Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Determination of PKa of Aspirin
Загружено:
Frank MassiahАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Determination of PKa of Aspirin
Загружено:
Frank MassiahАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1
Determining the pK
a
of aspirin
Student worksheet
Health and safety note
Wear eye protection and ensure no naked flames. 0.10 mol dm
3
sodium hydroxide solution is an
irritant. 95% ethanol is highly flammable. Aspirin and 95% ethanol are both harmful.
Principle
Aspirin is a weak acid. It partially ionises in water:
and its acid dissociation constant, K
a
, is given by:
often written simply as:
The pK
a
value is given by:
Taking logarithms, the following relationships are derived
or
When the acid is half-neutralised, [A
] = [HA], and pH = pK
a
.
By titrating a solution of the aspirin against a strong alkali, such as sodium hydroxide solution, the
pH at the half-way point can be determined and this gives the pK
a
of aspirin.
Aspirin and sodium hydroxide react in a 1:1 mole ratio:
Equipment and materials
Balance
50 cm
3
burette
250 cm
3
beaker
Glass stirring rod
10 cm
3
and 100 cm
3
measuring cylinders
Spatula
pH probe and pH meter
Aspirin Harmful
95% ethanol Highly flammable, Harmful
0.10 mol dm
3
sodium hydroxide solution
Irritant
2
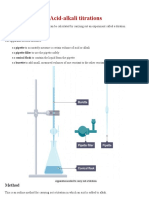
Method
1. Fill a burette with 0.10 mol dm
3
sodium hydroxide solution.
2. Weigh 0.36 g of aspirin into a 250 cm
3
beaker. Add 10 cm
3
of 95% ethanol, Stir with a glass rod
and when the solid has dissolved add 90 cm
3
of deionised water. Stir the mixture until it is
homogeneous.
3. Place a pH probe in the solution and connect it to a pH meter. Note: The pH probe should have
been calibrated using suitable buffer solutions.
4. Add 2 cm
3
quantities of sodium hydroxide solution from the burette to the beaker, stirring well
between additions and recording the pH.
5. Near the end-point the pH begins to rise rapidly. So after you have added 18 cm
3
of sodium
hydroxide solution begin adding it in 0.5 cm
3
portions. After about 22 cm
3
start adding in 2 cm
3
portions again. Continue until total of 36 cm
3
has been added.
Processing data
1. Plot a graph of pH against volume of
0.10 mol dm
3
sodium hydroxide
solution added.
2. From the graph, calculate the end-
point of the titration.
3. Check this against the expected
value by calculating the number of
moles of aspirin used (relative
molecular mass of aspirin = 180)
and, therefore, the volume of
0.10 mol dm
3
sodium hydroxide
solution needed to react with it in a
1:1 mole ratio.
4. From the graph, estimate the pH at
the half-way point of the titration.
This gives a value for the pK
a
of
aspirin.
5. Calculate the K
a
of aspirin.
pH
12
2
8
Volume of 0.10 mol dm
3
sodium hydroxide solution
added
pK
a
Half-way point
End point
Figure Illustrative titration graph for aspirin against
sodium hydroxide solution.
