Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Forged Steel Piston PDF
Загружено:
victover0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
220 просмотров14 страницNon-premium engines use pistons with cast iron domes and skirts and open-end rods. Premium engines (identified by the letters "PK" in the fifth and sixth positions of the model number) each piston is fitted with a fire ring, Compression Ring and one-piece oil control ring.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Forged Steel Piston.pdf
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документNon-premium engines use pistons with cast iron domes and skirts and open-end rods. Premium engines (identified by the letters "PK" in the fifth and sixth positions of the model number) each piston is fitted with a fire ring, Compression Ring and one-piece oil control ring.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
220 просмотров14 страницForged Steel Piston PDF
Загружено:
victoverNon-premium engines use pistons with cast iron domes and skirts and open-end rods. Premium engines (identified by the letters "PK" in the fifth and sixth positions of the model number) each piston is fitted with a fire ring, Compression Ring and one-piece oil control ring.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 14
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL
All information subject to change without notice.
6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION From Bulletin 18-60-98 1-259
1.17 PISTON AND PISTON RING
Series 60 engines currently use two types of pistons. Non-premium engines use pistons with cast
iron domes and skirts and open-end connecting rods. Premium engines (identified by the letters
PK in the fifth and sixth positions of the model number) built on or after March 16, 1998 use
pistons with forged steel domes, aluminum skirts, and closed-end connecting rods.
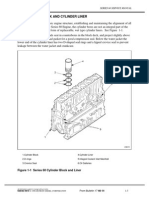
The cast iron cross-head piston is a two-piece piston consisting of a dome and a skirt. The dome
and skirt are held together by the piston pin. Ring grooves are machined in the piston dome. See
Figure 1-220.
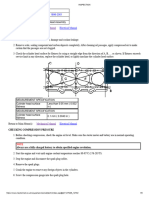
1.Piston Pin 6.Compression Ring
2.Piston Skirt 7.Fire Ring
3.Piston Dome and Bushing Assembly 8.Piston Dome
4.Oil Ring Expander 9.Three-piece Bushing
5.Oil Control Ring
Figure 1-220 Cast Iron Piston and Related Parts
NOTE:
Series 60G engine incorporates a different fire ring (3.5 mm) and compression ring. The
compression ring is identified with a purple stripe.
1.17 PISTON AND PISTON RING
All information subject to change without notice.
1-260 From Bulletin 18-60-98 6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION
Each piston is fitted with a fire ring, compression ring and one-piece oil control ring with
expander. See Figure 1-221 , and see Figure 1-222.
1.Oil Control Ring 8.Fire Ring *
2.Compression Ring * 9.Piston Dome
3.Fire Ring 10.Oil Ring Expander
4.Piston Dome 11.Oil Control Ring
5.Oil Ring Expander 12.Compression Ring *
6.Oil Control Ring 13.Fire Ring
7.Compression Ring *
* Identification Mark to Face Top of Dome
Figure 1-221 Figure Piston Ring Location
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL
All information subject to change without notice.
6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION From Bulletin 18-60-98 1-261
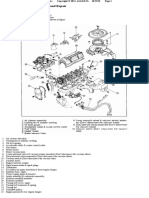
The forged steel cross-head piston is a two-piece piston consisting of a dome and a skirt. The
dome and skirt are held together by the piston pin. Ring grooves are machined in the piston
dome. See Figure 1-222.
1. Piston Pin 5. Oil Ring Expander
2. Piston Skirt 6. Oil Control Ring
3. Snap Ring 7. Compression Ring
4. Piston Dome 8. Fire Ring
Figure 1-222 Forged Steel Piston and Related Parts
1.17 PISTON AND PISTON RING
All information subject to change without notice.
1-262 From Bulletin 18-60-98 6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION
Each piston is fitted with a fire ring, compression ring and one-piece oil control ring with
expander.
The fire and compression rings are installed with the football" mark facing up, see
Figure 1-223.
Figure 1-223 Fire and Compression Ring Identification
A one-piece oil control ring is used in the third groove. The expander is of Spira-Lox
construction.
The forged steel piston uses a floating piston pin which rides on the one-piece bushing pressed
into the end of the connecting rod.
