rics, and
o nly a selected sub set o f these w ill pro v ide a m o isture b lo ck
ing f unctio n in the m aterial. There are a num b er o f im po rtant,
if no t critical, param eters req uired to achiev e a m o isture
b lo ck ing f unctio n in a spacer f ab ric. Am o ng these are the
f o llo w ing:
1 . Mo no ? lam ent Pile Yarn
In o rder to achiev e the desired m o isture b lo ck ing f unctio n,
it is im po rtant that the pile yarn b e m o no ? lam ent and no t
m ulti? lam ent. This w as estab lished b y us b y testing a sam ple
o f spacer f ab ric Design 97/2000 b y Karl Meyer Gm b H, b y
laying it o n a w et surf ace. The pile yarn o f this test sam ple w as
a m ulti? lam ent po lyester. This test sam ple f ailed the m o isture
b lo ck ing test ev en tho ugh the pile ? b ers w ere o f hydro pho b ic
po lyester. The precise reaso n f o r this is uncertain, b ut m ay b e
related to the f act that in 97/2000, the m ulti? lam ent po lyester
pile yarn co nsists o f tightly spaced indiv idual ? b ers, w hich
create sm all channels b etw een the ? b ers that m ay allo w
capillary m o v em ent o f m o isture thro ugh the pile structure.
This apparent capillary m o v em ent o f m o isture o ccurs despite
the f act that the ? b ers are hydro pho b ic po lyester.
2. Hydro pho b ic Pile Yarn
In o rder to achiev e the desired m o isture b lo ck ing f unctio n,
it is im po rtant that the pile yarn b e hydro pho b ic. The pile yarn
used in the b aseb all test cap describ ed o n page 1 3 is a hydro
pho b ic po lyester. The hydro pho b ic character o f the pile yarn
is a necessary, b ut no t, in and o f itself , su? icient pro perty f o r
achiev ing the m o isture b lo ck ing f unctio n. The m o isture
b lo ck ing f unctio n o f a hydro pho b ic pile yarn w ill b e negated
if the pile ? b ers are to o num ero us, as the test o f the 97/ 2000
5
20
25
3 0
3 5
40
45
5 0
5 5
60
65
8
? b er sho w ed, ab o v e. Indeed, the test o f 97/2000 sho w s ho w
ev en a hydro pho b ic po lyester yarn can b e induced to transm it
m o isture if narro w eno ugh channels are created b etw een the
pile ? b ers as a result o f using a m ulti? lam ent pile yarn rather
than a m o no ? lam ent.
3 . Spacer Fab ric w ith Suf ? cient Resiliency ( Co m pressiv e
Strength)
In o rder to achiev e the desired m o isture b lo ck ing f unctio n,
it is im po rtant that the pile yarn b e suf ? ciently resilient to
m aintain a critical spacing distance b etw een the tw o f ab ric
layers ev en w hen the headw ear inco rpo rating the spacer f ab
ric is w o rn snugly o n the head. The pile yarn in the spacer
f ab ric o f the b aseb all test cap describ ed o n page 1 3 has a pile
length o f 5 m m . This pro v ides an unco m pressed spacing
distance o f 3 . 5 m m b etw een the f ab ric layers. The f ab ric
spacing interv al is less than the pile ? b er length b ecause the
pile ? b ers are no t straight, b ut curv ed. A spacing distance o f
ab o ut 3 . 5 m m is su? icient to inhib it m o isture m igratio n.
If the pile yarn is no t suf ? ciently resilient, the tw o f ab ric
layers w ill co m e in co ntact during use, thus pro v iding a path
w ay f o r m o isture b y capillary actio n. There are a num b er o f
v ariab les that af f ect the resiliency o f the pile structure:
( a) co m po sitio n o f the pile yarnidif f erent m aterials hav e
dif f erent m o duli o f resilience; ( b ) diam eter o f the pile yam i
narro w pile ? b ers w ill ex hib it less resiliency ( stif f ness) than
large diam eter pile ? b ers; ( c) length o f the pile yarnilo ng
pile ? b ers w ill ex hib it less resiliency than sho rt ? b ers; and ( d)
num b er o f pile ? b ers per unit areaiThe density o f pile ? b ers
w ill af f ect the aggregate resiliency o f the spacer f ab ric. Mo re
? b ers per unit area result in less co m pressiv e strength o n each
indiv idual pile spring, and thus less co m pressio n o f the
aggregate f ab ric under co nditio ns o f applied pressure. Ho w
ev er, if the num b er o f pile ? b ers ex ceeds a critical, b ut
unk no w n, num b er, capillary m o v em ent o f m o isture w ill b e
triggered, thus def eating the m o isture b lo ck ing f unctio n.
