Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Coca Cola Sales and Distribution
Загружено:
Rajdeep Roy Chowdhury100%(2)100% нашли этот документ полезным (2 голоса)
2K просмотров15 страницCoca Cola Sales and Distribution Management
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документCoca Cola Sales and Distribution Management
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(2)100% нашли этот документ полезным (2 голоса)
2K просмотров15 страницCoca Cola Sales and Distribution
Загружено:
Rajdeep Roy ChowdhuryCoca Cola Sales and Distribution Management
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 15
Distribution Structure of
Coca Cola in India
Sales and Distribution Management Project
Project Submitted by:
Group 2
212011 HARSH VARDHAN VYAS
212025 RAJDEEP ROY CHOWDHURY
212029 SABYASACHI GUHA RAJA
212034 SUBHA SAHA
212036 SUNANDO MUKHERJEE
WMG 21
2
Table of Contents
Introduction .................................................................................................................................................. 3
Role of each intermediary - Distribution & Retail ......................................................................................... 4
Coca Cola System .......................................................................................................................................... 5
Sales Structure of Coca Cola ......................................................................................................................... 6
Territory Design in NCR ................................................................................................................................. 6
Margins ......................................................................................................................................................... 6
Infrastructure Required by Distributors........................................................................................................ 8
Coverage Plan Followed by Distributors ....................................................................................................... 8
Support Provided to Distributors by the Company ...................................................................................... 9
Performance Evaluation of Distributors ....................................................................................................... 9
Major Problems Faced by Distributors ......................................................................................................... 9
Logistics ....................................................................................................................................................... 10
Coca Colas Focus on Rural India Demands ................................................................................................ 11
Coca Cola Launches Online Store in India ................................................................................................... 12
Recommendations ...................................................................................................................................... 13
Conclusion ................................................................................................................................................... 14
References .................................................................................................................................................. 15
3
Introduction
The Coca-Cola Company re-entered India through its wholly owned subsidiary, Coca-Cola India Private
Limited and re-launched Coca-Cola in 1993 after the opening up of the Indian economy to foreign
investments in 1991. Since then its operations have grown rapidly through a model that supports
bottling operations, both company owned as well as locally owned and includes over 7,000 Indian
distributors and more than 2.2 million retailers. Today, Coca Colas brands are the leading brands in
most beverage segments. The Coca-Cola Company's brands in India include Coca-Cola, Fanta Orange,
Limca, Sprite, Thums Up, Burn, Kinley, Maaza, Minute Maid Pulpy Orange, Minute Maid Nimbu Fresh
and the Georgia Gold range of teas and coffees and Vitingo (a beverage fortified with micro-nutrients).
In India, the Coca-Cola system comprises of a wholly owned subsidiary of The Coca-Cola Company
namely Coca-Cola India Pvt Ltd which manufactures and sells concentrate and beverage bases and
powdered beverage mixes, a Company-owned bottling entity, namely, Hindustan Coca-Cola Beverages
Pvt Ltd; thirteen licensed bottling partners of The Coca-Cola Company, who are authorized to prepare,
package, sell and distribute beverages under certain specified trademarks of The Coca-Cola Company;
and an extensive distribution system comprising of customers, distributors and retailers. Coca-Cola
India Private Limited sells concentrate and beverage bases to authorized bottlers who are authorized to
use these to produce portfolio of beverages. These authorized bottlers independently develop local
markets and distribute beverages to grocers, small retailers, supermarkets, restaurants and numerous
other businesses. In turn, these customers make beverages available to consumers across India.
The Coca-Cola system in India has already invested USD 2 Billion till 2011, since its re-entry into India.
The company will be investing another USD 5 Billion till the year 2020. The Coca-Cola system in India
directly employs over 25,000 people including those on contract. The system has created indirect
employment for more than 1,50,000 people in related industries through its vast procurement, supply
and distribution system. They strive to ensure that the work environment is safe and inclusive and that
there are plentiful opportunities for people in India and across the world.
