Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
AP Government Court Cases Flash Cards
Загружено:
nimishtodiАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AP Government Court Cases Flash Cards
Загружено:
nimishtodiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
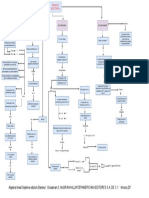
Fletcher v.
Peck
(1810)
McCulloch v.
Maryland (1819)
Gibbons v. Ogden
(1824)
Lochner v. NY
(1917)
Westcoast Hotels v.
Parrish (1937)
Heart of Atlanta
Motel v. US (1964)
South Dakota v. Dole
(1987)
United States v.
Lopez (1997)
Const: Article 1 Tax and Spend Clause,
Necessary and Proper Clause, Article 6
Supremacy Clause
State was trying to tax Federal Bank.
Supreme Court decides that National
Bank is Constitutional and that states cant
tax Federal Government. This case
strengthened Congressional power.
Const: Article 1- Contract Clause
sale was a binding contract, cannot be
invalidated even if illegally secured and as
a result the ruling lends further protection
to property rights against popular
pressures and is the earliest case of the
Court asserting its right to invalidate state
laws which are in conflict with or are
otherwise contrary to the Constitution.
Const: Amendment 14- Due Process
clause
Fourteenth Amendment protected an
individual's "general right to make a
contract in relation to his business. labor
law attempting to regulate the terms of
employment, and calling it an
"unreasonable, unnecessary and arbitrary
interference with the right and liberty of the
individual to contract."
Const: Article 1- Commerce Clause
"commerce," the Court held that
commerce is more than mere trafficthat
it is the trade of commoditiesit is also
intercourse. This broader definition
includes navigation. The Court interpreted
"among" as "intermingled with."
Intertrade between state could be
regulated by Congress
Const: Article 1- Commerce Clause
U.S. Congress could use the
Constitution's Commerce Clause power to
force private businesses to abide by the
Civil Rights Act of 1964. While it might
have been possible for Congress to
pursue other methods for abolishing racial
discrimination, the way in which Congress
did so, according to the Court, was
perfectly valid.
Upheld the constitutionality of minimum
wage legislation enacted by the State
of Washington, a Constitution permitted
the restriction of liberty of contract by state
law where such restriction protected the
community, health and safety or
vulnerable groups. Reverse of Lochner
Law
Const: Commerce Clause
Congress had broad lawmaking authority
under the Commerce Clause, the power
was limited, and did not extend so far from
"commerce" as to authorize the regulation
of the carrying of handguns, especially
when there was no evidence that carrying
them affected the economy on a massive
scale
Decided on the limitations the Constitution
places on the authority of the United
States Congress when it uses its authority
to influence the individual states in areas
of authority normally reserved to the
states. It upheld the constitutionality of a
federal statute that withheld federal funds
from states whose legal drinking age did
not conform to federal policy.
United States v.
Morrison (2000)
Smith v. Allwright
(1944)
Buckley v. Valeo
(1976)
Bush v. Gore (2000)
Citizens United v.
FEC (2010)
Baker v. Carr (1962)
Sims v. Reynolds
(1964)
Wesberry v. Sanders
(1964)
Const: 14
th
amendment Equal protection
clause
Smith challenged a law that required all
voters to be white. The Court agreed that
the law denied Smith his equal protection
under the law and overturned all-white
primaries. This case was a landmark
decision for voting rights.
Const: Article 1 Commerce Clause, 14th
amendment Power of Congress to
enforce equal protection under the law,
U.S. passed Violence Against Women Act
in 1994. Congress ruled that parts of the
VAWA were that gave victims of gender-
motivated violence to the right to sue in
federal court unconstitutional, because
Congress lacked authority to enact it
14
th
amendment Equal Protection
Clause, Article 2
Oversight of electors
the Florida Supreme Court ordered a
statewide manual recount. The Supreme
Court ruled that the statewide recount
violated the Equal Protection Clause
because there were different standards of
counting in different counties
Const: 1
st
amendment Freedom of
speech
In 1974, Congress amended the Federal
Election Campaign Act to add several
regulations on campaign contributions and
spending. Limitations on campaign
expenditures and independent
expenditures were struck down, saying
that campaign contributions and spending
were a form of political speech
Const: 14
th
amendment Equal Protection
Clause
Baker and other Tennessee citizens
alleged that a law designed to apportion
seats for the States General Assembly
was ignored. The Court agreed with Baker
and held that the Court does have
jurisdiction over matters of legislative
apportionment and other state
administration matters.
