Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Radomes
Загружено:
rascalangel0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
102 просмотров17 страницAntenna Radomes
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документAntenna Radomes
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
102 просмотров17 страницRadomes
Загружено:
rascalangelAntenna Radomes
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 17
Radomes
Ground based or Shipborne antenna should withstand:
High Winds
Icing
Other adverse weather conditions
They can be designed to meet above criteria
OR
Enclose the antenna in a Electromagnetically Transparent protective
shield
This shield is called a RADOME
Advantages
Cheaper
Antenna is lighter
Drive motor can be smaller
Radomes for Ground based radar are often in shape of
sphere or 3/4
th
of sphere
Aircraft radome should be
1. Strong
2. Aerodynamic
1. It is good mechanical structure
2. It is aerodynamic
3. Precipitation blows around it
Snow is not readily deposited
Electromagnetic properties of Radome
1. Low Loss
2. Adequate bandwidth
3. Should not raise side lobe level
4. Low VSWR
5. A low antenna noise temperature
6. Should not cause boresight to shift
Two major types of Radomes for Ground/Ship based
Radars
1. Rigid Radomes
2. Air Supported Radomes
1. Rigid Radomes
Has a space frame
3D lattice of primary load
bearing structure
Steel, aluminium or plastic
Dielectric panel enclosure
Eg. Teflon coated
fiberglass
Geodesic dome-spherical
structure made of simple
geometric shapes
Metal structures are most commonly used
Superior electrical performance
Thin for same strength
Less aperture blocking
Cheaper
Easier to fabricate transport and
assemble
Aluminium is typically used
Light wieght
Non-corrosive
No maintainance required
Panel Properties
Panels should be hydrophobic
Water forms into beads rather than film
Dimensions of beads < wavelength
No adverse effects of film
Shapes are usually quasi-random
To avoid periodicity and spurious sidelobes
Less sensitive to polarization
Typical performance figures
Loss due to metal space frame =0.5dB
Side lobe levels increase by 1dB
Boresight shift of 0.1mrad
Antenna noise temp increases by <5K
2. Air supported Radomes
Constructed from strong, flexible, rubberized
air tight material
Supported by air pressure from within
Electrically very thin (compared to wavelength)
Implies low loss(0.1dB)
Very small boresight error
Shape resembles a weather balloon with
vertical creases(stiches) called gores
Teflon fiberglass is commonly used material
2. Air supported Radomes cont
Can be folded into small package
Easy trasportation
Assembly
De-assemly
Life is limited by
Exposure to ultraviolet light
Surface erosion
Flexing of material in wind
Damage by flying debris
Can be designed to withstand winds from
100mph to 200mph
2. Air supported Radomes cont
Disadvantages
Maintaining internal pressure can be a
problem
Frequent and costly maintenance
Less rugged
Weather effects on rigid radomes
Important adv. Of rigid radomes -> ability to
withstand severe weather
Rime ice (artic regions)
Has little or no effect on
Spherical radomes
Trajectories of water
Droplets in air stream flowing
around large sperical radome do not impinge
upon the surface
Droplets of freezing rain though can collect on
the surface
Weather effects on rigid radomes cont
Dry snow does not stick to cold surface thus not
a problem
Wet snow on other hand sticks and effects
transmission properties
Snow can be removed by heating the surface
Expensive
Tie a rope and move around the radome
Thin films can form if panels are not
hydrophobic
Can cause attenuation of several dBs
Radome Wall Construction
a) Thin wall
Electrically thin wrt wavelength
D<0.05/sqrt()
b) Half wavelength
D /2
Theoritically non relecting
No losses other than ohmic losses
Limited bandwidth and incidence angles
c) A sandwich
3 layer
2 thin and relatively high dielectric
constant skins
Eg. Glass reinforced plastic
1 with low dielectric const. and /4 thick
Honeycomb or foam
Radome Wall Construction cont
d) B sandwich
Inverse of A sandwich
/4 thick skins with dielectric const. <the
core
e) C-sandwich
2 back to back A-sanwiches
Used when ordinary A-sandwitches do not
provide sufficient strength
f) Multilayer
More layers than c sandwich
Metallic Radomes
Thin metal sheets with periodic openings/slots
Good electrical and mechanical properties
Better able to handle Stress due to rain, dust,
lightning etc. and dissipate heat
Acts as frequncy selective surface (bandpass)
Reduces interference
Reduces nose on RCS of aircraft
When viewed by radar system not within its
passband
Disadvantage of narrow bandwidth
Rotodomes
Radomes which rotates in sync with antenna
Used in high prf pulse doppler etc.
