Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
List of Chapters:: Section 1. Wind Energy and Their Applications
Загружено:
Akshay GeraОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
List of Chapters:: Section 1. Wind Energy and Their Applications
Загружено:
Akshay GeraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
List of Chapters:
Preface
About the Editors
Section 1. Wind Energy and Their Applications
1. Wind Energy Resources: Theory, Design and
Applications 3
Fang Yao, Ramesh C. Bansal, Zhao Yang Dong,
Ram K. Saket and Jitendra S. Shakya
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Power intheWind
1.3 Wind Turbine Design Considerations
1.4 Grid ConnectedWind Farms
1.5 Hybrid Power Systems
1.6 Economics ofWind Power Systems
1.7 Conclusion
References
2. Wind Turbine Systems: History, Structure, and
Dynamic Mode
S. Masoud Barakati
2.1 Wind Energy Conversion System (WECS)
2.2 Overall Dynamic Model of theWind
Turbine System and Small Signal
Analysis
References
3. Wind Turbine Generation Systems Modeling for
Integration in Power Systems
Adri Junyent-Ferre and Oriol Gomis-Bellmunt
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Wind Turbine Modeling
3.3 Wind Modeling
3.4 Mechanical Transmission Modeling
3.5 Electrical Generator Modeling
3.6 Converter Modeling
3.7 Control Modeling
3.8 Electrical Disturbances
3.9 Conclusions
References
4. Technologies and Methods used inWind Resource
Assessment
Ravita D. Prasad and Ramesh C. Bansal
4.1 Introduction
4.2 Literature Review, Methods and
Software used in WRA
4.3 Wind Characteristics for Site
4.4 Find the Optimum Wind Turbine which
Yields High Energy at High Capacity
Factor
4.5 Uncertainties Involved in Predicting
Wind Speeds using the Different
Approaches of WRA
4.6 Concluding Remarks
References
5. Economic Analysis ofWind Systems
Ravita D. Prasad and Ramesh C. Bansal
5.1 Introduction
5.2 Wind System Economic Components
5.3 Economic Analysis Methods
5.4 Case Study for the Economic Analysis
of aWind Turbine
5.5 Conclusions
References
6. Line Side Converters inWind Power Applications
Ana Vladan Stankovic and Dejan Schreiber
6.1 Introduction
6.2 Line Side Converters
6.3 Principle of Operation
6.4 Control of a Line-Side Converter under
Balanced Operating Conditions
6.5 Line Side Converters under
Unbalanced Operating Conditions
6.6 Analysis of the PWM Converter under
Unbalanced Operating Conditions
6.7 Control Method for Input-Output
Harmonic Elimination of the PWM
Converter under Unbalanced Operating
Conditions
Handbook Of
Renewable Energy
Technology
Handbook Of Renewable Energy Technology
6.8 Examples
6.9 Concluding Remarks
References
7. Wake Effects fromWind Turbines on Overhead
Lines
Brian Wareing
7.1 Introduction
7.2 Literature Survey and Review of
any Modeling or Field TestWork
7.3 Effect of Wind Speed and Turbulence
on Overhead Lines
7.4 CENELEC Standards
7.5 Wind Tunnel Results
7.6 Comparison with Other Data
7.7 Effect of Multiple Turbines on the OHL
7.8 Solutions
7.9 Summary
References
Section 2. Solar Energy Systems
8. Solar Energy Calculations
Keith E. Holbert and Devarajan Srinivasan
8.1 Introduction
8.2 Earths Orbit
8.3 Solar Constant and Solar Spectra
8.4 Solar Angles
8.5 Collector Angles
8.6 Solar Irradiance .
8.7 Comparison to Measured Data
