Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Appendix
Загружено:
sukiyem89Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Appendix
Загружено:
sukiyem89Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Useful Anatomical Data of
Clinical Significance
Appendix
Table VII. Summary of the Movements of the
Knee Joint and the Muscles Producing
Those Movements 434
Table VIII. Summary of the Movements of the Ankle
Joint and the Muscles Producing Those
Movements 435
Digestive System 436
Table IX. Lengths and Capacities 436
Urinary System 436
Table X. Lengths and Capacities 436
Reproductive System 436
Table XI. Dimensions 436
Embryology 437
Table XII. The Size and Weight of the Developing
Human Embryo and Fetus 437
Respiratory System 426
Table I. Important Airway Distances (Adult) 426
Table II. Important Data Concerning the Trachea 426
Musculoskeletal System 427
Table III. Summary of the Movements of the
Shoulder Joint and the Muscles Producing
Those Movements 427
Table IV. Summary of the Movements of the
Elbow Joint and the Muscles Producing
Those Movements 429
Table V. Summary of the Movements of the
Wrist Joint and the Muscles Producing
Those Movements 430
Table VI. Summary of the Movements of the
Hip Joint and the Muscles Producing
Those Movements 432
Appendix Outline
Respiratory System
Important Airway Distances
(Adult)
a
a
Average figures given 12 cm.
Table I
Distances
Airway (approx.)
Incisor teeth to the vocal cords 5.9 in. (15 cm)
Incisor teeth to the carina 7.9 in. (20 cm)
External nares to the carina 11.8 in. (30 cm)
Important Data Concerning
the Trachea
a
a
Extension of the head and neck, as when maintaining
an airway in an anesthetized patient, may stretch the
trachea and increase its length by 25%. In the adult,
the carina may descend by as much as 3 cm on deep
inspiration. At the carina, the right bronchus leaves the
trachea at an angle of 25 from the vertical and the left
bronchus leaves the trachea at an angle of 45 from
the vertical. In children younger than 3 years, both
bronchi arise from the trachea at equal angles.
b
As children grow, the diameter in millimeters
corresponds approximately to their age in years.
Table II
Length (approx.) Diameter (approx.)
Adults 4.5 in. (11.4 cm) 1 in. (2.5 cm)
Infants 1.62 in. (45 cm) As small as 3 mm
b
Musculoskeletal System
Appendix 427
Summary of the Movements of the Shoulder Joint and the Muscles Producing
Those Movements
a
Table III
Segmental
Movements Muscles Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Nerve
b
Flexion Deltoid (anterior Clavicle Middle of lateral Axillary nerve C5, 6
fibers) surface of shaft
of humerus
Pectoralis major Clavicle Lateral lip bicipital Medial and lateral C5, 6
(clavicular groove of humerus pectoral nerves
part) from brachial
plexus
Biceps brachii
Long head Supraglenoid Tuberosity of Musculocutaneous C5, 6
tubercle of scapula radius, deep fascia nerve
of forearm
Short head Coracoid process
of scapula
Coraco- Coracoid process Medial aspect of Musculocutaneous C5, 6, 7
brachialis of scapula shaft of humerus nerve
Extension Deltoid Spine of scapula Middle of lateral Axillary nerve C5, 6
(posterior surface of shaft
fibers) of humerus
Latissimus dorsi Iliac crest, lumbar Floor of bicipital Thoracodorsal C6, 7, 8
fascia, spines of groove of nerve
lower six thoracic humerus
vertebrae, lower
three or four ribs,
and inferior angle
of scapula
Teres major Lower third lateral Medial lip of Lower subscapular C6, 7
border of scapula bicipital groove nerve
of humerus
Abduction Middle fibers Acromion process Middle of lateral Axillary nerve C5, 6
of deltoid of scapula surface of shaft
of humerus
Supraspinatus Supraspinous fossa Greater tuberosity Suprascapular C4, 5, 6
of scapula of humerus nerve