Used in AEWACS
Вам также может понравиться
- Corrosion Control For Avionics Equipment 2 PDFДокумент121 страницаCorrosion Control For Avionics Equipment 2 PDFfnk19Оценок пока нет
- Sheet Metal Forming ProcessesДокумент51 страницаSheet Metal Forming ProcessesLeo Dev WinsОценок пока нет
- Automotive Anodizing CДокумент17 страницAutomotive Anodizing CMereddy Sunil Kumar ReddyОценок пока нет
- Vda 5733 JB 2022 en Web RZ PDFДокумент131 страницаVda 5733 JB 2022 en Web RZ PDFSoufian BirjaliОценок пока нет
- Automotive Quality Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionОт EverandAutomotive Quality Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionОценок пока нет
- RTN Connect Dfa Dfa PDFДокумент24 страницыRTN Connect Dfa Dfa PDFKishanОценок пока нет
- Physical Vapour DepositionДокумент3 страницыPhysical Vapour Depositiontessaro1823Оценок пока нет
- 06 DFMA MethodologiesДокумент80 страниц06 DFMA MethodologiesFery MahardikaОценок пока нет
- RL TR 93 6Документ284 страницыRL TR 93 6ketab_doostОценок пока нет
- Acw 0219Документ2 страницыAcw 0219anna_malai078351Оценок пока нет
- Properties and Applicable Usage of PosmacДокумент3 страницыProperties and Applicable Usage of PosmacLucio PereiraОценок пока нет
- Flipp English - Reading ModuleДокумент76 страницFlipp English - Reading Modulemy LucyОценок пока нет
- Analysis On Automotive Paints and Coatings: Maria Victoria Chill S. Calumpiano Che-3Документ9 страницAnalysis On Automotive Paints and Coatings: Maria Victoria Chill S. Calumpiano Che-3Chill CalumpianoОценок пока нет
- Types of Ram: Managing and Troubleshooting PcsДокумент43 страницыTypes of Ram: Managing and Troubleshooting PcsCheerish Marie LegardaОценок пока нет
- RC Analysis 9136Документ80 страницRC Analysis 9136e2ycОценок пока нет
- Surface Texture Measurement Fundamentals For Metrology Center Open HouseДокумент54 страницыSurface Texture Measurement Fundamentals For Metrology Center Open HouseSushant VashisthaОценок пока нет
- Electronics Design ChecklistДокумент9 страницElectronics Design Checklistjkengg100% (1)
- ISO31000Документ33 страницыISO31000Soraya FariasОценок пока нет
- Concurrent EngineeringДокумент3 страницыConcurrent EngineeringAnonymous WmMP8H6JGОценок пока нет
- A DMAIC Approach To Printed Circuit Board Quality Improvement-1 PDFДокумент9 страницA DMAIC Approach To Printed Circuit Board Quality Improvement-1 PDFrogers4759Оценок пока нет
- 01 DFMA OverviewДокумент75 страниц01 DFMA Overviewanwar anwaryОценок пока нет
- Design FMEA UltraДокумент49 страницDesign FMEA UltrakumarОценок пока нет
- Product Life CycleДокумент30 страницProduct Life CycleQurat Ul Ain NaqviОценок пока нет
- Ansys Fluent Migration ManualДокумент59 страницAnsys Fluent Migration ManualOlukayode Niyi Ezekiel100% (1)
- ARaymond QC Thermal-Management Booklet 2019Документ16 страницARaymond QC Thermal-Management Booklet 2019TUNCAY GUMUSОценок пока нет
- FMEA For Manufacturing and Assembly Process: VJTI, Mumbai Siemens LTD., MumbaiДокумент9 страницFMEA For Manufacturing and Assembly Process: VJTI, Mumbai Siemens LTD., MumbaiKevin JordanОценок пока нет
- Root CauseДокумент31 страницаRoot CauseZaid Tariq AlabiryОценок пока нет
- Alufinishing TrainingДокумент36 страницAlufinishing Trainingantzz alljc100% (1)
- 8d's y 5 Por Que de NissanДокумент8 страниц8d's y 5 Por Que de NissanSergio RuizОценок пока нет
- Response To Omar's Response To FredericДокумент66 страницResponse To Omar's Response To FredericFred LamertОценок пока нет
- Plastic WeldingДокумент13 страницPlastic Weldingakshay tapkirОценок пока нет
- Visual Inspection Comparison of ISO and AWS: A. Hobbacher Cochabamba, 9th of July 2013Документ29 страницVisual Inspection Comparison of ISO and AWS: A. Hobbacher Cochabamba, 9th of July 2013cesargamboaОценок пока нет
- Fmea DesignДокумент29 страницFmea DesignEmperor89100% (2)