The connecting rod and solid-core piston pin do not have drilled center orfices for lubrication.
Oil for lubrication and cooling is supplied by oil spray from piston-cooling nozzles installed at
the bottom of each piston bore.
During engine operation, gas loads pushing down on the piston dome are taken directly by the
piston pin and connecting rod bushing. The piston skirt, being separate, is free from vertical load
distortion. Thermal distortion is also reduced as the piston dome expands. As the connecting rod
swings to one side on the downward travel of the piston, the major portion of the side thrust is
taken by the piston skirt.
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL
All information subject to change without notice.
6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION From Bulletin 18-60-98 1-263
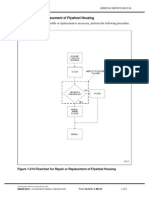
1.17.1 Repair or Replacement of Piston and Piston Ring
To determine if repair is possible or replacement is necessary, perform the following procedure.
See Figure 1-224.
Figure 1-224 Flowchart for Repair or Replacement of Piston and Piston Rings
1.17 PISTON AND PISTON RING
All information subject to change without notice.
1-264 From Bulletin 18-60-98 6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION
1.17.2 Removal and Cleaning of Piston and Piston Ring
Refer to section 1.18.2 for piston and connecting rod assembly removal procedure.
1.17.3 Disassembly of Piston and Piston Ring
Disassemble the piston and piston rings as follows:
1. Remove the piston rings with tool J 22405-02 . See Figure 1-225.
Figure 1-225 Removal of Piston Rings
NOTICE:
The pin, bushing, shirt and dome must be match-marked to
assure proper position and orientation.
2. Withdraw the piston pin and mark the front of the piston with a paint pencil, so it can be
returned to the correct cylinder location.
3. Perform the following steps on current cast iron piston domes:
[a] Separate the piston skirt from the piston dome. Mark the front of the dome ear and
skirt with a paint pencil, so they can be returned to the correct location.
[b] Remove the piston pin bearings, marking the front of them with a paint pencil, so
they can be returned to the correct location.
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL
All information subject to change without notice.
6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION From Bulletin 18-60-98 1-265
NOTE:
The lower pin bore bearings are removed from the pin bore first, by pushing the bearing
legs outward by hand at the split lines from inside the dome saddle ear. The upper
bearing may be held in the bore by oil on the back of the bearing, making removal from
the pin bore by hand difficult.
To avoid personal injury when blow drying, wear adequate
eye protection (safety glasses or face plate) and do not
exceed 276 kPa (40 lb/in.
2
) air pressure.
NOTICE:
Prying between the bearing back and dome bore may damage
the dome saddle bore or raise burrs which will make installation
of new bearings difficult.
DDC recommends that compressed air be directed between the dome pin bore and back of the
bearing at one end until the bearing pops up out of the bearing retaining hole.
1.17 PISTON AND PISTON RING
All information subject to change without notice.
1-266 From Bulletin 18-60-98 6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION
1.17.3.1 Inspection of Piston and Piston Rings
Clean the piston and piston rings prior to inspection as follows:
NOTICE:
Do not attempt to clean the piston skirt by glass beading. It will
remove the tinplating. Do not refinish or polish the piston pin.
1. Clean the piston components with fuel oil.
To avoid personal injury when blow drying, wear adequate
eye protection (safety glasses or face plate) and do not
exceed 276 kPa (40 lb/in.
2
) air pressure.
2. Dry the piston components with compressed air.
3. If fuel oil does not remove the carbon deposits, use a chemical solvent that will not harm
the tinplate on the piston skirt.
NOTICE:
After cleaning, do not leave glass beads in the piston dome. Do
not allow the glass beading to contact any area of the piston
pin bushing or pin bore. Glass beading will remove the
tinplating.
4. The piston dome, including the compression ring grooves, is not tin-plated and may be
wire-brushed to remove any hard carbon. Glass beading can be used to clean a piston
dome. Micro Bead Glass Shot MS-M 0.0736-0.1473 mm (.0029-.0058 in.) is
recommended. The machine used for this process must be able to withstand air pressures
of 552-689 kPa (80-100 lb/in.
2
).
NOTE:
Do not wire-brush the piston skirt.