Adduction Pectoralis major Sternum and upper Lateral lip of Medial and lateral C7, 8; T1
(sternal part) six costal bicipital groove pectoral nerves
cartilages of humerus
Latissimus dorsi Iliac crest, lumbar Floor of bicipital Thoracodorsal C6, 7, 8
fascia, spines of groove of humerus nerve
lower six thoracic
vertebrae, lower
three or four ribs,
inferior angle of
scapula
428 Appendix
(continued) Table III
Segmental
Movements Muscles Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Nerve
b
Teres major Lower third lateral Medial lip of Lower subscapular C6, 7
border of scapula bicipital groove nerve
of humerus
Teres minor Upper two thirds Greater tuberosity Axillary nerve C5, 6
lateral border of of humerus
scapula
Lateral Infraspinatus Infraspinous fossa Greater tuberosity Suprascapular C5, 6
rotation of scapula of humerus nerve
Teres minor Upper two thirds Greater tuberosity Axillary nerve C5, 6
lateral border of of humerus
scapula
Deltoid Spine of scapula Middle of lateral Axillary nerve C5, 6
(posterior surface of shaft
fibers) of humerus
Medial Subscapularis Subscapular fossa Lesser tuberosity Upper and lower C5, 6
rotation of humerus subscapular
nerves
Latissimus Iliac crest, lumbar Floor of bicipital Thoracodorsal C6, 7, 8
dorsi fascia, spines of groove of nerve
lower three or humerus
four ribs, inferior
angle of scapula
Teres major Lower third lateral Medial lip bicipital Lower subscapular C6, 7
border of groove of nerve
scapula humerus
Deltoid (anterior Clavicle Middle of lateral Axillary nerve C5, 6
fibers) surface of shaft
of humerus
a
Circumduction is a combination of all the movements described.
b
The predominant segmental nerve supply is indicated by boldface type.
Table III.
Musculoskeletal System
Appendix 429
Summary of the Movements of the Elbow Joint and the Muscles Producing
Those Movements
Table IV
Segmental
Movements Muscles Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Nerve
a
Flexion Brachialis Front of lower Coronoid process Musculocutaneous C5, 6
half of humerus of ulna nerve
Biceps brachii
Long head Supraglenoid Tuberosity of Musculocutaneous C5, 6
tubercle of radius, deep nerve
scapula fascia of forearm
Short head Coracoid process
of scapula
Brachioradialis Lateral Styloid process Radial nerve C5, 6, 7
supracondylar of radius
ridge of humerus
Pronator teres
Humeral head Medial epicondyle Lateral aspect of Median nerve C6, 7
of humerus shaft of radius
Ulnar head Coronoid process
of ulna
Extension Triceps
Long head Infraglenoid tubercle Olecranon Radial nerve C6, 7, 8
of scapula process of ulna
Lateral head Posterior surface of
shaft of humerus
Medial head Lower half of
posterior surface
of shaft of humerus
Anconeus Lateral epicondyle Olecranon Radial nerve C7, 8; T1
of humerus process of ulna
a
The predominant segmental nerve supply is indicated by boldface type.
430 Appendix
Summary of the Movements of the Wrist Joint and the Muscles Producing Those
Movements
Table V
Segmental
Movements Muscles Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Nerve
a
Flexion Flexor carpi Medial epicondyle Bases of second Median nerve C6, 7
radialis of humerus and third
metacarpal bones
Flexor carpi
ulnaris
Humeral head Medial epicondyle Pisiform bone, Ulnar nerve C7, 8
of humerus hook of hamate,
base of fifth
metacarpal bone
Ulnar head Olecranon process,
posterior border
of ulna
Palmaris longus Medial epicondyle Flexor Median nerve C7, 8
of humerus retinaculum,
palmar
aponeurosis
Flexor digitorum
superficialis
Humeroulnar Medial epicondyle Middle phalanx Median nerve C7, 8; T1
head of humerus, of medial four
coronoid process fingers
of ulna
Radial head Oblique line anterior
surface shaft of
radius
Flexor digitorum Anterior surface Distal phalanx Ulnar half C8; T1
profundus shaft of ulna, of medial four ulnar nerve,
