Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Better Health For Individuals
Загружено:
Ace CosmoОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Better Health For Individuals
Загружено:
Ace CosmoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
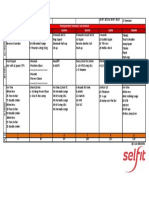
Better Health for Individuals
Meanings of health
Balance between a good physical, mental, emotional and spiritual
condition
Controlled by
individual
Early meanings
Healthy = no disease/physical illness
No consideration for mental/spiritual health
Dimensions of Health
Physical, social, mental and spiritual wellbeing = holistic view
Health level = interaction & balance between all dimensions.
Physical health
State of the physical body
Efficient functioning of:
Nutrition
Physical exercise
Decreases chance of:
Disease
Fitness up
Social Health
Interaction with others
Communicating/understanding positive relationships
Mental Health
Psychological and emotional well-being
Positive Factors:
Control stress levels
Productive work
Flexible manner
WHAT DOES HEALTH MEAN TO INDIVIDUALS?
Spiritual Health
Connection to surroundings/religion
Aspire to goal/better life
Relative nature of health
Individual health compared to others
Dynamic nature of health
Constant fluctuations occurring in one level of health
(Health continuum)
Personal Perceptions of Health
Varies from person to person
Factors include:
o Behavior
o Knowledge/experience
o Beliefs/attitude
o Environment
Perceptions of the Health of Others
Factors of perceiving others health:
Stereotypes
Media
Fitness levels
Living conditions
E.g. an individuals perception of health for a child (0-11yrs) may be
that they are constantly active with lots of friends in comparison to
an elderly, whose health focuses on decreasing disease/illness.
Implications of Different Perceptions of Health
Personal perception
Policy level; funding towards specific areas.
PERCEPTIONS OF HEALTH
Perceptions of health as social constructs
Recognizes people have different views based on their social
circumstances and what constitutes good health
Health behaviors of young people
Risk taking behaviors
Increasing rate of poor health
Positive health status
Regular research into health status, health outcomes and factors
influencing health
Health of young people continued to improve over time
Life expectancy up and mortality rates down
Social
Construct
Socioeconomic
status
income
education
employemnt
residence
geopgraphic location
rural/remote areas
urban = good service
cultural
background
ethnic meanings
e.g. aboriginal-
australian
gender
community
values and
expectations
Chronic disease reduced
Young people on themselves
Most young people perceive themselves as healthy
All stats and perceptions combined are at odds with common
beliefs held about young people
Differences among young people
Particular groups have lower health and well-being
Death rates of youth are 4 times higher
Those born between 91 and 01 will live 20 years less
Greater chance of chronic illness
Education is a significant factor
Protective:
Enhance level of health
E.g. wearing sunscreen
- Not smoking
Risk:
Development of poor health
E.g. not wearing sunscreen
- Smoking
PROTECTIVE AND RSK BEHAVIOUS
INFLUENCES ON THE HEALTH OF INDIVIDUALS
Health determinants
Positive or negative influence on our health
family
peers
media
religion
culture
knowledge
skill
genetics
attitudes
geopgraphic
location
access to health
services
technology
income
employment
education
Socioeconomic
factor
Environmental
Fctos
Sociocultural
Factors
Inidividual
Factors
Modifiable health determinants
Changed or controlled;
Nutrition
Physical wellbeing
Professional psychological help
Right decision-making (smoking etc.)
Non-modifiable health determinants
Cannot be changed or altered
Genetics
Environmental factors
Income
Disabilities-deaf/blind
Recognizes people have different views and factors on health
A person is solely responsible for their health
STRATEGIES TO PROMOTE THE HEALTH OF INDIVIDUALS
Health Promotion
Aimed at empowering people to increase control over their
health.