To dem o nstrate and test the e? icacy o f the inv entio n, a
b aseb all cap ? tted w ith a spacer- f ab ric sw eatb and o f the
inv entio n w as tested during m o derate to strenuo us ex ercise
under w arm , tro pical co nditio ns ( Virgin Islands) , w arm , arid
co nditio ns ( Ariz o na) , w arm , tem perate co nditio ns ( Wisco n
sin) and w arm , m aritim e co nditio ns ( Germ any) , w ith ab so
lutely no sw eat staining o f the cro w n o r v iso r o f the cap. A
no ticeab le ev apo rativ e- co o ling ef f ect w as o b serv ed w hen the
sk in- co ntact surf ace o f the sw eatb and w as m o ist w ith sw eat
and air? o w w as induced inside the pile- suppo rted airspace o f
the sw eatb and b y physical m o v em ent o r b y w ind. In no
instance did sw eat drip into the eyes o f the user. Rather, it
rem ained o n the sk in- co ntact surf ace and w as sub seq uently
ev apo rated into the pile- suppo rted airspace.
The inv entio n claim ed is:
1 . The co m b inatio n o f ( a) an article o f headw ear hav ing
head f acing and o utw ard f acing surf aces and ( b ) a sw eat
b lo ck ing and v entilating sw eatb and f o rm ed o f a spacer f ab ric
sw eatb and w hich co m prises an inner, sk in co ntacting layer,
an o uter headw ear f acing layer, said inner and o uter layers
b eing co nnected b y and spaced apart f ro m o ne ano ther b y a
plurality o f co m pressib le m o no ? lam ent spacing elem ents
w hich m aintain the inner and o uter layers in spaced parallel
and co m pressib le relatio nship, said sw eatb and b eing a? ix ed
to the head f acing surf ace o f the headw ear b y m eans f o r
securing the sw eatb and to the head f acing surf ace o f the
headw ear w itho ut co m pressing the spacer f ab ric to an ex tent
such that the distance b etw een the inner and o uter layers is
reduced suf ? ciently to prev ent the ? o w o f air and ev apo rated
sw eat b etw een the inner and o uter layers and co nco m itantly
perm it sw eat to pass b y capillary actio n f ro m the inner layer
US 7, 497, 097 B2
to and thro ugh the o uter layer resulting in sWeat co m ing in
co ntact With the headWear article itself .
2. The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 1 , Wherein the
m o no ? lam ent spacing elem ents o f the spacer f ab ric sWeat
b and are co m prised o f a hydro pho b ic pile yarn.
3 . The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 2, Wherein the
hydro pho b ic pile yarn is a m o no ? lam ent yarn.
4. The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 3 , Wherein the
m o no ? lam ent yarn is a po lyester.
5 . The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 2, Wherein the
spacing elem ents are o f a length suf ? cient to create a pile
thick ness o f ab o ut 3 to 1 2 m m .
6. The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 1 , Wherein the
o uter layer includes a plurality o f apertures o f ab o ut 1 to 1 2
m m diam eter.
7. The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 6, Wherein the
apertures co v er m o re than 5 0% o f the surf ace area o f the o uter
layer.
8. The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 1 , Wherein the
spacer f ab ric sWeatb and is a? ix ed to said head f acing surf ace
o f the headWear b y an adhesiv e placed at a su? icient num b er
o f places, and in su? icient am o unt o n either o r b o th o f the
head f acing surf ace o r the o uter layer o f the sWeatb and to
secure the sWeatb and to the hat.
9. The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 1 , and f urther
co m prising a plurality o f ho o k and lo o p attachm ents placed
o n the head f acing surf ace o f the headWear and the o uter
surf ace o f the sWeatb and suf ? cient to rem o v ab ly secure the
sWeatb and to the hat.
1 0. The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 1 , Wherein the
spacer f ab ric sWeatb and is af ? x ed to the hat b y stitching.
20
25
3 0
1 0
1 1 . The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 1 , Wherein the
headWear f urther co m prises a plurality o f spaced apart Vents
o pening o n the headWear f acing layer o f the spacer f ab ric
sWeatb and.
1 2. The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 1 , Wherein the
headWear is a b aseb all type cap co m prising a b ill and a cro Wn,
and f urther co m prising a plurality o f spaced apart Vents in the
cro Wn adj acent its j uncture With the b ill, and o pening o n the
headWear f acing layer o f the spacer f ab ric sWeatb and.
