Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
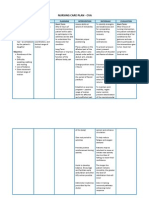
Cues Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Загружено:
Andrea BroccoliОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cues Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Загружено:
Andrea BroccoliАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CUes Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective:
Lisod kayo
ilihok tungod ani
akong tiil as
verbalized by the
patient
Objective:
Slowed
movement
Difficulty in
turning
Facial
grimace
when
trying to
move side
to side
Impaired physical
mobility
related to
neuromuscular
involvement(muscle
weakness and
numbness) as
manifested by
slowed movement,
difficulty in turning
and facial grimace
when trying to
move on side to side.
After 8 hours of
nursing care the
patient will be
able to:
Increases
physical
activity
Meets
mutually
defined goals
of increased
mobility
Verbalizes
feeling of
increased
strength and
ability to
move
Demonstrates
use of
adaptive
equipment
(e.g.,
wheelchairs,
walkers) to
increase
mobility
1. Screen for
mobility skills in the
following order:
(1) bed mobility;
(2) supported and
unsupported sitting;
(3) transition
movements such as
sit to stand, sitting
down, and
transfers; and
(4) standing and
walking activities.
Use a physical
activity tool if
available to evaluate
mobility.
Screening
mobility skills
helps provide
baselines of
performance
that can guide
mobility-
enhancement
programming
and allows
nursing staff to
integrate
movement and
practice
opportunities
into daily
routines and
regular and
customary
care. There are
many tools
available to
measure
physical
activity;
selection of the
appropriate
GOAL
PARTIALLY
MET!
After 8 hours
of nursing
care the
patient was
able to:
Increases
physical
activity
Meets
mutually
defined
goals of
increased
mobility
Verbalizes
feeling of
increased
strength
and ability
to move
2. Observe client for
cause
of impaired mobility.
Determine whether
cause is physical or
psychological
4. Before activity
observe for and, if
possible, treat pain.
Ensure that client is
not over sedated.
5. Consult with
physical therapist
for further
evaluation, strength
training, gait
training, and
development of a
tool depends
on the setting
and situation
Some clients
choose not to
move because
of
psychological
factors such as
an inability to
cope or
depression.
Pain limits
mobility and is
often
exacerbated
by movement.
Techniques
such as gait
training,
strength
training, and
exercise to
improve
mobility plan.
6. Obtain any
assistive devices
needed for activity,
such as walking
belts, walkers,
canes, crutches, or
wheelchairs, before
the activity begins.
7. If client is
immobile, perform
passive range of
motion (ROM)
exercises at least
twice a day unless
contraindicated;
repeat each
maneuver three
times.
balance and
coordination
can be very
helpful for
rehabilitating
clients
Assistive
devices can
help increase
mobility.
Passive ROM
exercises help
maintain joint
mobility,
prevent
contractures
and
deformities,
increase
circulation,
and promote a
feeling of
comfort and
well-being
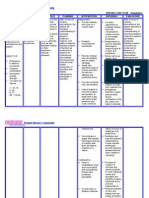
Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective:
No verbal cues"
Ineffective
Breathing Pattern
secondary to
Pulmonary
Tuberculosis with
pneumonia
Cues Nursing
Diagnosis
Planning Nursing
Intervention
Rationale Evaluation
Subjective:
no verbal cues
Objectives:
Use of
accessory
muscle
Dyspnea
Restlessness
Ineffective
Breathing
Pattern
secondary to
pulmonary
tuberculosis
with
pneumonia
After 8 hours
of nursing care
the patient will
be able to:
-Re-establish
and maintain
effective
respiratory
pattern via
oxygen
administration
thru nasal
cannula without
the use of
accessory
muscles and
other signs
of hypoxia
Monitor vital
signs
Assess
respiratory
rate, rhythm
and depth
These signs,
which should
be looked at in
total, are
checked to
monitor
functions
of the body.
