Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Tes Phono Logical Disorders in Children
Загружено:
megspandiАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Tes Phono Logical Disorders in Children
Загружено:
megspandiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
7216 ASHA 2200 Research Boulevard, Rockville, MD 20850 Phone: 301-296-5700 Fax: 301-296-5777
AMERICAN
SPEECH-LANGUAGE -
HEARING
ASSOCIATION
AMERICAN
SPEECH-LANGUAGE -
HEARING
ASSOCIATION
Treatment Efficacy Summary
Phonological Disorders in
Children
A phonological disorder is a deficit
in the production of speech sounds.
It may reflect an inability to articu-
late speech sounds correctly or to
understand differences among
speech sounds. Phonological
disorders in children can result from
physical or organic causes or may be
functional in nature. Phonological
disorders are among the most preva-
lent communication disabilities diag-
nosed in preschool and school-aged
children, affecting 10% of this popu-
lation. Children with phonological
disorders are also at risk for reading
and writing disabilities. If left unre-
solved, phonological disorders have
long-term consequences that may
interfere with an individual's future
social, academic, and vocational
well-being, largely resulting from
persistent, reduced intelligibility of
speech.
Clinical evidence has shown that
children with phonological disor-
ders benefit from treatment provid-
ed by speech-language pathologists.
The benefits of effective phonologi-
cal treatments have been widely doc-
umented in clinical and experimen-
tal studies dating from the 1960s.
i
According to data collected from
ASHA's National Outcomes
Measurement System (NOMS), 70%
of preschool-aged children who
received phonological treatment
exhibited improved intelligibility
and communication functioning.
ii
Moreover, approximately one half of
the children who were unintelligible
to familiar and/or unfamiliar people
at the beginning of treatment
progressed to a level where they
were understandable to all listeners.
The amount of treatment had a
significant impact on outcome. The
preschoolers who achieved intelligi-
ble speech received roughly twice as
much treatment as those children
who remained unintelligible.
The speech-language pathologist
assesses the phonological disorder
and develops a treatment plan to
correct speech sound production.
The goal of treatment is to improve
accuracy and use of speech sounds
to achieve maximum intelligibility in
both single words and connected
speech, as well as across all settings
in which children communicate.
There are a number of acceptable
treatment approaches. A single treat-
ment approach is not endorsed over
others. Each clinically accepted
method has been shown to result in
improved accuracy and use of
speech sounds.
i
Sommers, R. (1992). A review and critical analysis of treatment research
related to articulation and phonological disorders. Journal of
Communication Disorders, 25, 3-22.
ii
ASHA National Center for Treatment Effectiveness in Communication
Disorders (2003). ASHA Special Interest Division 1, Language Learning
and Education; Steering Committee (July 2003).
Contributor:
Judith Gierut, PhD
Indiana University
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- This Icon: Go Forwards Go Backwards ExitДокумент27 страницThis Icon: Go Forwards Go Backwards ExitrockxanderОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Research DesignДокумент28 страницResearch DesignnivojromafОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Non Parametric Test-1Документ26 страницNon Parametric Test-1megspandiОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Ethics in Research and PublicationДокумент5 страницEthics in Research and PublicationmegspandiОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Analytical Methods For Information Systems Professionals: Week 7 Lecture 2 Qualitative ResearchДокумент23 страницыAnalytical Methods For Information Systems Professionals: Week 7 Lecture 2 Qualitative ResearchmegspandiОценок пока нет
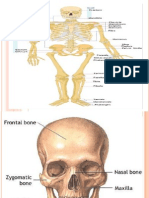