Responsibility for Health Promotion
Individuals
Personal behavior
Prevention of ill health achieved by making good choices and
living a healthy lifestyle
DEGREE OF CONTROL INDIVIDUALS CAN EXERT OVER THEIR
HEALTH
HEALTH AS A SOCIAL CONSTRUCT
Living conditions can restrict peoples ability to make good
choices
Empowerment
Community groups and schools
Alcoholics/gambling anonymous
School councilors/psychologists
Non-government organizations
Non-profitable
Provides counseling, support services e.g. the heart foundation,
cancer council, asthma foundation
Government
Commonwealth government: general well-being of the nation:
National tobacco campaign
Healthy Active Australia
State government: specific health promotion and disease
preventing programs:
Vehicle/passenger restrictions for p1 and p2
Allocated smoking areas
Local governments: implement state-controlled programs at
community level:
Swimming pool fenced
Lifestyle events
International Organizations
World Health Organization (WHO)
Responsible for health promotion
Health Promotion and Strategies
Lifestyle and behavioral approach
Reduce incident of risk behaviors:
Quit smoking campaign
Road Safety education
Preventative Medical approaches
Medical treatments/interventions to promote health:
Cancer screening
Childhood immunization
Public health approaches
Health promoting in schools and workplaces
Primary Prevention Stage:
Preventing illness
Immunization
Secondary Level Prevention
Reduce development of disease
o Monitoring blood pressure
o High cholesterol
Tertiary Prevention Strategies
Preventing chronic ill health through rehabilitation
o Asthma Management Plan
Gives health promotion direction through clear definitions, action
plans and positive involvement
OTTOWA CHARTER
Name Description Examples
DEVELOPING
PERSONAL
SKILLS
Provides an education to
enhance life skills to make
healthy choices
Health campaigns:
- Healthy Harold
- Nothing healthy
about a tan
commercial
CREATIVE
SUPPORTIVE
ENVIRONMENTS
Link between people and their
environment (work and living
conditions) and the
maintenance and care of the
physical environment
- Ads of cleanliness of
parks
- School shelter
- Local council support
STRENGTHEN
COMMUNITY
ACTION
Empowerment of the
communities to enhance self
help and social support to
develop flexible systems for
strengthening public
participation
- Hospitals
- Public transport
- Psychologists
- Charity fun runs
REORIENTE
HEALTH
SERVICE
Changes the focus off official
services to services that are
accessible to a variety of diverse
culture, communities and
society in general
- Heart foundation
- St Vincent De Paul
BUILDING
HEALTH PUBLIC
POLICY
Relation to legislation and laws
keeping society safe
- Use of seatbelt
- Intolerance of drink
driving
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Insanity Workout Calendar Months 1-2Документ2 страницыInsanity Workout Calendar Months 1-2jeanОценок пока нет
- Pe 10 Q2Документ152 страницыPe 10 Q2Lanie Tamacio Baday85% (20)
- Pe9 - q1 - Mod1 - Physical Activity and Physical Fitness Assessments - v3Документ27 страницPe9 - q1 - Mod1 - Physical Activity and Physical Fitness Assessments - v3Clark88% (17)
- P.E Quiz 1 - 10Документ4 страницыP.E Quiz 1 - 10Michalcova Realisan Jezza100% (1)
- Checking Assumptions of Normality Regression STATAДокумент3 страницыChecking Assumptions of Normality Regression STATAAce CosmoОценок пока нет
- Bonferroni TableДокумент1 страницаBonferroni TableAce CosmoОценок пока нет
- Consistency IIДокумент2 страницыConsistency IIAce CosmoОценок пока нет
- To What Extent Was Germany A Totalitarian State 1933-39Документ2 страницыTo What Extent Was Germany A Totalitarian State 1933-39Ace Cosmo100% (1)
- Germaine GreerДокумент2 страницыGermaine GreerAce CosmoОценок пока нет