Вам также может понравиться
- Study On AntacidДокумент6 страницStudy On Antacidsalucr7777777Оценок пока нет
- Lab 10.pdf - 316831Документ2 страницыLab 10.pdf - 316831ayaessam392002Оценок пока нет
- SOP For Water TestingДокумент50 страницSOP For Water Testinggreen solutionОценок пока нет
- Redox TitrationДокумент4 страницыRedox TitrationAh BoonОценок пока нет
- Experiment 7: Titration of An Antacid: Objective: in This Experiment, You Will Standardize A Solution of Base Using TheДокумент7 страницExperiment 7: Titration of An Antacid: Objective: in This Experiment, You Will Standardize A Solution of Base Using TheDALITSO CHIKOYAОценок пока нет
- Experiment 11Документ4 страницыExperiment 11Cody Chan100% (1)
- Tit RationДокумент7 страницTit RationgautamahujaОценок пока нет
- Determination of The Concentration of Acetic Acid in VinegarДокумент24 страницыDetermination of The Concentration of Acetic Acid in VinegarNadia Kama69% (13)
- Determination of Concentration of Acetic Acid in VinegarДокумент22 страницыDetermination of Concentration of Acetic Acid in VinegarFatin Izzati Hasnan100% (1)
- Ampicillin Sodium For Injection (Ampicillini Natrici Ad Injectionem)Документ2 страницыAmpicillin Sodium For Injection (Ampicillini Natrici Ad Injectionem)Deanita Zafirah LovezzОценок пока нет
- 8 - Lab8-Potentiometric Titration of Acid MixtureДокумент6 страниц8 - Lab8-Potentiometric Titration of Acid MixtureHoang Huong TraОценок пока нет
- TitrationjДокумент6 страницTitrationjslixsterОценок пока нет
- Phosphorus Acid TitrationДокумент2 страницыPhosphorus Acid TitrationJoséMaríaMoreОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Laboratory Report 13Документ6 страницChemistry Laboratory Report 13Jeff LamboОценок пока нет
- Volumetric Analysis of Aspirin 1. Purpose: CH229 General Chemistry Laboratory Dr. Deborah ExtonДокумент4 страницыVolumetric Analysis of Aspirin 1. Purpose: CH229 General Chemistry Laboratory Dr. Deborah ExtonSusána SgfОценок пока нет
- Product Analysis.Документ7 страницProduct Analysis.Jazzie D. CamañanОценок пока нет
- Determination of The Carbonate Content of A Soda-Ash SampleДокумент6 страницDetermination of The Carbonate Content of A Soda-Ash SampleLuisafe AquinoОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Aspirin TabletsДокумент5 страницAnalysis of Aspirin TabletsDorien Villafranco60% (5)
- Experiment A7 - Titration.v2Документ13 страницExperiment A7 - Titration.v2adel malikОценок пока нет
- Titration Level 2 LabnotebookДокумент3 страницыTitration Level 2 LabnotebookRolen Simcha Castillo SamsОценок пока нет
- RSCRateofhydrolysisofaspirinstudentsДокумент2 страницыRSCRateofhydrolysisofaspirinstudentsndee072Оценок пока нет
- Titration NotesДокумент3 страницыTitration Notesshaheer ahmedОценок пока нет
- Module Anachem Acid-Base 2Документ9 страницModule Anachem Acid-Base 2arejay castroОценок пока нет
- Titration Level 2 LabnotebookДокумент3 страницыTitration Level 2 LabnotebookxenaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Report - Titration of VinegarДокумент7 страницChemistry Report - Titration of VinegarSabestОценок пока нет
- The Titration of Acetic Acid in Vinegar: CHEM 122L General Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.4Документ16 страницThe Titration of Acetic Acid in Vinegar: CHEM 122L General Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.4Nur Najwa YunusОценок пока нет
- Experiment 3: Neutralization Capacity of Commercial Antacid AcidДокумент10 страницExperiment 3: Neutralization Capacity of Commercial Antacid AcidfizaОценок пока нет
- Isoelectric PointДокумент24 страницыIsoelectric PointSangeeta RayОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Core PracticalsДокумент6 страницChemistry Core PracticalssophiederryОценок пока нет
- Experiment 10Документ6 страницExperiment 10Rohit BiswasОценок пока нет
