Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Resources Chapter 32 Student
Загружено:
JA55EEИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Resources Chapter 32 Student
Загружено:
JA55EEАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
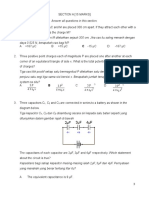
PSP Resources Chapter 32 Students Version
32-1 A coil with zero resistance has its ends labelled a and b. When a current is passed through the coil the
potential at a is higher than the potential at b. Which of the following would be consistent with this
situation? (Note, there may be more than one correct alternative.)
A. The current is constant and is directed from a to b.
B. The current is constant and is directed from b to a.
C. The current is increasing and is directed from a to b.
D. The current is decreasing and is directed from a to b.
E. The current is increasing and is directed from b to a.
F. The current is decreasing and is directed from b to a.
Answer:
32-2 Consider the circuit to the right. The switch S1 is closed. At the
instant the switch is closed, across which circuit element is the
voltage equal to the emf of the battery?
A. The resistor
B. The inductor
C. Each of the resistor and the inductor
D. Neither the resistor or the inductor
Answer:
32-3 Consider the same circuit as in 32-2. After a very long time across which circuit element is the voltage
equal to the emf of the battery?
A. The resistor
B. The inductor
C. Each of the resistor and the inductor
D. Neither the resistor and the inductor
Answer:
32-4 The switch in the figure is closed at t = 0 when the current I is zero.
When I = 15 mA, what is the potential difference across the
inductor?
A. 240 V
B. 60 V
C. 0
D. 180 V
E. 190 V
Answer:
32-5 When a switch is closed, completing an LR series circuit, the time needed for the current to reach one
half its maximum value is ____ time constants.
A. 0.250
B. 0.500
C. 0.693
D. 1.00
E. 1.44
Answer:
32-6 After a switch is thrown to remove the battery from a DC LR circuit, but the circuit is still left
complete, the time constant represents:
A. The time rate of change of the current in the circuit.
B. The time rate of change of the induced emf in the circuit.
C. The magnitude of the ratio of the current to the time rate of change of the current.
D. All of the above.
E. Only (a) and (b) above.
Answer:
32-7 You are performing an experiment which requires the highest possible magnetic energy density in the
interior of a very long current-carrying solenoid. While keeping the remaining parameters constant,
making which of the following changes increases the energy density of the solenoid? (More than one
choice may be correct.)
A. Increasing the number of turns per unit length on the solenoid.
B. Increasing the cross-sectional area of the solenoid.
C. Increasing only the length of the solenoid while keeping the number of turns per
unit length fixed.
D. Increasing the current in the solenoid.
E. Using a soft iron core in the solenoid.
Answer:
32-8 Consider the magnetic field generated by a long, straight current-carrying wire of radius R. At which
of the following locations is the magnetic energy density of the wire the largest?
A. r = 0, at the center of the wire
B. 0 < r < R
C. r = R, at the surface of the wire
D. R < r < 2R
E. The magnetic field density will be the same everywhere.
Answer:
32-9 Coaxial cable A has twice the length, twice the radius of the inner solid conductor, and twice the
radius of the outer cylindrical conducting shell of coaxial cable B. What is the ratio of the inductance
of cable A to that of cable B?
A.
B.
C. 2
D.
E.
Answer:
32-10 In each of the three cases shown, a time-varying
current is flowing through the larger coil that produces
a magnetic field. Rank the mutual inductance for the
three cases shown from smallest to largest.