The signs
reflect
changes in
function that
otherwise
might not be
observed
Respiratory
rate and
rhythm
changes are
early warning
signs
of impending
After 8 hours
of nursing care
the patient
was able to:ss
-Re-establish
and maintain
effective
respiratory
pattern via
oxygen
administration
thru nasal
cannula without
the use of
accessory
muscles and
other signs
of hypoxia
Assess for
pain/discomfo
rt
Administer
O2
regulated at 2 l/pm
via nasal cannula as
ordered and
administer
prescribed
respiratory
medications
respiratory
difficulties
That may
restrict
respiratory
effort
For
management
of underlying
pulmonary
condition and
respiratory
distress
Вам также может понравиться
- Holistic Home Remedies for Acute Low Back Pain: Incorporating Stretching and the McKenzie MethodОт EverandHolistic Home Remedies for Acute Low Back Pain: Incorporating Stretching and the McKenzie MethodОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan (CVA)Документ2 страницыNursing Care Plan (CVA)Mel Rodolfo50% (2)
- Start SMART, Finish Strong!: Master the Fundamental for Pain Free FitnessОт EverandStart SMART, Finish Strong!: Master the Fundamental for Pain Free FitnessОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Planlaehaaa67% (3)
- Immobility (Nursing Care)Документ7 страницImmobility (Nursing Care)RAОценок пока нет
- Physiotherapy Rehabilitation Guidelines - Lumbar Disectomy PDFДокумент6 страницPhysiotherapy Rehabilitation Guidelines - Lumbar Disectomy PDFsilkofosОценок пока нет
- NCP 3Документ2 страницыNCP 3Al PinedaОценок пока нет
- Therapeutic ExercisesДокумент50 страницTherapeutic ExercisesBalram Jha100% (3)
- NCPДокумент8 страницNCPJose Benit DelacruzОценок пока нет
- Physiotherapy Rehabilitation Guidelines - Lumbar DisectomyДокумент6 страницPhysiotherapy Rehabilitation Guidelines - Lumbar Disectomyalina4891Оценок пока нет
- Impaired Physical Mobility RT Neuromuscular Skeletal Impairment.Документ3 страницыImpaired Physical Mobility RT Neuromuscular Skeletal Impairment.Abegail Abaygar100% (2)
- NCP Hip FractureДокумент1 страницаNCP Hip FractureStephanie Lorraine Zuniga100% (5)
- Activity IntoleranceДокумент2 страницыActivity IntoleranceJenny Pearl PasalОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationEvan SmixОценок пока нет
- Li Satri Materi Bing - IIIДокумент9 страницLi Satri Materi Bing - IIILi SatryОценок пока нет
- Impaired Physical MobilityДокумент2 страницыImpaired Physical MobilityAl-Qadry NurОценок пока нет
- Activity and Exercise Marwan KD IДокумент24 страницыActivity and Exercise Marwan KD IKartikaUlfaAlfiyahОценок пока нет
- Spina Bifida NCPДокумент3 страницыSpina Bifida NCPCarpz Darpz100% (2)
- Rehabilitation Guidelines For Patients Undergoing Surgery For Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of The AnkleДокумент10 страницRehabilitation Guidelines For Patients Undergoing Surgery For Lateral Ligament Reconstruction of The AnkleVladGrosuОценок пока нет
- Total Hip Arthroplasty PDFДокумент10 страницTotal Hip Arthroplasty PDFWindy ZeniccОценок пока нет
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing InterventionДокумент2 страницыAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing InterventionSteffi MurielОценок пока нет
- NCP (Ideal) Nursing DiagnosisДокумент2 страницыNCP (Ideal) Nursing DiagnosisSilinna May Lee SanicoОценок пока нет
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rekonstruction PhysioplusДокумент13 страницAnterior Cruciate Ligament Rekonstruction PhysioplusAde Dian KurniawanОценок пока нет
