Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Avnrt VS Avrt
Загружено:
Dwi Nugroho PrastowoОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Avnrt VS Avrt
Загружено:
Dwi Nugroho PrastowoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Advanced AVNRT and AVRT
With differentiation
Advanced EP Training
()
April 24, 2011
Etiology: ()
1. AVNRT (n=1452): 50%
Typical (slow-fast) 90%
Atypical (fast-slow) 7%
Variant (intermediate) 9%
2. AVRT (n=1221): 42%
orthodromic (fast AP 90% or
slow AP 10%)
3. AT (n=245): 8%
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
12-lead ECG for
differential diagnosis
of SVTs (important!)
Retrograde P wave in SVT
(Tai CT et al. JACC 1997)
Short RP SVT
1. Slow-Fast AVNRT:
No apparent retrograde P wave: 50%
Pseudo R in V1 or pseudo-S in inferior
leads: 50%
2. Orthodromic AVRT: 70 ms<RP<PR
The presence of delta wave in NSR.
3. AT with PR prolongation: the presence of
AV block favors AT.
S-F AVNRT
Pseudo-R
Pseudo-S
NSR after IV adenosine
No pseudo-R and pseudo-S
S-F AVNRT
No apparent P wave
S-F AVNRT
P wave masked by QRS
S-F AVNRT
Pseudo-R and pseudo-S
S-F AVNRT
Pseudo-R and pseudo-S
Orthodromic AVRT
RP>70 ms, favor LL AP
MWPW (LL or LAL AP)
Long RP SVT
1. Fast-Slow AVNRT:
Positive p wave in V1 and negative p
wave in inferior leads.
2. Orthodromic AVRT using decremental
(slow) APs.
3. AT with normal PR interval.
EP study for
differential diagnosis
of SVTs
Favors AVNRT
1. The presence of dual AVN physiology:
upper or lower common pathway.
2. The critical prolongation (jump) of AH
interval during the initiation of SVT.
3. The concentric atrial activation:
especially a straight line from ECG-A-V
or A before V (SF AVNRT)
AVNRT
Antegrade SAVN: AH jump > 50 ms
Continuous curve AVNRT
Retrograde SAVN:
1.Long VA interval
2.CSO-A earliest.
Retrograde intermediate AVN:
1.Intermediate VA interval
2.His-A and CSO-A both earlier
AVNRT with retrograde eccentric
activation
Continuous curve AVNRT
(Tai CT et al. Circulation 1997)
Initiation of S-F AVNRT
Progressive AH prolongation with jump
Lower common pathway
V
V V V
A A
A
A
Progressive prolongation of VA interval
AVNRT with eccentric A activation
(Ong M. et al. IJ C 2007)
Favors AVRT
1. No decremental conduction during
pacing (except slow AP).
2. The eccentric atrial activation with short
VA interval (>70 ms)
3. VA interval increases >30 ms with
functional BBB.
LT AP with LBBB
(Josephson ME. P237)
Single VPC reset SVT
His refractory VPC
35-55 ms before the His deflection.
Advance the following A: AVRT
VPC without conducting to atrium but
terminate the SVT: rule out AT.
VPC from the sites other than RVA:
LV: for left side APs
RVOT: for septal APs
Ventricular Overdrive
Pacing (VOP) (10-40 ms
shorter than tachycardia)
during SVT
VOP entrains the SVT
VOP could not entrain SVT: AT
The same atrial activation sequence:
AVNRT or AVRT
The different atrial activation sequence: AT
The presence of lower common pathway:
AVNRT is more likely.
The presence of V-A-A-V response: AT
The presence of V-A-V response: favors
AVNRT or AVRT.
VOP during SVT
(Veenhuyzen G. et al. PACE 2011)
1. The retrograde A sequence is different during tachycardia and VOP
2. The presence of V-A-A-V response during VOP
AT
V
A
A
V
Hirao, K. et al. Circulation 1996;94:1027-1035
Para-Hisian pacing
Ablation Strategy of AVNRT
Make a correct diagnosis!!!