5. Clean the ring grooves with a suitable tool or a piece of an old compression ring that has
been ground to a bevel edge.
6. Clean the inside surfaces of the piston dome and skirt and the oil relief channels in the oil
ring grooves.
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL
All information subject to change without notice.
6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION From Bulletin 18-60-98 1-267
Inspect the piston and piston rings as follows:
1. Inspect the piston skirt and dome.
[a] Check the skirt and dome for score marks, cracks, damaged ring grooves or
overheating indications.
[b] If any of these indications are present, replace the piston.
NOTE:
Burn spots may indicate an obstruction in the connecting rod or piston pin oil passage.
2. Inspect the tapered fire ring groove (top) in the piston dome.
[a] Using the piston ring land step gage, J 35884-A or J 38609 , check tapered fire ring
groove. See Figure 1-226.
[b] Insert the center tang of the tool gage into the top piston ring groove ash. See
Figure 1-226.
[c] Hold the tool at a 90 angle to the ring groove to prevent false readings.
[d] With the center tang into the ring groove as far as it will go, there should be no
contact of the piston with the shoulders of the gage. If the gage makes contact at
point A or point B, the fire ring groove is worn beyond usable limits. Check the
groove clearance at 4 spots, at 90 intervals. Measure the ring land parallel to and at
90 to the wrist pin.
[e] If fire ring groove is worn beyond usable limits, replace piston dome.
1.Fire Ring Groove
Figure 1-226 Checking Fire Ring Groove
1.17 PISTON AND PISTON RING
All information subject to change without notice.
1-268 From Bulletin 18-60-98 6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION
3. Inspect tapered compression ring groove (second) in the piston dome.
[a] Using piston ring land step gage, check the groove as in the compression ring groove.
[b] If the compression ring groove is worn beyond usable limits, replace piston dome.
4. Inspect the piston pin.
[a] Check the piston pin for fretting, cracking or signs of overheating.
[b] If these are detected, replace piston pin.
[c] Measure piston pin outside diameter. Specifications are listed in Table 1-17.
[d] If piston pin used with a cast iron piston is out of specifications, replace with new
part.
NOTE:
If piston pin used with a cast iron piston is replaced for any reason, the piston pin
bushing for that cylinder must also be replaced.
5. Inspect the piston pin bushings used with cast iron piston as follows:
[a] Check the piston pin bushings for scoring, pitting, flaking, cracking, excessive wear,
or signs of overheating.
[b] If these conditions are present, the bearings must be replaced.
NOTE:
Early second keystone ring (SKR) design piston domes have an integral piston pin
bushing. The piston pin bushing cannot be replaced in these piston domes. If there is
distress to the piston pin bushing, the entire piston dome assembly must be replaced.
NOTICE:
If a piston pin bushing is replaced for any reason, the piston pin
for that cylinder must also be replaced.
6. Inspect the back of the upper bushing.
[a] Check the bushing for excessive fretting.
[b] If excessive fretting is evident, replace all three bushings.
[c] The corresponding fretting in the piston dome can be removed using crocus cloth,
wet with fuel oil.
7. Inspect the edges of the bearings and piston dome pin bore.
[a] Check the edges of the bearing and piston dome pin bore for dents and dings.
[b] If any are found, it is acceptable to remove burrs at the bearings or pin bore edges by
careful filing.
NOTE:
Remove any dirt or debris on the backs of the bearing or dome pin bore that may take
up clearance required for bearing or piston pin installation.
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL
All information subject to change without notice.
6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION From Bulletin 18-60-98 1-269
8. If the piston pin used with a forged steel piston is replaced for any reason, the connecting
rod bushing must be inspected for wear before the rod is installed. If the bushing is worn
beyond limits, the connecting rod must be replaced. Refer to section 1.17.3.1 for
connecting rod bushing inspection procedure.
9. Check the cylinder liner and block bore for excessive out-of-round, taper and high spots
which could cause failure of the piston. Specifications are listed in Table 1-15.
10. Check the block bore for excessive out-of-round, taper, and high spots which could cause
failure of the piston. Specifications are listed in Table 1-14.
