Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
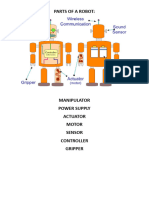
ICBT Manipulator Elements Sensors
Загружено:
Tharindu Eranga FernandoАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ICBT Manipulator Elements Sensors
Загружено:
Tharindu Eranga FernandoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
6/13/2013
1
Manipulator
Elements
Manipulator Elements
o Manipulator
o Actuators
oSensors
o End Effectors
o Controller
o Software
o Power supply
What is a Sensor?
o A sensor (also called detector) is a
converter that measures a physical
quantity and converts it into a signal
which can be read by an observer
or by an (today mostly electronic)
instrument
o Each sensor is based on a
transduction principle! ie a
conversion of energy from one form
to another
o Sensors measure a physical quantity!
they do not provide state
Why robot need SENSORS?
o "umans adapt to changes in
their environment in part by
using sensors to detect what is
going on in their environment
o Similarly sensor constitute robot#s
window to the environment A
robot needs sensing to be an
active participant in the
environment
o $he ability to adapt to particular
surroundings in one definition of
intelligence
Classes of Sensors
o Sensors for robots can be divided into three classes%
&nternal sensor (Proprioceptive)
E'ternal sensors (E'teroceptive)
Sensors fall somewhere in between( interloc)s
o Another classification of sensors is based on the emission of
energy
Active
Emits energy! eg radar
Passive
Passively receive energy eg camera
Internal Sensors
o Measures values internally to the system
o Earliest robots did not have internal sensors $hey
were programmed by setting up mechanical stops
to determine the limit of a movement
o $he first comple' sensors used by robots used
feedbac) information to ascertain the present
conditions or the position
o $he governor is a mechanical device that uses
ad*ustable spinning weights to control the
rotational speed of devices such as generators
and motors
o +or rotational *oints a shaft-encoder can be used to
detect very fine rotational movements
6/13/2013
2
External Sensors
o Measure and observe the robot
environment! ob*ects in it
o ,ne of the earliest sensor for
robots was a microswitch or
pressure sensor that would detect
when the robot had something in
its gripper
o -ater photoelectric devices were
also used to detect ob*ects in the
gripper
o -asers! cameras! radar! pro'imity
sensors can also be used as
e'ternal sensors
General sensor classification
General sensor classification Characteriin! sensor performance
o Measurement in real world environment is error prone
o .asic sensor response ratings(
Dynamic range: /atio between lower and upper limits! usually
in decibels
Range: 0ifference between min and ma'
Resolution: Minimum difference between two values
Linearity: 1ariation of output signal as function of the input
signal
Bandwidth or frequency: $he speed with which a sensor can
provide a stream of readings
Sensor performance in a situation
o Characteristics that are especially relevant for real world
environments
o Sensitivity: /atio of output change to input change
o Cross-Sensitivity: Sensitivity to environmental parameters
that are orthogonal to the target
parameters
o Error/ccuracy: 0ifference between the sensor#s output
and the true value
o Systematic/Deterministic Error: Caused by factors that
can be modeled (in theory)! eg!
