Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Circuit Breaker Time
Загружено:
Brenda Naranjo Moreno0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
37 просмотров6 страницCircuit breakers time-current characteristic curve could be shaped to allow adjustment of individual circuit breakers for proper coordination between upstream and downstream protective devices. The basic adjustable functions are: Continuous Current (Ir) Continuous Current is the magnitude of current that a circuit breaker can carry without tripping. The short-time pickup function determines the amount of current the circuit breaker will carry for a short period of time. The long-time delay causes the breaker to wait a certain amount of time to allow temporary in
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документCircuit breakers time-current characteristic curve could be shaped to allow adjustment of individual circuit breakers for proper coordination between upstream and downstream protective devices. The basic adjustable functions are: Continuous Current (Ir) Continuous Current is the magnitude of current that a circuit breaker can carry without tripping. The short-time pickup function determines the amount of current the circuit breaker will carry for a short period of time. The long-time delay causes the breaker to wait a certain amount of time to allow temporary in
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
37 просмотров6 страницCircuit Breaker Time
Загружено:
Brenda Naranjo MorenoCircuit breakers time-current characteristic curve could be shaped to allow adjustment of individual circuit breakers for proper coordination between upstream and downstream protective devices. The basic adjustable functions are: Continuous Current (Ir) Continuous Current is the magnitude of current that a circuit breaker can carry without tripping. The short-time pickup function determines the amount of current the circuit breaker will carry for a short period of time. The long-time delay causes the breaker to wait a certain amount of time to allow temporary in
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 6
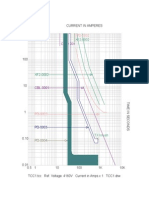
Circuit Breaker Time-Current
Characteristic Curve Made Easy
Circuit breakers time-current characteristic curve could be shaped to allow adjustment of individual
circuit breakers for proper coordination between upstream and downstream protective devices.
Time-Current Characteristics
The basic adjustable functions are:
Continuous Current (Ir)
Continuous Current
This is the magnitude of current that a circuit breaker can carry without tripping. Ir is a
percentage of the circuit breaker nominal rating (In).
Adjustment of this setting will vary the continuous current from about 20% to 100% of the
circuit breaker nominal rating (In).
Example:
In = 1000A
Adjusting the setting to 60% will make the maximum continuous current rating of the circuit
breaker to
= (60% x 1000) = 600 A
Long Time Delay
Long Time Delay
Long-time delay causes the breaker to wait a certain amount of time to allow temporary inrush
currents, such as starting a motor, to flow without tripping.
Usually, the time adjustment is on a multiple of the continuous current rating (Ir). A common
multiple is 6xIr as most motors draw current six (6) times its full load current during starting.
The setting depends on the motor driven load. The unit adjustment for this setting is seconds.
The long-time delay effects the position of an I
2
t slope which means that lower levels of
contiuous current setting will allow the circuit breaker to remain online for longer periods of
time.
Short Time Pickup
Short Time Pickup
Short-time pickup is used for discrimination or selective tripping. The short-time pickup
function determines the amount of current the circuit breaker will carry for a short period of
time, allowing downstream protective devices to clear short-circuits without tripping the
upstream device.
This setting could be adjustable from 1.5 to 10 times the trip unit continuous current setting (Ir).
For example, a 1000 ampere frame can be adjusted to trip anywhere from 1500 to 10,000 amps.
If this function is set to OFF position, the short-
time pickup and short-time delay will be disabled.
Short Time Delay
Short Time Delay
Short-time delay, used in conjunction with short-time pickup, controls the time duration before
a short-time pickup trip.
There are two modes:
Fixed time
A fixed instantaneous trip point, trips the breaker automatically and overrides any pre-
programmed settings.
I
2
t ramp
The I
2
t ramp mode is adjustable providing a short inverse time ramp. This allows better
coordination with downstream thermal-magnetic circuit breakers and fuses.