1.17.4 Assembly of Piston and Piston Rings
Prior to installing the piston rings, the ring gap of each piston ring must be measured.
1. Insert the piston rings inside of the cylinder liner one at a time, using a piston dome
(inserted upside down into the liner) to push the ring down. The piston dome should be
inserted into the liner, to the same depth as the ring being positioned.
2. For the oil control ring, insert the piston dome down into the liner, until the oil control
ring land is just into the liner. This will ensure that the rings are parallel with the top of
the liner, and that they are positioned in the liner within the normal area of ring travel.
3. After the three rings have been positioned in the liner, measure the ring gap of the top
ring with a feeler gage. See Figure 1-227. Remove the ring from the liner after the
measurement is complete.
Figure 1-227 Piston Ring Gap Measurement
1.17 PISTON AND PISTON RING
All information subject to change without notice.
1-270 From Bulletin 18-60-98 6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION
4. Repeat this procedure for each ring, and record your measurements. Allowable ring end
gaps are listed in Table 1-6.
Ring Ring End Gap
Fire Ring (2.5 mm [.098 in.] chrome) 0.40 - 0.87 mm (.016 - .034 in.)
Fire Ring (3.5 mm [.138 in.] plasma) 0.51 - 0.87 mm (.020 - .034 in.)
Compression Ring 0.81 - 1.31 mm (.032 - .051 in.)
Oil Control Ring 0.40 - 0.81 mm (.016 - .032 in.)
Table 1-6 Allowable Ring End Gap
Assemble the piston and piston pin rings as follows:
1. Install the ring expander in the oil control ring groove in the piston. See Figure 1-228.
1.Oil Control Ring 3.Piston
2.Oil Control Ring Groove 4.Oil Control Ring Expander
Figure 1-228 Piston Ring Installation
SERIES 60 SERVICE MANUAL
All information subject to change without notice.
6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION From Bulletin 18-60-98 1-271
2. Install the oil control ring by hand. See Figure 1-229.
NOTE:
The oil control ring may be installed in either direction.
NOTE:
Install expander into inside diameter groove of ring with expander spring gap located
180 from the oil control ring gap.
Figure 1-229 Oil Control Ring Installation
NOTE:
The oil control ring expander has a white paint stripe. Make sure the paint mark can be
seen after the oil control ring is installed at ring gap.
1.17 PISTON AND PISTON RING
All information subject to change without notice.
1-272 From Bulletin 18-60-98 6SE483 9610 1996 DETROIT DIESEL CORPORATION
Install the fire and compression rings as follows:
NOTICE:
To avoid breaking or overstressing the rings, do not spread them
any more than necessary to slip them over the piston dome.
1. Starting with the compression ring (second groove), install the compression ring and fire
ring with tool J 22405-02 . See Figure 1-230. Make sure the identifying dimple on the
rings is installed up, toward the dome of the piston. See Figure 1-223 for ring
identification and locations.