The beverage industry is a major driver of economic growth. A National Council of Applied Economic
Research (NCAER) study on the carbonated soft-drink industry indicates that this industry has an output
multiplier effect of 2.1. This means that if one unit of output of beverage is increased, the direct and
indirect effect on the economy will be twice of that. In terms of employment, the NCAER study notes
that "an extra production of 1000 cases generates an extra employment of 410 man days."
Coca Cola System Worldwide and India
At the core of Coca Colas business in India, as in the rest of the world is the production and distribution
network, which the company calls the Coca-Cola system. Globally, the Coca-Cola system includes Coca
Cola itself and more than 300 bottling partners. The Coca-Cola Company manufactures and sells
concentrate and beverage bases. The authorized bottlers combine concentrate or beverage bases as the
4
case may be with sweetener (depending on the product), water or carbonated water to produce
finished beverages. These finished beverages are packaged in authorized containers bearing Coca Colas
trademarks -- such as cans, refillable glass bottles, non-refillable PET bottles and tetra packs -- and are
then sold to wholesalers or retailers. In India, additionally, the Company also sells certain powdered
beverage mixes such as Vitingo.
The beverages reach the ultimate consumers through the companys customers: the grocers, small
retailers, hypermarkets, restaurants, convenience stores and millions of other businesses that are the
final points of distribution in the Coca-Cola system.
Role of each intermediary - Distribution & Retail
The Coca-Cola Company in India is governed from its corporate office located in Gurgaon. This office
manages the working of five zones covering whole of India.
The different and segregated zones are:
1. Northern zone
2. Eastern zone
3. Western zone
4. Southern zone
5. Andhra Pradesh zone
These zones are divided into various plants and offices which govern the area assigned to them. The
areas are the various distribution centres consisting of Distributors and Carry & Forward agents. Further
down the distribution chain comes, the retailers/customer for the company's product. They receive
goods from distributors and C&F agents. Finally consumer is the buyer accessing the product from the
retail shops or having them delivered to their homes.
The Coca-Cola Company typically has its reach taking its products to billions of people all around the
world using wide distribution networks. In India, the pace and speed at which Coca-Cola has widened its
business is truly amazing. Distribution network remains the biggest strength of the company
5
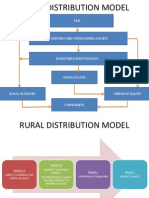
Coca Cola System
6
Sales Structure of Coca Cola
Territory Design in NCR
Full Coverage in Delhi NCR with 59 Routes for distribution
Coca Cola uses both owned and contracted vehicles to cover these routes
Margins
Margin per crate (comprising 24 bottles of 300 ml each) is Rs 20.
On the 200 ml pack size, margin is Rs 16 per crate.
Sales of the more affordable 200 ml pack size account for about 60 per cent of its total
carbonated soft drink (CSD) sales.
Non-CSD business accounts for 15 per cent.
Outsourced distribution so that trucks and other equipment needed for the purpose are no
longer owned by the company
AGM
Sales Manager
Area Sales Manager
Sales Executives
Market Development Executive / Pre-sellers
7
FINANCIAL TERMS
1) Profit Margin
a) To distributors
b) To retailers
1-1.5%
2-3%
2) Advance payment
a) to company
b) for refrigerators
1,00,000
5,000
3) Credit terms and policies
i) Credit amount
a)Company to distributor
b)Distributor to retailer
N/A
Can provide.
ii) Credit period One month(for retailers)
iii) Rate of interest N/A
4) Discounts provided
i) Cash discount N/A
ii)Quantity discount Variable
5)Frequency of visit by co. personnel to distributor:
a)Customer Executive/
Supervisor
b)TDM
Once in a week
Once in two months
8
Infrastructure Required by Distributors
HCCBPL is the largest bottling partner of The Coca-Cola Company in India. It is a part of The Coca-Cola
Companys Bottling Investments Group (BIG) and responsible for the manufacture, package, sale and
distribution of beverages under the trademarks of The Coca-Cola Company. As part of the Bottling
Investments Group of The Coca-Cola Company, HCCBPL has 24 bottling plants at strategic locations in
various states spread across India. They cover approximately 65% of bottling operations for the Coca-
Cola System in India. HCCBPL has an extensive distribution system spanning more than a million outlets
operating with world class execution standards and infrastructure. In addition to HCCBPL, there are
thirteen more licensed bottling partners who are also responsible for manufacture, package, distribution
and independently developing local markets to distribute beverages to grocers, small retailers,
supermarkets, restaurants and numerous other businesses.