8.8 Photovoltaic Energy Conversion
8.9 Concluding Remarks
References
9. Photovoltaic Systems 205
Ravita D. Prasad and Ramesh C. Bansal
9.1 Introduction
9.2 PV Modules
9.3 Types of PV Systems
9.4 Concluding Remarks
References
10. Solar Thermal Electric Power Plants 225
Keith E. Holbert
10.1 Introduction
10.2 Solar Thermal Systems
10.3 Concentrating Solar Power Systems
10.4 Low Temperature Solar Thermal
Approaches
10.5 Environmental Impact
10.6 Concluding Remarks
References
11. Maximum Power Point Tracking Charge Controllers
Ashish Pandey, Nivedita Thakur and Ashok Kumar
Mukerjee
11.1 Solar Battery Charging .
11.2 Various Sources of Losses
11.3 Charge Control in Battery Backed
PV Systems
11.4 Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)
11.5 Advance Issues and Algorithms .
11.6 Conclusion
11.7 Further Readings
References
12. Non-grid Solar Thermal Technologies
Mahendra S. Seveda, Narendra S. Rathore and
Vinod Kumar
12.1 Introduction
12.2 Solar Collectors
12.3 Solar Drying
12.4 Solar Cooking
12.5 Solar Water Heating
12.6 Solar Distillation
12.7 Solar Heating of Buildings
12.8 Conclusions
References .
13. Solar Tunnel Dryer A Promising Option for Solar
Drying
Mahendra S. Seveda, Narendra S. Rathore and
Vinod Kumar
13.1 Introduction
13.2 Principle of Drying .
13.3 Open Sun Drying .
13.4 Types of Solar Dryers
13.5 Factors Affecting Solar Drying .
13.6 Selection of Solar Dryers
13.7 Solar Tunnel Dryer
13.8 Case Studies on Solar Tunnel Dryer
for Drying Agricultural Product
(Embilica Offcinalis Pulp)
13.9 Case Studies on SolarTunnel Dryer for
Drying Industrial Product (Di-basic
Calcium Phosphate)
13.10 Conclusions
References
Section 3. Bio Fuels
14. Biomass as a Source of Energy
Mahendra S. Seveda, Narendra S. Rathore and
Vinod Kumar
14.1 Introduction
14.2 Types of Biomass
14.3 Energy Content of Biomass
Handbook Of Renewable Energy Technology
14.4 Harvesting Methods of Biomass
14.5 Conversion of Biomass
14.6 Thermo-Chemical Conversion of
Biomass
14.7 Biodiesel Production .
14.8 Bioethanol Production
14.9 Conclusions
References
15. Forest Biomass Production
Severiano Prez, Carlos J. Renedo, Alfredo Ortiz,
Mario Maana and Carlos Tejedor
15.1 Introduction
15.2 Bioclimatic Potential
15.3 Forest Species
15.4 Evaluation of Forest Biomass
15.5 Collection Systems for Forest Biomass
15.6 Environmental Impact Resulting from
the Generation and Exploitation of
Forest Biomass
15.7 Conclusions
References
16. Bioethanol
Alfredo Ortiz, Severiano Prez, Carlos J. Renedo,
Mario Maana and Fernando Delgado
16.1 Technical Fundamentals
16.2 Level of Development
16.3 Strengths andWeaknesses
16.4 Environmental Impact
16.5 Economics .
16.6 Combination with Conventional
Sources
16.7 Conclusions
References
17. Biodiesel
Carlos J. Renedo, Alfredo Ortiz, Severiano Prez,
Mario Maana and Inmaculada Fernndez
17.1 Fundamentals
17.2 Level of Development
17.3 Strengths andWeaknesses
17.4 Environmental Impact
17.5 Economics
17.6 Combination with Conventional
Sources
17.7 Conclusions
References
Section 4. Ocean and Small Hydro Energy Systems
18. Technologies and Methods used in Marine Energy
and Farm System Model
V. Patel Kiranben and M. Patel Suvin
18.1 Introduction
18.2 Marine Energy: How Much
Development Potential is There?
18.3 Understanding the Power of Marine
Energy .