2. Stagger the ring gaps around the piston. See Figure 1-230.
Figure 1-230 Piston Ring Positioning
3. Refer to section 1.18.4 for piston and connecting rod assembly procedure.
Вам также может понравиться
- Plymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceОт EverandPlymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceОценок пока нет
- Steel Piston PDFДокумент14 страницSteel Piston PDFvictoverОценок пока нет
- The Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementОт EverandThe Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementОценок пока нет
- Engine AssemblyДокумент13 страницEngine AssemblyJacob SilverstielkОценок пока нет
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitОт EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitОценок пока нет
- Connecting Rod PDFДокумент9 страницConnecting Rod PDFvictoverОценок пока нет
- Figure 1-126 Rear Oil Seal Removal: Series 60 Service ManualДокумент2 страницыFigure 1-126 Rear Oil Seal Removal: Series 60 Service ManualvictoverОценок пока нет
- A Book of Helpful Tips on Overhauling a Vintage Engine - Including Car, Motorbike and Lawn Mower EnginesОт EverandA Book of Helpful Tips on Overhauling a Vintage Engine - Including Car, Motorbike and Lawn Mower EnginesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Article Engine Cylinder Block DisassemblyДокумент17 страницArticle Engine Cylinder Block Disassembly94738183Оценок пока нет
- Toyota MR2 Spyder L4-1.8L (1ZZ-FE) 2001: Timing Chain: Service and RepairДокумент18 страницToyota MR2 Spyder L4-1.8L (1ZZ-FE) 2001: Timing Chain: Service and RepairROSA GIMENEZОценок пока нет
- Flywheel 2 PDFДокумент4 страницыFlywheel 2 PDFvictoverОценок пока нет
- Timin Chain CaravanДокумент9 страницTimin Chain Caravanfrancisco AlbaОценок пока нет
- DD15 Detroit DieselДокумент10 страницDD15 Detroit Dieselstarsky100% (4)
- Series 60 Service Manual: From Bulletin 6-60-98 1-157bДокумент2 страницыSeries 60 Service Manual: From Bulletin 6-60-98 1-157bvictoverОценок пока нет
- KTA50 - PistonДокумент9 страницKTA50 - PistonSebastian Nicușor PărăoanuОценок пока нет
- GM Engines v-6, V-8Документ23 страницыGM Engines v-6, V-8jads301179Оценок пока нет
- Harley Davidson 250 and 350 SprintДокумент8 страницHarley Davidson 250 and 350 SprintElan Mutt Schwartz75% (4)
- 3013C Pistons and Connecting Rods - Install - PDF Version 1 PDFДокумент4 страницы3013C Pistons and Connecting Rods - Install - PDF Version 1 PDFJaime Herrera LaraОценок пока нет
- Engine Disassembly Assembly 1Документ9 страницEngine Disassembly Assembly 1Moaed KanbarОценок пока нет
- Cylinder Head Gasket - Installation (01 - 2010 - ) (Cylinder Head Assembly) - ALLDATA Repair Toyota Camry 2.5LtsДокумент17 страницCylinder Head Gasket - Installation (01 - 2010 - ) (Cylinder Head Assembly) - ALLDATA Repair Toyota Camry 2.5LtsFran SanchezОценок пока нет
- Cylinder Block PDFДокумент2 страницыCylinder Block PDFvictoverОценок пока нет
- G3406 Connecting Rod BearingsДокумент4 страницыG3406 Connecting Rod BearingsnobodymagdesignОценок пока нет
- Piston Instrc4032Документ2 страницыPiston Instrc4032RickracerОценок пока нет
- Oilpump4afe PDFДокумент7 страницOilpump4afe PDFhanzhio elОценок пока нет
- Remove & Install Connecting Rod BearingsДокумент4 страницыRemove & Install Connecting Rod BearingsRichard ChuaОценок пока нет
- 1.6L 4cyl Diesel & Turbo DieselДокумент18 страниц1.6L 4cyl Diesel & Turbo DieselLeomir BrandaoОценок пока нет
- Ajuste de Valvulas PDFДокумент8 страницAjuste de Valvulas PDFRoberto Rincon Robles100% (1)
- A/C Compressor Servicing: Please Read This FirstДокумент22 страницыA/C Compressor Servicing: Please Read This FirstbaylorguyОценок пока нет
- 902 PistonДокумент42 страницы902 PistonSumit SinhaОценок пока нет
- Crankshaft Oil 4 PDFДокумент2 страницыCrankshaft Oil 4 PDFvictoverОценок пока нет