A. A,B,C
B. C,B,A
C. C,A,B
D. B,C,A
E. B,A,C
Answer:
Вам также может понравиться
- Applied Electronics I Model KIoTДокумент9 страницApplied Electronics I Model KIoTERMIAS AmanuelОценок пока нет
- Local Media474432381540653187-1Документ95 страницLocal Media474432381540653187-1Febejean LumbaОценок пока нет
- Electric Circuit AnalysisДокумент16 страницElectric Circuit AnalysisdarwishmajidОценок пока нет
- AST Practice AnsELECДокумент15 страницAST Practice AnsELECRovina LacunaОценок пока нет
- Majorship TLE ElectronicsДокумент12 страницMajorship TLE ElectronicsAnonymous gijMJlwS6Оценок пока нет
- ExtcДокумент10 страницExtcPrathamesh KeluskarОценок пока нет
- Ice Elecs 8 QueДокумент4 страницыIce Elecs 8 QueJojo TakatoОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper with SolutionsДокумент20 страницCBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper with SolutionsANUP KUMARОценок пока нет
- Sumulong College of Arts and Sciences: Midterm Examination 2 Semester, SY 2019-2020Документ5 страницSumulong College of Arts and Sciences: Midterm Examination 2 Semester, SY 2019-2020Manongdo AllanОценок пока нет
- Jto Exam PapersДокумент29 страницJto Exam Paperssatishkumartadela100% (3)
- Villamor Test - 2 PDFДокумент18 страницVillamor Test - 2 PDFLocrian IonianОценок пока нет
- Applied Electric Circuits Objective QuestionsДокумент35 страницApplied Electric Circuits Objective QuestionsGanesan KandasamyОценок пока нет
- Electricity WorksheetДокумент11 страницElectricity Worksheetsrijankanduri14Оценок пока нет
- Current Electricity MCQ PDFДокумент27 страницCurrent Electricity MCQ PDFSHAMLA BEEVI100% (3)
- MCQ Electrical FundamentalsДокумент6 страницMCQ Electrical FundamentalspriteshОценок пока нет
- Apllied Electric Circuit Objective Question and AnswerДокумент42 страницыApllied Electric Circuit Objective Question and AnswerGanesan KandasamyОценок пока нет
- BSNL JTO 2008 Sample Papers QuestionsДокумент14 страницBSNL JTO 2008 Sample Papers Questionsarunsamuel2002Оценок пока нет
- BSNL JTO (Junior Telecom Officers) Previous Year Question Papers With AnswersДокумент14 страницBSNL JTO (Junior Telecom Officers) Previous Year Question Papers With Answerss_muruganantham805378100% (17)
- Electronics Engineering FundamentalsДокумент77 страницElectronics Engineering FundamentalsLeonard Jobet Villaflor PantonОценок пока нет
- Mycbseguide: Class 12 - Physics Sample Paper 08Документ17 страницMycbseguide: Class 12 - Physics Sample Paper 08Divydarshan MishraОценок пока нет
- 2020 Set 4Документ34 страницы2020 Set 4Giridhar MeruvalaОценок пока нет
- EE133 Final-Examination MauhayДокумент8 страницEE133 Final-Examination MauhayJohn Zyrus MauhayОценок пока нет
- PHYS 2524 Final Exam Practice Circuits and ThermodynamicsДокумент12 страницPHYS 2524 Final Exam Practice Circuits and ThermodynamicsxiangliОценок пока нет
- Physics Test GeneratorДокумент17 страницPhysics Test GeneratorTweety PreetyОценок пока нет
- Correct Ans & Past Paper EE MCQSДокумент136 страницCorrect Ans & Past Paper EE MCQSAhmad USmanОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 and THYRISTORS (UNIT2)Документ71 страницаUnit 1 and THYRISTORS (UNIT2)Suraj KumarОценок пока нет
- Unit 10 Regents Physics Test (Circuits Review)Документ7 страницUnit 10 Regents Physics Test (Circuits Review)aznblehtnОценок пока нет
- Charged Sphere and Insulated RodДокумент13 страницCharged Sphere and Insulated RodRia MandasariОценок пока нет
- 12th Physics B-5Документ10 страниц12th Physics B-5Riya KakaniОценок пока нет
- BSNL Jto 2009 Questions: DimensionlessДокумент10 страницBSNL Jto 2009 Questions: DimensionlesstopotopОценок пока нет
- Microsoft Word - COMPILED 2Документ27 страницMicrosoft Word - COMPILED 2Tayseer SaudiaОценок пока нет
- Elecs 2008Документ4 страницыElecs 2008Denaiya Watton LeehОценок пока нет
- Jto QuestionsДокумент246 страницJto Questionsanirudha0012Оценок пока нет
