Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Centero WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual
Загружено:
raytangclАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Centero WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual
Загружено:
raytangclАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual
Version 2.1
Date: January 22, 2013
08-00029-02 Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
Revision History
Date Version Description
December 10, 2010 0.1 Document inception, SW integration
December 15, 2010 0.2 Added API/Stack Specific Commands
February 22, 2011 0.3 Added UART Integration
February 23, 2011 0.4 Added Case diagrams and explanations
February 23, 2011 0.5 Formatted and reviewed
February 28, 2011 0.6 SPI Integration reviewed
Formatted and reviewed
March 22, 2011 0.7 Removed API_ENERGY_LEFT and
API_ENERGY_MODEM_REQ
June 14, 2011 0.8 Redesign Figure 8
Changed API_UPDATE_POOLING_FREQ to
API_HEARTBEAT_FREQ
Changed API_POOLING to API_HEARTBEAT
Changed API_PROTOCOL_VERSION to
API_FW_VERSION
Added HART_NOTIFY_JOIN and HART_RADIO_RESET
commands
Corrections
June 29,2011 0.8 Added Example
October 18, 2011 0.9 Added Annex A,
Review
January 15, 2012 1.0 Added VN310 References and Pin Assignment
March 6, 2012 1.1 Added a note about the BOOT KB1 pin (boot switch)
April 5, 2012 1.2 Adding API_SET_COUNTRY_CODE command
May 11, 2012 1.2 Correcting the Example section: A response packet does
not include the Device Status byte
May 22, 2012 1.2 Correcting the Clock Polarity: 0 for the SPI connection
settings
September 07, 2012 1.3 Adding Stack Specific message: HART_GET_ASN
October 29, 2012 1.4 Update data format for User Board Messages
Adding §3.4.7, §3.4.8 and §3.8.4 to §3.8.7: two new Stack
Specific messages and Full API case diagrams
January 22, 2013 2.1 Added a pin assignment for the VN310 Full API loaded with
firmware v2.1.0 or newer: RDY line function is switched to
radio pin 12 (TMR1)
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 2/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
Table of Contents
1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................... 6
1.1 Document Purpose ..........................................................................................................................6
1.2 Audience .........................................................................................................................................6
2 Hardware Integration ................................................................................................................. 7
2.1 Pin-out and interfaces ......................................................................................................................7
2.2 UART Integration ........................................................................................................................... 10
2.2.1 Full Wake-Up Support without Flow Control (6 pins) ........................................................................................... 10
2.2.2 Modem Wake-Up Support (5 pins) with Flow Control ......................................................................................... 12
2.3 SPI Integration ............................................................................................................................... 14
2.3.1 Wake Up via HW Support ..................................................................................................................................... 14
2.3.2 No Wake-Up Support ............................................................................................................................................ 16
2.3.2.1 Message Flow .................................................................................................................................................... 16
2.3.2 SPI Settings............................................................................................................................................................ 16
3 Software Integration ................................................................................................................ 18
3.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 18
3.2 Communication Flow ..................................................................................................................... 19
3.2.1 API Message Format ............................................................................................................................................. 19
3.2.1.1 Message Header ........................................................................................................................................... 20
3.2.1.2 Special Characters ........................................................................................................................................ 20
3.3 API Messages ................................................................................................................................. 21
3.3.1 API_HW_PLATFORM (0x00) .................................................................................................................................. 21
3.3.1.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 21
3.3.1.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 21
3.3.2 API_FW_VERSION (0x01) ...................................................................................................................................... 21
3.3.2.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 21
3.3.2.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 22
3.3.3 API_MAX_BUFFER_SIZE (0x02) ............................................................................................................................. 22
3.3.3.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 22
3.3.3.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 22
3.3.4 API_MAX_SPI_SPEED (0x03) ................................................................................................................................. 22
3.3.4.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 22
3.3.4.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 22
3.3.5 API_UPDATE_SPI_SPEED (0x04) ............................................................................................................................ 22
3.3.5.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 23
3.3.5.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 23
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 3/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.3.6 API_MAX_UART_SPEED (0x05) ............................................................................................................................. 23
3.3.6.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 23
3.3.6.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 23
3.3.7 API_UPDATE_UART_SPEED (0x06) ........................................................................................................................ 23
3.3.7.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 23
3.3.7.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 24
3.3.8 API_HEARTBEAT_FREQ (0x07) - For SPI Only ........................................................................................................ 24
3.3.8.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 24
3.3.8.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 24
3.3.9 API_HEARTBEAT (0x08) –SPI Only ......................................................................................................................... 24
3.3.10 API_SET_COUNTRY_CODE (0x0C) ..................................................................................................................... 25
3.3.10.1 Request ..................................................................................................................................................... 25
3.3.10.2 Response .................................................................................................................................................. 25
3.4 Stack Specific Messages ................................................................................................................. 25
3.4.1 HART_GET_ASN (0x01) ......................................................................................................................................... 26
3.4.1.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 26
3.4.1.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 26
3.4.2 HART_SERVICE_REQUEST (0x03) .......................................................................................................................... 26
3.4.2.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 26
3.4.2.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 26
3.4.3 HART_SERVICE_DELETE (0x04) ............................................................................................................................. 26
3.4.3.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 27
3.4.3.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 27
3.4.4 HART_NOTIFY_JOIN (0x05) ................................................................................................................................... 27
3.4.4.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 27
3.4.4.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 27