calibration of a laser sensor
o Random Error: eg! hue instability of camera! blac) level
noise of camera
o Re!roduci"ility: /eproducibility of sensor results
Simple on"off touch sensor
o A simple switch
6/13/2013
3
#otentiometer
o $he resistance change as the )nob rotates
Whis$ers
o Springy wire suspended
through conductive
2hoop3
o 0eflection causes contact
with 2hoop3
o /eaches beyond robot a
few centimeters
o Simple! cheap! provides
the binary output
%umpers
o $he bumper is connected
to a microswitch
o 4hen the bumper hits on
something the microswitch
gives an output
&nidirectional
Reed s'itch
Omnidirectional
Reed s'itch
Roller contact
s'itch
(i!ht sensors
o Photoresistor (-0/)
o Photodiode
o 0ifferential photodiode
o Phototransistor
)hermal sensor
o $hermal resistor
/esistance of the sensor varies with the temperature
$wo types of thermal resistors
o P$C
o 5$C
Вам также может понравиться
- Lecture-2 Sensors and ActuatorsДокумент39 страницLecture-2 Sensors and ActuatorsDeepak TendolkarОценок пока нет
- Sensors PPT NotesДокумент23 страницыSensors PPT NotesUday sonwaneОценок пока нет
- Sensor Design: Analog and Digital SensorsДокумент4 страницыSensor Design: Analog and Digital SensorsBot StefanОценок пока нет
- Robotics Unit3 SensorsДокумент120 страницRobotics Unit3 SensorsJanarthanan BalakrishnasamyОценок пока нет
- Sensors Used in Robotics: Instituto Tecnológico Superior de HuichapanДокумент41 страницаSensors Used in Robotics: Instituto Tecnológico Superior de HuichapanLuis Ángel Ramírez NavaОценок пока нет
- Sensor For RobotДокумент4 страницыSensor For RobotMegha OmshreeОценок пока нет
- SENSOR in RoboticsДокумент20 страницSENSOR in RoboticsAlawy FoulyОценок пока нет
- HAMA - EC603 - Chapter 2 - Sensor PDFДокумент27 страницHAMA - EC603 - Chapter 2 - Sensor PDFArvinthran Thennarayasu KrishnanОценок пока нет
- Unit 4Документ45 страницUnit 4apakkiОценок пока нет
- Electronics in Robotics: BY HUM Anoi DsДокумент28 страницElectronics in Robotics: BY HUM Anoi DsShrey SuriОценок пока нет
- Module 2Документ61 страницаModule 2yashpalsingh80726Оценок пока нет
- Contactless Liquid Level ControllerДокумент5 страницContactless Liquid Level ControllerRyan Christian NantesОценок пока нет
- Sensor: Microsensor Reaches A Significantly Higher Speed and Sensitivity Compared WithДокумент7 страницSensor: Microsensor Reaches A Significantly Higher Speed and Sensitivity Compared WithMaratur RoifahОценок пока нет
- Robotics PT-IIДокумент19 страницRobotics PT-IIrutik paikraoОценок пока нет
- Sensors and Data Acquisition: Radar GunДокумент91 страницаSensors and Data Acquisition: Radar GunBurak Bildirici100% (1)
- PLC Level 1Документ46 страницPLC Level 1Mohamed MamdouhОценок пока нет
- SensorsДокумент31 страницаSensorsRameshОценок пока нет
- Face Lock SensorДокумент11 страницFace Lock SensorSadia Tasneem NishatОценок пока нет
- Ch2 Measurement Analysis and ActuationДокумент48 страницCh2 Measurement Analysis and ActuationAmina YasminОценок пока нет
- IoT SensorsДокумент15 страницIoT Sensorsbikash20ugОценок пока нет
- Types of Sensors in RoboticsДокумент30 страницTypes of Sensors in Roboticsky naОценок пока нет
- OIE 751 ROBOTICS Unit 3 Class 3 (14-9-2020)Документ10 страницOIE 751 ROBOTICS Unit 3 Class 3 (14-9-2020)MICHEL RAJОценок пока нет
- البحث الاولДокумент15 страницالبحث الاولMohamed ElzabalawyОценок пока нет
- 2.sensors and TransducersДокумент100 страниц2.sensors and TransducersKelvin RaoОценок пока нет
- 4 Sensor Communication DesignДокумент60 страниц4 Sensor Communication DesignAdam AndualemОценок пока нет
- Different Types of Sensors With Their ApplicationsДокумент9 страницDifferent Types of Sensors With Their ApplicationsaixintechОценок пока нет
