Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Carbohydrates 2
Загружено:
isprikitik3Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Carbohydrates 2
Загружено:
isprikitik3Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
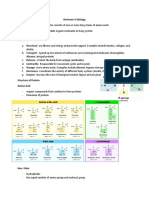
CARBOHYDRATES
Polysaccharides, glycosaminoglycans,
glycoproteins and proteoglycans
Antibiotic glycosides
Polysaccharide
Classes
According to structure homopolysaccharides
and heteropolysaccharides
According to function storage, structural and
recognition
Cellulose
the most abundant natural polymer on earth
the principal strength and support of trees
and plants
can also be soft and fuzzy - in cotton
Cellulose glucose polymer, structural function in plant
cell wall, insoluble and not digestible in human gut
Dietary fiber (roughage)
Complex carbohydrates with some protein
components
Soluble fiber complex starches amylopectins
and other pectins
Insoluble fiber contains cellulose
Importance of dietary fiber
Promotes peristaltic movement, decreasing
transit time in the gut
Binds toxins and carcinogens, reducing colon
and other cancers
Binds cholesterol, reducing blood cholesterol
Termites can digest the cellulose in
wood, and cattle can digest the
cellulose in grass, because bacteria in
their digestive tracts produce the
enzyme cellulase, which hydrolyzes the
-glycosidic linkage in cellulose.
Chitin
Repeating monomer N-acetyl--D-
glucosamine
Found in exoskeleton of insects and
crustaceans
Found in cell walls of yeast, fungi and algae
Other Structural Polysaccharides
Alginates - Ca-binding polymers in algae
Agarose and agaropectin - galactose polymers
Pectin- another component of plant cell walls
galacturonic acid polymer
Bacterial cell walls
An example of peptidoglycan in S. aureus
Heteropolysaccharides linked by peptides
(tetrapeptide and pentapeptide
Disaccharide unit has N-acetylmuramic acid
and N-acetylglucosamine
The structure of the
peptidoglycan structure of
bacterial cell wall of S.
aureus
Starch
Electron micrograph of starch
granules in plant cells
Has 2 forms amylose (10-30%)
and amylopectin (70-90%)
Amylose (1,4) links with one
reducing end
Amylopectin branches every 12-
30 residues
Branches provide a mechanism
for quickly releasing (or storing)
glucose units for (or from)
metabolism
Amylose and Amylopectin
The starch-iodine complex.
Amylose occurs as a helix with
six residues per turn. In the
starch-iodine complex, the
iodine molecules are parallel to
the long axis of the helix. Four
turns of the helix are shown
here. Six turns of the helix,
containing 36 glucosyl residues,
are required to produce the
characteristic blue color of the
complex.
Glycogen
Electron micrograph of
glycogen granules in animal
cells
constitutes up to 10% of liver
mass and 1-2% of muscle
mass
is stored energy for the
organism
Highly branched structure
branches every 8-12 residues
A comparison of the degrees of branching in amylopectin and glycogen.
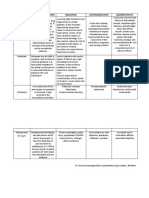
Glycosaminoglycans
Polysaccharide in which one of the sugars in
the repeating disaccharide is an amino sugar
and the other sugar is negatively charge due
to a sulfate or a carboxylic group
Components of proteoglycans
Serve important functions in cells and tissues
glycosaminoglycans
Chondroitin sulfates and keratan sulfate
components of connective tissues;
Heparin a natural anticoagulant, prevents
blood clot
Hyaluronic acid a component of vitreous
humor of the eye and the lubricating fluid of
the joints
Proteoglycans
A family of glycoproteins whose carbohydrate moeities
are predominantly glycosaminoglycans attached to ser
residues in the protein
Functions interact with other molecules through
receptor domains in the cell membrane; link components
in the extracellular matrix; binds cells in the extracellular
matrix; modulate cell growth processes
Examples
Versican has 2409 amino acid residues
Serglycin has alternatin ser and gly residues
Decorin small proteoglycan secreted by fibroblast and
found in the extracellular matrix of connective tissues
Syndecan transmembrane proteoglycan
Cartilage proteoglycan responsible for flexibility and
resiliency
Proteoglycans
Hyaluronicacid
forms the
backbone of
proteoglycan
structures such
as those found in
cartilage.