3.4.5 HART_GET_INITIAL_INFO (0x06)........................................................................................................................... 27
3.4.5.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 27
3.4.5.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 27
3.4.6 HART_RADIO_RESET (0x07) .................................................................................................................................. 27
3.4.6.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 27
3.4.6.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 27
3.4.7 HART_WRITE_ADDITIONAL_DEVICE_STATUS (0x08) ............................................................................................ 28
3.4.7.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 29
3.4.7.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 29
3.4.8 HART_CLEAR_MSA (0x09) ..................................................................................................................................... 29
3.4.8.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 29
3.4.8.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 29
3.5 User Board Messages ..................................................................................................................... 30
3.5.1 DAQ_FW_WIRELESS (0x00) ................................................................................................................................... 30
3.5.1.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 30
3.5.1.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 30
3.5.2 DAQ_BURST_PIPE_0(/1/2) (0x01 – 0x03) ............................................................................................................. 31
3.5.2.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 31
3.5.2.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 31
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 4/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.5.3 DAQ_FW_WIRED (0x04) ....................................................................................................................................... 31
3.5.3.1 Request ......................................................................................................................................................... 31
3.5.3.2 Response ...................................................................................................................................................... 31
3.6 Response ACK ................................................................................................................................ 31
3.6.1 Message format .................................................................................................................................................... 31
3.7 Response NACK.............................................................................................................................. 32
3.7.1 Message format .................................................................................................................................................... 32
3.8 WirelessHART Full API case diagrams.............................................................................................. 33
3.8.1 Burst Activation & Service Request ...................................................................................................................... 33
3.8.2 Burst Disabling & Service Deletion........................................................................................................................ 35
3.8.3 Service Task at Join ............................................................................................................................................... 36
3.8.4 WHART Device Status ........................................................................................................................................... 37
3.8.5 Device Status: Configuration Changed Flag .......................................................................................................... 38
3.8.6 Device Status: More Status Available (MSA) flag handled by the Radio............................................................... 39
3.8.7 Device Status: More Status Available (MSA) flag handled by the AP ................................................................... 41
4 Examples .................................................................................................................................. 44
4.1 Hart Wireless Command Forwarding (command 1) ......................................................................... 44
4.1.1 Request ................................................................................................................................................................. 44
4.1.2 Response ............................................................................................................................................................... 44
4.2 Hart Wired Command Forwarding (command 105) ......................................................................... 45
4.2.1 Request data ......................................................................................................................................................... 45
4.2.2 Response data ....................................................................................................................................................... 45
5 Annexes ................................................................................................................................... 46
5.1 Annex A - Command Implementation Reference............................................................................. 46
5.2 Annex B - Country Codes and radio maximum output power ........................................................... 51
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 5/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
1 Introduction
1.1 Document Purpose
The WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual provides information on how to integrate the customer’s
board with the Nivis VN220 or VN310 radio modem, defines various communication solutions based on the
UART/SPI interface, and defines APIs to communicate with the VN220/VN310.
1.2 Audience
The purpose of this document is to provide all necessary data to achieve hardware integration of the
VN220/VN310 radio modem within a data acquisition, sensor or communication interface board generically
called application board.
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 6/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
2 Hardware Integration
2.1 Pin-out and interfaces
The following section presents the pin assignment of the VN220/VN310 radio modem.
An external processing entity can communicate with the VN220/VN310 using either an UART interface
(using UART2) or a SPI interface. The UART1 port is used for Serial firmware upload, and, in some
applications, it is used to communicate to the HART modem residing on the Wireless HART Modem board.
Note: Please consult the “08-00023-01_Nivis_VN220_HW_Integration_Application_Note.pdf”, “08-00032-
01_Nivis_VN310H_HW_Integration_Application_Note.pdf” or “08-00041-01 Nivis VersaNode 310 Hardware
Integration AppNote” (for VN310 with Full API v2.0.1 or newer) for details about KBI1 pin (no. 27 for VN220 or no.
39 for VN310). It is used as a boot switch in order to boot different firmware images (ISA100 or Wireless HART)
based on the position of the switch. For WirelessHART firmware this pin must be held LOW. The VN220/VN310
bootloader sets this pin as an input, with the internal weak pull-up enabled.
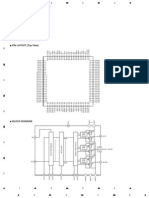
Figure 1 VN220 Pin Assignment
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 7/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
UART2_RTS 1 55 TMS
UART2_CTS TCK
UART2_RX TDI
UART2_TX TDO
UART1_RTS JTAG_RTCK
GND RESET_B
UART1_CTS GND
UART1_RX V_IN
UART1_TX ADC0
I2C_SDA VN310 ADC1
I2C_SCL
PINOUT ADC2
TMR1 ADC3
TMR0 GND
GND KBI_4
SPI_SCK KBI_3
SPI_MOSI KBI_2
SPI_MISO KBI_1
SPI_SS RTC_INT_B
KBI_0 GPIO_12
RTC_FOUT 20 36 GPIO_11
GPIO_1
GPIO_2
GPIO_3
GPIO_7
GND
KBI_5
ADC2_VREFL
ADC1_VREFL
ADC2_VREFH
ADC1_VREFH
KBI_6
GPIO_10
GPIO_8
GPIO_9
GND
Figure 2 VN310 Pin Assignment
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 8/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
The following picture shows the pins for UART2 and SPI interfaces from the VN220/VN310 radio modem
and their equivalent signals:
(ExtRTS) EXTRTS 1 UART-RTS (ExtRTS) EXTRTS 1 UART-RTS
(ExtCTS) EXTCTS 2 UART-CTS (ExtCTS) EXTCTS 2 UART-CTS
(RX) UART2-RXD 3 TX (RX) UART2-RXD 3 TX
(TX) UART2-TXD 4 RX (TX) UART2-TXD 4 RX
(RDY) KBI3 29/41 RDY_RADIO (RDY) TMR1 12 RDY_RADIO
(WKU) KBI4 30/42 WKU_RADIO (WKU) KBI4 42 WKU_RADIO
External/ External/
VN220/VN310 (for VN310 VN310 (starting with VN310 Full
Application Application
valid up to Full API v2.0.x) API v2.1.0)
Processor Processor
GND GND GND GND
(CLK) SPI-SCK 13/15 SCLK (CLK) SPI-SCK 13/15 SCLK
(MOSI) SPI-MOSI 14/16 MOSI (MOSI) SPI-MOSI 14/16 MOSI
(MISO) SPI-MISO 15/17 MISO (MISO) SPI-MISO 15/17 MISO
(SS) SPI-SS 16/18 SS (SS) SPI-SS 16/18 SS
Figure 3 Pin connections for communication between VN220/VN310 radio modem and Application Board
Important Note: The application processor UART-RTS should be connected to ExtRTS (pin 1) and UART-
CTS should be connected To ExtCTS (pin 2).