- Sensor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент5 страницSensor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDaniel MacukaОценок пока нет
- Rohini 50779875870Документ4 страницыRohini 50779875870Suthin .vОценок пока нет
- 56emerging Trends in RoboticsДокумент10 страниц56emerging Trends in RoboticsshibilikОценок пока нет
- Unit-3 SensorsДокумент40 страницUnit-3 Sensorsmubin.pathan765Оценок пока нет
- Sensor Classification and How To Choose A SensorДокумент7 страницSensor Classification and How To Choose A SensorAkhilesh Reddy KarraОценок пока нет
- Auto and Control Unit 1 Notes FinalДокумент18 страницAuto and Control Unit 1 Notes Finalsupriya kharageОценок пока нет
- Sensors and ActuatorsДокумент109 страницSensors and ActuatorsDr-Amit Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Robotic NotesДокумент46 страницRobotic Noteskeerthana murugeswaranОценок пока нет
- Stepper MotorsДокумент47 страницStepper MotorsGyan KirtiОценок пока нет
- Robotics 6Документ35 страницRobotics 6nadiaОценок пока нет
- Rac Module 1Документ118 страницRac Module 1Zaheer AhamedОценок пока нет
- Sensors Question Bank For All 5 Units - Unit V Part BДокумент10 страницSensors Question Bank For All 5 Units - Unit V Part BSUBIKSHAA GUNASEKARANОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1Документ9 страницAssignment 1Alimin AnniОценок пока нет
- Electronic Component Computer Processor Light Computer Tactile SensorДокумент6 страницElectronic Component Computer Processor Light Computer Tactile SensorFrezer BelayОценок пока нет
- Position, Proximity and Motion Sensor: Prepared byДокумент27 страницPosition, Proximity and Motion Sensor: Prepared bySpidy PoudelОценок пока нет
- SensorsДокумент27 страницSensorslykarossele.nuestroОценок пока нет
- Sensors and ActuatorsДокумент13 страницSensors and Actuatorssushanta Kumar ReddyОценок пока нет
- Basic Inro - RobotsДокумент9 страницBasic Inro - RobotsAwais khalidОценок пока нет
- Sensors and Transducers: Mechatronics - Unit 1, Chapter 2Документ41 страницаSensors and Transducers: Mechatronics - Unit 1, Chapter 2Vinay KОценок пока нет
- Submiteed By: Muhammad Farhan Malik ROLL # BEE-09-165 Class: 4-B Department of Electric Engineering University of Lahore Islamabad CampusДокумент18 страницSubmiteed By: Muhammad Farhan Malik ROLL # BEE-09-165 Class: 4-B Department of Electric Engineering University of Lahore Islamabad Campussalman28100Оценок пока нет
- Asme Iit Roorkee Section: Basic ElectronicsДокумент31 страницаAsme Iit Roorkee Section: Basic ElectronicsDheeraj BudhirajaОценок пока нет
- Sensor: 1.proximity SensingДокумент4 страницыSensor: 1.proximity SensingMarvick Abuy MilarpezОценок пока нет
- Different Types of Sensors With Their ApplicationsДокумент6 страницDifferent Types of Sensors With Their ApplicationsaixintechОценок пока нет
- Sensor PDFДокумент8 страницSensor PDFConstanzaОценок пока нет
- 1.) RESISTIVE SENSORS: The Resistive Sensors Can Be Defined As The Resistance of A Sensor Can BeДокумент3 страницы1.) RESISTIVE SENSORS: The Resistive Sensors Can Be Defined As The Resistance of A Sensor Can BeSanjana SehrawatОценок пока нет
- Notes - Unit - 4Документ25 страницNotes - Unit - 4shubhtrip4Оценок пока нет
- 06 Chapter+6 SensorsДокумент92 страницы06 Chapter+6 Sensorsபுருஷோத்தமன் ரவீந்திரன்Оценок пока нет
- UNIT III Motion, Proximity, Ranging, Force, Magnetic and HeadingДокумент84 страницыUNIT III Motion, Proximity, Ranging, Force, Magnetic and HeadingAlemeОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - ASVДокумент24 страницыUnit 1 - ASVAnup S. Vibhute DITОценок пока нет
- Transducer and SensorДокумент92 страницыTransducer and SensorFemi PrinceОценок пока нет
- DAQ Lec3Документ30 страницDAQ Lec3AbdelRahman MahmoudОценок пока нет
