Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Zero Crossing Detector and Window Detector
Загружено:
Timoth DevОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Zero Crossing Detector and Window Detector
Загружено:
Timoth DevАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
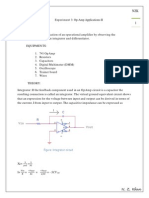
Experiment 6 : ZERO CROSSING DETECTOR, WINDOW DETECTOR AND
SCHMITT TRIGGER
AIM: To design and construct zero crossing detector, window detector and Schmitt trigger
and test their working.
COMPONENTS AND EQUIPEMENTS REQUIRED:
Bread board, 741 IC, resistors, capacitors, Function generator, CRO, regulated power supply
THEORY:
Comparator is a circuit that produces two output state +V
sat
and -V
sat
by comparing the
input signal with a reference voltage. If the input signal is applied to the inverting terminal of
op-amp then for input voltages less than V
ref
, the output is equal to +V
sat
and for input
voltages greater than v
ref
, the output voltage is equal to V
sat
. If the reference voltage is zero,
then the comparator can be used as zero crossing detector. If the applied input signal is a
sinusoid, then for positive half cycle, the output is V
sat
and for negative half cycle, the
output is +V
sat
thus producing a square wave. That is the zero- crossing detector can be used
to convert a sinusoidal wave form to a square wave.
Fig.6.1. Zero Crossing detector
PROCEDURE:
1. Place 741 IC on the bread board and connect external components.
2. Connect dual power supply to op-amp.
3. Apply sinusoidal input of 5v p-p and 1khz frequency.
4. Observe the output and plot input and output waveforms on graph sheet.
Model graph:
Fig.6.2
WINDOW DETECTOR:
Sometimes one may like to mark the instant at which an unknown input is between two
threshold levels. This can be achieved by a circuit called window detector. The circuit
diagram for window detector is shown in figure. Since the current through both operational
amplifiers is zero, the branch with three 10 resistors acts as a voltage divider network. The
input voltage is applied to non-inverting terminal and reference voltage is applied to inverting
terminal of both op-amps. However the reference voltage applied to inverting terminals are
not equal. The reference voltage at inverting terminal of op-amp1 is
((1220)/(10+10+10))=8V and the reference voltage at inverting terminal of op-amp2 is
((1210)/(10+10+10))=4V. If the input voltage is between 0 and 4v, the output of both op-
amps is equal to V
sat
. As a result LED1 switches on. Remaining two LEDs are in off
condition. If the input coltage v
i
lies between 4 and 8, then the output of opamp 1 is + v
sat
and
opam 2 is -V
sat
. This swithes LED 1 to off state and LED 2 to on state. The LED 3 is in off
condition. When the input voltage is greater than 8 volts, the out put of both opamps is +v
sat.
Therefore LED3 is in on condition. Therefore depending on which of the LEDs are in on, we
can find the input voltage levels.
Fig.6.3. Window Detector
PROCEDURE:
1. Place 741 IC on the bread board and connect external components.
2. Connect dual power supply to op-amp.
3. Connect a variable input voltage source to non-inverting terminal.
4. Vary the input voltage and observe the switching of LEDs.
THEORITICAL PRACTICAL LED1 LED2 LED3
0 < v
i
< 4 ON OFF OFF
4 < v
i
< 8 OFF ON OFF
8 < v
i
< 12 OFF OFF ON
SCHMITT TRIGGER:
The other name for Schmitt trigger is regenerative comparator. In Schmitt trigger positive
feedback is used which forces the op-amp to drive in saturation. The voltage divider network
connected at the output, provide positive feedback. The input voltage is applied to the
inverting terminal. The voltage at non-inverting terminal can be obtained using superposition
theorem. Let us assume initially V
i
< V
N
, then the output is equal to V
sat
.
12V
AD8011AN
3
2
4
7
6
Vi
AD8011AN
3
2
4
7
6
1
R1
10k
5
R2
10k
R3
10k
9
0
7
LED2
LED3
LED1
2
R5
4.7k
3
R6
4.7k
8
R7
5.6k
4
R8
5.6k
6
0
0
-12V
Opamp2
Opamp1
The voltage at non-inverting terminal is
1
2
1 2 1 2
ref
sat
N
V R
V R
V
R R R R
----------------------(1)
This voltage is known as V
UTP.