- Task-Related Training ApproahДокумент21 страницаTask-Related Training ApproahGulzar AhmadОценок пока нет
- Physiotherapy in Spinal Cord InjuryДокумент31 страницаPhysiotherapy in Spinal Cord InjuryKhyathi SriОценок пока нет
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortДокумент2 страницыImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortRis NapolisОценок пока нет
- NCP OsteomyelitisДокумент3 страницыNCP OsteomyelitisClariss Alota100% (2)
- Activity Intolerance Related To Generalized WeaknessДокумент4 страницыActivity Intolerance Related To Generalized WeaknessIvy MinaОценок пока нет
- 2 - Eclectic Approach For Stroke ManagementДокумент41 страница2 - Eclectic Approach For Stroke Managementpunit lakraОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент10 страницNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaОценок пока нет
- Walking Aids - PhysiopediaДокумент6 страницWalking Aids - PhysiopediaNana Ann PaaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To MovementsДокумент42 страницыIntroduction To MovementsRamalingam KanagarajОценок пока нет
- Total Hip ArthroplastyДокумент10 страницTotal Hip ArthroplastyClaudioОценок пока нет
- Impaired Physical Mobility...Документ3 страницыImpaired Physical Mobility...Christy BerryОценок пока нет
- NCP For Impaired MobilityДокумент4 страницыNCP For Impaired MobilityBettinaFernandoОценок пока нет
- Post Op Cervical Fusion PDFДокумент3 страницыPost Op Cervical Fusion PDFNICOLÁS ANDRÉS AYELEF PARRAGUEZОценок пока нет
- AmputationДокумент2 страницыAmputationFabian Ugalino Pino Jr.100% (3)
- BDH NCP Medical FormДокумент9 страницBDH NCP Medical FormRegie CanoОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент4 страницыNCPAldrece CastroverdeОценок пока нет
- Lec9 Basic Concepts of Spinal Management With ExerciseДокумент21 страницаLec9 Basic Concepts of Spinal Management With Exercisesana mumtazОценок пока нет
- Multiple Sclerosis Physical TherapyДокумент5 страницMultiple Sclerosis Physical TherapyFaishol Reza AdiyaksaОценок пока нет
- Efficacy of A Short-Term Physiotherapy Intervention Strategy in The Initial Stages of Multiple Sclerosis, A Case ReportДокумент10 страницEfficacy of A Short-Term Physiotherapy Intervention Strategy in The Initial Stages of Multiple Sclerosis, A Case ReportSailaja NandennagariОценок пока нет
- Motor Relearning ProgramДокумент10 страницMotor Relearning ProgramjalykAmazing75% (4)
- Physiotherapy Rehabilitation Guidelines - Knee ArthrosДокумент7 страницPhysiotherapy Rehabilitation Guidelines - Knee ArthrosmatameaОценок пока нет
- Physical Education and Health: Quarter 1 - Module 1-2 (Week)Документ11 страницPhysical Education and Health: Quarter 1 - Module 1-2 (Week)Marlyn GuiangОценок пока нет
- MODULE 1 - THXДокумент13 страницMODULE 1 - THXZgama AbdulrahmanОценок пока нет
- Physical Education Non-Locomotor and LocomotorДокумент13 страницPhysical Education Non-Locomotor and LocomotorAnthony MarzanОценок пока нет
- Activity Intolerance Related To ImmobilizationДокумент3 страницыActivity Intolerance Related To ImmobilizationAgronaSlaughterОценок пока нет
- Active Movements: Dr:Maryam Memon Lecturer: JmiprsДокумент33 страницыActive Movements: Dr:Maryam Memon Lecturer: JmiprsAazeen memonОценок пока нет
- Impaired Physical Mobility. NCPДокумент1 страницаImpaired Physical Mobility. NCPwguino100% (3)
- Role of Physio in Neurological Disorders.Документ17 страницRole of Physio in Neurological Disorders.Maheen AnwaarОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент4 страницыUntitledCristi GaborОценок пока нет