Coca Cola India is currently making huge investments to increase bottling lines, adding new bottling
plants, enhancing back-end chain infrastructure across the country.
Coverage Plan Followed by Distributors
The routes formulated by HCCBPL (Hindustan Coca Cola Beverages Pvt. Ltd. (India) for distribution of
products are as follows:
Key Accounts: These key institutional customers contribute a large piece of the total sales of the
Company. It mainly consists of organizations that buy large quantities of a product in one single
transaction. Because of their volumes and bargaining power the Company offers one month or 15 days
credit. They include Defence canteens, Clubs, fine dine restaurants, hotels, Corporate houses etc.
Future Consumption: The segment consists of outlets of Coca-Cola products holding decent amount of
stock meant for future consumption. This is done to ensure the product is available all time. They
include Food courts, Departmental stores, Super markets etc.
Immediate Consumption: Stocks need to be replenished on daily basis for immediate consumption form
retail stores. The stocks of products in these outlets are sold on the same day and very few bottles may
be left for next day such outlets include retailers, canteens of educational institutions, small sized bars
and restaurants, and unorganized retailers.
General: In this route a few but specific areas are grouped and served in one go. These include remote
areas, rural places, and hill stations with less density of populations.
Coca-Cola India (CCI) built a distribution network in combination with its bottling partners and contract
manufacturers. In urban areas, it distributes products directly from bottling plants to retailers. However,
owing to lack of proper infrastructure and difficult access to the remote villages, it modified its
distribution chains and adopted the three-tier hub and spoke distribution model, to penetrate into the
rural areas and increase its sales. Besides its distribution network, CCI adopted Right Execution Daily
(RED) strategy for effective execution of its distribution mainly in urban areas, which boosted the sales
9
of the company. RED ensures the proper display, availability and activation of companys products in the
retail stores.
Support Provided to Distributors by the Company
Coca-Cola India Private provides syrup concentrate & beverage bases to authorized bottlers in strategic
geographical location who mix this syrup with other ingredients like water, sugar etc. which they further
distribute to the retailers
Coca cola is using Push strategy in which they use its sales force and trade promotion money to induce
intermediaries to carry, promote and sell the product to end users i.e. consumers. For example, Coca
cola is giving free pet bottles, trade discounts, publicity material, point of sale display etc. to
distributors, agency owners and retailers
Performance Evaluation of Distributors
Sales quota attainment
Inventory management
Average order size placed
Market coverage(calls made by distributor everyday)
Infrastructure
Volume generated
Third party audit
Complaints handling
Major Problems Faced by Distributors
Intense competition with PepsiCo
Depleting Margins
Multiple Channels.
Environmental Issues faced by the Coca Cola Company such as the pesticide issue, ban on
sale of Coke products in Kerala in 2006 etc resulted in depleted sales
From company : discounts/incentives given at the end of the month
From retailer : bad debts/run away
10
Logistics
Attributes of Coca Cola Logistics
Average order size
a) Distributor to company
b) Retailer to Distributer
Based on Demand, Season
Based on Demand, Season
Order placement
a) Distributor to company
b) Retailer to distributer
Phone
Distributor Representative
Transit Time 2 Days
Order frequency Daily
Inventory Maintained 1 day
Unsold/Damaged Merchandise Replaced
Mode of Transportation
(company to distributor)
Company vehicle
Warehousing
a) Storage Capacity
b) Ownership
Minimum 30 m
2
Owned / Rented
Reverse Logistics
Reverse Logistics is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient, cost effective
flow of raw materials, in-process inventory, finished goods and related information from the point of
consumption to the point of origin for the purpose of recapturing value or proper disposal.
As far as managing the returns are concerned companies re-use them, re-sell them, leave them to a
third party or destroy them. But companies are more likely to benefit if they can also make use of the
information that comes back with returned merchandise.