If the input voltage is less than V
UTP
, the output is v
sat
. When the input crosses beyond V
UTP
,
the output switches to v
sat
.
Now the voltage at non-inverting terminal is equal to
1
2
1 2 1 2
ref
sat
N
V R
V R
V
R R R R
--------------------(2)
The above voltage is known as V
LTP
When the input voltage is less than V
LTP
, the output voltage switches from V
sat
to +V
sat
.
Note that V
LTP
< V
UTP .
The difference between these two voltages is known as Hysteresis and can be written as
2
1 2
2
sat
H UTP LTP
V R
V V V
R R
Because of hysteresis, the circuit triggers at a higher voltage for increasing signals than for
decreasing ones.
DESIGN:
2
1 2
2 1 2
1
1 2
3 1 2
3.5 and 2
2(12)
1 , 3.36 , 3.3
2( )
1.5
0.97
1
|| 770 ..
720
UTP LTP
H UTP LTP
ref
UTP LTP
ref
ref
Let V V V V
R
V V V
R R
If R k then R k So select R k
V R
V V
R R
Substituting the values we get V V
So select V V
R R R ohms
Select ohms
PROCEDURE:
1. Place 741 IC on the bread board and connect external components.
2. Connect dual power supply to op-amp.
3. Apply sinusoidal input of 5v p-p and 1kHz frequency.
4. Observe the output and plot input and output waveforms on graph sheet.
5. Find the values of V
LTP
and V
UTP
and compare with theoretical values.
Transfer Characteristics
To find the transfer characteristics of Schmitt trigger consider the circuit
shown in figure
The UTP and LTP of the circuit is 5.7 volts and 3.3 volts respectively. Connect the power
supply at input increase the voltage from 0 to 10 volts and note down the output voltage.
Next decrease the input voltage from 10 to 0 volts and note down the readings. Plot a graph
between input voltage and out put voltage.
Model graph
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
-15
-10
-5
0
5
10
15
iNPUT Vi
O
U
T
P
U
T
V
o
HTP LTP
Vsat
-Vsat
Fig. Transfer Characteristics of Schmitt trigger
Result: The circuits for zero crossing detector, window detector and schmitt trigger were
designed and analysed.
Viva Questions
1. What are the non-linear applications of op-amp?
2. Explain the operation of i) inverting comparator ii) Non-inverting
comparator.
3. Explain the applications of comparator.
4. What are the applications of op-amp? Explain any one practical
application.
5. What is the other name for Schmitt trigger?
6. Which feedback is used in Schmitt trigger?
7. Define i) UTP ii) LTP
8. Define Hysteresis
9. With an example, explain how the Schmitt trigger circuit can be used to
design an on-off controller.