- Mixture of Carbonate BicarbonateДокумент9 страницMixture of Carbonate BicarbonateIan Justine SanchezОценок пока нет
- Determination of Concentration Acetic Acid in VinegarДокумент11 страницDetermination of Concentration Acetic Acid in VinegarKicauan KataОценок пока нет
- Experiment 3: Neutralization Capacity of Commercial Antacid AcidДокумент10 страницExperiment 3: Neutralization Capacity of Commercial Antacid AcidfizaОценок пока нет
- Bio - Analytical Prac Report 1Документ4 страницыBio - Analytical Prac Report 1Megha VallabhОценок пока нет
- Titration Level 2: Buenaventura AimsДокумент3 страницыTitration Level 2: Buenaventura AimsManelli Faten BuenaventuraОценок пока нет
- Titration Level 2: Krizzi AimsДокумент3 страницыTitration Level 2: Krizzi AimsKrizzi Dizon Garcia100% (1)
- Experiment 3Документ3 страницыExperiment 3Siti Rahmah YahyaОценок пока нет
- Aspirin - Back Titratiuon Lab2Документ3 страницыAspirin - Back Titratiuon Lab2patrice green - SteadmanОценок пока нет
- Albumin Solution, HumanДокумент3 страницыAlbumin Solution, HumanMulayam Singh Yadav67% (3)
- Concentration ReportДокумент27 страницConcentration ReportfarahhanamejeniОценок пока нет
- ION EXCHANGE Analysis Testing Procedures GeneralДокумент50 страницION EXCHANGE Analysis Testing Procedures GeneralJinalОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 11Документ3 страницыLab Report 11PaulОценок пока нет
- ASPIRIN Project FileДокумент8 страницASPIRIN Project FileSumit SinhaОценок пока нет
- Acid Base Titration PDFДокумент7 страницAcid Base Titration PDFNovitaWahyuniDly0% (1)
- Oxalic Acid +NaOHДокумент4 страницыOxalic Acid +NaOHTalpyn RakhymОценок пока нет
- IBHL Investigations: Investigating Acids Aim: Claudia Braganza IBHL Chemistry Grade 12Документ13 страницIBHL Investigations: Investigating Acids Aim: Claudia Braganza IBHL Chemistry Grade 12tennisrox94100% (1)
- Lab ManualsДокумент13 страницLab ManualsMuhammad AffifudinОценок пока нет
- Acid Base TitrationsДокумент6 страницAcid Base Titrationssadya98100% (1)
- Lab 11 Acids, Bases, PH, Hydrolysis, and BuffersДокумент10 страницLab 11 Acids, Bases, PH, Hydrolysis, and BuffersChing Wai Yong67% (3)
- Analytical Method of Mercury, Arsenic, Cadmium, Lead and Chromium in FertilizersДокумент8 страницAnalytical Method of Mercury, Arsenic, Cadmium, Lead and Chromium in FertilizersGenaro PalacioОценок пока нет
- Titration Level 2: Steven de La Cruz AimsДокумент3 страницыTitration Level 2: Steven de La Cruz AimsStevensito tpsОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Aspirin Tablet PDFДокумент5 страницAnalysis of Aspirin Tablet PDFAnonymous TmwS3ZmseОценок пока нет
- Vinegar Titration LAB 1Документ22 страницыVinegar Titration LAB 1Amirah AbidinОценок пока нет
- BufferДокумент3 страницыBufferJessie MorgadoОценок пока нет
- Determination of Vitamin CДокумент2 страницыDetermination of Vitamin CWalwin HareОценок пока нет
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisОт EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterОт EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterОценок пока нет
- Sept 26 2019 U6D Module 2 Uncertainty in Measurement ClassworkДокумент1 страницаSept 26 2019 U6D Module 2 Uncertainty in Measurement ClassworkFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Mar 9 2021 U6a Phase Separation QuestionsДокумент2 страницыMar 9 2021 U6a Phase Separation QuestionsFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Jan 8 2020 Unit 2 Mod 2 and 3 WorksheetДокумент2 страницыJan 8 2020 Unit 2 Mod 2 and 3 WorksheetFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Feb 27 2020 Unit 2 Mod 2 and Mod 3 Practice SheetДокумент2 страницыFeb 27 2020 Unit 2 Mod 2 and Mod 3 Practice SheetFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Chem MC Practice Paper1Документ8 страницUnit 2 Chem MC Practice Paper1Frank MassiahОценок пока нет