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 9/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
2.2 UART Integration
The following settings are used for the UART interface:
Default Baud rate: 38400
Bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop Bits: 1
Applications using the API interface will be provided with a means of adjusting the UART communications
speed/baud rate. The change in baud rate by the application processor will be ‘approved’ by the RF
processor to ensure it can still reliably communicate.
Note: Lower UART baud rates are likely to be the bottleneck in the system. If a user requires higher system
performance, the SPI interface is recommended.
There are two solutions based on UART communication:
Full wake-up support (6 pins) without Flow Control
Modem wake-up support (5 pins) with Flow Control
The application can select which solution to use, depending on its processor capabilities and requirements.
The UART2 signals have a “HIGH” logic level of +3Vdc, and a “LOW” logic level of 0Vdc.
2.2.1 Full Wake-Up Support without Flow Control (6 pins)
This version is used when the application processor enters low power mode for extended time periods and
must be notified before the message exchange. The application board and the modem are equally powered
to wake up the destination and initiate a transfer.
VN220/VN310 Application CPU
RX
TX
ExtRTS
ExtCTS
WKU
RDY
GND
Figure 4 Full API – UART, Full wake-up support w/o Flow Control (6 pins)
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 10/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
Signal name Direction Use
TX Output
As in UART communication, TX and RX are used for data transfer;
RX Input
This signal is active low and is used by the modem to indicate a want-to-
ExtCTS Output send state. The signal will return to high state after a high to low transition
of the ExtRTS signal.
This signal is active low and is used by the application CPU to indicate a
ExtRTS Input ready-to-receive state. It will Implicitly confirm the acquisition of ExtCTS low
signal to the modem.
This signal is active low and is used by the modem to indicate a ready-to-
RDY Output receive state. It will be generated as a response to the application CPU
WKU signal.
This signal is active high and is used by the application CPU to wake up the
radio modem CPU from hibernation and to signal the intention to
WKU Input
communicate with the modem. Keeping this line active will block the
modem from entering the low power mode (sleep).
* Changes in the control signals’ active states (low or high) can be made upon request, to accommodate
custom hardware
ExtCTS
ExtRTS
TX
WKU
RDY
Rx
Figure 5 6 pin UART flow control
There is no flow control for transmitting. Once a message transmission has started, it will flow
without restrictions and without awareness of the receiving capability of the destination. The
destination should be capable of receiving bytes at the arriving speed.
There are no critical timings in handshaking due to the direct wakeup. ExtRTS is asserted as a
response to ExtCTS becoming active, the message will start being transmitted by the modem as a
result of ExtRTS becoming active. Similarly, RDY becomes active as a result of WKU rising and
transmission to the modem should start as a result of RDY becoming active.
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 11/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
There may be a delay of approximately 2ms between the rise of the WKU signal and the fall of the
RDY signal if the modem is sleeping. The modem waits for a message for a minimum of 3ms before
entering low power/sleeping mode.
After activating the ExtCTS signal, the modem will wait for a maximum of 25ms for the application
processor to become ready to receive.
After recognizing the end of an incoming valid message, the modem will not wait for the next
message and may stay ON only to complete current tasks. A second message should be preceded
by another WKU signal.
If RDY is active at the moment of rising WKU, a maximum 5ms pulse should be generated on the
WKU line.
After receiving a byte, the modem will wait for 5ms and then will stop listening. The application
processor should ensure a fairly continuous stream of bytes for a given message in order to keep
the radio modem in listening mode and prevent it from entering low power mode.
2.2.2 Modem Wake-Up Support (5 pins) with Flow Control
This version is used when the application processor is always ready to exchange messages. It is based on
the UART hardware flow control protocol and the four lines keep regular significance. As in the case of an
activity intensive application that requires the application processor to be ON, the modem can still go to low
power mode for long periods and will be woken up by the application processor through a wake-up signal
added as the 5-th line (WKU).
VN220/VN310 Application CPU
RX
TX
Ext RTS
Ext CTS
WKU
GND
Figure 6 Full API – UART, VN220/VN310 wake-up support w/ Flow Control (5 pins)
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 12/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
Signal name Direction Use
TX Output
RX Input As in UART communication with hardware flow control:
ExtCTS Output TX and Rx are used for data transfer;
ExtRTS and ExtCTS controls the flow of data, those are active low signals
ExtRTS Input
Used by the application CPU to alert the modem if a data exchange needs to be
initiated. This is an active high signal and a positive pulse will wake up the modem.
WKU Input
Keeping this line in high state will block the modem from entering in low power mode
(sleep).
WKU
TX
RX
ExtCTS
ExtRTS
Figure 7 5 pin UART interface flow control
The modem has hardware flow control enabled in its peripheral to allow it to tolerate slower or
heavily loaded application processors. This feature (transparent hold/resume) should be used with
moderation since the modem will remain awake and consume power during the stops. A 5ms delay
over the time needed for continuous transmission is tolerated for any message; subsequently, a
timeout will occur and the modem will enter low power mode, stopping the UART module.
The WKU line is linked to an interrupt that brings the modem out of low power mode. While the
modem is running the UART module is on and capable of handling receiving/transmitting bytes. After
waking up, the modem will wait for at least 3ms for incoming bytes. After recognizing the end of an
incoming valid message, the modem will not wait for the next message and may stay ON only to
complete current tasks. A second message should be preceded by another WKU signal.
Keeping the WKU active will prevent the modem from entering low power.
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 13/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
2.3 SPI Integration
Applications using the SPI interface are provided with a means of adjusting the SPI communications speed -
the API Command API_UPDATE_SPI_SPEED. The change in speed by the application processor will be
‘approved’ by the RF processor.
The radio modem processor is the master of communication. If the application processor has any message
to be read by the radio processor, it can signal the master by using the WKU signal.