- Germaine GreerДокумент4 страницыGermaine GreerAce CosmoОценок пока нет
- Germaine GreerДокумент2 страницыGermaine GreerAce CosmoОценок пока нет
- Pressman EnglishДокумент40 страницPressman Englishudi969Оценок пока нет
- Soccer For Life U13 U17 Training Plan and PeriodizationДокумент6 страницSoccer For Life U13 U17 Training Plan and Periodizationsoccer1361Оценок пока нет
- Programação Intense 2 SemanaДокумент1 страницаProgramação Intense 2 SemanaIgor TavaresОценок пока нет
- Topic: The Bicycle - The Future Means of Transportation: A. IntroductionДокумент3 страницыTopic: The Bicycle - The Future Means of Transportation: A. IntroductionHoàng Yến PhùngОценок пока нет
- CCE (Updated)Документ31 страницаCCE (Updated)Zuhair Samion (Bmss)Оценок пока нет
- Hyperextensions Band W, Y and TS: Squat Deadlift Bench OHP Estimated Max PR's 11/2/2015 Tuesday WednesdayДокумент33 страницыHyperextensions Band W, Y and TS: Squat Deadlift Bench OHP Estimated Max PR's 11/2/2015 Tuesday WednesdayJames BuchanОценок пока нет
- ProPG - GYM - Acoustic-GuidanceДокумент85 страницProPG - GYM - Acoustic-Guidancealeisterparadigma666Оценок пока нет
- Ielts Speaking Transcript 1 3Документ3 страницыIelts Speaking Transcript 1 3Hồng NhiОценок пока нет
- Effect of Game Specific Aerobic Training On Motor Fitness Components Among Handball PlayersДокумент3 страницыEffect of Game Specific Aerobic Training On Motor Fitness Components Among Handball PlayersSENTHIL KUMARAN SОценок пока нет
- 6 Myths About YogaДокумент2 страницы6 Myths About YogaAditya BakshiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Physical Fitness: Intended Learning OutcomeДокумент7 страницChapter 1: Physical Fitness: Intended Learning OutcomeTrazona Joemar E.Оценок пока нет
- Muscle Memo Workout - Guitar Coach MagДокумент28 страницMuscle Memo Workout - Guitar Coach Magpeterd87Оценок пока нет
- The Exercise PrescriptionДокумент68 страницThe Exercise PrescriptionDario MoralesОценок пока нет
- News Bharatkasankalp Com List of Best Gym in DehradunДокумент4 страницыNews Bharatkasankalp Com List of Best Gym in DehradunSANJAY PANDEYОценок пока нет
- Physical Education and Health Grade 12 1st SemesterДокумент4 страницыPhysical Education and Health Grade 12 1st SemesterFranzcine100% (3)
- Strength Training Program and 1RM CalculatorДокумент24 страницыStrength Training Program and 1RM CalculatorshotfollowОценок пока нет
- Cult Fitness Franchise & Centre Opportunities Under 40 CharactersДокумент27 страницCult Fitness Franchise & Centre Opportunities Under 40 CharactersVishwasОценок пока нет
- Lesson 3 Q2Документ32 страницыLesson 3 Q2John michael SumagaysayОценок пока нет
- Part I: Directions For Your EssayДокумент2 страницыPart I: Directions For Your EssayNATHAN D ANGELOОценок пока нет
- Std. Physical Education Notes of Lesson-2020-21Документ10 страницStd. Physical Education Notes of Lesson-2020-21Loverboy VlОценок пока нет
- HighNote3 U3 Test BДокумент3 страницыHighNote3 U3 Test BWioleta KujawskaОценок пока нет
- 30 Day Push Up ChallengeДокумент1 страница30 Day Push Up ChallengeHarold ApostolОценок пока нет
- Physical Education and Health Grade 11 Quiz AnswersДокумент12 страницPhysical Education and Health Grade 11 Quiz AnswersColeen ColladoОценок пока нет
- BBI2002 SCL 7 WEEK 8 AdamДокумент3 страницыBBI2002 SCL 7 WEEK 8 AdamAMIRUL RIDZLAN BIN RUSIHAN / UPMОценок пока нет
- Utilization of Time Motion Analysis in The Development of Training Programs For Surfing AthletesДокумент8 страницUtilization of Time Motion Analysis in The Development of Training Programs For Surfing AthletesCharles MitchellОценок пока нет
- 8 Week Shred 1470077297538Документ2 страницы8 Week Shred 1470077297538Jesus Castro Machuca0% (1)