18.4 Global Development of Marine Energy
18.5 Possible Impacts .
18.6 OceanWave Energy .
18.7 Ocean Tide Energy
18.8 Mathematical Modeling of Tidal Schemes
18.9 Global Environmental Impact
18.10 Operating Tidal Power Schemes
18.11 Conclusions
References
19. Operational Challenges of Low Power Hydro
Plants
Arulampalam Atputharajah
19.1 Introduction
19.2 Low Power Hydro Plants
19.3 Micro Hydro Plants
19.4 Concluding Remarks
References
20. Frequency Control in Isolated Small Hydro Power
Plant
Suryanarayana Doolla
20.1 Introduction
20.2 Mathematical Modeling of an Isolated
SHP Plant
20.3 Frequency Control using On/Off
Control Valve with Reduced Size of
Dump Load
20.4 Frequency Control using Servo Motor
Along with On/Off Control Valve
20.5 Conclusions
References
Section 5. Simulation Tools, Distributed Generation
and Grid Integration
21. Simulation Tools for Feasibility Studies of
Renewable Energy Sources
Juan A. Martinez-Velasco and Jacinto Martin-
Arnedo
21.1 Introduction
21.2 Modeling for Feasibility Studies
21.3 Economic Modeling
21.4 Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction
21.5 Simulation Tools
21.6 Application Examples
21.7 Discussion
References
Handbook Of Renewable Energy Technology
22. Distributed Generation: A Power System
Perspective
Hitesh D. Mathur, Nguyen Cong Hien, Nadarajah
Mithulananthan, Dheeraj Joshi and Ramesh C.
Bansal
22.1 Introduction
22.2 Distributed Generation Systems
22.3 Impact of Distributed Generation on
Electrical Power System
22.4 Conclusions
References
23. DG Allocation in Primary Distribution Systems
Considering Loss Reduction
Duong Quoc Hung and Nadarajah Mithulananthan
23.1 Introduction
23.2 Distributed Generation
23.3 Loss Reduction in Distribution Systems
23.4 Loss Reduction Using DG
23.5 Numerical Results
23.6 Conclusions
References
24. Renewable-Based Generation Integration in
Electricity Markets with Virtual Power Producers
Zita A. Vale, Hugo Morais and Hussein Khodr
24.1 Introduction
24.2 Electricity Markets and DG
24.3 Virtual Power Producers (VPP)
24.4 VPP and Electricity Market Simulation
24.5 Conclusions and Future Perspectives
References
Section 6. Induction Generators,Power Quality,
Power Electronics and Energy Planning for
Renewable Energy Systems
25. Modern Power Electronic Technology for the
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
Vinod Kumar, Ramesh C. Bansal, Raghuveer
R. Joshi, Rajendrasinh B. Jadeja and Uday P.
Mhaskar
25.1 Introduction
25.2 Various Topologies of Power Electronic
Converters
25.3 CurrentWind Power Technology
25.4 Future Trends inWind-Power Technology
25.5 Grid-Interconnection Requirements for
Wind Farms: Overview
25.6 Power Electronics in Photovoltaic (PV)
System
25.7 Recent Trends in Energy-Storage
Technologies
25.8 Conclusions
References
26. Analysis of Induction Generators for Renewable
Energy Applications
Kanwarjit S. Sandhu
26.1 Introduction
26.2 Equivalent Circuit Model of Induction
Machine
26.3 Slip in Terms of Per Unit Frequency
and Speed
26.4 Grid Connected Induction Generator
26.5 Self-Excited Induction Generators [SEIG]
26.6 Conclusions
Appendix
References .