There are two solutions based on SPI communication:
Wake up via HW support
No wake-up support
The application can select which solution to use depending on its processor capabilities and requirements.
The SPI signals have a “HIGH” logic level of +3Vdc, and a “LOW” logic level of 0Vdc.
2.3.1 Wake Up via HW Support
This version will be used when the application processor needs extra time for wake up, before being able to
receive an SPI message. Two additional GPIO pins will be used to that effect:
RDY will be used to wake up the application processor by the RF processor
WKU will be used to wake up the RF processor by the application processor
If the RF processor has data to send to the application processor, it will raise the RDY to HIGH indicating its
intention to send the data. The application processor raises WKU to HIGH for maximum of 10ms (typical 1-
2ms) to indicate that it is ready to receive the data.
If WKU becomes HIGH, the RF processor will start to send the SPI message in maximum 2ms (typically a
few microseconds).
If the application processor has data to send to the RF processor, it creates a 1 ms pulse on WKU. The RF
processor will query the application processor at the next 250 ms timing. For this reason the Polling Rate is
not used in this configuration.
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 14/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
T1 T1
RDY
WKU
RADIO_SPI_STR T6 T7
T2 T3
SS T4 T5
S
SCK/MISO/MOSI
250ms 500ms
0ms
Min Max Typical Comment
T1 - 10 ms - Until WKU becomes high and implicitly depends on the wake up
time of the application processor
T2 - 10 ms 1-2 ms Time to wake up the application processor
T3 0.001 ms 10 ms - Nivis recommends on the application processor side, to reset the
WKU signal after the STX byte reception (or at least the WKU
signal should be reset during the packet reception). Otherwise, if
the WKU signal is reset after the packet reception, an
unnecessary transmission of a polling message at the next 250
ms timing(see Figure 7) is triggered on RF processor side
T4 - 10 ms 0.01 If Nivis recommendation for T3 is respected, typically T4 will be
ms smaller than T3.
T5 - - - Depends of packet length and SPI frequency.
T5[ms]=PacketLen[bytes]*8*1000/SPI_Freq[kHz]
As example, for default SPI_Freq = 100 kHz,
T5_Min[ms]=7*8*1000/100=0.56, where: 7=Mininum API packet
length
T6 - 200 ms - Missing if no response back
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 15/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
T7 0.1 ms 10 ms 1 ms Is used to notify the RF processor when the application
processor has data to send. The Nivis recommendation for T7 is
to not go beyond the 250 ms boundary (see Figure 7) in order to
prevent, on the RF processor, treating the T7 as T3 (response to
its last RDY pulse) and implicitly to prevent possible unexpected
data receiving by the application processor, even if as long as
the WKU is active, should mean that the application processor is
wake up and should be able to receive data from RF processor.
Missing if no response back.
2.3.2 No Wake-Up Support
This version is used when the application processor does not require additional time for wake up. In this
architecture the application processor will wake up on the SS (Slave Select) transition and will be able to
receive SPI messages without any extra GPIO handshaking.
2.3.2.1 Message Flow
Since in this version the application processor cannot signal the RF processor, the RF processor sends a
polling message at every polling period, if there is no other message to be sent. The polling period can be
changed by the application processor using API Commands (API_HEARTBEAT_FREQ).
However, when the RF processor sends a request message, it polls the application processor after 250ms
irrespective of the current polling period.
RF processor originator:
1. RF processor sends request message (REQ/RSP flag is 0)
2. RF processor sends polling message after 250ms and during this message the application processor
sends back a response or ACK message (REQ/RSP flag is 1, message ID is the same as in the request)
Application processor originator:
1. RF processor sends any message (may be polling message if not any message), application processor
sends back request message (REQ/RSP flag is 0).
2. RF processor sends response or ACK message (REQ/RSP flag is 1, message ID is the same as on
request)
NOTE: If the RF processor detects a valid incoming message from the application processor, it will keep
sending the STX character until it receives the complete message.
2.3.2 SPI Settings
The following settings are used for SPI communication:
Default Speed: 100 KHz
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 16/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
Max Speed: Processor dependant
Clock polarity: 0 (data is captured on the first UCLK edge and changed on the following edge)
Clock phase: 0 (data is captured on the first UCLK edge and changed on the following edge)
Figure 8: SPI Signals: SCLK, MOSI, MISO
The Most Significant Bit is transmitted first in the byte. The data is latched on the rising edge of SCLK.
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 17/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3 Software Integration
3.1 Overview
The figure below shows the software modules for each unit and how the application processor interfaces
with the VN220/VN310 RF modem processor:
VN220/VN310 Processor Application Processor
EVENTS
WiredHART
Stack
API API USER
API
WirelessHART Handler Handler APP
Stack
DRM DVs NVM
NVM
SRV BURSTS
Figure 9 Full API based field device logical modules
VN220/VN310 Processor’s Software Modules:
WiredHARTStack and WirelessHARTStack both reside on the Nivis VN220/VN310 radio, including
all HART (wired and wireless) OSI levels.
API Handler– this module processes the API, STACK, USER BOARD messages.
NVM is the persistent memory on the radio.
DRM/SRV modules are implementing the delayed response mechanism used for some HART
commands and the bandwidth handling.
Event module is triggering various alarms.
Most commands are processed on the radio module; commands related to device variables and
bursts are forwarded via API to the application processor for processing. The application processor
sends the API response to the radio; it will be further sent on wired/RF interface, depending on the
request’s source.
Important: For information about which module (VN220/VN310 processor or application processor)
is responsible to decode and respond to a certain command, please refer to Annex A.
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 18/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
Application Processor Software Modules:
App block represents the user specific application
API handler – Similar to the radio module
NVM - persistent memory on the application board
DVs/Bursts modules. The DV module defines and handles the user defined device variables. The
Burst module keeps burst related data and handles publishing device variables according to the
HART specifications
Note: The Full API version available with Nivis WirelessHART v1.5.x does not have support for
event notifications generated by the application processor. This will be a future enhancement of
Nivis WirelessHART v2.0 solution.