- 2001 Toyota Prius L4-1.5L (1NZ-FXE) Hybrid: Timing Chain: Service and RepairДокумент13 страниц2001 Toyota Prius L4-1.5L (1NZ-FXE) Hybrid: Timing Chain: Service and Repairfernando ortizОценок пока нет
- SECTION 303-01B: Engine - 4.6L and 5.4L 2000 F-150 Workshop Manual AssemblyДокумент35 страницSECTION 303-01B: Engine - 4.6L and 5.4L 2000 F-150 Workshop Manual AssemblyHassan Vela VenegasОценок пока нет
- 1971 Johnson 60HP Outboards Service Manual PDFДокумент5 страниц1971 Johnson 60HP Outboards Service Manual PDFChrisStainton0% (1)
- Husqvarna 611238238782 - 61Документ6 страницHusqvarna 611238238782 - 61Mauro OliveiraОценок пока нет
- Replacement: - Oil Pump AssyДокумент1 страницаReplacement: - Oil Pump AssyJoel Majeed StroudeОценок пока нет
- 1.8.7.1 Inspection of Crankshaft Oil Seal: Series 60 Service ManualДокумент2 страницы1.8.7.1 Inspection of Crankshaft Oil Seal: Series 60 Service ManualvictoverОценок пока нет
- Cat C-13 Valve LashДокумент6 страницCat C-13 Valve LashEwgeny100% (5)
- Mercedes-Benz Sprinter W906 - Complete EngineДокумент155 страницMercedes-Benz Sprinter W906 - Complete EngineMucowera Asha100% (2)
- Engine Assembly - Dismantle and Assemble (Engine Removed) (21 134 8)Документ30 страницEngine Assembly - Dismantle and Assemble (Engine Removed) (21 134 8)judas1432Оценок пока нет
- Power Steering Pump Service and Repair, 1999 Toyota Truck 4 Runner 2WDДокумент8 страницPower Steering Pump Service and Repair, 1999 Toyota Truck 4 Runner 2WDCarlos VillaltaОценок пока нет
- Small Engine Day 2Документ18 страницSmall Engine Day 2Selazinap LptОценок пока нет
- DV100 SMДокумент51 страницаDV100 SMjacklyn ade putraОценок пока нет
- Camry Solara SEV6Документ13 страницCamry Solara SEV6arturmikieОценок пока нет
- Detroit 8.2 v8Документ25 страницDetroit 8.2 v8Jose Juan Davila100% (3)
- Corolla LE Sedan RepairДокумент17 страницCorolla LE Sedan RepairmaximlevОценок пока нет
- Manual de Motor Elantra-Tiburón 1998 G4GRДокумент6 страницManual de Motor Elantra-Tiburón 1998 G4GRRodolfo SilvaОценок пока нет
- Timing Chain Components & Instalation Toyota Hilux 22R-E: Preparation of RemovalДокумент7 страницTiming Chain Components & Instalation Toyota Hilux 22R-E: Preparation of RemovalPablo FernandezОценок пока нет
- Foote-Jones 8000 Series Gear Reducer ManualДокумент20 страницFoote-Jones 8000 Series Gear Reducer ManualbwelzОценок пока нет
- Cylinder Head Assembly: Service and RepairДокумент6 страницCylinder Head Assembly: Service and RepairJose PichinteОценок пока нет
- Figure 1-17 Location of Engine Serial and Model Numbers: Series 60 Service ManualДокумент2 страницыFigure 1-17 Location of Engine Serial and Model Numbers: Series 60 Service ManualvictoverОценок пока нет
- 4d94e Shop ManualДокумент25 страниц4d94e Shop Manualyeudys100% (4)
- Manual: 292 Engine Kt-150 SeriesДокумент20 страницManual: 292 Engine Kt-150 SeriesSuwan Noo ThomsonОценок пока нет
- Install Cylinder HeadДокумент5 страницInstall Cylinder HeadbagoesОценок пока нет
- Engine Overhaul 2.2LДокумент29 страницEngine Overhaul 2.2LalbertoОценок пока нет
- 3Документ6 страниц3George GuerreroОценок пока нет
- Unit Injector - Install: Installation ProcedureДокумент6 страницUnit Injector - Install: Installation ProceduredayanaОценок пока нет
- Water Pump PDFДокумент2 страницыWater Pump PDFvictoverОценок пока нет
- 8.2.3.2 Checking 12-Rib Poly-Vee Belt-Driven 50 DN Alternator Belt TensionДокумент2 страницы8.2.3.2 Checking 12-Rib Poly-Vee Belt-Driven 50 DN Alternator Belt TensionvictoverОценок пока нет
- 1.16.1 Repair or Replacement of Flywheel HousingДокумент2 страницы1.16.1 Repair or Replacement of Flywheel HousingvictoverОценок пока нет
- Engine Coolant 2 PDFДокумент3 страницыEngine Coolant 2 PDFvictoverОценок пока нет
- ThorpeДокумент267 страницThorpezaeem73Оценок пока нет
- Epreuve Anglais EG@2022Документ12 страницEpreuve Anglais EG@2022Tresor SokoudjouОценок пока нет
- BS 7974 2019Документ68 страницBS 7974 2019bcyt00Оценок пока нет