Instantaneous Pickup
Instantaneous Pickup
Instantaneous Pickup is used to trip the circuit breaker with no intentional delay at any current
between 2 and 40 times the breakers continuous ampere setting (I
r
).
Example:
Continuous Current Setting (I
r
) = 60% x I
n
= 600 A
Instantaneous pickup = 10 x I
r
= 10 x 600 = 6000 A
A setting higher than the fixed instantaneous override will automatically trips the breaker at the
fixed instantaneous override regardless of the instantaneous pickup setting.
Вам также может понравиться
- Unit 2. Presen SimlpleДокумент4 страницыUnit 2. Presen SimlpleBrenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- UNIT 53 Verb-IngДокумент4 страницыUNIT 53 Verb-IngBrenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- Unit 13 Present Perfect and Past 1 - BLUE BOOKДокумент3 страницыUnit 13 Present Perfect and Past 1 - BLUE BOOKBrenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- Unit 51auxiliary VerbДокумент2 страницыUnit 51auxiliary VerbBrenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- Unit 31 Must and CanДокумент3 страницыUnit 31 Must and CanBrenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- UNIT 50 Questions 2Документ4 страницыUNIT 50 Questions 2Brenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- UNIT 51 ToДокумент2 страницыUNIT 51 ToBrenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- Current in Amperes: PD-0003 PD-0003Документ1 страницаCurrent in Amperes: PD-0003 PD-0003Brenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- UNIT 53 Verb-IngДокумент4 страницыUNIT 53 Verb-IngBrenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- 1line001 DRWДокумент1 страница1line001 DRWBrenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- TCC2 2Документ1 страницаTCC2 2Brenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- Exercises Unit 49Документ4 страницыExercises Unit 49Brenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- Somebody Will Clean The Room LaterДокумент6 страницSomebody Will Clean The Room LaterBrenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- Current in Amperes: PD-0003 PD-0003Документ1 страницаCurrent in Amperes: PD-0003 PD-0003Brenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- UNIT 20. (I'm) Goig To (Do)Документ5 страницUNIT 20. (I'm) Goig To (Do)Brenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- Unit 9Документ8 страницUnit 9Brenda Naranjo Moreno100% (6)
- Unit 13 Present Perfect and Past 1 - BLUE BOOKДокумент3 страницыUnit 13 Present Perfect and Past 1 - BLUE BOOKBrenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- Supplementary ExercisesДокумент30 страницSupplementary ExercisesBrenda Naranjo Moreno33% (3)
- Infinitive Past Simple Past Participle TraducciónДокумент6 страницInfinitive Past Simple Past Participle TraducciónBrenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- Dear KarenДокумент2 страницыDear KarenBrenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- Infinitive Past Simple Past Participle TraducciónДокумент1 страницаInfinitive Past Simple Past Participle TraducciónBrenda Naranjo MorenoОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- New Mechanical Schedule (Weekly and Monthly)Документ31 страницаNew Mechanical Schedule (Weekly and Monthly)aeronkay20Оценок пока нет
- University of Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal SubjectДокумент40 страницUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal SubjectbobОценок пока нет
- Tubing Thread Type, External Upset Tubing, Yaosheng Non Upset Tubing ManufacturerДокумент2 страницыTubing Thread Type, External Upset Tubing, Yaosheng Non Upset Tubing ManufacturerEDWIN M.PОценок пока нет