Const: 1
st
amendment Free Speech
The nonprofit group Citizens United
wanted to air a film critical of Hillary
Clinton. The Court found portions of the
BCRA unconstitutional (restrictions
on corporations (including nonprofit
corporations) and unions from spending
on "electioneering communications") Court
ruled that the law violated free speech
rights of corporations.
Const: Article 1 Section 2
decision requires each state to draw its
U.S. Congressional districts so that they
are approximately equal in population as
meant by the framers in the by the
people phrase.
effectively reduced the representation of
rural districts
Const: Equal Protection Clause
state legislature districts had to be roughly
equal in population. struck down state
senate inequality based their decision on
the principle of "one person, one vote"
Shaw v. Reno (1993)
Clinton v. New York
City (1998)
United States v.
Nixon (1973)
Immigration and
Naturalization
Service v. Chadha
(1983)
Marbury v. Madison
(1803)
McCulloch v.
Maryland (1819)
Gibbons v. Odgen
(1824)
Dred Scott v.
Sanford (1857)
Const: Presentment Clause
line-item veto as granted in the Line Item
Veto Act of 1996 violated the Presentment
Clause because it gave president the
power to unilaterally amend or repeal
parts of statutes that had been duly
passed by Congress
Const: Equal Protection Clause
redistricting based on race must be held to
a standard of strict scrutiny under
the equal protection clause. On the other
hand, bodies doing redistricting must be
conscious of race to the extent that they
must ensure compliance with the Voting
Rights Act.
Const: Separation of Powers
the one-house legislative veto violated the
constitutional separation of powers
Congress may not promulgate a statute
granting to itself a legislative veto over
actions of the executive branch
inconsistent with
the bicameralism principle and
Presentment Clause of the United States
Constitution.
Const: Article II- Separation of Powers
The Court stated that the doctrine of
executive privilege entitles the president to
confidentiality from the courts if the
evidence involves matters of national
security or other sensitive information, but
the president cannot withhold evidence
involving non-sensitive information when
needed for a criminal investigation.
Const: Article III
Created judicial review The landmark
decision helped define the boundary
between the constitutionally
separate executive and judicial branches.
Said that the federal government had no
power to regulate slavery in the territories,
and that people of African descent (both
slave and free) were not protected by
the Constitution and were not U.S.
citizens.
Вам также может понравиться
- Panama Canal PresentationДокумент1 страницаPanama Canal PresentationnimishtodiОценок пока нет
- Panama Canal Note Taking Guide and PaperДокумент2 страницыPanama Canal Note Taking Guide and PapernimishtodiОценок пока нет
- Griswold V Connecticut Court InfoДокумент1 страницаGriswold V Connecticut Court InfonimishtodiОценок пока нет
- AP US Government Flash CardsДокумент9 страницAP US Government Flash Cardsnimishtodi100% (1)
- Int Mat ModДокумент209 страницInt Mat ModDeepak Sakkari100% (1)
- Intro To ModelДокумент14 страницIntro To ModelAnuta CostinelОценок пока нет
- Student Solutions Manual For Introduction To Probability With Statistical ApplicationsДокумент58 страницStudent Solutions Manual For Introduction To Probability With Statistical Applicationsnimishtodi100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- Composition PsychologyДокумент1 страницаComposition PsychologymiguelbragadiazОценок пока нет
- Children's LiteratureДокумент13 страницChildren's Literaturerexson de villaОценок пока нет