Ablation of slow or intermediate AVN
1. Anatomic approach: PMA
2. Electrogram approach: small A, large V
3. J T during RF
How to avoid AV block?
1. ablation during A pacing
2. avoid ablation during SVT or V pacing.
3. You have only one second to stop RF!!!
JT under during RF
Transient second degree AVB
Flat and horizontal Kochs Triangle
(Lee PC et al. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2009)
RAO LAO
Ablation Strategy of AVRT
Make a correct diagnosis!!!
Localization of the APs: 12-lead ECG
algorithm and intracardiac recordings.
Antegrade approach: for RT AP
Retrograde approach: for LT AP
1. V site (subvalvular): small A, large V, stable
ablation catheter
2. A site (ante- or retro-grade): larger A, unstable
ablation catheter
Delta Wave in NSR
(Chiang CE et al. AJC 1996)
Whats on the other side
Cases Discussion
Case 1
VT, PSVT with RBBB or preexcitated tachycardia?
RA burst + Isuprel induce SVT
AVNRT with Wenkebach AV block then 1:1 conduction
Whats the mechanism of SVT?
S-F AVNRT
PSVT with LBBB
RVS1S2 induced PSVT
500 270
Retrograde-intermediate AVN or AP?
AH=188 ms HA=158 ms
VPC terminate SVT: AVN or AP?
347 ms 347 ms
293 ms
V pacing during SVT: AVN or AP?
350 ms
372 ms
Lower common pathway
Mapping retrograde pathway and terminate
SVT (after ablation of antegrade SAVN)
RAO LAO
Ablation of
Antegrade
SAVN
Ablation of
retrograde
intermediate
AVN
Case 2
A 28 Y/O male fireman had recurrent attacks of tachycardia during exercise
RVOT-VT, PSVT with LBBB or Preexcited tachycardia?
NSR
(Intermittent Preexcitation)
AP location?
RVS1S1 350 ms
350
RVS1S1 340 ms
Sudden VA block
Favors AP
340
RVS1S2 500/310 ms
F-S echo
RAS1S2 Induced Tachycardia
Wide QRS complex tachycardia:
VT?, or Preexcitated tachycardia? PSVT with LBBB
Wide QRS Tachycardia
TCL= 256 ms
Question?
Whats the mechanism of Wide QRS
complex tachycardia?
VT? Preexcitated tachycardia? PSVT with
LBBB?
Whats the next step to D.D?
PSVT with LBBB
VPC terminate tachycardia
Can rule out AT
Without conduction to A
VPC
VOP terminate tachycardia
Sudden VA block
AVNRT is not likely
No lower common pathway
The same A sequence
Initiation of NQRS tachycardia
NQRS Tachycardia
TCL= 244 ms shorter than SVT with LBBB (256 ms)
Favor left side AP?
VPC reset SVT
His refractory VPC
248 233
Ablation site: RPS
Success within 5 seconds
VA block
RF on
Immediate recurrence within 5
RF off
Ablation site 1: RPS
Success within 3 seconds
VA block
Immediate recurrence within 3
Ablation site 2: RPS
Ablation site: LMS
Success within 5 seconds
VA block
Ablation site 3: LMS
Transient CAVB
PS APs
(Chiang CE et al. Circulation 1996)
MS APs
(Chang SL et al. JCE 2005)
Test
Small & narrow P waveRA & LA depolarization simultaneously
Diagnosis: SF AVNRT with 2:1 AV block
A P wave in the midpoint between the two QRS beats
Test
AT with 2:1 AV block?
Whats the next step?