27. Control of Doubly Fed Induction Generators under
Balanced and Unbalanced Voltage Conditions
Oriol Gomis-Bellmunt and Adri Junyent-Ferr
27.1 Introduction
27.2 Nomenclature .
27.3 General Considerations .
27.4 Control of the Doubly Fed Induction
Generator under Balanced Conditions
27.5 Control of the Doubly Fed Induction
Generator under Unbalanced Conditions
27.6 Simulation Results
27.7 Conclusions
References
28. Power Quality Instrumentation and Measurement
in a Distributed and Renewable Environment
Mario Manana, Alfredo Ortiz, Carlos J. Renedo,
SeverianoPerez and Alberto Arroyo
28.1 Introduction
28.2 Regulatory Framework .
28.3 State-of-the-art .
28.4 Instrumentation Architecture .
28.5 PQ Monitoring Surveys in Distributed
and Renewable Environments
28.6 Summary
References
29. Energy Resource Allocation in Energy Planning
Sandip Deshmukh
29.1 Introduction to Energy Planning Process
29.2 Energy Requirement and Energy
Resource Estimations
29.3 Energy Resource Allocation .
29.4 Region Dependent Development in
Energy Planning
29.5 Conclusions
References
Index
Вам также может понравиться
- Design, Analysis and Applications of Renewable Energy SystemsОт EverandDesign, Analysis and Applications of Renewable Energy SystemsAhmad Taher AzarОценок пока нет
- Emerging Trends in Energy Storage Systems and Industrial ApplicationsОт EverandEmerging Trends in Energy Storage Systems and Industrial ApplicationsDr. PrabhansuОценок пока нет
- Distributed Energy Resources in Microgrids: Integration, Challenges and OptimizationОт EverandDistributed Energy Resources in Microgrids: Integration, Challenges and OptimizationRajeev Kumar ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Design and Performance Optimization of Renewable Energy SystemsОт EverandDesign and Performance Optimization of Renewable Energy SystemsMamdouh AssadОценок пока нет
- Wind Power in Power SystemsОт EverandWind Power in Power SystemsThomas AckermannРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Future Energy: Improved, Sustainable and Clean Options for our PlanetОт EverandFuture Energy: Improved, Sustainable and Clean Options for our PlanetОценок пока нет
- Complementarity of Variable Renewable Energy SourcesОт EverandComplementarity of Variable Renewable Energy SourcesJakub JuraszОценок пока нет
- Renewable Energy Systems: Modelling, Optimization and ControlОт EverandRenewable Energy Systems: Modelling, Optimization and ControlAhmad Taher AzarОценок пока нет
- Microgrid Technologies Sharmeela Full ChapterДокумент67 страницMicrogrid Technologies Sharmeela Full Chapterbrian.collier318100% (14)
- Power Electronics Converters and their Control for Renewable Energy ApplicationsОт EverandPower Electronics Converters and their Control for Renewable Energy ApplicationsArezki FekikОценок пока нет
- Distributed Energy Resources in Local Integrated Energy Systems: Optimal Operation and PlanningОт EverandDistributed Energy Resources in Local Integrated Energy Systems: Optimal Operation and PlanningGiorgio GraditiОценок пока нет
- Power Quality in Power Systems and Electrical MachinesОт EverandPower Quality in Power Systems and Electrical MachinesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (11)
- Electrochemical Technologies for Energy Storage and Conversion, 2 Volume SetОт EverandElectrochemical Technologies for Energy Storage and Conversion, 2 Volume SetОценок пока нет
- Modeling and Control Dynamics in Microgrid Systems with Renewable Energy ResourcesОт EverandModeling and Control Dynamics in Microgrid Systems with Renewable Energy ResourcesRamesh C. BansalОценок пока нет
- Residential Microgrids and Rural ElectrificationsОт EverandResidential Microgrids and Rural ElectrificationsP. SanjeevikumarРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Advanced Technologies in Electric Vehicles: Challenges and Future Research DevelopmentsОт EverandAdvanced Technologies in Electric Vehicles: Challenges and Future Research DevelopmentsVijayakumar GaliОценок пока нет