11
Reverse logistics plays an important role in the Coca Cola distribution. Greening is not the only
motivation; this reduces the packaging cost considerably for them. The % of recycled component in
bottles and cans is already a KPI for the beverage manufacturers.
There is a big scope for greening the supply-chains from a packaging perspective - the hierarchy is
Prevent > Minimize > Reuse > Recycle > Dispose.
Two main enablers for achieving this are:
1. Just in time delivery (Minimize packaging )
2. Reverse logistics for packaging materials (Reuse and Recycle)
Cokes global supply chain is a vastly complex network of plants, bottlers, warehouses and customers,
along with multiple product lines following multiple supply chains with differing objectives. The
challenge: achieving consistent reporting and having real-time information on which to base tactical and
strategic decision making
Because the same set of rules was not used throughout the company, the existing metrics system wasnt
sufficient for Coke. Even when using different KPIs (Key Performance Indicators), simple things like
stock out and fill rate were different.
With the implementation of Advanced Planning & Optimization (APO) and SAP software, Coke combined
the right intelligence that was relevant for its routes and markets and hence optimized its cost and
delivery schedules.
Coca Colas Focus on Rural India Demands
Coca-Cola India is betting big on the rural markets and has recast its distribution strategy to get more
people to sample its beverages, especially in the rural region.
The centralized distribution system of transporting the product directly from the bottling plants to
retailers, as used in urban market was futile for rural market which resulted in innovative Hub and
spoke distribution system. The stock was transported from the bottling plants to hubs and then from
hubs to spokes (situated in small towns) and from spokes to retailers who catered to the demands in
rural areas. A well designed marketing strategy with strong and efficient supply chain and logistics
ensured Coca-Colas presence with increase in coverage.
12
Hindustan Coca-Cola has introduced fountain machines on trucks and they take it to haats, melas and
other such gatherings, and serve Coca Cola or our other beverages in a cup at 5 and it works very well,
as there are rarely any permanent shop in these gatherings.
In the process of exploring Indian rural market the Coca-Cola has come out with eco-friendly cooler
eKOCool' operating through solar energy. Limited hours power supply in rural areas is one of the most
important factor for not offering chilled soft drink products to consumers in rural areas. To address the
issue Coca-Cola India came out with this innovation using a renewable energy resource. eKOCool' can
store two crates having 48 glass bottles of 300 ml each. Apart from this it can light up the store and
charge mobile. This has given Coca-cola India a competitive advantage to penetrate into remote rural
areas. The results are promising, a test market done by placing 20 eKOCool' coolers in a rural area near
Agra has given sales jump of nearly 5 times.
Coca Cola Launches Online Store in India
Coca-Cola has launched Coke2Home.com, an online store for home delivery of the groups various
beverage products. This is one of the rare such instances of a large consumer products maker getting
into direct selling through an online channel in India.
The website is run by Hindustan Coca-Cola Beverages Pvt Ltd, the largest bottling partner of The Coca-
Cola Company in India. The service is currently available in Ahmadabad, Bangalore, Chennai,
Gandhinagar, Hyderabad and Mumbai only. Customers need to book their orders before 12 noon to get
products home-delivered the same day. You can also place bulk order or monthly supplies of products.
Minimum order for delivery is Rs 300, as of now. The company accepts multiple modes of payment,
including cash on delivery cash card, credit card, debit card and net banking.
13
What is interesting is how the firm has structured the venture to sell its products which in effect
amounts to multi-brand e-tailing in which foreign investment is not allowed. We are getting in touch
with the Coca-Cola spokesperson in India for more details and will update when we have more
information.
Early in 2013, the countrys top FMCG firm Hindustan Unilever said it is looking at building capabilities
for e-commerce as a stronger distribution channel. The firm had not given details whether it is looking at
launching its own e-com property as a direct sales venture or wants to strengthen its existing network
catering to other e-tailers who sell its products.
Recommendations
Try and not cannibalize brands taken over by coke such as Gold Spot and Canada Dry to promote
their own brands/create space for Coca Cola products. If possible reintroduce them like Thumps-
up and Limca.
Introduce other worldwide successful products available in the Coca Cola brand that are yet to
be introduced in India.