Вам также может понравиться
- Experiment - 05Документ17 страницExperiment - 05Sagar SharmaОценок пока нет
- Triangular Wave Generator Using Op Amp - WaveformsДокумент6 страницTriangular Wave Generator Using Op Amp - WaveformsNagendrababu VasaОценок пока нет
- Emitter FollowerДокумент8 страницEmitter FollowerjerlineprincyОценок пока нет
- 2b RectifierДокумент21 страница2b RectifierLove StrikeОценок пока нет
- Experiment PE LABДокумент5 страницExperiment PE LABsureshfm1100% (1)
- LIC Manual NewДокумент84 страницыLIC Manual NewVandhana PramodhanОценок пока нет
- Aim: To Test Differentiator and Integrator Circuits Using Ua741op-AmpДокумент8 страницAim: To Test Differentiator and Integrator Circuits Using Ua741op-AmpAvinash Nandakumar100% (1)
- BJTДокумент6 страницBJTengineerluvОценок пока нет
- Transformer Coupled AmplifierДокумент6 страницTransformer Coupled AmplifierXyrex CalangОценок пока нет
- Applications of Opamp As Comparators & Schmitt TriggerДокумент4 страницыApplications of Opamp As Comparators & Schmitt TriggerPaul JambormiasОценок пока нет
- Ecet321l - E1 - Single Stage Ce AmplifierДокумент9 страницEcet321l - E1 - Single Stage Ce AmplifierKenneth DomingoОценок пока нет
- Analog Circuits SyllabusДокумент5 страницAnalog Circuits SyllabusVilayil jestinОценок пока нет
- Presentation On A Variable Audio Frequency Oscillator Using Op-Amp 741Документ13 страницPresentation On A Variable Audio Frequency Oscillator Using Op-Amp 741Moriyom MouОценок пока нет
- Name of The Experiment-Design & Simulation of Differentiator Amplifier Using 741 Op-Amp IC. Instrument/ Components Required - Proteus Simulator. TheoryДокумент3 страницыName of The Experiment-Design & Simulation of Differentiator Amplifier Using 741 Op-Amp IC. Instrument/ Components Required - Proteus Simulator. TheoryBidyut Prasad dalai100% (1)
- ADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFДокумент21 страницаADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFJk RinkuОценок пока нет
- Experiment No:9: Op-Amp As A DifferentiatorДокумент2 страницыExperiment No:9: Op-Amp As A DifferentiatorBhadresh Renuka100% (1)
- Half Wave Rectification Experiment - 3: TheoryДокумент10 страницHalf Wave Rectification Experiment - 3: TheoryLakshayОценок пока нет
- Op Amp IntegratorДокумент14 страницOp Amp IntegratorMuhammad Haroon50% (2)
- RC Phase Shift OscillatorДокумент3 страницыRC Phase Shift Oscillatoreseses100% (1)
- Amplifiers and OscillatorsДокумент10 страницAmplifiers and OscillatorsKapil ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- Analog Communications Lab Manual - AsraoДокумент128 страницAnalog Communications Lab Manual - AsraoAllanki Sanyasi RaoОценок пока нет
- Network Analysis and Synthesis QBДокумент11 страницNetwork Analysis and Synthesis QBGowthamОценок пока нет
- Single Tuned Amplifier: Experiment:5Документ2 страницыSingle Tuned Amplifier: Experiment:5hari007kmrОценок пока нет
- Exp 11 Voltage Regulator Using IC 723Документ5 страницExp 11 Voltage Regulator Using IC 723Savio Pereira67% (3)
- EDC Lab ManualДокумент45 страницEDC Lab ManualChirag Sachdeva100% (2)
- Analog Communications Lab ManualДокумент61 страницаAnalog Communications Lab ManualSriLakshmi RaheemОценок пока нет
- EDC Question BankДокумент13 страницEDC Question BankvenzkrishОценок пока нет
- 9 CE AmplifierДокумент5 страниц9 CE AmplifierAnsh PratapОценок пока нет
- AIC Lab ManualДокумент36 страницAIC Lab ManualSangamesh V AngadiОценок пока нет
- Expt No. 03 - To Design and Test Op Amp Integrator For Given FrequenciesДокумент7 страницExpt No. 03 - To Design and Test Op Amp Integrator For Given FrequenciesPrakash Narkhede100% (1)