- University of San Agustin Pre-Board Exam ReviewДокумент8 страницUniversity of San Agustin Pre-Board Exam ReviewRoyce SumagaysayОценок пока нет
- CH 27-30Документ69 страницCH 27-30Richard Hammond50% (2)
- C. OrbitsДокумент7 страницC. OrbitsKristine Pamela Asistio AndalОценок пока нет
- Midterm 2023Документ5 страницMidterm 2023Thanushree.SОценок пока нет
- 12th Science Preboard Exam Physics QuestionsДокумент9 страниц12th Science Preboard Exam Physics QuestionsSharma BhavnaОценок пока нет
- Angel Education Half Yearly Exam Physics 2017-2018Документ3 страницыAngel Education Half Yearly Exam Physics 2017-2018Atul Verma0% (1)
- Electricity Book QuestionsДокумент6 страницElectricity Book QuestionsshellyОценок пока нет
- 2013 E.C. BASIC ELECTRICITY Entrance Exam For EEP.Документ6 страниц2013 E.C. BASIC ELECTRICITY Entrance Exam For EEP.Ziyad Mohammed100% (1)
- Electricity QuestionnaireДокумент4 страницыElectricity QuestionnaireRenie FedericoОценок пока нет
- Test 2Документ16 страницTest 2edwardОценок пока нет
- Electronic Devices and Electronic Circuits: QuestionsДокумент51 страницаElectronic Devices and Electronic Circuits: QuestionsRohit SahuОценок пока нет
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Part 2Документ9 страницElectronic Devices and Circuits Part 2Renz Benhar Ocon BobadillaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 03 PP Xii PhysicsДокумент6 страницChapter 03 PP Xii Physicsstudywithak77Оценок пока нет
- 일반물리학및실험2 과제풀이 (2011-2학기Документ7 страниц일반물리학및실험2 과제풀이 (2011-2학기choiyunjungОценок пока нет
- 26 HambatanlistrikДокумент11 страниц26 Hambatanlistriklhakim_100Оценок пока нет
- PHYSICS H.Y 12th REVISION SHEETДокумент6 страницPHYSICS H.Y 12th REVISION SHEETGeetanjli GuptaОценок пока нет
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)От EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)Оценок пока нет
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsОт EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1От EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Оценок пока нет
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10От EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Оценок пока нет
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)От EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- New Standard Airbus Tanker Makes First Flight - Defense News: Aviation International NewsДокумент2 страницыNew Standard Airbus Tanker Makes First Flight - Defense News: Aviation International NewsJA55EEОценок пока нет
- Airbus A330/A340 Flight Control SystemДокумент6 страницAirbus A330/A340 Flight Control SystemJA55EEОценок пока нет
- A330-Auto Flight PDFДокумент164 страницыA330-Auto Flight PDFJA55EEОценок пока нет
- Design 1 ReadingДокумент26 страницDesign 1 ReadingJA55EEОценок пока нет
- Potential Flow and Stream FunctionДокумент13 страницPotential Flow and Stream FunctionJA55EEОценок пока нет
- Solar Water HeatersДокумент25 страницSolar Water HeatersJA55EEОценок пока нет
- Bioenergy ProductionДокумент164 страницыBioenergy ProductionJA55EEОценок пока нет
- A330 Jam Flight LawsДокумент3 страницыA330 Jam Flight LawsnzcruiserОценок пока нет
- Embedded Generation Connection Guide PDFДокумент43 страницыEmbedded Generation Connection Guide PDFSunrider2014Оценок пока нет
- Engineering Bernoulli EquationДокумент19 страницEngineering Bernoulli EquationJA55EEОценок пока нет
- MVC - AnswersДокумент12 страницMVC - AnswersJA55EEОценок пока нет
- Notes LT1Документ21 страницаNotes LT1deathesОценок пока нет
- Potential Flow and Stream FunctionДокумент13 страницPotential Flow and Stream FunctionJA55EEОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 1 MoSДокумент1 страницаTutorial 1 MoSJA55EEОценок пока нет
- Development of Lightweight SteelДокумент6 страницDevelopment of Lightweight SteelJA55EEОценок пока нет