- Dynamic Oring SealingДокумент49 страницDynamic Oring SealingRobert ChristoОценок пока нет
- FMEA Guide QДокумент161 страницаFMEA Guide Qmilou88Оценок пока нет
- Flooring Spec No RDSO-2017-CG-05 For Rubberized FlooringДокумент15 страницFlooring Spec No RDSO-2017-CG-05 For Rubberized FlooringIshanОценок пока нет
- MIL STD 785RevB PDFДокумент88 страницMIL STD 785RevB PDFPradeep RОценок пока нет
- Tensile TesterДокумент12 страницTensile Testerlhanx2Оценок пока нет
- Design For Reliability June 2007Документ42 страницыDesign For Reliability June 2007Teshome DengisoОценок пока нет
- Houston Impact of J-STD-001F and IPC-A-610F ChangesДокумент36 страницHouston Impact of J-STD-001F and IPC-A-610F Changes安靖Оценок пока нет
- POM2.4 - Designing Products & ServicesДокумент49 страницPOM2.4 - Designing Products & ServicesAkash ChandakОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15Документ70 страницChapter 15Renee Pascual SalipotОценок пока нет
- Failure Mode Effect AnalysisДокумент36 страницFailure Mode Effect AnalysisCharanjeet SinghОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Reliability Engineering - CERN 06.11Документ48 страницIntroduction To Reliability Engineering - CERN 06.11Solanke AnuОценок пока нет
- RCM Establishing Preventive Maintenance RequirementsДокумент9 страницRCM Establishing Preventive Maintenance RequirementsKenn EvangelioОценок пока нет
- Control of The Mat Gloss BalanceДокумент3 страницыControl of The Mat Gloss Balancejulio100% (1)
- 008 Selection of Alternative Material For Car Roof PanelДокумент10 страниц008 Selection of Alternative Material For Car Roof PanelyasinОценок пока нет
- Install LantekДокумент39 страницInstall LantekTruta Ionut67% (3)
- En12944Документ10 страницEn12944Rui MendesОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Engineering Subjects Full ListДокумент21 страницаMechanical Engineering Subjects Full Listabhigoyal1989Оценок пока нет
- Mil STD 1179eДокумент37 страницMil STD 1179eTobias WonkОценок пока нет
- Industrial Lighting and Productivity 1Документ16 страницIndustrial Lighting and Productivity 1Carlos TorresОценок пока нет
- AD 2000-Merkblatt B 13 English Vom 07-2012Документ44 страницыAD 2000-Merkblatt B 13 English Vom 07-2012GÖKHAN İNCİRLİОценок пока нет
- Plastics Product DesignДокумент295 страницPlastics Product DesignMousam ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- Grenzebach Coating Technology enДокумент7 страницGrenzebach Coating Technology enSAmits SethiОценок пока нет
- StereolithographyДокумент13 страницStereolithographyonkar masekar0% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S0029801819301623 Main PDFДокумент16 страниц1 s2.0 S0029801819301623 Main PDFrascalangelОценок пока нет
- 08048605Документ11 страниц08048605rascalangelОценок пока нет
- Am DSBFC Systems (By Larry E. Gugle K4rfe)Документ9 страницAm DSBFC Systems (By Larry E. Gugle K4rfe)rascalangelОценок пока нет
- 08048605Документ11 страниц08048605rascalangelОценок пока нет
- Radar System Engineering Sub-Unit 2Документ46 страницRadar System Engineering Sub-Unit 2rascalangelОценок пока нет
- Radar System Engineering Sub-Unit 3Документ23 страницыRadar System Engineering Sub-Unit 3rascalangelОценок пока нет
- Micro Strip Antennas OverviewДокумент118 страницMicro Strip Antennas OverviewDenny SaputraОценок пока нет
- Hart ApplicationGuide - r7.1Документ194 страницыHart ApplicationGuide - r7.1rascalangelОценок пока нет
- Momo Chutney (Sauce) IngredientsДокумент1 страницаMomo Chutney (Sauce) IngredientsrascalangelОценок пока нет
- Masala Crab Fry - Goan Style - Worth A TryДокумент6 страницMasala Crab Fry - Goan Style - Worth A TryrascalangelОценок пока нет
- Pipe Flow Expert TrainingДокумент6 страницPipe Flow Expert TrainingcihuyОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Pipe NetworksДокумент14 страницAnalysis of Pipe NetworksAhmad Sana100% (2)