Create a premium Cola Drink market e.g. the market Canada Dry created for itself.
Create a premium bottled water market.
Market soda products more effectively by tying up with liquor brands that do not have
surrogate soda products.
Enter the powder cola soda market and effectively market the product as antacid.
Coca Cola can diversify into health drinks and food products (like PepsiCo), as consumers today
are very health conscious.
Ensure local brands of Parle which were taken over and are continued under the Coca Cola
brand and are equally marketed. Case in point distribution of Thumps-up and Limca are quite
weak more so in the high volume small SKUs across retails of various segments. Also, in most
post mix vending machines Thumps-up and Limca are not available.
Coca Cola must ensure they have full stock of all their products in the outlets they handle.
Coca Cola must have a speedy delivery system of its goods to the retailers at any given point of
time.
Promotional campaigns must be held in order to improve the sales of products that are not
moving in the market (certain brands of Coca-Cola like Nimbu Fresh etc.).
Coca Cola can implement more modified and better QPDS(Quantity Purchase and Display
Schemes) in order to increase their sales figures.
14
Efficient ways to handle complaints from the retailers must be designed by the Coca Cola.
Fortnightly visit of the marketing heads to major retail outlets must be done in order to know
the market, how the current sales& distribution is working and what more strategies can be
implemented to enhance the process and sales.
Conclusion
The sales and distribution network of Coca-Cola has also been found to be very strong and almost
flawless. Hindustan Coca-Cola Beverages (P) Ltd. has had the first mover advantage when it entered the
market and it has capitalized on that advantage to grab the market share. Franchisee who takes care of
the companys operations has been found to be competent and so the company does not interfere in
their work. The franchisees are also required to report to the company at specific time intervals.
Franchisee based operations combined with the companys operations add strength to the overall
presence of the company in the market.
15
References
http://www.coca-colaindia.com/ourcompany/coca_cola_system.html
http://www.coca-colaindia.com/ourcompany/bottling_partners.html
http://techcircle.vccircle.com/2013/05/31/beverage-maker-coca-cola-launches-online-store-in-india-is-
it-looking-at-multi-brand-e-tailing/
http://www.thehindubusinessline.com/companies/cokes-new-mantra-made-in-india-for-
india/article5664891.ece
http://marketinomics.com/consumer-behavior-2/how-coca-cola-did-it-in-india/
Вам также может понравиться
- Britannia Supply ChainДокумент19 страницBritannia Supply Chaindevil@MANAGE88% (8)
- WWII Engineer Amphibian TroopsДокумент162 страницыWWII Engineer Amphibian TroopsCAP History Library67% (3)
- 01 - Accounting For Managers PDFДокумент151 страница01 - Accounting For Managers PDFAmit Kumar PandeyОценок пока нет
- Coca Cola Distribution ChannelДокумент2 страницыCoca Cola Distribution ChannelLalit Kumar92% (12)
- Coca Cola Sales and DistributionДокумент57 страницCoca Cola Sales and DistributionShoyeb Bagwan50% (6)
- Report on Segmentation for 3 Brands of Coca-Cola CompanyДокумент12 страницReport on Segmentation for 3 Brands of Coca-Cola CompanyAshvinОценок пока нет
- Flyaudio in An 08 Is250 With Factory Nav InstructionsДокумент2 страницыFlyaudio in An 08 Is250 With Factory Nav InstructionsAndrewTalfordScottSr.Оценок пока нет
- Cultural Values in Indian Cosmetic BrandsДокумент16 страницCultural Values in Indian Cosmetic BrandsRajdeep Roy Chowdhury0% (1)