interosseous fingers radial half
membrane median nerve
Flexor pollicis Anterior surface Distal phalanx Anterior C8; T1
longus shaft of radius of thumb interosseous
branch of
median nerve
Extension Extensor carpi Lateral supracondylar Base of second Radial nerve C6, 7
radialis longus ridge of humerus metacarpal bone
Extensor carpi Lateral epicondyle of Base of third Deep branch C7, 8
radialis brevis humerus metacarpal bone of radial nerve
Extensor carpi Lateral epicondyle Base of fifth Deep branch C7, 8
ulnaris of humerus metacarpal bone of radial nerve
Extensor Lateral epicondyle Middle and distal Deep branch of C7, 8
digitorum of humerus phalanges of radial nerve
medial four
fingers
Musculoskeletal System
Appendix 431
(continued) Table V
Segmental
Movements Muscles Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Nerve
a
Extensor indicis Shaft of ulna and Extensor Deep branch of C7, 8
interosseous expansion of radial nerve
membrane index finger
Extensor digiti Lateral epicondyle Extensor Deep branch of C7, 8
minimi of humerus expansion of radial nerve
little finger
Extensor pollicis Shaft of ulna and Base of distal Deep branch of C7, 8
longus interosseous phalanx of thumb radial nerve
membrane
Abduction Flexor carpi Medial epicondyle Bases of second Median nerve C6, 7
radialis of humerus and third
metacarpal bones
Extensor carpi Lateral Base of second Radial nerve C6, 7
radialis longus supracondylar metacarpal bone
ridge of humerus
Extensor carpi Lateral epicondyle Bases of third Deep branch of C7, 8
radialis brevis of humerus metacarpal bone radial nerve
Abductor pollicis Shafts of radius Base of first Deep branch of C7, 8
longus and ulna metacarpal bone radial nerve
Extensor pollicis Shaft of ulna and Base of distal Deep branch of C7, 8
longus interosseous phalanx of thumb radial nerve
membrane
Extensor pollicis Shaft of radius and Base of proximal Deep branch of C7, 8
brevis interosseous phalanx of thumb radial nerve
membrane
Adduction Flexor carpi
ulnaris
Humeral head Medial Pisiform bone, Ulnar nerve C7, 8
epicondyle of hook of
humerus hamate, base
of fifth
metacarpal bone
Ulnar head Olecranon process
of ulna
Extensor carpi Lateral epicondyle Base of fifth Deep branch of C7, 8
ulnaris of humerus metacarpal radial nerve
bone
a
The predominant segmental nerve supply is indicated by boldface type.
Musculoskeletal System
432 Appendix
Summary of the Movements of the Hip Joint and the Muscles Producing
Those Movements
a
Table VI
Segmental
Movements Muscles Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Nerve
b
Flexion Iliacus Iliac fossa Lesser trochanter Femoral nerve L2, 3
of femur
Psoas Body of twelfth Lesser trochanter Lumbar plexus L1, 2, 3
thoracic vertebra, of femur
transverse
processes, bodies
and intervertebral
discs of the five
lumbar vertebrae
Rectus femoris
Straight head Anterior inferior Patella Femoral nerve L2, 3, 4
iliac spine
Reflected head Ilium above
acetabulum
Sartorius Anterior superior Upper medial Femoral nerve L2, 3
iliac spine surface of shaft
of tibia
Extension Gluteus Outer surface of Iliotibial tract, Inferior gluteal L5; S1, 2
(a posterior maximus ilium, sacrum, gluteal nerve
movement coccyx, sacrotuber- tuberosity of
of the flexed ous ligament femur
thigh)
Biceps femoris Long head: ischial Head of fibula Tibial nerve L5; S1, 2
tuberosity (sciatic nerve)
Semitendinosus Ischial tuberosity Upper part of Tibial nerve L5; S1, 2
medial surface of (sciatic nerve)
shaft of tibia
Semimembra- Ischial tuberosity Medial condyle of Tibial nerve L5; S1, 2
nosus tibia (sciatic nerve)
Adductor magnus Ischial tuberosity Adductor tubercle Tibial nerve L2, 3, 4
of femur (sciatic nerve)
Abduction Gluteus medius Outer surface of Greater Superior gluteal L5; S1