- Human SkeletonДокумент6 страницHuman SkeletonmegspandiОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- MuseumsДокумент15 страницMuseumsmegspandiОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Annotated Bibliography On Internet AddictionДокумент4 страницыAnnotated Bibliography On Internet AddictionJanet Martel100% (3)
- 194-Article Text-295-1-10-20191216Документ6 страниц194-Article Text-295-1-10-20191216Helda Aida PermataОценок пока нет
- Running Head: Writing A Report About Academic Self - Discipline QuestionnaireДокумент23 страницыRunning Head: Writing A Report About Academic Self - Discipline QuestionnaireAmanda AnandythaОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Module 11 VygotskyДокумент7 страницModule 11 Vygotskyqueene rose ihara100% (1)
- Principles and Methods of Teaching Syllabus 16Документ7 страницPrinciples and Methods of Teaching Syllabus 16sinayanan83% (12)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Remedial Instruction in Reading Definition of TermsДокумент15 страницRemedial Instruction in Reading Definition of TermsAnaОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Dissociation: Dissociated Parts of Your PersonalityДокумент2 страницыDissociation: Dissociated Parts of Your PersonalityVeronica Hernandez100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Constructivist Assessment RubricДокумент3 страницыConstructivist Assessment Rubricapi-247486256Оценок пока нет
- Jariel HRM M6Документ6 страницJariel HRM M6Lorenz JarielОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Constructivisme N NeedhamДокумент4 страницыConstructivisme N Needhamalong_izahОценок пока нет
- Sir Efs Session Plan - Pec'sДокумент2 страницыSir Efs Session Plan - Pec'skristofferОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- RSL Standardisation Assessment and Commentary MUSPRA 231 Live Music PerformanceДокумент2 страницыRSL Standardisation Assessment and Commentary MUSPRA 231 Live Music PerformanceRicki ArmstrongОценок пока нет
- Interviewing Officers: (This Is An Optional Process)Документ2 страницыInterviewing Officers: (This Is An Optional Process)Leumas gao-ayОценок пока нет
- Deped FormativeДокумент2 страницыDeped FormativeLouie Sonny RiveraОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Sample Lesson Plan Using 7'esДокумент3 страницыSample Lesson Plan Using 7'esMaricel Cebrero Santiago100% (2)
- Arbitrary Value Statistical Limit Descriptive Equivalent SymbolДокумент4 страницыArbitrary Value Statistical Limit Descriptive Equivalent SymbolMarz EspadaОценок пока нет
- KBSRДокумент30 страницKBSRafarz2604Оценок пока нет
- Prevention - Music and How It Affects My MoodДокумент3 страницыPrevention - Music and How It Affects My MoodYouth in Science and Business FoundationОценок пока нет
- A. Mastering The Lost Art of Check-In: Case StudyДокумент2 страницыA. Mastering The Lost Art of Check-In: Case StudyChristine Lucenio100% (1)
- Demonstration - ANANDДокумент22 страницыDemonstration - ANANDAnand gowda100% (1)
- DLL - Mapeh 6 - Q3 - W4Документ4 страницыDLL - Mapeh 6 - Q3 - W4Joyce RodriguezОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Poetry Lesson The Adventures of IsabelДокумент5 страницPoetry Lesson The Adventures of Isabeleva.benson100% (3)
- Models For Implementation of The Learning CampДокумент12 страницModels For Implementation of The Learning CampHenry MartinezОценок пока нет
- Silent WayДокумент9 страницSilent WayPiotr LorekОценок пока нет
- PE8GS-Id-h-24 2. Monitors Periodically Progress TowardsДокумент2 страницыPE8GS-Id-h-24 2. Monitors Periodically Progress TowardsSerLem WellОценок пока нет
- NATAN - Activity 2 (Human Resource Management)Документ3 страницыNATAN - Activity 2 (Human Resource Management)Denmark David Gaspar NatanОценок пока нет
- Brain Based and Organizer ChartДокумент26 страницBrain Based and Organizer ChartRyan MerzaОценок пока нет
- Counseling Special Populations - SNNPДокумент67 страницCounseling Special Populations - SNNPSittie Nabila Panandigan100% (2)
- Action Plan in Remedial TeachingДокумент2 страницыAction Plan in Remedial TeachingMaricel JanoyogОценок пока нет
- List of Books: S.N Author Title Publication ISBN QTY RemarkДокумент2 страницыList of Books: S.N Author Title Publication ISBN QTY RemarkTemesgen EndalewОценок пока нет