3.2 Communication Flow
Communication between the application processor and the RF modem processor is request/response
packets based. All request packets must be followed by a response/ACK/NACK. The receiving processor
must respond in maximum 250 ms, otherwise the message will be sent repeatedly. A response message
must meet the following criteria:
the Req/Rsp flag from the Message Header must be 1 (See section API Message Format)
the Message ID field is the same as in the request
the message class may be ACK/NACK
3.2.1 API Message Format
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
STX 1 0xF1 This is the start character for every message. When it is received,
the receiver discards any other Rx message in progress and starts
receiving this new message.
Message Header 1 See Message Header
Message Type 1 Depends on Message Class in the Message Header
Message ID 1 Used for correspondence between request and response
Data Size 1 The number of data bytes in the message (without the CRC field)
Data 0…X The request/response message data
CRC 2 CRC is based on a standard CRC algorithm (CCITT-CRC, 0x1021
as the polynomial) and includes everything between, but not
including, the STX and CRC. The initial value is 0xFFFF.
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 19/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.2.1.1 Message Header
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Description Message Class Request/ Reserved
Response
The Request/Response bit indicates whether a message is a request or a response: 0 = Request,
1=Response.
The following message classes are available:
Field Size Values Comments
(Bits)
Message 4 1 = Reserved
Class 2 = Reserved
3 = STACK_SPECIFIC
4 = API
5 = ACK
6 = NACK
7 = USER_BOARD
3.2.1.2 Special Characters
There are two special characters described inside below table:
Char Values Comments
STX 0xF1 Start of packet
CHX 0xF2 Escape character
The STX is a special character that indicates the start of a new packet. The sender is allowed to abort the
current packet and start a new packet by sending the STX in the middle of a packet. Therefore, the packet
data needs to be protected if it contains any STX character. The escape character CHX is used for this
purpose.
Note: The CRC field is calculated based on the un-escaped packet data.
All packet characters including the CRC field (excluding the STX field) will be escaped with the escape
character CHX, i.e. if any of the characters in the packet is:
STX (0xF1): It will be replaced with two characters: 0xF2 (CHX) and 0x0E (1’s complement of 0xF1),
CHX (0xF2):It will be replaced with two characters: CHX (0xF2) and 0x0D (1’s complement of 0xF2).
In other words, whenever the receiver receives a CHX character, it should discard it and the next character
is 1’s complemented.
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 20/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.3 API Messages
The table below lists the message types for message class API:
Message Type Values Description
API_HW_PLATFORM 0 Reads API Hardware version from RF modem ()
API_FW_VERSION 1 Reads API Communication Protocol version from RF modem ()
API_MAX_BUFFER_SIZE 2 Reads API buffer size from RF modem ()
API_MAX_SPI_SPEED 3 Reads max SPI speed from RF modem ()
API_UPDATE_SPI_SPEED 4 Sets SPI speed to RF modem ()
API_MAX_UART_SPEED 5 Reads max UART speed from RF modem ()
API_UPDATE_UART_SPEED 6 Sets UART speed to RF modem ()
API_HEARTBEAT_FREQ 7 Sets POLLING frequency of RF modem (for SPI only) ()
API_HEARTBEAT 8 Polling message (for SPI only) ()
API_SET_COUNTRY_CODE 12 Sets the country code on RF modem side ()
Command Direction:
Radio modem CPU to application CPU
Application CPU to radio modem CPU
3.3.1 API_HW_PLATFORM (0x00)
This message is used by the application processor to read the hardware platform processor type of the radio
modem processor.
3.3.1.1 Request
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1 0x00
3.3.1.2 Response
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1 2
Data 2 Processor Type MSB first
0x0000 - MSP430
0x0001 - HCS08
0x0002 - ARM7
0x0003 - ARM9
3.3.2 API_FW_VERSION (0x01)
This message is used by the application processor to read the version of the API Communication Protocol
from the radio modem processor.
3.3.2.1 Request
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1 0x00
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 21/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.3.2.2 Response
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1 0x02
Data 2 Protocol version MSB first
MSB Byte - Major version
LSB Byte - Minor version
(e.g. 0x0102 -> Version 01.02)
3.3.3 API_MAX_BUFFER_SIZE (0x02)
This message is used by the application processor to read the maximum size of the receive buffer of the
radio modem processor.
3.3.3.1 Request
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
Data Size 1 0
3.3.3.2 Response
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
Data Size 1 2
Data 2 API buffer size in bytes MSB first
3.3.4 API_MAX_SPI_SPEED (0x03)
This message is used by the application processor to read the maximum SPI speed supported by the radio
modem processor.
3.3.4.1 Request
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
Data Size 1 0
3.3.4.2 Response
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
Data Size 1 0 or 1
Data 1 1 – N/A The minimum speed
2 – N/A for VN220/VN310 is
3 – N/A 100kHz
4 – 100 kHz
5 – 200 kHz
6 – 250 kHz
7 – 500 kHz
8 – 1 MHz
9 – 2 MHz
3.3.5 API_UPDATE_SPI_SPEED (0x04)
This message is used by the application processor to update the SPI speed of the radio modem processor.
The default SPI speed is 100 KHz. The application processor can read the maximum SPI speed supported
using API_MAX_SPI_SPEED.
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 22/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.3.5.1 Request
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
Data Size 1 1
Data 1 1 – N/A 4 is default
2 – N/A (100 KHz)
3 – N/A
4 – 100 kHz
5 – 200 kHz
6 – 250 kHz
7 – 500 kHz
8 – 1 MHz
9 – 2 MHz
3.3.5.2 Response
ACK – if the request is accepted. The SPI clock speed is changed immediately and the ACK is sent at the
new clock speed.
NACK – if the request is not accepted.
3.3.6 API_MAX_UART_SPEED (0x05)
This message is used by the application processor to read the maximum baud rate supported by the radio
modem processor.