Glycoproteins
Glycoproteins contain carbohydrate units
covalently bonded to a polypeptide chain
antibodies are glycoproteins
Oligosaccharide portion of glycoproteins act as
antigenic determinants
Among the first antigenic determinants discovered
were the blood group substances
In the ABO system, individuals are classified according
to four blood types: A, B, AB, and O
At the cellular level, the biochemical basis for this
classification is a group of relatively small membrane-
bound carbohydrates
Glycoproteins
Fish in the
Antartic is
prevented from
freezing
because of this
glycoprotein
Glycoproteins as antigen determinants
(distinction between blood group
types depend on the oligosaccharide
Вам также может понравиться
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Complex CarbohydratesДокумент47 страницComplex CarbohydratesumamaheshcoolОценок пока нет
- Polysaccharides 3Документ37 страницPolysaccharides 3King of Science ytОценок пока нет
- CARBOHYDRATESPART2Документ25 страницCARBOHYDRATESPART2France Jan First SaplacoОценок пока нет
- Heteropolysaccharides Lecture For 1st Yr MBBS by DR Waseem KausarДокумент20 страницHeteropolysaccharides Lecture For 1st Yr MBBS by DR Waseem KausarIMDCBiochem67% (6)
- 1 Macromolecule 2ndQДокумент82 страницы1 Macromolecule 2ndQAllysa ChanОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrates NotesДокумент24 страницыCarbohydrates Notesapi-178321548Оценок пока нет
- CarbsДокумент36 страницCarbsRalph FalculanОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrates: Chapter 7 (Part II)Документ19 страницCarbohydrates: Chapter 7 (Part II)Omer KareemОценок пока нет
- BIOCHEMISTRYДокумент12 страницBIOCHEMISTRYZebina GenoringОценок пока нет
- BIOMOLECULES (Part 2) - CARBOHYDRATESДокумент7 страницBIOMOLECULES (Part 2) - CARBOHYDRATESAmrit SinghОценок пока нет
- Chem ReportДокумент43 страницыChem ReportMarielle VentulaОценок пока нет
- Figure 7.16 Acetals and Ketals Can Be Formed From Hemiacetals and Hemiketals, RespectivelyДокумент29 страницFigure 7.16 Acetals and Ketals Can Be Formed From Hemiacetals and Hemiketals, RespectivelylklkelwlОценок пока нет
- CarbohydratesДокумент16 страницCarbohydratessabreen hiresОценок пока нет
- Block 1 SummaryДокумент230 страницBlock 1 Summarymelisha.uysОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry: A Short CourseДокумент31 страницаBiochemistry: A Short CourseEli JohnsonОценок пока нет
- Chap 2 Unit 2Документ39 страницChap 2 Unit 2harshit khareОценок пока нет
- Lecture4 BiochemistryДокумент35 страницLecture4 BiochemistryEssam HassanОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrates PDFДокумент31 страницаCarbohydrates PDFDara Arabella AndalesОценок пока нет
- Biological+Macromolecules KalmaДокумент40 страницBiological+Macromolecules Kalmajudy andradeОценок пока нет
- CarbohydratemetabolismДокумент88 страницCarbohydratemetabolismEthio funОценок пока нет
- Metabolisme 2017Документ57 страницMetabolisme 2017rini dwi wahyuningsihОценок пока нет
- OutputДокумент12 страницOutputMarielle VentulaОценок пока нет
- Biographic of YogiДокумент22 страницыBiographic of YogiKaveen VijayОценок пока нет
- CarbohydratesДокумент22 страницыCarbohydratesgifty NambeyeОценок пока нет
- Reviewer in Biology Protein-A Large Macromolecules Consists of One or More Long Chains of Amino AcidsДокумент9 страницReviewer in Biology Protein-A Large Macromolecules Consists of One or More Long Chains of Amino AcidsDanilo PerezОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrate Part IДокумент32 страницыCarbohydrate Part IHamza QaziОценок пока нет
- ScienceДокумент43 страницыScienceK Sai ShankarОценок пока нет
- Cell PhysiologyДокумент45 страницCell PhysiologyHimani JhaОценок пока нет
- CarbohydrateДокумент43 страницыCarbohydrateHaleem HafizОценок пока нет
- Chem ReportДокумент58 страницChem ReportMarielle VentulaОценок пока нет
- CARBOHYDRATESДокумент5 страницCARBOHYDRATESChristine Kylene AycardoОценок пока нет