Test: VOP 2:1 to 1:1 conduction
Вам также может понравиться
- DR K Chan - Ecg For SVT Made EasyДокумент66 страницDR K Chan - Ecg For SVT Made Easyapi-346486620Оценок пока нет
- Ekg Panum or OsceДокумент69 страницEkg Panum or OsceGladish RindraОценок пока нет
- ECG Interpretation UnismaДокумент178 страницECG Interpretation UnismadefinaОценок пока нет
- Ecg For InternsДокумент25 страницEcg For InternszeshooОценок пока нет
- Learning Ecg ModulesДокумент150 страницLearning Ecg ModulesdodiОценок пока нет
- JVP Examination For GPДокумент43 страницыJVP Examination For GPNovenZefanyaОценок пока нет
- Electrical Axis: Fast & Easy Ecgs - A Self-Paced Learning ProgramДокумент29 страницElectrical Axis: Fast & Easy Ecgs - A Self-Paced Learning ProgramMihaela PrisacaruОценок пока нет
- EkgДокумент67 страницEkgFendi Rafif Dad'sОценок пока нет
- ECG InterpretationДокумент73 страницыECG Interpretationsultan khabeebОценок пока нет
- ECG Interpretation TheoryДокумент4 страницыECG Interpretation TheorySteph PiperОценок пока нет
- The P WaveДокумент13 страницThe P Wave成失Оценок пока нет
- ElectrocardiogramДокумент52 страницыElectrocardiogramTuong HoangManhОценок пока нет
- Implementation of Low Delay Dual Chamber Pacemaker Using VerilogДокумент4 страницыImplementation of Low Delay Dual Chamber Pacemaker Using VerilogMeghanand KumarОценок пока нет
- Basics and Interpretation: Sif HansdottirДокумент65 страницBasics and Interpretation: Sif Hansdottirwenny1186100% (1)
- Bundle Branch BlockДокумент37 страницBundle Branch BlocksyukronchalimОценок пока нет
- Dr. Firman Leksmono SP - JP Basic ECG Interpretation For StudentДокумент54 страницыDr. Firman Leksmono SP - JP Basic ECG Interpretation For Studentadela_97line100% (2)
- Dysrhythmias: Sinus Node Dysrhythmias Tachycardia, and Sinus ArrhythmiaДокумент5 страницDysrhythmias: Sinus Node Dysrhythmias Tachycardia, and Sinus ArrhythmiaKayelyn-Rose Combate100% (1)
- Electrocardiography: Dr. Anand PatelДокумент155 страницElectrocardiography: Dr. Anand PatelDeepika PatelОценок пока нет
- Basics of Pacing CombinedДокумент54 страницыBasics of Pacing CombinedMichael Susanto100% (1)
- Advanced ECG BBB PGДокумент47 страницAdvanced ECG BBB PGdragon66Оценок пока нет
- Electrophysiological Properties of Cardiac MyocytesДокумент39 страницElectrophysiological Properties of Cardiac Myocytesapi-19916399Оценок пока нет
- HBP C315HIS Implant Procedure-eLearnДокумент35 страницHBP C315HIS Implant Procedure-eLearnRichiОценок пока нет
- WK 6 Study QsДокумент7 страницWK 6 Study Qsapi-479720222Оценок пока нет
- Anaesthesia and Atrial FibrillationДокумент15 страницAnaesthesia and Atrial FibrillationNaresh Dhawan100% (1)
- Dr. Adeel Ahmed Waheed: House Officer M-4Документ84 страницыDr. Adeel Ahmed Waheed: House Officer M-4Hussain AzharОценок пока нет
- EKG Clep TestДокумент13 страницEKG Clep TestElissa LafondОценок пока нет
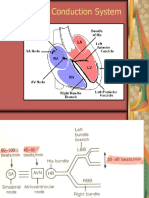
- Electrical Conduction Pathway: Course Lesson Student Email Atika - Salsabila91@ui - Ac.idДокумент12 страницElectrical Conduction Pathway: Course Lesson Student Email Atika - Salsabila91@ui - Ac.idlemon kyuteaОценок пока нет
- EKG InterpretationДокумент63 страницыEKG InterpretationMiriam Cindy MathullaОценок пока нет