- 5.) Common Drain AmplifierДокумент5 страниц5.) Common Drain AmplifierJuay Mae Riano100% (1)
- ECE Experiment No 5Документ11 страницECE Experiment No 5GeeK GuYОценок пока нет
- Integrator DiffentiatorДокумент7 страницIntegrator Diffentiatorআব্দুল্লাহ আল ইমরানОценок пока нет
- EC6411 Circuit & Devices Lab ManualДокумент93 страницыEC6411 Circuit & Devices Lab ManualKALAIMATHIОценок пока нет
- Experiment No. 4: Integrator and Differentiator Using 741 Op-AmpДокумент4 страницыExperiment No. 4: Integrator and Differentiator Using 741 Op-AmpPrasad mohiteОценок пока нет
- Vlsi Lab 1Документ11 страницVlsi Lab 1Shawon karmokar JotyОценок пока нет
- Intro Op AmpДокумент44 страницыIntro Op AmpNimish PrabhakarОценок пока нет
- Experiment No.2: Colpitt OscillatorДокумент3 страницыExperiment No.2: Colpitt OscillatorBhadresh Renuka50% (2)
- Differentiator ExperimentДокумент25 страницDifferentiator ExperimentAlyaa Nadzirah Binti Shbini100% (1)
- Submitted By: Rameshkumar Lakshmi Prabha Abirami R LoganandhiniДокумент22 страницыSubmitted By: Rameshkumar Lakshmi Prabha Abirami R LoganandhiniAbirami RajaОценок пока нет
- Applied Electronics II (Chapter 4)Документ34 страницыApplied Electronics II (Chapter 4)Ermias MesfinОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 ComparatorsДокумент54 страницыUnit 3 ComparatorsSoundararajan RajagopalanОценок пока нет
- 3.analysis of Class B AmplifiersДокумент24 страницы3.analysis of Class B AmplifiersMbugua DuncanОценок пока нет
- Experiment: Title: DC Power Supply Unit: Transformer ObjectiveДокумент14 страницExperiment: Title: DC Power Supply Unit: Transformer ObjectiveLian Ai Chen100% (1)
- Differential AmplifierДокумент15 страницDifferential AmplifierrppvchОценок пока нет
- Network AnalysisДокумент22 страницыNetwork AnalysisShravan Kumar NamdeoОценок пока нет
- EXPT:-Study of Decade Counter Using IC 7490 Apparatus: - IC 7490, Bradboard, Single Stand Wires TheoryДокумент2 страницыEXPT:-Study of Decade Counter Using IC 7490 Apparatus: - IC 7490, Bradboard, Single Stand Wires TheoryPoonam Gholap100% (1)
- AC Circuits: Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsДокумент16 страницAC Circuits: Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsHiếu Dương100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Manual OgataДокумент53 страницыChapter 8 Manual OgataKalim UllahОценок пока нет
- EXP17 Class A Power AmplifierДокумент3 страницыEXP17 Class A Power AmplifierMohammed Dyhia AliОценок пока нет
- Solved ProblemsДокумент24 страницыSolved ProblemsParth Cholera100% (1)
- To Use A Multimeter To (A) Identify Base of Transistor, (B)Документ6 страницTo Use A Multimeter To (A) Identify Base of Transistor, (B)aff bearОценок пока нет
- The Class B Push Pull AmplifierДокумент4 страницыThe Class B Push Pull AmplifierMaryum Ali100% (1)
- Class B Complementary Symmetry Power AmplifierДокумент15 страницClass B Complementary Symmetry Power AmplifierMuthukrishnan Vijayan VijayanОценок пока нет
- IntegratorДокумент38 страницIntegratorSyed AshmadОценок пока нет
- Circuits and Simulation Lab ManualДокумент99 страницCircuits and Simulation Lab Manualkasim_1983Оценок пока нет
- Constant-Gain MultiplierДокумент10 страницConstant-Gain Multiplierstreamer akoОценок пока нет
- List of Experiments: Ic Applications Lab Minimum Twelve Experiments To Be ConductedДокумент6 страницList of Experiments: Ic Applications Lab Minimum Twelve Experiments To Be ConductedAmy OliverОценок пока нет
- Ic Applications Lab NewДокумент12 страницIc Applications Lab NewSandy RonaldoОценок пока нет
- ACT - 1 - Paper 1 ResonanceДокумент27 страницACT - 1 - Paper 1 ResonanceTridipta MishraОценок пока нет