- CarbohidratosДокумент8 страницCarbohidratosElena OlmedoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 - Carbohydrates: MonosaccharidesДокумент5 страницChapter 8 - Carbohydrates: MonosaccharidesAlexis MunyentwaliОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrate Lect - OkkkkkДокумент51 страницаCarbohydrate Lect - OkkkkkM.AhmedОценок пока нет
- 2 CH 3 and 4 Su 2010Документ55 страниц2 CH 3 and 4 Su 2010Isis BaltodanoОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1B. Introduction To BiochemistryДокумент73 страницыLecture 1B. Introduction To BiochemistryAngella Reece IsraelОценок пока нет
- BIO 001 2nd LectДокумент62 страницыBIO 001 2nd LectDavid AkinwandeОценок пока нет
- GlycosaminoglycansДокумент31 страницаGlycosaminoglycansAmal100% (1)
- Carbohydrate Classification of Carbohydrate Metabolism and Regulation of CarbohydrateДокумент14 страницCarbohydrate Classification of Carbohydrate Metabolism and Regulation of CarbohydratesukОценок пока нет
- Notes in Biochemistry, Biotechnology, MicrobiologyДокумент4 страницыNotes in Biochemistry, Biotechnology, MicrobiologyiyarashanazОценок пока нет
- Biopolymer 170227202537Документ76 страницBiopolymer 170227202537aminsuhadiОценок пока нет
- Digestion & Metabolism of Carbohydrate, Fat and Protein in Non-RuminantsДокумент62 страницыDigestion & Metabolism of Carbohydrate, Fat and Protein in Non-Ruminantsrana adnan ejazОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrates ClassificationДокумент20 страницCarbohydrates Classificationzikri manggala putraОценок пока нет
- CarbohydratesДокумент77 страницCarbohydratesJey TeeОценок пока нет
- Complex CarbohydratesДокумент34 страницыComplex Carbohydratesa30139286Оценок пока нет
- The Plant Cell WallДокумент56 страницThe Plant Cell WallAngeline BayudanОценок пока нет
- 1142 L6 CarbohydratesДокумент27 страниц1142 L6 CarbohydratesjanindujayathmaОценок пока нет
- 6 BiomoleculesДокумент78 страниц6 BiomoleculesPrecious Ryza G. BautistaОценок пока нет
- Role of Organelles in The Metabolism 141221Документ44 страницыRole of Organelles in The Metabolism 141221Erdem Altun100% (1)
- Chemistry of Carbohydrates 2023Документ37 страницChemistry of Carbohydrates 2023andrade.sanchithaОценок пока нет
- The Cell: Composition, Structure and FunctionДокумент50 страницThe Cell: Composition, Structure and FunctionJally Mae Catam-isanОценок пока нет
- L-6 - Biomolecules-Feb 24, 2020Документ60 страницL-6 - Biomolecules-Feb 24, 2020Sunil YadavОценок пока нет
- UNIT II Glycoproteins: (Chapter 46 - Harper's)Документ6 страницUNIT II Glycoproteins: (Chapter 46 - Harper's)Aine CebedoОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Midterm Carbohydrates: ClassificationsДокумент21 страницаBiochemistry Midterm Carbohydrates: ClassificationsArah Lyn ApiagОценок пока нет
- Pre Test: Prepared By: Patricia PradoДокумент51 страницаPre Test: Prepared By: Patricia PradoLovely AlosadoОценок пока нет
- UPRB Biol 3011 Cap 3 2022Документ104 страницыUPRB Biol 3011 Cap 3 2022Alexander FigueroaОценок пока нет
- Glycoproteins and Proteoglycans TTVДокумент34 страницыGlycoproteins and Proteoglycans TTVcraigОценок пока нет
- CarbohydratesДокумент39 страницCarbohydratesWardah AliОценок пока нет
- Ao Final ProgramДокумент16 страницAo Final Programisprikitik3Оценок пока нет
- Drugs Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse EffectsДокумент2 страницыDrugs Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effectsisprikitik3Оценок пока нет
- Evaluation - For External Trainings 06222017Документ1 страницаEvaluation - For External Trainings 06222017isprikitik3Оценок пока нет
- God's Creation: Christianity Is An Abrahamic, Monotheistic Religion Based On The Life and OralДокумент2 страницыGod's Creation: Christianity Is An Abrahamic, Monotheistic Religion Based On The Life and Oralisprikitik3Оценок пока нет
- Biochemistry 1.6 - ABO Blood Typing and Crossmatching (A1 Group 6)Документ68 страницBiochemistry 1.6 - ABO Blood Typing and Crossmatching (A1 Group 6)isprikitik3Оценок пока нет
- Crown Lengthening of ToothДокумент4 страницыCrown Lengthening of Toothisprikitik3Оценок пока нет
- Recommendation LetterДокумент1 страницаRecommendation Letterisprikitik3Оценок пока нет