ilium trochanter of nerve
femur
Gluteus minimus Outer surface of Greater Superior L5; S1
ilium trochanter of gluteal nerve
femur
Sartorius Anterior superior Upper medial Femoral nerve L2, 3
iliac spine surface of shaft
of tibia
Tensor fasciae Iliac crest Iliotibial tract Superior gluteal L4, 5
latae nerve
Piriformis Anterior surface of Greater Sacral plexus L5; S1, 2
sacrum trochanter of
femur
Appendix 433
(continued) Table VI
Segmental
Movements Muscles Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Nerve
a
Adduction Adductor longus Body of pubis Posterior surface Obturator nerve L2, 3, 4
of shaft of femur
Adductor brevis Inferior ramus of Posterior surface Obturator nerve L2, 3, 4
pubis of shaft of femur
Adductor magnus Inferior ramus of Posterior surface Obturator nerve L2, 3, 4
(adductor fibers) pubis, ramus of of shaft of femur,
ischium, ischial adductor tubercle
tuberosity of femur
Pectineus Superior ramus of Upper end of Femoral nerve L2, 3
pubis shaft of femur
Gracilis Inferior ramus of Upper part of Obturator nerve L2, 3
pubis, ramus of shaft of tibia on
ischium medial surface
Lateral Piriformis Anterior surface of Greater trochanter Sacral plexus L5; S1, 2
rotation sacrum of femur
Obturator Inner surface of Greater trochanter Sacral plexus L5; S1
internus obturator membrane of femur
Obturator Outer surface of Greater trochanter Obturator nerve L3, 4
externus obturator membrane of femur
Superior Spine of ischium Greater trochanter Sacral plexus L5; S1
gemellus of femur
Inferior gemellus Ischial tuberosity Greater trochanter Sacral plexus L5; S1
of femur
Quadratus Ischial tuberosity Quadrate tubercle Sacral plexus L5; S1
femoris on upper end of
posterior
surface of femur
Gluteus maximus Outer surface of Iliotibial tract, Inferior gluteal L5; S1, 2
ilium, sacrum, gluteal tuberosity nerve
coccyx, of femur
sacrotuberous
ligament
Medial Gluteus medius Outer surface of Greater trochanter Superior gluteal L5; S1
rotation ilium of femur nerve
Gluteus Outer surface of ilium Greater trochanter Superior gluteal L5; S1
minimus of femur nerve
Tensor fasciae Iliac crest Iliotibial tract Superior L4, 5
latae gluteal nerve
a
Circumduction is a combination of all the movements described.
b
The predominant segmental nerve supply is indicated by boldface type.
Musculoskeletal System
434 Appendix
Summary of the Movements of the Knee Joint and the Muscles
Producing Those Movements
Table VII
Segmental
Movements Muscles Origin Insertion Nerve Supply Nerve
a
Flexion Biceps femoris
Long head Ischial tuberosity Head of fibula Tibial nerve L5; S1, 2
Short head Shaft of femur Common
peroneal
nerve
Semitendinosus Ischial tuberosity Upper part of Tibial nerve L5; S1, 2
medial surface
of shaft of tibia
Semimem- Ischial tuberosity Medial condyle of Tibial nerve L5; S1, 2
branosus tibia
Gastrocnemius Medial, lateral Via Achilles tendon Tibial nerve S1, 2
condyles of into calcaneum
femur
Extension Quadriceps
femoris: rectus
femoris
Straight head Anterior inferior Patella Femoral nerve L2, 3, 4
iliac spine
Reflected head Ilium above
acetabulum
Vastus lateralis Upper end and Patella Femoral nerve L2, 3, 4
shaft of femur
Vastus medialis Upper end and Patella Femoral nerve L2, 3, 4
shaft of femur
Vastus inter- Shaft of femur Patella Femoral nerve L2, 3, 4
medius
Medial Sartorius Anterior superior Upper medial Femoral nerve L2, 3
rotation iliac spine surface of shaft
of tibia
Gracilis Interior ramus of Upper part of shaft Obturator nerve L2, 3
pubis, ramus of tibia on medial
of ischium surface
Lateral Biceps femoris
rotation Long head Ischial tuberosity Head of fibula Tibial nerve L5; S1, 2
Short head Shaft of femur Common L5; S1, 2
peroneal
nerve
a
The predominant segmental nerve supply is indicated by boldface type.