- Wind Energy Engineering: A Handbook for Onshore and Offshore Wind TurbinesОт EverandWind Energy Engineering: A Handbook for Onshore and Offshore Wind TurbinesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Advanced Frequency Regulation Strategies in Renewable-Dominated Power SystemsОт EverandAdvanced Frequency Regulation Strategies in Renewable-Dominated Power SystemsSandeep DhundharaОценок пока нет
- Hybrid MicrogridДокумент69 страницHybrid MicrogridRamanan MОценок пока нет
- Smart Power Distribution Systems: Control, Communication, and OptimizationОт EverandSmart Power Distribution Systems: Control, Communication, and OptimizationОценок пока нет
- Decision Science and Operations Management of Solar Energy SystemsОт EverandDecision Science and Operations Management of Solar Energy SystemsОценок пока нет
- Distributed Generation Systems: Design, Operation and Grid IntegrationОт EverandDistributed Generation Systems: Design, Operation and Grid IntegrationРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Renewable-Energy-Driven Future: Technologies, Modelling, Applications, Sustainability and PoliciesОт EverandRenewable-Energy-Driven Future: Technologies, Modelling, Applications, Sustainability and PoliciesJingzheng RenОценок пока нет
- Geothermal Power Plants: Principles, Applications, Case Studies and Environmental ImpactОт EverandGeothermal Power Plants: Principles, Applications, Case Studies and Environmental ImpactРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (3)
- Microwaves in Organic SynthesisОт EverandMicrowaves in Organic SynthesisAntonio de la HozОценок пока нет
- (IET Energy Engineering 2) Nand Kishor, Jesus Fraile-Ardunuy - Modeling and Dynamic Behaviour of Hydropower Plants-The Institution of Engineering and Technology (2017)Документ280 страниц(IET Energy Engineering 2) Nand Kishor, Jesus Fraile-Ardunuy - Modeling and Dynamic Behaviour of Hydropower Plants-The Institution of Engineering and Technology (2017)eclatdore758Оценок пока нет
- Operation of Distributed Energy Resources in Smart Distribution NetworksОт EverandOperation of Distributed Energy Resources in Smart Distribution NetworksРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Dynamic Modeling and Simulation of Hybrid Power Systems Based On Renewable EnergyДокумент91 страницаDynamic Modeling and Simulation of Hybrid Power Systems Based On Renewable EnergySai Srinivas100% (1)
- Handbook of Green Information and Communication SystemsОт EverandHandbook of Green Information and Communication SystemsAlagan AnpalaganОценок пока нет
- Active Electrical Distribution Network: Issues, Solution Techniques, and ApplicationsОт EverandActive Electrical Distribution Network: Issues, Solution Techniques, and ApplicationsSanjeevikumar PadmanabanОценок пока нет
- Emerging Nanoelectronic DevicesОт EverandEmerging Nanoelectronic DevicesAn ChenОценок пока нет
- Solar TreeДокумент68 страницSolar TreeAyushi KhandelwalОценок пока нет
- Se 250Документ18 страницSe 250Shubhangi PawarОценок пока нет
- RE 512 Renewable Energy SystemsДокумент4 страницыRE 512 Renewable Energy SystemsLove Brat SaxenaОценок пока нет
- B.E. 8th Sem ELE - III-EC IIIДокумент3 страницыB.E. 8th Sem ELE - III-EC IIISantosh AloneОценок пока нет
- WindandSolarBasedEnergySystemsforCommunities 1 PDFДокумент325 страницWindandSolarBasedEnergySystemsforCommunities 1 PDFCarlos SamaniegoОценок пока нет
- PSO BookДокумент5 страницPSO BookSyed Zain Ul AbideenОценок пока нет
- A Minor Project Report: Solar Panel With Sun Position TrackingДокумент38 страницA Minor Project Report: Solar Panel With Sun Position TrackingNavajeethОценок пока нет
- Hydrogen Production, Separation and Purification For Energy by Angelo Basile and All 490pgДокумент490 страницHydrogen Production, Separation and Purification For Energy by Angelo Basile and All 490pgADRIAN TURCUОценок пока нет
- Lista Ebooks Ebsco AcpДокумент3 страницыLista Ebooks Ebsco AcpAdolfo MoscosoОценок пока нет
- Final Year ReportДокумент71 страницаFinal Year ReportRadhi Musa100% (3)
- Anilakumaranvadakkepurakkel Designofa 2019Документ89 страницAnilakumaranvadakkepurakkel Designofa 2019RusnacОценок пока нет
- Green Energy M A Parvez Mahmud Full ChapterДокумент67 страницGreen Energy M A Parvez Mahmud Full Chapterkeith.bosak875100% (5)