- Laplace Transforms with MATLABДокумент3 страницыLaplace Transforms with MATLABJoão Gabriel LimaОценок пока нет
- Matlab Tutorial For SlopefieldДокумент7 страницMatlab Tutorial For SlopefieldJA55EEОценок пока нет
- Partial FractionsДокумент1 страницаPartial FractionsJA55EEОценок пока нет
- Magnetic Force Particle ChargedДокумент20 страницMagnetic Force Particle ChargedJA55EEОценок пока нет
- PhysicsДокумент12 страницPhysicsJA55EEОценок пока нет
- Ch29 StudentДокумент12 страницCh29 StudentJA55EEОценок пока нет
- Vehicle Specifications LADA Granta Cross LADAДокумент1 страницаVehicle Specifications LADA Granta Cross LADARoy Eber Gutierrez TamboОценок пока нет
- Solenoid Engine: A Zero-Emission AlternativeДокумент24 страницыSolenoid Engine: A Zero-Emission Alternativemrcopy xerox100% (1)
- 2 Phase Hybrid Stepper Motor Specifications and DimensionsДокумент1 страница2 Phase Hybrid Stepper Motor Specifications and DimensionsJulio ConfortoОценок пока нет
- 16410Документ16 страниц16410uddinnadeemОценок пока нет
- Performance of A Grid-Connected Photovoltaic System in MalaysiaДокумент10 страницPerformance of A Grid-Connected Photovoltaic System in Malaysiahaerur roziОценок пока нет
- Epic ECM Fan Coil Unit Jan 212 - MAY18Документ8 страницEpic ECM Fan Coil Unit Jan 212 - MAY18Theo VasilescuОценок пока нет
- 1.fabrication of Steam Power PlantДокумент25 страниц1.fabrication of Steam Power PlantClement StephensonОценок пока нет
- User Manual: HMC9000 Diesel Engine ControllerДокумент53 страницыUser Manual: HMC9000 Diesel Engine ControllerRahmat Nur IlhamОценок пока нет
- IOP 2 Exercises G120X V1.2 03.2020Документ59 страницIOP 2 Exercises G120X V1.2 03.2020Steven CanalesОценок пока нет
- Ater Chillers: Operating and Maintenance ManualДокумент68 страницAter Chillers: Operating and Maintenance ManualDelmiro MartinОценок пока нет
- Electric Vehicle Powertrain ArchitectureДокумент5 страницElectric Vehicle Powertrain Architecturegowri sankar NОценок пока нет
- Senrigan-GP-45 Brushless Gimbal Instruction ManualДокумент17 страницSenrigan-GP-45 Brushless Gimbal Instruction ManualEduardo Lozano FloresОценок пока нет
- Current-Fed Step-Up DC/DC Converter For Fuel Cell Applications With Active Overvoltage ClampingДокумент7 страницCurrent-Fed Step-Up DC/DC Converter For Fuel Cell Applications With Active Overvoltage Clampingsigit kurniawanОценок пока нет
- Electrical - PPT - V 03 01 17Документ55 страницElectrical - PPT - V 03 01 17IMRANОценок пока нет
- DataSheetДокумент3 страницыDataSheetWilliam VargasОценок пока нет
- So-Low: General SpecificationsДокумент6 страницSo-Low: General SpecificationsPharmacist OneОценок пока нет
- Falk CatalogДокумент20 страницFalk CatalogHugo RubimОценок пока нет
- Opamp TesterДокумент2 страницыOpamp TesterbalubobbyОценок пока нет
- PB SeriesДокумент108 страницPB SeriesGerman LiernurОценок пока нет
- Pipe Size For ACДокумент8 страницPipe Size For ACLamii BedoОценок пока нет
- Rbs/Bts Signal Cabling: DF PanelДокумент1 страницаRbs/Bts Signal Cabling: DF PanelMayuSalanggaОценок пока нет
- Dura Products Product-Catalogue PDFДокумент306 страницDura Products Product-Catalogue PDFMahmoud MorsiОценок пока нет
- DRV8306Документ46 страницDRV8306Lu HoaОценок пока нет
- Commercial Shipping CatalogueДокумент87 страницCommercial Shipping CatalogueSuresh Kumar SaripalliОценок пока нет
- VDI HandlingДокумент8 страницVDI HandlingRhio HandikaОценок пока нет
- PC300 5 400 5 PDFДокумент748 страницPC300 5 400 5 PDFRodrigo Valenzuela100% (1)
- 700IA89..AV-EMX20CLC 55W (L - MBP) - DatasheetДокумент5 страниц700IA89..AV-EMX20CLC 55W (L - MBP) - Datasheetmohamad tajvidiОценок пока нет
- Mps-Vx Series Hybrid Solar Inverter Product Data SheetДокумент1 страницаMps-Vx Series Hybrid Solar Inverter Product Data SheetSoos JozsefОценок пока нет
- Lubchart 2013Документ1 страницаLubchart 2013JUANОценок пока нет
- Register TransferДокумент8 страницRegister TransferA's Was UnlikedОценок пока нет