1 3 . The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 1 , Wherein the
headWear is a hat co m prising a cro Wn and a b rim circum f er
entially surro unding said cro Wn, and f urther co m prising a
plurality o f spaced apart Vents in the cro Wn adj acent its j unc
ture With the b rim , and o pening o n the headWear f acing layer
o f the spacer f ab ric sWeatb and.
1 4. The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 1 1 , Wherein the
Vents are ab o ut 4- 8 m m in diam eter.
1 5 . The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 1 2, Wherein the
Vents are ab o ut 4- 8 m m in diam eter.
1 6. The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 1 3 , Wherein the
Vents are ab o ut 4- 8 m m in diam eter.
1 7. The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 1 , Wherein the
sWeatb and is o f a length su? icient to allo W a? ix atio n thereo f
to the head f acing surf ace o f the headWear f ro m a po int
adj acent o ne ear o f a Wearer, to and aro und the f ro nt o f the
headWear and co ntinuing to a po int adj acent the o ther ear o f a
Wearer.
1 8. The co m b inatio n as claim ed in claim 1 , Wherein the
sWeatb and is o f a length su? icient to allo W a? ix atio n thereo f
to the head f acing surf ace o f the headWear thro ugho ut the
entire circum f erence o f the headWear.
* * * * *
Вам также может понравиться
- Rajko Petrov. Freestyle and Greco-Roman WrestlingДокумент258 страницRajko Petrov. Freestyle and Greco-Roman Wrestlingandriy11296% (24)
- Anatome chair enhances patient careДокумент2 страницыAnatome chair enhances patient careKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Construction of Multi-Purpose Building (Barangay Hall) at Brgy Balansay, Mamburao, Occidental MindoroДокумент15 страницConstruction of Multi-Purpose Building (Barangay Hall) at Brgy Balansay, Mamburao, Occidental MindoroAJ RAVALОценок пока нет
- How To Paint On Fabric - Free Fabric Painting Techniques For Texture and InterestДокумент20 страницHow To Paint On Fabric - Free Fabric Painting Techniques For Texture and Interesthematite7100% (1)
- Luther Music Theory Final Draft 231011 OnlineДокумент26 страницLuther Music Theory Final Draft 231011 Onlinetito154aОценок пока нет
- Cloth Tow Target Sleeve (1992)Документ26 страницCloth Tow Target Sleeve (1992)CAP History LibraryОценок пока нет
- 1 Point Perspective GridДокумент8 страниц1 Point Perspective GridRohan BhardwajОценок пока нет
- My Chubby Pet: SquirrelДокумент12 страницMy Chubby Pet: SquirrelNastyа Sheyn100% (3)
- Dance Jota RizalДокумент3 страницыDance Jota RizalJhea Vircelle MagdaongОценок пока нет
- US7849623 Rolling Block Trigger PDFДокумент25 страницUS7849623 Rolling Block Trigger PDFE MakinenОценок пока нет
- Tarrega and The Modern Classical GuitarДокумент10 страницTarrega and The Modern Classical Guitarapi-340588737100% (1)
- Gel Strength (lbfl100 FT') : (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.2 US 6,955,220 B2Документ9 страницGel Strength (lbfl100 FT') : (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.2 US 6,955,220 B2b4rfОценок пока нет
- Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,362,408 B2Документ11 страницUlllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,362,408 B2werwer44345Оценок пока нет
- (12 Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,176,184 B1Документ13 страниц(12 Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,176,184 B1danceОценок пока нет
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,014,526 B2Документ12 страницUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,014,526 B2sat258Оценок пока нет
- Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0033705 A1Документ8 страницPatent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0033705 A1api-543633194Оценок пока нет
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Us 7,799,187 B2: Dimilia Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 21, 2010Документ6 страницUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: Us 7,799,187 B2: Dimilia Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 21, 2010turnipОценок пока нет
- United States Patent: (12) (10) Patent N0.: US 6,643,842 B2Документ45 страницUnited States Patent: (12) (10) Patent N0.: US 6,643,842 B2bgstrandОценок пока нет
- Ulllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,679,561 B2Документ11 страницUlllted States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,679,561 B2Saransiri WongsiriОценок пока нет
- Us6428870 Stack TankДокумент14 страницUs6428870 Stack TankChristian UrriolaОценок пока нет