- Design & Fabrication of Hybrid Power Generation Using Photo Voltic & Wind TurbineДокумент15 страницDesign & Fabrication of Hybrid Power Generation Using Photo Voltic & Wind TurbineMuiz SaddozaiОценок пока нет
- And Domkundawar, S., A Course in Power Plant Engineering, Dhanpatrai (2002)Документ2 страницыAnd Domkundawar, S., A Course in Power Plant Engineering, Dhanpatrai (2002)Dr. Gollapalli NareshОценок пока нет
- Ebook Green Energy PDF Full Chapter PDFДокумент67 страницEbook Green Energy PDF Full Chapter PDFwilliam.brewer330100% (25)
- PBPO008E FrontmatterДокумент13 страницPBPO008E FrontmatterParameswararao Billa67% (3)
- RES Prev QN PapersДокумент7 страницRES Prev QN Paperspara thavalaОценок пока нет
- Solar Farms: Design & Construction: Impacts To Utility Distribution SystemsДокумент34 страницыSolar Farms: Design & Construction: Impacts To Utility Distribution SystemsMoe Abdul HamidОценок пока нет
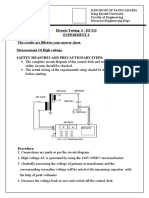
- Kingdom of Saudi Arabia King Khalid University Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering DeptДокумент4 страницыKingdom of Saudi Arabia King Khalid University Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering DeptMAHAMMAD ILIYASОценок пока нет
- Video 5 - MCB CatalogueДокумент146 страницVideo 5 - MCB CatalogueArt RaОценок пока нет
- UCI274HДокумент8 страницUCI274H3efooОценок пока нет
- A FaultДокумент49 страницA FaultJonatanОценок пока нет
- Bistable MultivibratorДокумент6 страницBistable MultivibratorblaagicaОценок пока нет
- Sheet 3Документ3 страницыSheet 3Mohab SamehОценок пока нет
- NGVДокумент3 страницыNGVkalesh005Оценок пока нет
- Electrical Design CalculationsДокумент34 страницыElectrical Design CalculationsAji Istanto Rambono86% (7)
- Fuse Link SizeДокумент14 страницFuse Link Sizebilly12379224Оценок пока нет
- SP230 SP231 SP232Документ2 страницыSP230 SP231 SP232Enmanuel DiazОценок пока нет
- Presentation in EnglishДокумент13 страницPresentation in EnglishspalaniyandiОценок пока нет
- Three Phase Circuits Graph PDFДокумент110 страницThree Phase Circuits Graph PDFBenish CmОценок пока нет
- Walker PV TechnologyДокумент53 страницыWalker PV TechnologyaakashtrivediОценок пока нет
- Phase Segregated Busbar Differential Protection: Pt. PLN (Persero) Uip IiiДокумент10 страницPhase Segregated Busbar Differential Protection: Pt. PLN (Persero) Uip IiiBravery DamanikОценок пока нет
- Tut Sheet PDFДокумент3 страницыTut Sheet PDFLalitSisodiaОценок пока нет
- Installation Manual HPS RangeДокумент23 страницыInstallation Manual HPS Rangeအောင် ဘွားОценок пока нет
- Experiment - 7 Design of Wiring Lay-Out For A Residence and Estimate The Quantity of Materials Pre - Lab QuestionsДокумент10 страницExperiment - 7 Design of Wiring Lay-Out For A Residence and Estimate The Quantity of Materials Pre - Lab Questionszohair ahmedОценок пока нет
- Kiran P B180894ee Pe Exp4Документ7 страницKiran P B180894ee Pe Exp4khyati patelОценок пока нет
- Fermator Operation Manual PDFДокумент8 страницFermator Operation Manual PDFMuhammad Dzulfiqar100% (1)
- Design Life of Thermal Power PlantДокумент2 страницыDesign Life of Thermal Power Plantdnageshm4n244100% (2)
- Catalogue Motor Protection Relay MPR200nXДокумент1 страницаCatalogue Motor Protection Relay MPR200nXPardeep KhosaОценок пока нет
- 2015-06 - NESP - Energy Sector Study of Nigeria - 2nd EditionДокумент152 страницы2015-06 - NESP - Energy Sector Study of Nigeria - 2nd Editionazuka62Оценок пока нет
- Pemeliharaan Peralatan Listrik Dan Mekanik Pembangkit PDFДокумент213 страницPemeliharaan Peralatan Listrik Dan Mekanik Pembangkit PDFFebby Hadi PrakosoОценок пока нет
- Customer NameДокумент8 страницCustomer Namesyed Hassan50% (4)
- S Instructions: Installation / Operation / MaintenanceДокумент27 страницS Instructions: Installation / Operation / MaintenanceEduardo CordovaОценок пока нет
- PriceList Chint FEB 2018 Issue V2Документ6 страницPriceList Chint FEB 2018 Issue V2August Ponge100% (1)
- Data SheetДокумент6 страницData SheetTuấn Âm Thanh Hi-endОценок пока нет
- Steam Turbine Stop Valve TestingДокумент22 страницыSteam Turbine Stop Valve TestingAbdulyunus Amir100% (3)
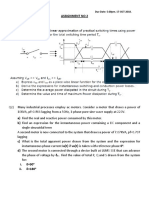
- Assignment No 2Документ3 страницыAssignment No 2Ali NawazОценок пока нет