Musculoskeletal System
Appendix 435
Summary of the Movements of the Ankle Joint and the Muscles Producing
Those Movements
Table VIII
Nerve Segmental
Movements Muscles Origin Insertion Supply Nerve
a
Dorsiflexion Tibialis anterior Shaft of tibia, Medial cuneiform, Deep peroneal L4,5
interosseous base of first nerve
membrane metatarsal bone
Extensor hallucis Shaft of fibula, Base of distal Deep peroneal L5, S1
longus interosseous phalanx of great nerve
membrane toe
Extensor digitorum Shaft of fibula, Dorsal extensor Deep peroneal L5, S1
longus interosseous expansion of nerve
membrane lateral four toes
Peroneus tertius Shaft of fibula, Base of fifth Deep peroneal L5, S1
interosseous metatarsal bone nerve
membrane
Plantar- Gastrocnemius Medial, lateral Via Achilles tendon Tibial nerve S1,2
flexion condyles of into calcaneum
femur
Soleus Shaft of tibia Via Achilles tendon Tibial nerve S1,2
and fibula into calcaneum
Plantaria Lateral supra- Calcaneum Tibial nerve S1,2
condylar ridge
of femur
Peroneus longus Shaft of fibula Base of first Superficial L5; S1,2
metatarsal and peroneal nerve
medial cuneiform
Peroneus brevis Shaft of fibula Base of fifth Superficial L5; S1,2
metatarsal bone peroneal nerve
Tibialis posterior Shaft of tibia, Tuberosity of Tibial nerve L4,5
fibula, in- navicular
terosseous
membrane
Flexor digitorum Shaft of tibia Distal phalanges Tibial nerve S2,3
longus of lateral four toes
Flexor hallucis Shaft of fibula Base of distal Tibial nerve S2,3
longus phalanx of big toe
a
The predominant segmental nerve supply is indicated by boldface type.
Digestive System
436 Appendix
Lengths and Capacities
a
The curved course taken by a nasogastric tube from the cardiac orifice to the pylorus is usually
longer, 610 in. (1525 cm).
Table IX
Region (approx.) Lengths (approx.) Capacities (Approx.)
Esophagus 10 in. (25 cm)
Stomach
a
Lesser curvature 4.85.6 in. (1214 cm) 1,500 mL
Duodenum 10 in. (25 cm)
Jejunum 8 ft (2.4 M)
Ileum 12 ft (3.7 M)
Appendix 35 in. (813 cm)
Ascending colon 5 in. (13 cm)
Transverse colon 15 in. (38 cm)
Descending colon 10 in. (25 cm)
Sigmoid colon 1015 in. (2538 cm)
Rectum 5 in. (13 cm)
Anal canal 1.5 in. (4 cm)
Gallbladder 2.83.9 in. (710 cm) 3050 mL
Cystic duct 1.5 in. (3.8 cm)
Bile duct 3 in. (8 cm)
Urinary System
Lengths and Capacities
Table X
Capacity
Organ Lengths (approx.) (approx.)
Ureter 10 in. (25 cm)
Bladder 500 mL
Male urethra 8 in. (20 cm)
Penile 6 in. (15.7 cm)
Membranous 0.5 in. (1.25 cm)
Prostatic 1.25 in. (3 cm)
Female urethra 1.5 in. (3.8 cm)
Reproductive System
Dimensions Table XI
Organ Dimensions (approx.)
Male
Testis 2 1 in. (5 2.5 cm)
Vas deferens 18 in. (45 cm)
Penis (erect) 6 in. (15 cm)
Female
Ovary 1.5 0.75 in. (4 2 cm)
Uterine tube 4 in. (10 cm)
Uterus 3 2 1 in. (8 5 2.5 cm)
Vagina 3 in. (8 cm)
Embryology
Appendix 437
The Size and Weight of the
Developing Human Embryo
and Fetus
Table XII
Age of
Conception CrownRump
(weeks) Length (mm) Weight (g)
4 5 0.02
5 8
8 23 1
12 56 14
16 112 105
20 160 310
24 203 640
28 242 1,080
32 277 1,670
36 313 2,400
Full term 350 3,300
CD Figure APP-1 Critical times in the maturation of the human fetus during which
mutant genes, drugs, or environmental factors may alter normal development of specific
structures.