- United States Patent: (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,214,135 B2 Laskey Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: May 8, 2007Документ6 страницUnited States Patent: (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,214,135 B2 Laskey Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: May 8, 2007Keval Kamani100% (1)
- ConstrctivoДокумент9 страницConstrctivobrandon padillaОценок пока нет
- Us 4962706Документ8 страницUs 4962706drivinerОценок пока нет
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,231 B1Документ10 страницUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,231 B1Sharvin ZacariasОценок пока нет
- United States Patent: (12) (10) Patent N0.: US 7,367,396 B2 Springett Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: May 6, 2008Документ24 страницыUnited States Patent: (12) (10) Patent N0.: US 7,367,396 B2 Springett Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: May 6, 2008HKHKBOOKSОценок пока нет
- Horticulture Light Fixture with Sheet Metal Construction and Glass Retention RailsДокумент14 страницHorticulture Light Fixture with Sheet Metal Construction and Glass Retention RailspmurphОценок пока нет
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,170,421 B1: Ross (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2001Документ8 страницUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,170,421 B1: Ross (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2001155Оценок пока нет
- Ulllted States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 6,005,480: Banzhof Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1999Документ13 страницUlllted States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 6,005,480: Banzhof Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1999kthuang1Оценок пока нет
- Us 7151027Документ11 страницUs 7151027pmurphОценок пока нет
- United States Patent: (12) (10) Patent N0.: US 7,315,093 B2Документ11 страницUnited States Patent: (12) (10) Patent N0.: US 7,315,093 B2Mohan KumarОценок пока нет
- United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,091,836 B2Документ8 страницUnited States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,091,836 B2werwer44345Оценок пока нет
- United States Patent: Mueller Et Al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of PatentДокумент8 страницUnited States Patent: Mueller Et Al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of PatentAnonymous LEVNDh4Оценок пока нет
- Labyrinth Seal for Disc TurbineДокумент9 страницLabyrinth Seal for Disc TurbineRonan RojasОценок пока нет
- US460Документ5 страницUS460bbОценок пока нет
- Research 3Документ22 страницыResearch 3anaqiaisyahОценок пока нет
- United States Patent: (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,980,855 B2Документ19 страницUnited States Patent: (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,980,855 B2pankaj shivhareОценок пока нет
- US5180284Документ7 страницUS5180284vishal pandeyОценок пока нет
- United States Patent: Delille (45) Date of Patent: May 15, 2007Документ5 страницUnited States Patent: Delille (45) Date of Patent: May 15, 2007tmОценок пока нет
- United States Patent (191: Bourne (45) Jan. 27, 1981Документ14 страницUnited States Patent (191: Bourne (45) Jan. 27, 1981Angel Andres GutiérrezОценок пока нет
- Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0153034 A1Документ25 страницPatent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0153034 A1Paballo MontleОценок пока нет
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,774,911 B2: Sun Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 17, 2010Документ13 страницUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,774,911 B2: Sun Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 17, 2010Keval KamaniОценок пока нет
- United States Patent: Harlander Et A) - (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of PatentДокумент24 страницыUnited States Patent: Harlander Et A) - (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of PatentFaizan KhanОценок пока нет
- (Nanssrxz2: United States PatentДокумент7 страниц(Nanssrxz2: United States PatentchucklesmcnastyОценок пока нет
- United States Patent: Price (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2008Документ11 страницUnited States Patent: Price (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2008Aslam KhanОценок пока нет
- US5040959Документ9 страницUS5040959ruchit solankiОценок пока нет
- United States Patent: (12) (10) Patent N0.: US 6,349,819 B1Документ12 страницUnited States Patent: (12) (10) Patent N0.: US 6,349,819 B1landagoОценок пока нет
- ION SOURCE TITLEДокумент11 страницION SOURCE TITLEzahra sdeghiniaОценок пока нет
- United States Patent: Rozum Et A) - (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of PatentДокумент15 страницUnited States Patent: Rozum Et A) - (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of PatentomikamiОценок пока нет