- FEB 4 2016 3rd Form Pop QuizДокумент1 страницаFEB 4 2016 3rd Form Pop QuizFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Industry Location Factors WorksheetДокумент28 страницIndustry Location Factors WorksheetFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 UV-vis Spectroscopy ExerciseДокумент2 страницыUnit 2 UV-vis Spectroscopy ExerciseFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Feb 4 2015 3rd Form Form Atomic StructureДокумент1 страницаFeb 4 2015 3rd Form Form Atomic StructureFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Feb 7 For Feb 13 2020 3rd Form Homework Acids and BasesДокумент2 страницыFeb 7 For Feb 13 2020 3rd Form Homework Acids and BasesFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Feb 2 2017 Group 3.3 Test Acids Bases Metals and NonmetalsДокумент1 страницаFeb 2 2017 Group 3.3 Test Acids Bases Metals and NonmetalsFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Feb 4 2015 Homework 3rd Form Various TopicsДокумент1 страницаFeb 4 2015 Homework 3rd Form Various TopicsFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Matthew Correia Worksheet Chemical Bonding and Types of SubstancesДокумент1 страницаMatthew Correia Worksheet Chemical Bonding and Types of SubstancesFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Reactivity of Metals and Nonmetals MATTHEW CORREIAДокумент6 страницReactivity of Metals and Nonmetals MATTHEW CORREIAFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certifi Cate of Secondary EducationДокумент20 страницUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certifi Cate of Secondary Educationnairah2000Оценок пока нет
- Chem 0620 Nov 2011 Paper 2Документ20 страницChem 0620 Nov 2011 Paper 2Frank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Fri Oct 18 2013 MATTHEW CORREIA Electrolysis and EnergeticsДокумент3 страницыFri Oct 18 2013 MATTHEW CORREIA Electrolysis and EnergeticsFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Matthew Correia Dot and Cross Diagrams WorksheetДокумент2 страницыMatthew Correia Dot and Cross Diagrams WorksheetFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- MATTHEW CORREIA Acids Bases and Salts WORKSHEETДокумент4 страницыMATTHEW CORREIA Acids Bases and Salts WORKSHEETFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- 0620 w13 QP 11 PDFДокумент20 страниц0620 w13 QP 11 PDFHaider AliОценок пока нет
- Jan 26 2018 5th Form Classwork AlkanesДокумент3 страницыJan 26 2018 5th Form Classwork AlkanesFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Chemistry 620 - 2011 - Ques Paper - 11Документ16 страницIGCSE Chemistry 620 - 2011 - Ques Paper - 11MinakshiОценок пока нет
- Chem 0620 Nov 2013 Paper 2Документ16 страницChem 0620 Nov 2013 Paper 2Frank MassiahОценок пока нет
- SEPT 18 2017 5th Form Worksheet Electrolysis FOR MARKSДокумент1 страницаSEPT 18 2017 5th Form Worksheet Electrolysis FOR MARKSFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Nov 27 2019 5C Alternative Across The Board Test Nov 2019Документ3 страницыNov 27 2019 5C Alternative Across The Board Test Nov 2019Frank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Worksheet: 5 Form Classwork AlcoholsДокумент2 страницыWorksheet: 5 Form Classwork AlcoholsFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry Nomenclature WorksheetДокумент2 страницыOrganic Chemistry Nomenclature WorksheetFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Mar 17 2020 5TH FORM PRACTICE QUESTIONSДокумент2 страницыMar 17 2020 5TH FORM PRACTICE QUESTIONSFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- Mole Titration and Conversion WorksheetДокумент2 страницыMole Titration and Conversion WorksheetFrank Massiah100% (1)