3.3.6.1 Request
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
Data Size 1 0
3.3.6.2 Response
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
Data Size 1 1
Data 1 1 – 9600 3 is default
2 – 19200 (38400)
3 – 38400
4 – 115200
3.3.7 API_UPDATE_UART_SPEED (0x06)
This message is used by the application processor to update the baud rate of radio modem processor. The
default baud rate is 38400. The application processor can read the maximum baud rate supported using the
API_MAX_UART_SPEED command.
3.3.7.1 Request
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
Data Size 1 1
Data 1 1 – 9600
2 – 19200
3 – 38400
4 – 115200
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 23/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.3.7.2 Response
ACK – if the request is accepted. The ACK message is sent with the new baud rate.
NACK - if the request is not accepted.
3.3.8 API_HEARTBEAT_FREQ (0x07) - For SPI Only
3.3.8.1 Request
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
Data Size 1 1
Data 1 1 – Not used 4 is default
2 – Not used This command is used only in the SPI Non Wakeup
3 – Not used solution.
4 – 500 ms
5–1s
6 – 60 s
3.3.8.2 Response
ACK – if the request is accepted.
NACK – if the request is not accepted.
3.3.9 API_HEARTBEAT (0x08) –SPI Only
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
Data Size 1 0
Data - Used for receiving messages from the application
processor
This message is used only in the SPI interface to allow the application processor to send any message
(either a new request or a response to a previously received request).
In the SPI non wake-up solution, this message is sent 250ms after sending a request message or at every
API_HEARTBEAT_FREQ (default 500ms) period to check whether the application processor has a
message to send.
Note: Please note that the application processor can send its message during the reception of any message
(not necessarily an API_HEARTBEAT message) from the radio modem processor.
If the radio modem processor detects an incoming message (start byte STX) during the transmission of any
message, it will read it by sending STX bytes, if required, after sending the current message.
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 24/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.3.10 API_SET_COUNTRY_CODE (0x0C)
This message is used by the application processor to configure the Country Code parameter of the radio.
The Country Code is a numerical value defined according to the ISO3166 standard.
You can find the list with corresponding maximum RF power output that will be used for each country code
in Annex B, at the end of this document. Note that this feature of variable RF power output is available only
for the VN310H radios. On VN220 radios the RF power output will be approximately +10dBm regardless of
the country code set.
3.3.10.1 Request
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
Data Size 1 2 The country code is a 2-byte parameter
Data 2 country Country code value shall be compliant with ISO3166.
code
value
3.3.10.2 Response
ACK – if the request is accepted.
NACK – if the request is not accepted.
3.4 Stack Specific Messages
The table below lists the message types for the message class STACK_SPECIFIC:
Message Type Value Comments
reserved 0
HART_GET_ASN 1 AP retrieves the ASN (Absolute Slot Number) from the VN Radio
()
reserved 2
HART_SERVICE_REQUEST 3 Bandwidth request ()
HART_SERVICE_DELETE 4 Delete service ()
HART_NOTIFY_JOIN 5 Radio has joined the network ()
HART_GET_INITIAL_INFO 6 Information needed at communication start ()
HART_RADIO_RESET 7 Radio informs Application Processor it has been reset ()
HART_WRITE_ADDITIONAL_DEV 8 AP sends the current values of the Device Status Bytes ()
ICE_STATUS
HART_CLEAR_MSA 9 The Master cleared the MSA bit and the AP must be notified ()
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 25/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
Command Direction:
Radio modem CPU to application CPU
Application CPU to radio modem CPU
3.4.1 HART_GET_ASN (0x01)
This message is used by the Application Processor to read the ASN (Absolute Slot Number) from the VN
Radio. The ASN is the 5-bytes sequence number of the WirelessHART 10 msec timeslot [i.e. on the VN
Radio side, the ASN is constantly increased with one every 10 msec].
Remark: this command is available starting with the v2.1.1 VN radio firmware.
3.4.1.1 Request
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1 0
3.4.1.2 Response
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1
Data 5 The 5-bytes ASN value All bytes in network order
3.4.2 HART_SERVICE_REQUEST (0x03)
This message is used by the application processor to send a bandwidth request to the radio modem. The
radio modem will send the request to the Network Manager. When the Network Manager response is
received by the radio and forwarded to the user board via API interface with the same message class/type
as in the request
3.4.2.1 Request
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1
Data 7 Generating Command Id – 2 All bytes in network order
bytes
Burst Message – 1 byte
Burst Period – 4 bytes
3.4.2.2 Response
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1
Data 3[/8] Command Id – 2 bytes All bytes in network order
Return code (might be
Delayed Response code)
[Burst Message – 1 byte]
[Burst Period – 4 bytes]
3.4.3 HART_SERVICE_DELETE (0x04)
This message is used by the application processor to close one of its services.
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 26/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.4.3.1 Request
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1
Data 1 Burst Message – 1 byte All bytes in network order
3.4.3.2 Response
ACK – if there are no errors in the request packet.
NACK – if there are any errors in the request packet.
3.4.4 HART_NOTIFY_JOIN (0x05)
This message is used by the radio modem processor to inform the application processor it has successfully
joined the network.
3.4.4.1 Request
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1 0
3.4.4.2 Response
ACK – if there are no errors in the request packet.
NACK – if there are any errors in the request packet.
3.4.5 HART_GET_INITIAL_INFO (0x06)
This message is used by the radio modem processor to read the initial information from the application CPU.
It will be issued only after a hardware reset or a power cycling of the VN220/VN310.
3.4.5.1 Request
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1 0
3.4.5.2 Response
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1 2
Data 3 Number of Device Variables All bytes in network order
Number of Burst Channels
Number of Event Channels
3.4.6 HART_RADIO_RESET (0x07)
This message is used by the radio modem processor to inform the application processor it has been reset.
This is redundant, it will not be used in the next release, HART_GET_INITIAL_INFO is sufficient for
communication initialization.
3.4.6.1 Request
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1 0
3.4.6.2 Response
ACK – if there are no errors in the request packet.
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 27/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
NACK – if there are any errors in the request packet.
3.4.7 HART_WRITE_ADDITIONAL_DEVICE_STATUS (0x08)
This message is used by the application processor to inform the Radio that a change in the Device Status
bytes occurred.