- Machiavelli's Political Philosophy and Jamaican PoliticsДокумент2 страницыMachiavelli's Political Philosophy and Jamaican PoliticsAndre RobinsonОценок пока нет
- ERP ConceptsДокумент27 страницERP ConceptsPranav JainОценок пока нет
- The Normal Distribution and Sampling Distributions: PSYC 545Документ38 страницThe Normal Distribution and Sampling Distributions: PSYC 545Bogdan TanasoiuОценок пока нет
- Right To Information: National Law University AND Judicial Academy, AssamДокумент20 страницRight To Information: National Law University AND Judicial Academy, Assamsonu peterОценок пока нет
- How A Type 4 Multiverse WorksДокумент4 страницыHow A Type 4 Multiverse WorksIdkОценок пока нет
- Ingrid Gross ResumeДокумент3 страницыIngrid Gross Resumeapi-438486704Оценок пока нет
- D3Документ2 страницыD3zyaОценок пока нет
- Spaces For Conflict and ControversiesДокумент5 страницSpaces For Conflict and ControversiesVistalОценок пока нет
- RMC No. 23-2007-Government Payments WithholdingДокумент7 страницRMC No. 23-2007-Government Payments WithholdingWizardche_13Оценок пока нет
- AN6001-G16 Optical Line Terminal Equipment Product Overview Version AДокумент74 страницыAN6001-G16 Optical Line Terminal Equipment Product Overview Version AAdriano CostaОценок пока нет
- Order of Nine Angles: RealityДокумент20 страницOrder of Nine Angles: RealityBrett StevensОценок пока нет
- Solaris Hardening Guide v1Документ56 страницSolaris Hardening Guide v1GusGualdОценок пока нет
- Faculty of Computer Science and Information TechnologyДокумент4 страницыFaculty of Computer Science and Information TechnologyNurafiqah Sherly Binti ZainiОценок пока нет
- DIN EN 12516-2: January 2015Документ103 страницыDIN EN 12516-2: January 2015ReytingОценок пока нет
- Jane AustenДокумент2 страницыJane Austendfaghdfo;ghdgОценок пока нет
- The Confederation or Fraternity of Initiates (1941)Документ82 страницыThe Confederation or Fraternity of Initiates (1941)Clymer777100% (1)
- CHP 11: Setting Goals and Managing The Sales Force's PerformanceДокумент2 страницыCHP 11: Setting Goals and Managing The Sales Force's PerformanceHEM BANSALОценок пока нет
- Bruxism Hypnosis Script No. 2Документ12 страницBruxism Hypnosis Script No. 2Eva Jacinto100% (2)
- Posterior Cranial Fossa Anesthetic ManagementДокумент48 страницPosterior Cranial Fossa Anesthetic ManagementDivya Rekha KolliОценок пока нет
- Algebra Lineal Septima Edicion Stanley I. Grossman S. Mcgraw-Hilliinteramericana Editores S.A. de C.V Mexico, DFДокумент1 страницаAlgebra Lineal Septima Edicion Stanley I. Grossman S. Mcgraw-Hilliinteramericana Editores S.A. de C.V Mexico, DFJOSE JULIAN RAMIREZ ROJASОценок пока нет
- Sokkia GRX3Документ4 страницыSokkia GRX3Muhammad Afran TitoОценок пока нет
- Khenpo Tsultrim Gyamtso Rinpoche - Meditation On EmptinessДокумент206 страницKhenpo Tsultrim Gyamtso Rinpoche - Meditation On Emptinessdorje@blueyonder.co.uk100% (1)
- CDS11412 M142 Toyota GR Yaris Plug-In ECU KitДокумент19 страницCDS11412 M142 Toyota GR Yaris Plug-In ECU KitVitor SegniniОценок пока нет
- 3RD Last RPHДокумент5 страниц3RD Last RPHAdil Mohamad KadriОценок пока нет
- Disciplinary Literacy Strategies To Support Transactions in Elementary Social StudiesДокумент11 страницDisciplinary Literacy Strategies To Support Transactions in Elementary Social Studiesmissjoseph0803Оценок пока нет
- Co-Publisher AgreementДокумент1 страницаCo-Publisher AgreementMarcinОценок пока нет
- Waa Sik Arene & Few Feast Wis (FHT CHT Ste1) - Tifa AieaДокумент62 страницыWaa Sik Arene & Few Feast Wis (FHT CHT Ste1) - Tifa AieaSrujhana RaoОценок пока нет
- Money Habits - Saddleback ChurchДокумент80 страницMoney Habits - Saddleback ChurchAndriamihaja MichelОценок пока нет