- ATSP (Asked To See Patient) BookletДокумент24 страницыATSP (Asked To See Patient) BookletCindy WongОценок пока нет
- Basic ECGДокумент152 страницыBasic ECGTuấn Thanh VõОценок пока нет
- Mitral StenosisДокумент50 страницMitral Stenosissruthimeena6891Оценок пока нет
- ECG IMM 2020.docx.2Документ25 страницECG IMM 2020.docx.2Abdul QuyyumОценок пока нет
- 20 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Ophthamology PDFДокумент46 страниц20 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Ophthamology PDFSisterzzShopDua0% (1)
- Ekg FastlaneДокумент10 страницEkg FastlaneAida UzunovicОценок пока нет
- Revised AntiarrhythmicsДокумент29 страницRevised AntiarrhythmicsDang CuevasОценок пока нет
- Advanced 12-Lead InterpretationДокумент30 страницAdvanced 12-Lead InterpretationRohini SelvarajahОценок пока нет
- Pericardial EffusionДокумент3 страницыPericardial EffusionNita Hurek100% (1)
- Captopril Renography: Physiologic Principle - Loss of Preferential Vasoconstriction of The EfferentДокумент3 страницыCaptopril Renography: Physiologic Principle - Loss of Preferential Vasoconstriction of The EfferentSri HariОценок пока нет
- ECG Fast and Easy chp12 PDFДокумент40 страницECG Fast and Easy chp12 PDFkikyfauziaОценок пока нет
- Corrected ElectrolytesДокумент2 страницыCorrected Electrolytesdragon66100% (1)
- Paces Station 4: Communication Skills & Ethics: Your Role: Problem: PatientДокумент5 страницPaces Station 4: Communication Skills & Ethics: Your Role: Problem: Patientthap87Оценок пока нет
- ECG Interpretation in One PageДокумент2 страницыECG Interpretation in One PageRyan AycockОценок пока нет
- Focal Atrial Tachycardia I: Clinical Features, DiagnosisДокумент10 страницFocal Atrial Tachycardia I: Clinical Features, Diagnosisapi-26166949Оценок пока нет
- HUTTДокумент25 страницHUTTdrdj14100% (1)
- 439 3 Electrophysiology & ECG BasicsДокумент34 страницы439 3 Electrophysiology & ECG BasicsjpoutreОценок пока нет
- Cardiac Rhythm Device ManagementДокумент35 страницCardiac Rhythm Device ManagementCorina DiaconescuОценок пока нет
- Dysrhytmia NotesДокумент11 страницDysrhytmia NoteshannahhwolfОценок пока нет
- Obesity, OSA and Bariatric SurgeryДокумент49 страницObesity, OSA and Bariatric SurgeryanaeshklОценок пока нет
- Ecg Pathology 02Документ95 страницEcg Pathology 02Andi MP Manurung100% (1)
- Action Potential of Cardiac MusclesДокумент16 страницAction Potential of Cardiac Muscleswaqas_xsОценок пока нет
- MRCP Revision NotesДокумент14 страницMRCP Revision NotesSharanyMustafaОценок пока нет
- Heart MuscleДокумент10 страницHeart Muscle22194Оценок пока нет
- EXAM-MITRAL VALVE DISEASE - Reda SoДокумент5 страницEXAM-MITRAL VALVE DISEASE - Reda SoReda SoОценок пока нет
- Hepatic Vein FlowДокумент14 страницHepatic Vein FlowJORGEОценок пока нет
- Basic EP IntervalsДокумент13 страницBasic EP IntervalsdrharoonmohdОценок пока нет
- Management of HypertensionДокумент93 страницыManagement of Hypertensionhasibsb28Оценок пока нет
- Cardiac ArrhythmiasДокумент14 страницCardiac ArrhythmiasArvin John ManuelОценок пока нет
- Management of Malignant Ventricular Arrhytmia - Dr. Achmad LefiДокумент32 страницыManagement of Malignant Ventricular Arrhytmia - Dr. Achmad LefiStanley GunawanОценок пока нет