Reprinted with permission, Arey 1966.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- Hand and Foot AnatomyДокумент1 страницаHand and Foot AnatomyMike BozinОценок пока нет
- 500 Anatomy SBA (Pastest) PDFДокумент94 страницы500 Anatomy SBA (Pastest) PDFDr. Mohamed Elzaki100% (2)
- AnatomyДокумент34 страницыAnatomyShubham Hiralkar100% (2)
- SAQs AnatomyДокумент238 страницSAQs AnatomyDrHassan Ahmed Shaikh80% (5)
- Exam MCQ Clinanatomy 2022-23Документ21 страницаExam MCQ Clinanatomy 2022-23CHoudhary Hassan WarraichОценок пока нет
- Blood Supply of Whole BodyДокумент60 страницBlood Supply of Whole BodyProsanjit Majumder100% (1)
- Wrist Anatomy and Surgical Approaches: Roy Cardoso, MD, Robert M. Szabo, MD, MPHДокумент22 страницыWrist Anatomy and Surgical Approaches: Roy Cardoso, MD, Robert M. Szabo, MD, MPHMd Ahsanuzzaman PinkuОценок пока нет
- Bovine Anatomy An Illustrated Text 2nd EditionДокумент185 страницBovine Anatomy An Illustrated Text 2nd Editionluis feo100% (4)
- Kompartemen SindromДокумент9 страницKompartemen SindromPutri PratiwiОценок пока нет
- Ulnar Nerve AnatomyДокумент7 страницUlnar Nerve AnatomyAndrea AlavaОценок пока нет
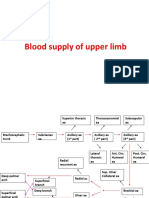
- Blood Supply of Upper LimbДокумент36 страницBlood Supply of Upper Limbteklay100% (2)
- Lec 11 UL Forarm Anterior CompartmentДокумент32 страницыLec 11 UL Forarm Anterior CompartmenthusseinОценок пока нет
- Hand AnatomyДокумент96 страницHand AnatomyaaamirrrОценок пока нет
- GROSS HSB A Prelim 2018Документ18 страницGROSS HSB A Prelim 2018nge257Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy PDFДокумент76 страницAnatomy PDFPredrag RacicОценок пока нет
- Summary of Gross PDFДокумент161 страницаSummary of Gross PDFPauline MakahamadzeОценок пока нет
- STUDY GUIDE-LOCOMOTOR-2019 1st YearДокумент30 страницSTUDY GUIDE-LOCOMOTOR-2019 1st YearhamdyyalyОценок пока нет
- Blood Vessels of Upper LimbДокумент23 страницыBlood Vessels of Upper Limbkhalid_shinasОценок пока нет
- Muscles of The Upper Limb - Listed Alphabetically Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery NotesДокумент10 страницMuscles of The Upper Limb - Listed Alphabetically Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery NotesAjay Pal NattОценок пока нет
- Ten Tips To Simplify The Spaghetti WristДокумент8 страницTen Tips To Simplify The Spaghetti WristSabina HritacОценок пока нет
- Dissection Anatomy Upper LimbДокумент71 страницаDissection Anatomy Upper LimbShivamОценок пока нет
- USMLE Step 1 Board Exam High Yield Anatomy For MedicineДокумент7 страницUSMLE Step 1 Board Exam High Yield Anatomy For Medicinesirp328100% (2)
- Anatomy MnemonicsДокумент39 страницAnatomy Mnemonicslynk7870% (1)
- UntitledДокумент378 страницUntitledSaransh JainОценок пока нет
- Mcem Anatomy MCQДокумент37 страницMcem Anatomy MCQMOHAMMED ANEEZОценок пока нет
- Intro To Ortho Anatomy PDFДокумент55 страницIntro To Ortho Anatomy PDFlanghalilafaОценок пока нет
- Chung, Kevin C. - Essentials of Hand Surgery-JP Medical Publishers (2015)Документ815 страницChung, Kevin C. - Essentials of Hand Surgery-JP Medical Publishers (2015)normОценок пока нет
- Master Anatomy ChartДокумент21 страницаMaster Anatomy ChartMonica Moya100% (4)
- Overview of The Anatomy of The Upper and Lower LimbsДокумент59 страницOverview of The Anatomy of The Upper and Lower LimbsCher TangОценок пока нет
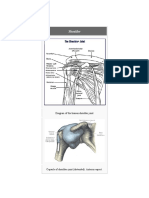
- Clinical Anatomy of Upper Limb Joints and MusclesДокумент92 страницыClinical Anatomy of Upper Limb Joints and Musclesgechanatomy100% (1)