- Rehabilitation in Spinal Cord InjuryДокумент2 страницыRehabilitation in Spinal Cord InjuryAudry ArifinОценок пока нет
- Cancer Management ProtocolДокумент4 страницыCancer Management ProtocolBhavagnaОценок пока нет
- BrunnstormДокумент46 страницBrunnstormAkshata NadgirОценок пока нет
- Anatomia 20iv 20toraceДокумент59 страницAnatomia 20iv 20toraceSufletoiiОценок пока нет
- Parkinson GeriatricsДокумент36 страницParkinson Geriatricsrabiakhalid2520Оценок пока нет
- Occupational Therapy For Spinal Cord Injury PatientsДокумент8 страницOccupational Therapy For Spinal Cord Injury Patientsvenkata ramakrishnaiahОценок пока нет
- NCP Acl TearДокумент2 страницыNCP Acl TearEd Pascasio100% (2)
- Rehab-Plans-and-Exercises Hip-Arthroscopy Protocol-For-Physiotherapy-Following-SurgeryДокумент2 страницыRehab-Plans-and-Exercises Hip-Arthroscopy Protocol-For-Physiotherapy-Following-SurgeryMellow Moon RecordsОценок пока нет
- 1, Show Flow Arrows 2. Provide Profile and Levels 3. Submit Computations 'Документ2 страницы1, Show Flow Arrows 2. Provide Profile and Levels 3. Submit Computations 'Andrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- For Structural Engineer To Check/comment: The MRT 7 ProjectДокумент1 страницаFor Structural Engineer To Check/comment: The MRT 7 ProjectAndrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- André Gil Sabanal: Education SkillsДокумент1 страницаAndré Gil Sabanal: Education SkillsAndrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- SVAR ReviewerДокумент3 страницыSVAR ReviewerAndrea Broccoli100% (1)
- RW-3A HD: 2000 RW-3B HD: 2001 - 3000: The MRT 7 ProjectДокумент2 страницыRW-3A HD: 2000 RW-3B HD: 2001 - 3000: The MRT 7 ProjectAndrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- Community Health Nursing Compre.2015with RatioДокумент8 страницCommunity Health Nursing Compre.2015with RatioAndrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- CHN & CD Pre-Board TestДокумент6 страницCHN & CD Pre-Board TestAndrea Broccoli100% (1)
- FDC Billing DavaoДокумент2 страницыFDC Billing DavaoAndrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- BSN II Comprehensive Examination 2nd Sem 2017Документ12 страницBSN II Comprehensive Examination 2nd Sem 2017Andrea Broccoli100% (1)
- Community Health Nursing: Practice of Nursing in Local/national Health DepartmentsДокумент6 страницCommunity Health Nursing: Practice of Nursing in Local/national Health DepartmentsAndrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- Gi Exam2016Документ28 страницGi Exam2016Andrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- Midterm Quiz - NCM 106.2016Документ4 страницыMidterm Quiz - NCM 106.2016Andrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- Melody & Juling MCIДокумент13 страницMelody & Juling MCIAndrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- TPF 4 Work Plan and Methodology 02-12-15 (Final) ANDREДокумент30 страницTPF 4 Work Plan and Methodology 02-12-15 (Final) ANDREAndrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- Introductio N To Informatic S: Lectur e 7: Modelin G TH e Worl DДокумент13 страницIntroductio N To Informatic S: Lectur e 7: Modelin G TH e Worl DAndrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- Introductio N To Informatic S: Lectur e 6: Histor y of Compute Rs (Par T II)Документ23 страницыIntroductio N To Informatic S: Lectur e 6: Histor y of Compute Rs (Par T II)Andrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Vitae: Andre Gil I. SabanalДокумент9 страницCurriculum Vitae: Andre Gil I. SabanalAndrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- Checklist of Eligibility Requirements For Consulting ServicesДокумент2 страницыChecklist of Eligibility Requirements For Consulting ServicesAndrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент4 страницыNCPAndrea BroccoliОценок пока нет