- Medical TerminologiesДокумент14 страницMedical TerminologiesShannine Del Rosario BeridaОценок пока нет
- Sdi 2011Документ311 страницSdi 2011Mohammed Ahmad Al-MuhurОценок пока нет
- BASIC ECG READING For Nle NOVEMBER 2018Документ63 страницыBASIC ECG READING For Nle NOVEMBER 2018Sharmaine KimmayongОценок пока нет
- ACLS Megacode Checklist For StudentsДокумент3 страницыACLS Megacode Checklist For StudentsKhrisha Anne DavilloОценок пока нет
- 1st Line Medication of An e CartДокумент5 страниц1st Line Medication of An e CartColette Marie PerezОценок пока нет
- Dubin ECG Reference SheetsДокумент13 страницDubin ECG Reference SheetsEllie100% (1)
- ECG and ArrhythmiaДокумент44 страницыECG and ArrhythmiaSamdiSutantoОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Myocardial InfarctionДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology of Myocardial InfarctionYhr YhОценок пока нет
- EKG Interpretasi Dan Lethal Aritmia: Aan NuraeniДокумент34 страницыEKG Interpretasi Dan Lethal Aritmia: Aan NuraeniCitra Marchelina Novilini100% (1)
- ECG Lead LL Interpretation AnswersДокумент28 страницECG Lead LL Interpretation AnswersAgustina Tri P. DОценок пока нет
- Supraventricular TachycardiaДокумент9 страницSupraventricular TachycardiaclubsanatateОценок пока нет
- Prof. Randa Cardiac ArrhythmiasДокумент57 страницProf. Randa Cardiac ArrhythmiasMohan MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Athletic Physicals FormДокумент4 страницыAthletic Physicals FormlukОценок пока нет
- ACLS PharmacologyДокумент6 страницACLS PharmacologyEunice Angela Fulgueras80% (5)
- Off Pump CABGДокумент8 страницOff Pump CABGRajat KapurОценок пока нет
- Management of Severe Local Anaesthetic ToxicityДокумент2 страницыManagement of Severe Local Anaesthetic Toxicitymonir61Оценок пока нет
- 45 Tahun Dengan Manifestasi Stokes-Adams Attack: Laporan KasusДокумент7 страниц45 Tahun Dengan Manifestasi Stokes-Adams Attack: Laporan KasusKena BenОценок пока нет
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsДокумент10 страницAntiarrhythmic DrugsUma MounaОценок пока нет
- CardiomyopathiesДокумент48 страницCardiomyopathiesTanvir AhmedОценок пока нет
- Temporary PacemakerДокумент35 страницTemporary Pacemakerromeorobin07Оценок пока нет
- A Simplified ECG GuideДокумент4 страницыA Simplified ECG Guidejalan_z96% (27)
- Defibrillation & DC Shock: Ns. Retno Setyawati, M.Kep., SP - KMBДокумент34 страницыDefibrillation & DC Shock: Ns. Retno Setyawati, M.Kep., SP - KMBdanur ciyeeОценок пока нет
- Anti ArrhythmicsДокумент46 страницAnti Arrhythmicsnk999999Оценок пока нет
- Pre-Excitation Syndromes in Children: Dr.K.MaheshДокумент105 страницPre-Excitation Syndromes in Children: Dr.K.MaheshNischal ShahОценок пока нет
- Skill Lab #7: Abnormal ECG Interpretation and Treatment: Aed/DДокумент10 страницSkill Lab #7: Abnormal ECG Interpretation and Treatment: Aed/Dاكرم صالحينОценок пока нет
- TPSVДокумент28 страницTPSVGeraldine CortesОценок пока нет
- EKG - Assignment Without AnswersДокумент10 страницEKG - Assignment Without AnswersJon Millhollon100% (1)
- Rate and RhythmДокумент10 страницRate and RhythmSamanta Luiza de AraujoОценок пока нет