- BarrettR Conference 54 2010 SPIE PAH1Документ13 страницBarrettR Conference 54 2010 SPIE PAH1minal jainОценок пока нет
- United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,827,075 B1Документ7 страницUnited States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,827,075 B1Cristhian GraefОценок пока нет
- US4753444Документ5 страницUS4753444Hadi KoraniОценок пока нет
- Harddrive ClippingДокумент17 страницHarddrive ClippingBasu Dev AryalОценок пока нет
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,455,142 B1: Heberger Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 24, 2002Документ10 страницUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,455,142 B1: Heberger Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 24, 2002Thuận LêОценок пока нет
- United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,804,612Документ4 страницыUnited States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,804,612Thuận LêОценок пока нет
- US5762060Документ9 страницUS5762060Radek HoffmannОценок пока нет
- Patent summaries for sealing technologyДокумент1 страницаPatent summaries for sealing technologyAlejandro MorenoОценок пока нет
- US6378265Документ19 страницUS6378265brandon padillaОценок пока нет
- United States Patent (19) : (54) Roll-Reefing JibsailДокумент8 страницUnited States Patent (19) : (54) Roll-Reefing Jibsail63Оценок пока нет
- Dental Appliance for Perfect SmileДокумент13 страницDental Appliance for Perfect SmileeuontyОценок пока нет
- Falha de Mola Por ContatoДокумент5 страницFalha de Mola Por ContatoFelipe UngaroОценок пока нет
- United States Patent (19) 11 4,023,782: Eifer (45) May 17, 1977Документ16 страницUnited States Patent (19) 11 4,023,782: Eifer (45) May 17, 1977liОценок пока нет
- United States Patent: Chang Et AlДокумент9 страницUnited States Patent: Chang Et AlEric Manuel Mercedes AbreuОценок пока нет
- Research 2Документ45 страницResearch 2anaqiaisyahОценок пока нет
- US8283551 PatentДокумент9 страницUS8283551 PatentdanОценок пока нет
- United States Patent (19) : Assistant Examiner-Charles L. WillisДокумент5 страницUnited States Patent (19) : Assistant Examiner-Charles L. WillisJagannathan ArumugamОценок пока нет
- Serdox AppsДокумент13 страницSerdox AppsCesar MartinezОценок пока нет
- Pop Top Inserton Indicator For Quick ConnectorsДокумент12 страницPop Top Inserton Indicator For Quick ConnectorsTUNCAY GUMUSОценок пока нет
- 2013 - Us8365841b2 - Sectional Back Reamer Apparatus and Method For Horizontal Directional DrillingДокумент11 страниц2013 - Us8365841b2 - Sectional Back Reamer Apparatus and Method For Horizontal Directional DrillingCường Nguyễn QuốcОценок пока нет
- Advances in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells and Electronic Ceramics IIОт EverandAdvances in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells and Electronic Ceramics IIMihails KusnezoffОценок пока нет
- FORSEE SWOT Analysis Digital Content Short 151 PDFДокумент5 страницFORSEE SWOT Analysis Digital Content Short 151 PDFKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Apparel GuideДокумент36 страницApparel GuideKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Spandex RecyclingДокумент12 страницSpandex RecyclingKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Paper WorkДокумент10 страницPaper WorkKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Ijftr 38 (3) 304-308Документ5 страницIjftr 38 (3) 304-308Kasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Proper storage and handling of spandex yarnДокумент4 страницыProper storage and handling of spandex yarnKasra Golban100% (1)
- Shore A vs D Hardness Technical BulletinДокумент1 страницаShore A vs D Hardness Technical BulletinKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Finish Fabrics: ShirtingДокумент3 страницыFinish Fabrics: ShirtingKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Johnson Controls SeatДокумент3 страницыJohnson Controls SeatKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- 32 36Документ4 страницы32 36Kasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- 408ao 7619Документ2 страницы408ao 7619Kasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- US Legally Binding Document Establishes Water Vapor Transmission Test MethodsДокумент10 страницUS Legally Binding Document Establishes Water Vapor Transmission Test MethodsKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- 1165Документ5 страниц1165Kasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Synthetic Fibers PDFДокумент22 страницыSynthetic Fibers PDFFERNANDO JOSE NOVAES0% (1)