- SOP Blood TranfussionДокумент3 страницыSOP Blood TranfussionDiana SafitriОценок пока нет
- Sample Size and PowerДокумент19 страницSample Size and PowerSuryaprakash Reddy ChappidiОценок пока нет
- Mechanisms Case StudyДокумент13 страницMechanisms Case Studyshane_tin143Оценок пока нет
- Impacted Maxillary Canine Surgical ExposureДокумент8 страницImpacted Maxillary Canine Surgical Exposureabdul samad noorОценок пока нет
- Welling 2019Документ9 страницWelling 2019riskiОценок пока нет
- 5-3 IOM-repair or ReplaceДокумент37 страниц5-3 IOM-repair or ReplaceProfesseur Christian DumontierОценок пока нет
- CPC 2011 AnswersДокумент20 страницCPC 2011 AnswersBeverly Gracious100% (1)
- Research Paper DiabetesДокумент8 страницResearch Paper Diabetesapi-359023534Оценок пока нет
- Naturalpath Intake Form - ADULTДокумент5 страницNaturalpath Intake Form - ADULTcms_gcoles100% (1)
- Generic Name: Classification: IndicationДокумент2 страницыGeneric Name: Classification: IndicationKristine YoungОценок пока нет
- 50 ItemsДокумент6 страниц50 ItemsPaul EspinosaОценок пока нет
- Anorexia EssayДокумент8 страницAnorexia Essayapi-329344597Оценок пока нет
- Dafpus SGB 20Документ32 страницыDafpus SGB 20Anggie Pradetya MaharaniОценок пока нет
- HHS Public Access: How Schizophrenia Develops: Cognitive and Brain Mechanisms Underlying Onset of PsychosisДокумент25 страницHHS Public Access: How Schizophrenia Develops: Cognitive and Brain Mechanisms Underlying Onset of PsychosisNoriОценок пока нет
- Dialysis Event Surveillance ManualДокумент56 страницDialysis Event Surveillance ManualAnitha SОценок пока нет
- NeocortexДокумент1 страницаNeocortexZeromalisNilОценок пока нет
- Black Seed The Remedy For Everything But DeathДокумент3 страницыBlack Seed The Remedy For Everything But DeathImi CreaОценок пока нет
- Class II Correction....Документ7 страницClass II Correction....Yudia PangestiОценок пока нет
- List of English Speaking Doctors in BerlinДокумент19 страницList of English Speaking Doctors in BerlinAnggêr JamungОценок пока нет
- Neoplasia: Nomenclature Epidemiology OncogenesДокумент7 страницNeoplasia: Nomenclature Epidemiology OncogenespriyaОценок пока нет
- Medical Surgical Nursing OrthopedicДокумент22 страницыMedical Surgical Nursing Orthopedicroger80% (5)
- Pro DrugДокумент4 страницыPro DrugIbnu SinaОценок пока нет
- Labor and DeliveryДокумент7 страницLabor and Deliveryplethoraldork100% (20)
- Drug StudyДокумент7 страницDrug StudyGladys NacionОценок пока нет
- Core Essay Draftt CommentsДокумент2 страницыCore Essay Draftt CommentsleharОценок пока нет
- Robatherm Medical EngДокумент20 страницRobatherm Medical Engtanbqtb030% (1)
- Braden ScaleДокумент1 страницаBraden ScaleRandall StevensОценок пока нет
- Vonlays: A Conservative Esthetic Alternative To Full-Coverage CrownsДокумент6 страницVonlays: A Conservative Esthetic Alternative To Full-Coverage CrownsDavid Gomez0% (1)
- Postpartum Hemorrhage Post Placenta Previa Centralis-Conservative Management. Astrit M. GashiДокумент4 страницыPostpartum Hemorrhage Post Placenta Previa Centralis-Conservative Management. Astrit M. GashiAstrit GashiОценок пока нет
- Edan CadenceДокумент78 страницEdan CadenceerikaОценок пока нет