- Coco ColaДокумент18 страницCoco Colanaveen bhataiaОценок пока нет
- Permit Part-2 Process-Oriented Permit in SAPДокумент13 страницPermit Part-2 Process-Oriented Permit in SAPsachinWebDОценок пока нет
- The Supply Chain Management of Cadbury Dairy MilkДокумент3 страницыThe Supply Chain Management of Cadbury Dairy MilkCahyo EdiОценок пока нет
- HUL, ITC & Godrej (Supply Chain Management Comparision)Документ39 страницHUL, ITC & Godrej (Supply Chain Management Comparision)Jeetesh Kumar92% (12)
- HUL Supply ChainДокумент20 страницHUL Supply ChainAbhishesh Suman77% (13)
- Coca-Cola Porter's Five Forces Analysis and Diverse Value-Chain Activities in Different AreasДокумент33 страницыCoca-Cola Porter's Five Forces Analysis and Diverse Value-Chain Activities in Different AreasRoula Jannoun67% (6)
- Godrej Consumer Products Limited: An FMCG LeaderДокумент23 страницыGodrej Consumer Products Limited: An FMCG Leadersaurabh50% (2)
- Hindustan Unilever Limited (HUL)Документ17 страницHindustan Unilever Limited (HUL)priyankasinghal100% (20)
- Coca-Cola Distribution NetworkДокумент20 страницCoca-Cola Distribution NetworkPranav Mehta100% (4)
- Supply Chain of Itc CigarattesДокумент21 страницаSupply Chain of Itc CigarattesIqbal Singh86% (7)
- Coca-Cola India Term PaperДокумент9 страницCoca-Cola India Term PaperRagunandan RavichandranОценок пока нет
- Coca-Cola vs. Pepsi outbound logistics analysis in IndiaДокумент21 страницаCoca-Cola vs. Pepsi outbound logistics analysis in IndiaJon100% (1)
- Sales and Distribution of HULДокумент17 страницSales and Distribution of HULAnkit Patodia100% (1)
- Employee Training and DevelopmentДокумент33 страницыEmployee Training and DevelopmentMoogii50% (2)
- Coca Cola Porter S Five Forces Analysis and Diverse Value Chain Activities in Different Areas PDFДокумент33 страницыCoca Cola Porter S Five Forces Analysis and Diverse Value Chain Activities in Different Areas PDFLouise AncianoОценок пока нет
- Cococola Sales StrategyДокумент19 страницCococola Sales StrategyArpita SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Godrej SCMДокумент6 страницGodrej SCMRahul MehrotraОценок пока нет
- Distribution Channel at Coca-ColaДокумент11 страницDistribution Channel at Coca-Colaabhi_03873% (30)
- Sales and Distribution Management at Coca-ColaДокумент37 страницSales and Distribution Management at Coca-ColaMitsitgwalior Seventoeleven75% (12)
- Distribution BritanniaДокумент5 страницDistribution Britanniaarun0% (1)
- Study of Supply Chain at Big BasketДокумент10 страницStudy of Supply Chain at Big BasketPratul Batra100% (1)
- Kinetics of Acetone Hydrogenation For Synthesis of Isopropyl Alcohol Over Cu-Al Mixed Oxide CatalystsДокумент9 страницKinetics of Acetone Hydrogenation For Synthesis of Isopropyl Alcohol Over Cu-Al Mixed Oxide Catalysts李国俊Оценок пока нет
- HUL S&D ManagementДокумент21 страницаHUL S&D ManagementKuldipak KheradiyaОценок пока нет
- Supply Chain of CadburyДокумент14 страницSupply Chain of Cadburykunal100% (3)
- Amul Supply Chain ManagementДокумент6 страницAmul Supply Chain ManagementgsahaОценок пока нет
- Distribution Channel of CadburyДокумент3 страницыDistribution Channel of Cadburyshashank vyas57% (7)
- Supply Chain and Distribution Strategy of Coca Cola in IndiaДокумент22 страницыSupply Chain and Distribution Strategy of Coca Cola in IndiaShivani ShuklaОценок пока нет
- India's Thirst For Rural MarketДокумент19 страницIndia's Thirst For Rural MarketVedant VarshneyОценок пока нет
- Hul Distribution ModelДокумент5 страницHul Distribution ModelBhavik LodhaОценок пока нет