- Request LetterДокумент1 страницаRequest Letterisprikitik3Оценок пока нет
- Individual Reflections Format (CPH)Документ2 страницыIndividual Reflections Format (CPH)isprikitik3Оценок пока нет
- Clinical Chemistry (Lecture) - PrelimsДокумент12 страницClinical Chemistry (Lecture) - Prelimsisprikitik3100% (1)
- ImmunityДокумент70 страницImmunityisprikitik30% (2)
- MycologyДокумент3 страницыMycologyisprikitik3Оценок пока нет
- Must Knows IIДокумент3 страницыMust Knows IIisprikitik3Оценок пока нет
- Must Knows IДокумент38 страницMust Knows Iisprikitik3Оценок пока нет
- EN AST BAOSR6x09 USДокумент2 страницыEN AST BAOSR6x09 UScarineОценок пока нет
- Section C: Half Yearly Examination 2022-23 Biotechnology Paper-1 (Theory)Документ6 страницSection C: Half Yearly Examination 2022-23 Biotechnology Paper-1 (Theory)xipilev161Оценок пока нет
- MAximizing Protein Value: Impact of Enzyme On Poultry CultivationДокумент28 страницMAximizing Protein Value: Impact of Enzyme On Poultry CultivationHeru DumadiОценок пока нет
- Cell Membrane StructureДокумент9 страницCell Membrane StructureBeyhОценок пока нет
- Glycolysis SummaryДокумент3 страницыGlycolysis Summaryapi-327731714Оценок пока нет
- PharmacodynamicsДокумент18 страницPharmacodynamicsApurba Sarker ApuОценок пока нет
- Workshop Realtime Ready - CostДокумент129 страницWorkshop Realtime Ready - CostMia AdhaОценок пока нет
- F-09-05 Manual Instruire Medicala Si de Produs MAI 2022Документ54 страницыF-09-05 Manual Instruire Medicala Si de Produs MAI 2022Silvia GОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 Proteins and Their SynthesisДокумент58 страницChapter 9 Proteins and Their SynthesissujsamОценок пока нет
- Metabolic Biochemistry: 1 Dr. Suheir EreqatДокумент20 страницMetabolic Biochemistry: 1 Dr. Suheir EreqatIbrahim BarhamОценок пока нет
- Protein Breads: Nutrition FactsДокумент2 страницыProtein Breads: Nutrition FactsD.ElderОценок пока нет
- Bandeali-Farmer2012 Article High-DensityLipoproteinAndAtheДокумент7 страницBandeali-Farmer2012 Article High-DensityLipoproteinAndAtheDainius JakubauskasОценок пока нет
- hw499 - Unit 4 AssignmentДокумент10 страницhw499 - Unit 4 Assignmentapi-546774909Оценок пока нет
- BIO307 Lecture 7 (Enzyme Kinetics III)Документ11 страницBIO307 Lecture 7 (Enzyme Kinetics III)Phenyo Mmereki100% (2)
- Dyslipidemia: Darmono SSДокумент35 страницDyslipidemia: Darmono SSLa Ode Rinaldi0% (1)
- Free Radicals and Antioxidants 071222Документ44 страницыFree Radicals and Antioxidants 071222desyОценок пока нет
- Lecture 17-Cell BiologyДокумент46 страницLecture 17-Cell BiologyJhon Jairo SarmientoОценок пока нет
- BCM 2522 L1-MinДокумент15 страницBCM 2522 L1-MinLutendo Assurance MadzivhaaОценок пока нет
- Genetic Code 2020Документ20 страницGenetic Code 2020PAVITHRA SОценок пока нет
- Luna Universal QPCR & RT-QPCR: Now Includes Luna Cell Ready Module and KitsДокумент12 страницLuna Universal QPCR & RT-QPCR: Now Includes Luna Cell Ready Module and KitsAndreea MunteanuОценок пока нет
- 4-Bio Factsheets - Protein SynthesisДокумент4 страницы4-Bio Factsheets - Protein SynthesisAbir OmarОценок пока нет
- Ch450 and Ch451: Biochemistry - Defining Life at The Molecular LevelДокумент19 страницCh450 and Ch451: Biochemistry - Defining Life at The Molecular LevelHasan AnandaОценок пока нет
- Polymerase Chain ReactionДокумент34 страницыPolymerase Chain Reactionmokshgoyal2597100% (4)
- Nutritional Requirements of Poultry - Poultry - Merck VeterinarДокумент23 страницыNutritional Requirements of Poultry - Poultry - Merck VeterinarSamapanОценок пока нет
- Shrimps - A Nutritional PerspectiveДокумент6 страницShrimps - A Nutritional PerspectiveUchida Titis Sari DewiОценок пока нет
- SC 6243Документ1 страницаSC 6243Faizah Dwi TirtasariОценок пока нет
- Paper1 H Influenzae PDFДокумент19 страницPaper1 H Influenzae PDFRoseОценок пока нет
- ATP-ADP CycleДокумент1 страницаATP-ADP CycleAlvin DenadoОценок пока нет
- Basics of Genome SequencingДокумент10 страницBasics of Genome Sequencingk.sachinОценок пока нет
- 2012 AkДокумент14 страниц2012 AkSamuel RobertsОценок пока нет