- 1Документ3 страницы1Stook01701Оценок пока нет
- Recruitment SelectionДокумент11 страницRecruitment SelectionMOHAMMED KHAYYUMОценок пока нет
- Manual E07ei1Документ57 страницManual E07ei1EiriHouseОценок пока нет
- Project Management TY BSC ITДокумент57 страницProject Management TY BSC ITdarshan130275% (12)
- Financial Management 2E: Rajiv Srivastava - Dr. Anil Misra Solutions To Numerical ProblemsДокумент5 страницFinancial Management 2E: Rajiv Srivastava - Dr. Anil Misra Solutions To Numerical ProblemsParesh ShahОценок пока нет
- MEd TG G07 EN 04-Oct Digital PDFДокумент94 страницыMEd TG G07 EN 04-Oct Digital PDFMadhan GanesanОценок пока нет
- Intelligent DesignДокумент21 страницаIntelligent DesignDan W ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- List of Iconic CPG Projects in SingaporeДокумент2 страницыList of Iconic CPG Projects in SingaporeKS LeeОценок пока нет
- ENT 300 Individual Assessment-Personal Entrepreneurial CompetenciesДокумент8 страницENT 300 Individual Assessment-Personal Entrepreneurial CompetenciesAbu Ammar Al-hakimОценок пока нет
- Final Selection Criteria Tunnel Cons TraДокумент32 страницыFinal Selection Criteria Tunnel Cons TraMd Mobshshir NayeemОценок пока нет
- Semi Detailed Lesson PlanДокумент2 страницыSemi Detailed Lesson PlanJean-jean Dela Cruz CamatОценок пока нет
- Virtual Assets Act, 2022Документ18 страницVirtual Assets Act, 2022Rapulu UdohОценок пока нет
- DMIT - Midbrain - DMIT SoftwareДокумент16 страницDMIT - Midbrain - DMIT SoftwarevinОценок пока нет
- Guardcam InstructionsДокумент12 страницGuardcam InstructionsCompuFix RepairsОценок пока нет
- Siemens Rapidlab 248, 348, 840, 845, 850, 855, 860, 865: Reagents & ControlsДокумент2 страницыSiemens Rapidlab 248, 348, 840, 845, 850, 855, 860, 865: Reagents & ControlsJuan Carlos CrespoОценок пока нет
- Midi Pro Adapter ManualДокумент34 страницыMidi Pro Adapter ManualUli ZukowskiОценок пока нет
- 385C Waw1-Up PDFДокумент4 страницы385C Waw1-Up PDFJUNA RUSANDI SОценок пока нет
- 레벨 테스트Документ2 страницы레벨 테스트BОценок пока нет
- Antibiotic Zone Interpretation Guide PDFДокумент2 страницыAntibiotic Zone Interpretation Guide PDFFarandy Insan Sejati100% (2)
- All Day Breakfast: .Served With Cappuccino or Espresso or Lime Juice or TeaДокумент7 страницAll Day Breakfast: .Served With Cappuccino or Espresso or Lime Juice or TeaBryan KuoKyОценок пока нет
- Google Tools: Reggie Luther Tracsoft, Inc. 706-568-4133Документ23 страницыGoogle Tools: Reggie Luther Tracsoft, Inc. 706-568-4133nbaghrechaОценок пока нет
- Csu Cep Professional Dispositions 1Документ6 страницCsu Cep Professional Dispositions 1api-502440235Оценок пока нет
- International Security Notes International Security NotesДокумент34 страницыInternational Security Notes International Security NotesBEeNaОценок пока нет
- Dec JanДокумент6 страницDec Janmadhujayan100% (1)
- Application of Geoelectric Method For GroundwaterДокумент11 страницApplication of Geoelectric Method For GroundwaterMunther DhahirОценок пока нет
- Production of Bioethanol From Empty Fruit Bunch (Efb) of Oil PalmДокумент26 страницProduction of Bioethanol From Empty Fruit Bunch (Efb) of Oil PalmcelestavionaОценок пока нет
- Decision Trees For Management of An Avulsed Permanent ToothДокумент2 страницыDecision Trees For Management of An Avulsed Permanent ToothAbhi ThakkarОценок пока нет
- Creative Polymer Clay: Over 30 Techniques and Projects for Contemporary Wearable ArtОт EverandCreative Polymer Clay: Over 30 Techniques and Projects for Contemporary Wearable ArtОценок пока нет
- Bulletproof Seduction: How to Be the Man That Women Really WantОт EverandBulletproof Seduction: How to Be the Man That Women Really WantРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (170)