- Distribution Network For BritanniaДокумент5 страницDistribution Network For BritanniaSaba Dabir100% (3)
- Hindustan Coca - Cola Beverages Pvt. LTD., Bidadi, BangaloreДокумент14 страницHindustan Coca - Cola Beverages Pvt. LTD., Bidadi, BangaloreOM Kumar89% (9)
- Distribution Channels of CocaДокумент6 страницDistribution Channels of CocaAlka Aggarwal100% (1)
- VijetaДокумент2 страницыVijetaPandharinath Rameshrao Chidrawar100% (1)
- Coca Cola Final DissertationДокумент103 страницыCoca Cola Final Dissertationrahul786iips100% (1)
- Coca Cola Distribution Strategy MMДокумент14 страницCoca Cola Distribution Strategy MMShaan Pat100% (4)
- Summer Training Red Project Report CocacolaДокумент84 страницыSummer Training Red Project Report Cocacolagurunathambabu100% (2)
- HUL (Supply Chain)Документ19 страницHUL (Supply Chain)rohan_jangid8100% (4)
- Difference BW HUL and P&G Distribution Structure PDFДокумент14 страницDifference BW HUL and P&G Distribution Structure PDFRahul Mehay100% (1)
- Nestle CaseДокумент14 страницNestle CasePranav NyatiОценок пока нет
- Nestle India DistributionДокумент28 страницNestle India DistributionSantanu KararОценок пока нет
- Itc Supply ChainДокумент18 страницItc Supply Chainrukhsar nasimОценок пока нет
- Nestle Distribution NetworkДокумент21 страницаNestle Distribution NetworkGurdit Singh AjmaniОценок пока нет
- Spice RushДокумент3 страницыSpice RushNavpreet Singh RandhawaОценок пока нет
- Bisleri Vedica Go-To-Market Strategy for Premium Bottled WaterДокумент22 страницыBisleri Vedica Go-To-Market Strategy for Premium Bottled WaterRaghav RohilaОценок пока нет
- FBM, Arrow Case StudyДокумент10 страницFBM, Arrow Case Studyasunishupratuswapu100% (1)
- The Rise of India's Iconic Amul BrandДокумент57 страницThe Rise of India's Iconic Amul Brandranson dantis100% (1)
- Sales and Distribution Manaagement in HULДокумент18 страницSales and Distribution Manaagement in HUL'Gitesh ⎝⏠⏝⏠⎠ Patil'Оценок пока нет
- CocaCola GroupPresentationДокумент30 страницCocaCola GroupPresentationSharanya RamasamyОценок пока нет
- Supply Chain Management Process and Its ImplementationДокумент11 страницSupply Chain Management Process and Its ImplementationMrityunjay Saikia100% (1)
- Channel Distribution Coca-ColaДокумент11 страницChannel Distribution Coca-ColaRicky Sh100% (1)
- CIA-I Channel Analysis Report of Coca-Cola's Distribution and Supply Chain NetworksДокумент32 страницыCIA-I Channel Analysis Report of Coca-Cola's Distribution and Supply Chain NetworksRitika HalderОценок пока нет
- Harsh Khandelwal - 21361 - Finance - Agile Capital ServicesДокумент30 страницHarsh Khandelwal - 21361 - Finance - Agile Capital ServicesChikun MarriageОценок пока нет
- Department of Tourism and Hospitality MangementДокумент25 страницDepartment of Tourism and Hospitality MangementPritom PyareОценок пока нет
- Coca-Cola Project Report on Execution Mapping in RED OutletsДокумент93 страницыCoca-Cola Project Report on Execution Mapping in RED OutletsMithlesh SinghОценок пока нет
- Sales and Distribution of Coca-ColaДокумент26 страницSales and Distribution of Coca-ColaPiyoosh BajoriaОценок пока нет
- Coca Cola Porter S Five Forces Analysis and Diverse Value Chain Activities in Different Areas PDFДокумент33 страницыCoca Cola Porter S Five Forces Analysis and Diverse Value Chain Activities in Different Areas PDFLouise AncianoОценок пока нет
- Roll No 10Документ7 страницRoll No 10Sangharsh RamtekeОценок пока нет
- INDUSTRY PROFILE-updatedДокумент18 страницINDUSTRY PROFILE-updatedFALCO1234Оценок пока нет
- SDM Question: Explain The Distribution Style of Any Indian Company. (250 Words)Документ2 страницыSDM Question: Explain The Distribution Style of Any Indian Company. (250 Words)SAMHITA SRIDHARОценок пока нет