The Field Device Status Byte is a collection of bits which reflect a certain state of the Field Device. The More
Status Available (MSA) flag/bit is part of this byte. Please check the chapter 3.7.4 WHART Device Status
for more information.
If the MSA flag is set, it means that a condition/fault was detected in the AP. The condition/fault is given by
the Additional Status Bytes, defined by the WHART standard as follows [payload of WHART command 48]:
As a result, once the AP decided that its status changed, it should perform the following two actions:
- First, set the MSA bit within the Device Status, so that the Master is informed about the condition;
the Device Status byte is included in each User Board Message and is the first byte of this
command.
- Secondly, send to the Radio the current Additional Status Bytes [i.e. Device-Specific Status,
Extended Device Status, Standardised Status] with this specific Full API command, so that the
Radio contains the updated values
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 28/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
The AP designers can define its Device-Specific Status according to the Field Device needs. For more
information about the Standardised Status bytes, please refer to the HCF_SPEC-183 document.
Please also check the Full API case diagrams at section 3.8.7 for more information on this functionality.
3.4.7.1 Request
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1
Data 26 AP Device Status Byte – 1 byte All bytes in network order. Cmd 48 Payload in
Cmd48 Payload - 25 bytes the above order [Byte 0 – first; Byte 24 - last]
3.4.7.2 Response
ACK – if there are no errors in the requested packet
3.4.8 HART_CLEAR_MSA (0x09)
This message is used by the Radio to notify the AP that the Master acknowledged the More Status Available
flag within the Field Device Status Byte. Therefore, the Master has the latest information regarding the Field
Device Status and knows about the current conditions/failures.
It is recommended that, if there is no other condition/failure on the AP side, the AP also clears the MSA bit
upon reception of this command. If the AP continuously sets the MSA bit, bandwidth is decreased [because
the Master issues Command 48], which may lead to a latency in the network.
Please also check the Full API case diagrams at section 3.8.7 for more information on this functionality.
3.4.8.1 Request
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1 0
3.4.8.2 Response
ACK – if there are no errors in the requested packet
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 29/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.5 User Board Messages
The table below lists the message types for the message class USER_BOARD:
Message Type Value Comments
DAQ_FW_WIRELESS 0 Forward wireless HART command (/)
DAQ_BURST_PIPE_0 1 Published command on burst channel 0 ()
DAQ_BURST_PIPE_1 2 Published command on burst channel 1 ()
DAQ_BURST_PIPE_2 3 Published command on burst channel 2 ()
DAQ_FW_WIRED 4 Forward wired HART command (/)
Command Direction:
Radio modem CPU to application CPU
Application CPU to radio modem CPU
All those messages are issued by the application processor either as a response to a forwarded HART
command (DAQ_FW_WIRELESS) or as a published command (DAQ_BURST_PIPE_0 …
DAQ_BURST_PIPE_2).
The Field Device Status byte reflects both the Radio’s and AP’s status. Therefore, both processors must
have access to this status byte. The 2.1.3 version of the stack offers access to the Device Status byte [i.e. it
is included in the User Board message payload].
Please refer to the HART specifications in order to see the command’s request/response format.
Radio response may be ACK or NACK.
3.5.1 DAQ_FW_WIRELESS (0x00)
3.5.1.1 Request
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1
Data Device Status Byte +Wireless As defined in HART Specs
Hart Command Request
3.5.1.2 Response
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1
Data Device Status Byte + Wireless As defined in HART Specs
Hart Command Response
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 30/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.5.2 DAQ_BURST_PIPE_0(/1/2) (0x01 – 0x03)
3.5.2.1 Request
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1
Data Device Status Byte + Hart As defined in HART Specs
Command Response
3.5.2.2 Response
ACK
3.5.3 DAQ_FW_WIRED (0x04)
3.5.3.1 Request
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1
Data Device Status Byte
Wired Hart Command As defined in HART Specs
Request
3.5.3.2 Response
Field Size (Bytes) Values Comments
Data Size 1
Data Wired Hart Command As defined in HART Specs
Response
3.6 Response ACK
The ACK response confirms that the API request message (Request/Response field = 0) identified by the
“Message ID” field has been properly received (CRC was successfully validated) and interpreted (the
message was successfully validated based on the Message Class and Message Type fields).
Based on the received ACK response, the receiver should remove the already sent API request message
identified by the ACK “Message ID” field and no retry mechanism must be applied for this request.
3.6.1 Message format
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
STX 1 When this character is received, the receiver discards any other Rx
message in progress and starts receiving this new message.
Message 1 0x58 ACK
Header
Message 1 0 = Data received properly
Type 1 = Message processed and sent via RF channel
2 = Message processed and sent via MODEM channel
3 = Change to API accepted (i.e. SPI Speed Change)
Message ID 1 0xNN NN = Message ID used in referencing this message transaction.
Data Size 1 0x0 The number of data bytes in the buffer
CRC 2
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 31/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.7 Response NACK
The NACK response confirms that the API request message (Request/Response field = 0) identified by the
“Message ID” field has been properly received (CRC was successfully validated) but there is inconsistent
data inside the API message (e.g. Message Type or/and Class unknown, the requested operation/s fail(s)).
3.7.1 Message format
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
STX 1 When this character is received, the receiver discards any other Rx
message in progress and starts receiving this new message.
Message 1 0x68 NACK
Header
Message Type 1 0xXX 1 = CRC Fail
2 = Data Overrun
3 = Packet Incomplete
4 = Parity Error
5 = API Not Initialized
6 = API Command Error
7 = API Busy
8 = API Error
9 = Stack Error
10 = Unsupported feature in this release
Message ID 1 0xNN NN = Message ID used in referencing this message transaction.
Data Size 1 0x0 The number of data bytes in the buffer
CRC 2
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 32/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.8 WirelessHART Full API case diagrams
3.8.1 Burst Activation & Service Request
Note: The same diagram can be used in case the command 103 is received by the application processor
requesting a lower publish period. In that case, replace command 109 with command 103 in the following
diagram.