- Sensors in Internet of ThingsДокумент5 страницSensors in Internet of ThingsAnkshu RayОценок пока нет
- Sensors and Actuators 1Документ37 страницSensors and Actuators 1Ansh PanchalОценок пока нет
- IG Client Sentiment Report 2020-12-03 12 - 00 PDFДокумент36 страницIG Client Sentiment Report 2020-12-03 12 - 00 PDFEno Ronaldfrank OguriОценок пока нет
- Dive Scubapro - Air2 3rd - Maintenance ProcedureДокумент5 страницDive Scubapro - Air2 3rd - Maintenance Proceduremanonpom100% (1)
- Dubai Holding FactsheetДокумент2 страницыDubai Holding FactsheetHarley soulОценок пока нет
- Spectral Analysis of The ECG SignalДокумент2 страницыSpectral Analysis of The ECG SignalCamilo BenitezОценок пока нет
- Winter Student Enrichment PacketДокумент9 страницWinter Student Enrichment PacketshelleyallynОценок пока нет
- A Guide To Become A Succesful Marine EngineerДокумент99 страницA Guide To Become A Succesful Marine EngineerTammam Hassan100% (1)
- 1.vedantu - Class 3 To 5 - BrochureДокумент1 страница1.vedantu - Class 3 To 5 - BrochureDeepak SharmaОценок пока нет
- Ai R16 - Unit-6Документ36 страницAi R16 - Unit-6RakeshОценок пока нет
- MOEMS 2020 Questions Paper Division EДокумент20 страницMOEMS 2020 Questions Paper Division EHarleenaDivs50% (4)
- SOM-based Generating of Association RulesДокумент5 страницSOM-based Generating of Association RulesKishor PeddiОценок пока нет
- TRG TRC001 en PsychrometryДокумент89 страницTRG TRC001 en PsychrometryhonismeОценок пока нет
- Wartsila O Env Multi Stage Flash EvaporatorsДокумент2 страницыWartsila O Env Multi Stage Flash EvaporatorsRichard Periyanayagam0% (1)
- Pre Delivery Inspection Checklist For Home Oxygen ConcentratorДокумент2 страницыPre Delivery Inspection Checklist For Home Oxygen ConcentratorPranavKaisthaОценок пока нет
- Module - 5Документ92 страницыModule - 5Anand AОценок пока нет
- ISO IEC 11801-5 - IT - Generic Cabling For Data CentreДокумент63 страницыISO IEC 11801-5 - IT - Generic Cabling For Data Centreshazwanshaiful1Оценок пока нет
- University of Central Punjab: Object Oriented ProgrammingДокумент3 страницыUniversity of Central Punjab: Object Oriented ProgrammingChoudhary MuneebОценок пока нет
- Ipcrf Core Values 2019 - FinalДокумент23 страницыIpcrf Core Values 2019 - FinalFrendelyn p. Gador100% (4)
- Final Report 2Документ110 страницFinal Report 2Aftab AliОценок пока нет
- CES Wrong Answer SummaryДокумент2 страницыCES Wrong Answer SummaryВладислав КомаровОценок пока нет
- Daftar Ebook Tentang LeanДокумент2 страницыDaftar Ebook Tentang LeanChilmar Buchari100% (1)
- Rociadores - FT - GFS-100B - GL SeriesДокумент2 страницыRociadores - FT - GFS-100B - GL SeriesJimmy FernándezОценок пока нет
- 48 Sociology: B.A./B.Sc.: Elective and OptionalДокумент4 страницы48 Sociology: B.A./B.Sc.: Elective and OptionalMОценок пока нет
- Bioinformatics Computing II: MotivationДокумент7 страницBioinformatics Computing II: MotivationTasmia SaleemОценок пока нет
- Legislation Statutory Inspection ChecklistДокумент2 страницыLegislation Statutory Inspection ChecklistAry PutraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 - Process CostingДокумент83 страницыChapter 10 - Process CostingXyne FernandezОценок пока нет
- Bird Strike ThesisДокумент7 страницBird Strike Thesisarianadavishighpoint100% (2)
- Nassaji - Schema TheoryДокумент37 страницNassaji - Schema TheoryAtiq AslamОценок пока нет
- BITS Pilani: Scale Up and Post Approval ChangesДокумент56 страницBITS Pilani: Scale Up and Post Approval ChangesshrikantmsdОценок пока нет
- No 1 Method ValidationДокумент2 страницыNo 1 Method ValidationdanaciortanОценок пока нет
- Refraction Experiment-PekaДокумент8 страницRefraction Experiment-PekaA. Suhaimi100% (3)