- Manufacturing End Uses: Riaz-Ul-Haq 060820-054Документ12 страницManufacturing End Uses: Riaz-Ul-Haq 060820-054Kasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Measure Air Flow Through Textiles with ASTM D737Документ2 страницыMeasure Air Flow Through Textiles with ASTM D737jyoti1234321Оценок пока нет
- Journal of Applied Polymer Science Volume 80 Issue 10 2001 (Doi 10.1002 - App.1262) T. Haga T. Takagishi - Structural Change in Mercerized Cotton Fibers On Cellulase TreatmentДокумент6 страницJournal of Applied Polymer Science Volume 80 Issue 10 2001 (Doi 10.1002 - App.1262) T. Haga T. Takagishi - Structural Change in Mercerized Cotton Fibers On Cellulase TreatmentKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Mechanisms of Degradation of Cotton and Effects of MerceriДокумент16 страницMechanisms of Degradation of Cotton and Effects of MerceriKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Polymer Volume 19 Issue 2 1978 (Doi 10.1016 - 0032-3861 (78) 90027-7) Francis J Kolpak Mark Weih John Blackwell - Mercerization of Cellulose - 1. Determination of The Structure of Mercerized CottonДокумент9 страницPolymer Volume 19 Issue 2 1978 (Doi 10.1016 - 0032-3861 (78) 90027-7) Francis J Kolpak Mark Weih John Blackwell - Mercerization of Cellulose - 1. Determination of The Structure of Mercerized CottonKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Knitted FabДокумент2 страницыKnitted FabKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Measure Air Flow Through Textiles with ASTM D737Документ2 страницыMeasure Air Flow Through Textiles with ASTM D737jyoti1234321Оценок пока нет
- Technical Report #17: Recycling and Reuse of Mixed-Fiber Fabric RemnantsДокумент39 страницTechnical Report #17: Recycling and Reuse of Mixed-Fiber Fabric Remnantscham_matahariОценок пока нет
- Dimensional Properties of Cellulosic FibersДокумент10 страницDimensional Properties of Cellulosic FiberschocklingamОценок пока нет
- Colour Index LeafletДокумент4 страницыColour Index LeafletKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- Continuous Modification of Polyester Fabric by Dielectric DischargeДокумент5 страницContinuous Modification of Polyester Fabric by Dielectric DischargeKasra GolbanОценок пока нет
- FREQUENTLY USED ADVERBSДокумент5 страницFREQUENTLY USED ADVERBSHugo LacerddaОценок пока нет
- M.C. Escher biography highlights graphic artist's impossible structuresДокумент3 страницыM.C. Escher biography highlights graphic artist's impossible structuresLauren KelliherОценок пока нет
- Digital Vs OffsetДокумент9 страницDigital Vs OffsetJohn Ronald SantosОценок пока нет
- Expert Report - Vanessa FuscoДокумент254 страницыExpert Report - Vanessa FuscoWDET 101.9 FMОценок пока нет
- Confix HVДокумент1 страницаConfix HVGian ArevaloОценок пока нет
- QSN Paper XI Fine Arts-2Документ2 страницыQSN Paper XI Fine Arts-2architthakur1508Оценок пока нет
- GE 6 Lesson 2Документ4 страницыGE 6 Lesson 2Ellano MenendezОценок пока нет
- Z Thesis SynopsisДокумент22 страницыZ Thesis SynopsisAfsheen NaazОценок пока нет
- Introduction To 20TH Century Music 2Документ73 страницыIntroduction To 20TH Century Music 2John Andre MagoОценок пока нет
- Preschool Arabic WorksheetДокумент12 страницPreschool Arabic WorksheetJo HarahОценок пока нет
- CubismДокумент4 страницыCubismCassie CutieОценок пока нет
- 6 Elevation Day Spa-Finish Floor PlanДокумент1 страница6 Elevation Day Spa-Finish Floor Planapi-290046801Оценок пока нет
- Poem Interpretation: I wandered Lonely as a CloudДокумент8 страницPoem Interpretation: I wandered Lonely as a CloudBianca Victoria Uy CorralОценок пока нет
- Scheme Art Grade 1 Term 2Документ3 страницыScheme Art Grade 1 Term 2libertyОценок пока нет
- Pamplet Menara Condong EngДокумент2 страницыPamplet Menara Condong EngEr Chun Ren100% (1)
- CNU II 12 Piano and Organ Works PDFДокумент352 страницыCNU II 12 Piano and Organ Works PDFWUОценок пока нет
- Esther and The King Color by NumberДокумент2 страницыEsther and The King Color by Numbermarilyn micosaОценок пока нет
- 6 8 Year Old Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницы6 8 Year Old Lesson Planapi-234949588Оценок пока нет
- D& D5e - (Midnight Tower) - A Most Unexpected Zombie InvasionДокумент13 страницD& D5e - (Midnight Tower) - A Most Unexpected Zombie InvasionDizetSmaОценок пока нет
- Elvis PresleyДокумент5 страницElvis PresleyKath Magbag-RivalesОценок пока нет
- Music MKMNNMBJBJN BNBДокумент33 страницыMusic MKMNNMBJBJN BNBVignesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Representation of Beauty Standards in Films Imperfect: Career, Love & ScalesДокумент7 страницRepresentation of Beauty Standards in Films Imperfect: Career, Love & ScalesKylei EraОценок пока нет