- Wear It Well: Reclaim Your Closet and Rediscover the Joy of Getting DressedОт EverandWear It Well: Reclaim Your Closet and Rediscover the Joy of Getting DressedРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- The Age of Agile: How Smart Companies Are Transforming the Way Work Gets DoneОт EverandThe Age of Agile: How Smart Companies Are Transforming the Way Work Gets DoneРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (5)
- Crochet Cute Dolls with Mix-and-Match Outfits: 66 Adorable Amigurumi PatternsОт EverandCrochet Cute Dolls with Mix-and-Match Outfits: 66 Adorable Amigurumi PatternsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- The Magic of Crystals and Gems: Unlocking the Supernatural Power of Stones (Magical Crystals, Positive Energy, Mysticism)От EverandThe Magic of Crystals and Gems: Unlocking the Supernatural Power of Stones (Magical Crystals, Positive Energy, Mysticism)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (7)
- Rip It!: How to Deconstruct and Reconstruct the Clothes of Your DreamsОт EverandRip It!: How to Deconstruct and Reconstruct the Clothes of Your DreamsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (10)
- 250 Japanese Knitting Stitches: The Original Pattern Bible by Hitomi ShidaОт Everand250 Japanese Knitting Stitches: The Original Pattern Bible by Hitomi ShidaРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (7)
- Basic Black: 26 Edgy Essentials for the Modern WardrobeОт EverandBasic Black: 26 Edgy Essentials for the Modern WardrobeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (10)
- 50 Fat Quarter Makes: Fifty Sewing Projects Made Using Fat QuartersОт Everand50 Fat Quarter Makes: Fifty Sewing Projects Made Using Fat QuartersAme VersoРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (6)
- Make Your Mind Up: My Guide to Finding Your Own Style, Life, and Motavation!От EverandMake Your Mind Up: My Guide to Finding Your Own Style, Life, and Motavation!Рейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (391)
- DIY Updos, Knots, & Twists: Easy, Step-by-Step Styling Instructions for 35 Hairstyles—from Inverted Fishtails to Polished Ponytails!От EverandDIY Updos, Knots, & Twists: Easy, Step-by-Step Styling Instructions for 35 Hairstyles—from Inverted Fishtails to Polished Ponytails!Рейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (7)
- The Black Pullet: Science of Magical TalismanОт EverandThe Black Pullet: Science of Magical TalismanРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (23)
- The Ultimate Book of Outfit Formulas: A Stylish Solution to What Should I Wear?От EverandThe Ultimate Book of Outfit Formulas: A Stylish Solution to What Should I Wear?Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (23)
- Laws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesОт EverandLaws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (9)
- Friendship Bracelets: All Grown Up Hemp, Floss, and Other Boho Chic Designs to MakeОт EverandFriendship Bracelets: All Grown Up Hemp, Floss, and Other Boho Chic Designs to MakeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- Fabric Manipulation: 150 Creative Sewing TechniquesОт EverandFabric Manipulation: 150 Creative Sewing TechniquesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (13)
- A Lapidary of Sacred Stones: Their Magical and Medicinal Powers Based on the Earliest SourcesОт EverandA Lapidary of Sacred Stones: Their Magical and Medicinal Powers Based on the Earliest SourcesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Modern Ladies' Tailoring: A basic guide to pattern draftingОт EverandModern Ladies' Tailoring: A basic guide to pattern draftingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (13)
- Adorable Baby Knits: 25 Patterns for Boys and GirlsОт EverandAdorable Baby Knits: 25 Patterns for Boys and GirlsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- The Mary Brooks Picken Method of Modern DressmakingОт EverandThe Mary Brooks Picken Method of Modern DressmakingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)