- Dd311 Specification Sheet EnglishДокумент4 страницыDd311 Specification Sheet EnglishJose Antonio Sanchez SegoviaОценок пока нет
- Catalogo Unidad Condensadora YD360, 480, 600 AmericanaДокумент19 страницCatalogo Unidad Condensadora YD360, 480, 600 AmericanaCoordinador1 ServiciosОценок пока нет
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: MD Maruf Hossain, Mohd. Hasan AliДокумент9 страницRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: MD Maruf Hossain, Mohd. Hasan AliJuan MОценок пока нет
- Transistor (Ukr)Документ31 страницаTransistor (Ukr)Uday RaiОценок пока нет
- A Guide To Photovoltaic (PV) System Design and Installation: California Energy CommissionДокумент40 страницA Guide To Photovoltaic (PV) System Design and Installation: California Energy CommissionKuroko TetsuyaОценок пока нет
- Erturk 2008 Smart Mater. Struct. 17 065016 PDFДокумент15 страницErturk 2008 Smart Mater. Struct. 17 065016 PDFsuyОценок пока нет
- 6.1 Mastering IELTS Writing Task 1 (PDFeBook) PDFДокумент228 страниц6.1 Mastering IELTS Writing Task 1 (PDFeBook) PDFHarsh Patel100% (6)
- Fabric CuttingДокумент13 страницFabric CuttingShahjahanBadshaRony100% (1)
- Dextra Precast Pipe Racks Brochure 2020 ENДокумент5 страницDextra Precast Pipe Racks Brochure 2020 ENCivix VarixОценок пока нет
- Service Manual: (Gasoline & L.P. Gas)Документ86 страницService Manual: (Gasoline & L.P. Gas)julianmata67% (3)
- C-00 & Er 91april - May-2012Документ39 страницC-00 & Er 91april - May-2012John SandaОценок пока нет
- Tesla CoilДокумент23 страницыTesla CoilredfordОценок пока нет
- Formal Report Expt 5 ColloidsДокумент6 страницFormal Report Expt 5 ColloidsJessica Christel MaglalangОценок пока нет
- Your Guide To Hydraulic FracturingДокумент1 страницаYour Guide To Hydraulic FracturingMartin GriffinОценок пока нет
- Final Project ReportДокумент23 страницыFinal Project ReportMayank SainiОценок пока нет
- Shell Pakistan Stock in Trade: Horizontal AnalysisДокумент12 страницShell Pakistan Stock in Trade: Horizontal Analysisfahad pansotaОценок пока нет
- Biomedicalbenchmark™ © 2011 Ecri Institute. All Rights Reserved. 1Документ3 страницыBiomedicalbenchmark™ © 2011 Ecri Institute. All Rights Reserved. 1Chaphidzun NakMadridista SejaetieОценок пока нет
- GC - How It Works - Agilent - SusanPérezДокумент19 страницGC - How It Works - Agilent - SusanPérezsusanbperezОценок пока нет
- Ace3 0620.06 GB PDFДокумент12 страницAce3 0620.06 GB PDFduhgrandoОценок пока нет
- ShipRight - Design Code For Unmanned Marine Systems - 2017Документ39 страницShipRight - Design Code For Unmanned Marine Systems - 2017RISHABH JAMBHULKARОценок пока нет
- Why Buildings Fall Down How Structures FailДокумент60 страницWhy Buildings Fall Down How Structures FaillyeshiunОценок пока нет
- Retigo Vision CatalogueДокумент32 страницыRetigo Vision Cataloguesuonodimusica0% (1)
- A Project Report: Solar Cum Thermoelectric Refrigeration SystemДокумент27 страницA Project Report: Solar Cum Thermoelectric Refrigeration SystemPawan KumarОценок пока нет
- Discussion & Conclusion Dry Fractionation MuzДокумент4 страницыDiscussion & Conclusion Dry Fractionation MuzAhmad MuzammilОценок пока нет
- Operations Manual 18WДокумент137 страницOperations Manual 18Wto_john100% (1)
- ProductBrochure A35F A40F EN 21A1006561 2010-12Документ24 страницыProductBrochure A35F A40F EN 21A1006561 2010-12Muhammad Ridha FatriantaОценок пока нет
- RBK-1 Details For Relay SettingДокумент3 страницыRBK-1 Details For Relay SettingWinny MathewОценок пока нет