- A DNS Study of Entrainment in An Axisymmetric Turbulent Jet As An Episodic ProcessДокумент25 страницA DNS Study of Entrainment in An Axisymmetric Turbulent Jet As An Episodic ProcessmyskyshepherdОценок пока нет
- Technical Vocational Livelihood: Shielded Metal Arc WeldingДокумент7 страницTechnical Vocational Livelihood: Shielded Metal Arc Weldingtibo bursioОценок пока нет
- 0056Документ204 страницы0056rameshaarya99Оценок пока нет
- Analysis of Axial Flow FansДокумент7 страницAnalysis of Axial Flow FanshonghieutrОценок пока нет
- Module 15 - UNIT III - PolymersДокумент12 страницModule 15 - UNIT III - PolymersJhess GaliciaОценок пока нет
- Module 7 - Complex and ERD Well PlanningДокумент36 страницModule 7 - Complex and ERD Well Planningchristianleal123Оценок пока нет
- Energy Levels MS PDFДокумент3 страницыEnergy Levels MS PDFLoh Jun XianОценок пока нет
- CH 1 Solid State SsnotesДокумент29 страницCH 1 Solid State SsnotesAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yОценок пока нет
- Jominy End Quench TestДокумент3 страницыJominy End Quench TestaasdcdcОценок пока нет
- FMDS1303 - Steam TurbinesДокумент55 страницFMDS1303 - Steam TurbinesSergio BragaОценок пока нет
- Williams Landel Ferry - JACS55 PDFДокумент7 страницWilliams Landel Ferry - JACS55 PDFrishikeshmandawadОценок пока нет
- 15 CH 4 Columns and StructsДокумент22 страницы15 CH 4 Columns and StructsgОценок пока нет
- Advance Boiler Control SystemДокумент44 страницыAdvance Boiler Control SystemJeEJyZaОценок пока нет
- TechNote - B008-20-Basic C-Shaped Wall Stud Behavior-WEBFINALДокумент6 страницTechNote - B008-20-Basic C-Shaped Wall Stud Behavior-WEBFINALsahanОценок пока нет
- Mig Guide From Zero PDFДокумент10 страницMig Guide From Zero PDFHugo SalazarОценок пока нет
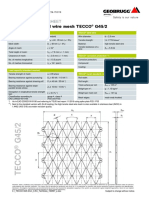
- High-Tensile Steel Wire Mesh TECCO G45/2: Technical Data SheetДокумент1 страницаHigh-Tensile Steel Wire Mesh TECCO G45/2: Technical Data SheetGUNAОценок пока нет
- Piezo Low FrequencyДокумент21 страницаPiezo Low Frequencygastelum fernandezОценок пока нет
- Blower Double Impeller bl520002 Technical Data Sheet en v3Документ2 страницыBlower Double Impeller bl520002 Technical Data Sheet en v3Docu CenterОценок пока нет
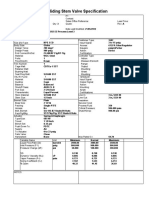
- Data Sheet Control Valve FisherДокумент9 страницData Sheet Control Valve FisherFIRMANSYAHОценок пока нет
- Determination of Angle of Divergence of Laser Beam: Physics Open Ended Experiment ReportДокумент10 страницDetermination of Angle of Divergence of Laser Beam: Physics Open Ended Experiment ReportDeepak ZillaОценок пока нет
- A Compressor Surge Control System: Combination Active Surge Control System and Surge Avoidance SystemДокумент7 страницA Compressor Surge Control System: Combination Active Surge Control System and Surge Avoidance SystemAbbas MohajerОценок пока нет
- Paper 2 1Документ16 страницPaper 2 16brk8sjszqОценок пока нет
- Heat Ad Mass Transfer in A Cooling Tower With Special Attention To The Tower Characteristic RatioДокумент5 страницHeat Ad Mass Transfer in A Cooling Tower With Special Attention To The Tower Characteristic RatioAathithyayanSoundararajanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 14Документ14 страницLecture 14Adam SurtiОценок пока нет
- Boiler Manual Umpp PDFДокумент53 страницыBoiler Manual Umpp PDFRanjanaWajeОценок пока нет
- Reaction Rates Worksheet-1452167356Документ6 страницReaction Rates Worksheet-1452167356feta cumaniОценок пока нет
- Anchor Scan ParametersДокумент3 страницыAnchor Scan ParametersMagician PeruОценок пока нет
- Instruction Manual: DS-2000 Series Reflecting and Refracting TelescopesДокумент44 страницыInstruction Manual: DS-2000 Series Reflecting and Refracting TelescopesBrandon BohannonОценок пока нет