- Worksheet Alkanes and Alkenes WorksheetДокумент1 страницаWorksheet Alkanes and Alkenes WorksheetFrank MassiahОценок пока нет
- IddДокумент15 страницIddslidesputnikОценок пока нет
- Return To Mecca - ExtractДокумент2 страницыReturn To Mecca - ExtractSheni OgunmolaОценок пока нет
- Investigatory Project For Class 12th ChemistryДокумент6 страницInvestigatory Project For Class 12th ChemistrywarriorОценок пока нет
- Mbeba Chemistry PDFДокумент131 страницаMbeba Chemistry PDFMapalo Chirwa100% (1)
- IMO55 2021 T1 Solutions EngДокумент11 страницIMO55 2021 T1 Solutions EngLazar SavicОценок пока нет
- Vc649a - Aerowhip - Foam Stabilizers in Non-Dairy and Vegetable ToppingsДокумент2 страницыVc649a - Aerowhip - Foam Stabilizers in Non-Dairy and Vegetable ToppingspedrazasОценок пока нет
- Acid Adsorption and Stability of Nitrocellulose J. Phys. Chem., 1931, 35 (2), PP 536-539Документ4 страницыAcid Adsorption and Stability of Nitrocellulose J. Phys. Chem., 1931, 35 (2), PP 536-539Alexey GuskovОценок пока нет
- Definition, Classification, Importance, General PropertiesДокумент11 страницDefinition, Classification, Importance, General PropertiesBalram NeupaneОценок пока нет
- Chemical Ammonia Report PDFДокумент72 страницыChemical Ammonia Report PDFAli J. Hojeij100% (1)
- Exercise - IV: Subjective Level-IIДокумент2 страницыExercise - IV: Subjective Level-IIAmudala HemashviniОценок пока нет
- Noble GasesДокумент3 страницыNoble GasessadasdОценок пока нет
- Astm 4590Документ3 страницыAstm 4590Gyna SH67% (3)
- Higher Thinking QuestionsДокумент4 страницыHigher Thinking QuestionsCaron AsgaraliОценок пока нет
- The Lanthanides and Their ComplexesДокумент8 страницThe Lanthanides and Their ComplexesShotosroy Roy TirthoОценок пока нет
- Chemical Technology Self Study Topic: Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)Документ11 страницChemical Technology Self Study Topic: Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)Paridhi GargОценок пока нет
- Sultanate of Oman: Oil & Gas Directory Middle East - 2010Документ9 страницSultanate of Oman: Oil & Gas Directory Middle East - 2010James KentОценок пока нет
- Saes A 007 - 1 PDFДокумент1 страницаSaes A 007 - 1 PDFmuhammad bilalОценок пока нет
- 20electrochemistry Best Slides 2Документ145 страниц20electrochemistry Best Slides 2Muhammad Nauman KhalidОценок пока нет
- 12-0-2016 Cpi, Equip - Plant Design-QuestionaireДокумент3 страницы12-0-2016 Cpi, Equip - Plant Design-QuestionaireShania Caroline CanaoОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Matters Textbook Answers Chapter 3Документ3 страницыChemistry Matters Textbook Answers Chapter 3MahamIsmail93% (15)
- Platinum Alloys For Shape Memory ApplicationsДокумент15 страницPlatinum Alloys For Shape Memory ApplicationsKursalОценок пока нет
- 1 Manufacture: A Typical Analysis of Commercial Chlorosulfonic Acid Would Be AsДокумент6 страниц1 Manufacture: A Typical Analysis of Commercial Chlorosulfonic Acid Would Be Asapi-19738746Оценок пока нет
- BIODEДокумент17 страницBIODEBayikati PavaniОценок пока нет
- ChemistryДокумент26 страницChemistryRaag JivaniОценок пока нет
- Carbon CompoundsДокумент22 страницыCarbon CompoundsJaechel Vhien TatuОценок пока нет
- Module 4 Chemical BondingДокумент23 страницыModule 4 Chemical BondingJulie Anne Manggurit (Grade-10 Tesla)Оценок пока нет
- Presentation Heat Treatment-Induction HardeningДокумент37 страницPresentation Heat Treatment-Induction HardeningRizwanОценок пока нет
- 100 Passage Based Chemistry Questions SolutionsДокумент17 страниц100 Passage Based Chemistry Questions SolutionsChemistry courseОценок пока нет
- AL 6XN SourceBookДокумент56 страницAL 6XN SourceBookdrbeyerОценок пока нет
- Optimization Studies in Sulfuric Acid Production: 1. AbstractДокумент6 страницOptimization Studies in Sulfuric Acid Production: 1. Abstractdiegotorete1994Оценок пока нет