- Retail Management Project - Group 2 - WMG21Документ16 страницRetail Management Project - Group 2 - WMG21Rajdeep Roy ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- New Zealand TradeДокумент13 страницNew Zealand TradeRajdeep Roy ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- New Zealand TradeДокумент13 страницNew Zealand TradeRajdeep Roy ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Case Study - Titan WatchesДокумент5 страницCase Study - Titan WatchesGaurav GoyalОценок пока нет
- Project On Indian Trade With Euro ZoneДокумент11 страницProject On Indian Trade With Euro ZoneRajdeep Roy ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Consumer Protection Laws in India - Group 3Документ6 страницConsumer Protection Laws in India - Group 3Rajdeep Roy ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Econometrics ProjectДокумент17 страницEconometrics ProjectAkash ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- Solar Winds OrionAPM DatasheetДокумент4 страницыSolar Winds OrionAPM DatasheetArun J D'SouzaОценок пока нет
- Alvarez vs. COMELECДокумент5 страницAlvarez vs. COMELECvanessa3333333Оценок пока нет
- Impact of COVIDДокумент29 страницImpact of COVIDMalkOo AnjumОценок пока нет
- Lfa Sop 00067Документ6 страницLfa Sop 00067Ahmed IsmaillОценок пока нет
- DESIGN AND FABRICATION TURBO WOOD STOVE TIET OriginalДокумент71 страницаDESIGN AND FABRICATION TURBO WOOD STOVE TIET OriginalSHIELDОценок пока нет
- 2022 Semester 2 Letter To Parents - FinalДокумент7 страниц2022 Semester 2 Letter To Parents - FinalRomanceforpianoОценок пока нет
- Wizard's App Pitch Deck by SlidesgoДокумент52 страницыWizard's App Pitch Deck by SlidesgoandreaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 Leader-Centred PerspectivesДокумент24 страницыLecture 2 Leader-Centred PerspectivesLIVINGSTONE CAESARОценок пока нет
- Philippine Supreme Court Acquits Man of Estafa Due to Lack of KnowledgeДокумент2 страницыPhilippine Supreme Court Acquits Man of Estafa Due to Lack of KnowledgeUrsulaine Grace FelicianoОценок пока нет
- Black Bruin Hydraulic Motors On-Demand Wheel Drives EN CДокумент11 страницBlack Bruin Hydraulic Motors On-Demand Wheel Drives EN CDiego AlbarracinОценок пока нет
- March 2017Документ11 страницMarch 2017Anonymous NolO9drW7MОценок пока нет
- bq76pl455 RegistersДокумент132 страницыbq76pl455 RegistersAhmet KARAОценок пока нет
- PartlowControllerCatalog PDFДокумент98 страницPartlowControllerCatalog PDFvinh nguyen theОценок пока нет
- CE 462 Construction ManagementДокумент100 страницCE 462 Construction Managementmonicycle companyОценок пока нет
- Keystone - Contractors - Book 16 05 12 FinalДокумент9 страницKeystone - Contractors - Book 16 05 12 Finalfb8120Оценок пока нет
- CLS1Документ3 страницыCLS1Shaina Kaye De GuzmanОценок пока нет
- JESTEC TemplateДокумент11 страницJESTEC TemplateMuhammad FakhruddinОценок пока нет
- Foreign Direct Investment in Mongolia An Interactive Case Study (USAID, 2007)Документ266 страницForeign Direct Investment in Mongolia An Interactive Case Study (USAID, 2007)Oyuna Bat-OchirОценок пока нет
- Indian companies involved in trade dispute caseДокумент15 страницIndian companies involved in trade dispute caseakshay daymaОценок пока нет
- Plastic Waste Powerpoint TemplateДокумент39 страницPlastic Waste Powerpoint TemplateVinh Lê KhảiОценок пока нет
- Akriti Shrivastava CMBA2Y3-1906Документ6 страницAkriti Shrivastava CMBA2Y3-1906Siddharth ChoudheryОценок пока нет
- Is 4032 - 1985Документ45 страницIs 4032 - 1985yogeshbadyalОценок пока нет