- SA PowerBu D9225Документ86 страницSA PowerBu D9225juanlasserre9444Оценок пока нет
- Protection Cathodic PDFДокумент123 страницыProtection Cathodic PDFBoussaid SouheilОценок пока нет
- Eaglerise Profile 2010Документ18 страницEaglerise Profile 2010李昊Оценок пока нет
- T7S 1250 PR231/P LS/I in 1250A 3p F FДокумент3 страницыT7S 1250 PR231/P LS/I in 1250A 3p F FAldair PeraltaОценок пока нет
- Insulation Coordination Study Report - 2019phxp0901u PDFДокумент16 страницInsulation Coordination Study Report - 2019phxp0901u PDFSudhir Ravipudi100% (1)
- LJP Prereport Simulation and Manufacturing PDFДокумент15 страницLJP Prereport Simulation and Manufacturing PDFcommando1180Оценок пока нет
- Sircover Series - Manual CHANGEOVER Switches: General CharacteristicsДокумент2 страницыSircover Series - Manual CHANGEOVER Switches: General CharacteristicsThilinaОценок пока нет
- Phase-Control Alternatives For Single-Phase AC Motors Offer Smart, Low-Cost, SolutionsДокумент8 страницPhase-Control Alternatives For Single-Phase AC Motors Offer Smart, Low-Cost, SolutionsAdedotun J. AgbemukoОценок пока нет
- Principles Of: Electr IcityДокумент19 страницPrinciples Of: Electr IcityMarion Lacre MacalaladОценок пока нет
- Epas G9 M Q3 W3-W4Документ4 страницыEpas G9 M Q3 W3-W4ALLYSSA MAE PELONIAОценок пока нет
- 0330 572 Pve B 125 00Документ122 страницы0330 572 Pve B 125 00RohitОценок пока нет
- Speed Regulation An Induction Motor Using Reference Adaptive ControlДокумент5 страницSpeed Regulation An Induction Motor Using Reference Adaptive ControlAtakan OzturKОценок пока нет
- C1786 PDFДокумент3 страницыC1786 PDFbob loblawОценок пока нет
- Tube Headphone Amplifier Schematic TypoДокумент11 страницTube Headphone Amplifier Schematic TypoFrancisco RøedОценок пока нет
- Southern Cable CatalogДокумент62 страницыSouthern Cable Catalogahish_8955% (20)
- 1MRK505031-BEN B en General Differential Protection RED 521 1.0Документ20 страниц1MRK505031-BEN B en General Differential Protection RED 521 1.0muraliОценок пока нет
- MV Distribution Circuit-Breakers LF1 - LF2 - LF3 ... - Schneider ElectricДокумент11 страницMV Distribution Circuit-Breakers LF1 - LF2 - LF3 ... - Schneider ElectricAdelAlcebaiОценок пока нет
- Condition Assessment - HT MachineДокумент20 страницCondition Assessment - HT MachineFerozMujawar0% (1)
- COMVIBOXДокумент52 страницыCOMVIBOXRoberto HernandezОценок пока нет
- Energy Reductions in The Pulp-And-Paper Industry by Upgrading Conventional Pumping Systems Through The Installation of Vfds - A Case StudyДокумент6 страницEnergy Reductions in The Pulp-And-Paper Industry by Upgrading Conventional Pumping Systems Through The Installation of Vfds - A Case StudytorinomgОценок пока нет
- PM100P - ManualДокумент8 страницPM100P - ManualAlin VasileОценок пока нет
- CXL 70-3LW H PDFДокумент3 страницыCXL 70-3LW H PDFManuel EspnzaОценок пока нет
- Coulomb's Law PacketДокумент4 страницыCoulomb's Law PacketMohit MjОценок пока нет
- Z4-8MK3 Manual en v1.2Документ32 страницыZ4-8MK3 Manual en v1.2NharperОценок пока нет
- Detector 70-02 - Photo Smoke Detector Model CPD-7157 - 2010Документ4 страницыDetector 70-02 - Photo Smoke Detector Model CPD-7157 - 2010DM2Оценок пока нет
- Smith Charts&antenna PDFДокумент5 страницSmith Charts&antenna PDFMilan MakwanaОценок пока нет
- Best X DC BrochureДокумент46 страницBest X DC Brochureأياام زمانОценок пока нет
- Veterinary Radiography, A Workbook For Students (VetBooks - Ir) PDFДокумент131 страницаVeterinary Radiography, A Workbook For Students (VetBooks - Ir) PDFDragos HodorОценок пока нет
- 01 Vacon AC Drives Basic CourseДокумент43 страницы01 Vacon AC Drives Basic CourseKarthik Sriramakavacham100% (2)