- Gateway initiates burst activation by sending Command 109 with burst mode "on" to the Field Device
(transition 1);
- VN forwards the command to the Application Processor through the API (transition 2);
- Application Processor sends a service request to the VN (transition 3). From now on the
VN220/VN310 will manage its service request retry and Delayed Response mechanisms, until it will
have received the service from Network Manager (transition 4);
- After receiving a DRInit code for the service request (transition 5) the Application Processor will
respond (through API forwarding) with a Delayed Response Initiated code (transition 6);
- Gateway will resend Command109, as long as a Delayed Response code (DRInit or DRRuning) is
received (transitions 8, 14);
- The Network Manager allocates the requested service on VN (transition 4.4);
- A new Command 109 request is received from Gateway (transition 14) and forwarded to the
Application Processor (transition 15);
- The Application Processor will send a new Service Request message which will be responded
successfully by the VN (transition 16). The success response from the VN is a consequence of
transition 4.4;
- The burst is actually activated on Application Processor and Command109 responded with Success
Code (transition 19, 20);
- The Application Processor starts sending burst messages using DAQ_BUST_PIPE messages.
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 33/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
Field Device
API
Gateway VN AppProcessor NetworkMngr
1) Cmd109req-burst on 2) Forward Cmd109req
3) SrvcReq
4.1) Cmd799 – srvc req
5) SrvcRsp - DRinit
7) Cmd109rsp-DRinit 6) Forward Cmd109rsp
4.2) Cmd799 – srvc rsp - DR
4.3) Cmd799 – srvc req
8) Cmd109req-burst on 9) Forward Cmd109req
10)SrvcReq
11) SrvcRsp - DRrunning
13) Cmd109rsp-DRrunning 12) Forward Cmd109rsp
4.4) Cmd799 – srvc rsp - Success
14) Cmd109req-burst on 15) Forward Cmd109req
4.5) Add 16)SrvcReq
service
on radio 17) SrvcRsp - Success
18) Activate burst,
20) Cmd109rsp-Success 19) Forward Cmd109rsp update period, start
internal timers
Burst Forward Burst
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 34/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.8.2 Burst Disabling & Service Deletion
Field Device
API
Gateway VN AppProcessor NetworkMngr
1) Cmd109req-burst off 2) Forward Cmd109req
3) Stop burst
5) Cmd109rsp-Success 4) Forward Cmd109rsp
6.1)SrvcDel
6.2) Cmd801 – srvc delete
6.3) Cmd801 – srvc delete Success
6.4) Delete
Srvc on radio
- Gateway initiates burst deactivation, by sending Command 109 with burst mode "off" (transition 1);
- VN forwards Command109 to the Application Processor through the API (transition 2);
- Burst is immediately deactivated on Application Processor, command 109 responded with Success
code (transitions 3, 4, 5) .After this, the Application processor will not send any burst messages ;
- Application Processor requests service deletion to VN (transition 6.1), which will forward the service
deletion request to the Network Manager (transition 6.2).
- The Network Manager will respond with success (transition 6.3) and the VN will delete the service
from the service list (transition 6.4).
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 35/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.8.3 Service Task at Join
Field Device
API
Gateway VN AppProcessor NetworkMngr
1) Notify Join
2) Initialize SrvcTask
for active bursts in
3.1) SrvcReq persistent memory
4.1) Cmd799 – srvc req
3.2) SrvcRsp
4.2) Cmd799 – srvc resp (DR/Success)
Yes
Service *Repeat steps 3,
OK 4 for a while
5) Add Srvc
No
Service
OK
5’) Disable burst
Yes
Burst Forward Burst 6) Start Burst
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 36/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
- When VN informs Application Processor that it has successfully joined the network (transition 1),
burst information should be retrieved from the persistent memory (transition 2);
- If Application Processor wakes up with active bursts, it should start a Service Task, requesting
services for these bursts from VN, until they will have been granted by Network Manager (see 3.8.1
Burst Activation & Service Request );
- If by any reason this service allocation should fail, Application Processor should decide, after a while
the deactivation of the specific burst (transition 5’) or retry indefinitely.
3.8.4 WHART Device Status
- The Field Device Status is a collection of Status bits defined by the WHART standard as follows
[HCF_SPEC-99]:
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 37/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.8.5 Device Status: Configuration Changed Flag
Application
Gateway VN310 radio
Processor
CMD 103 Req
Forward (Radio DevStatus byte + CMD 103 Req) [DS = 0x00]
Response (AP DevStatus byte + CMD 103 Resp) [DS = 0x40]
2 1
Forward (Radio+AP DevStatus byte + CMD 103 Resp) [DS = 0x40]
CMD 105 Req
Forward (Radio DevStatus byte + CMD 105 Req) [DS = 0x40]
3
Response (AP DevStatus byte + CMD 105 Resp) [DS = 0x00]
4
Forward (Radio+AP DevStatus byte + CMD 105 Resp) [DS = 0x40]
CMD 38 Req
5
CMD 38 Resp [DS = 0x00]
6
- Extract the AP DevStatus byte and check which
- Read radio’s device status and take the necessary
status bits were changed by AP
actions in case it is needed
- If ConfigChanged bit is set => save it into NV
- Reset the bits that were set by the radio
1 memory and increment the ConfigurationChanged
- Execute CMD103 2
counter [persistent data]
- Set the configuration changed flag
- store the new DevStatus byte, it will be sent to
- Send the response via FULL API
the Master
- send the response to the Gateway
- Read radio’s device status and take the necessary
actions in case it is needed
- Reset the bits that were set by the radio
3 4 - The ConfigChanged flag was reset in the
- Forward CMD105 with the actual DevStatus byte
meantime by the AP
- Execute CMD105
- Send the response via FULL API
- The Radio shall respond to CMD38
- The Gateway shall reset the ConfigChanged bit by - If the received ConfigChangedCounter matches
5 6
sending CMD38 [payload=ConfigChangedCounter] the internal one => reset the ConfigChangedFlag
bit of the Device Status byte
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 38/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
Remarks:
- This status bit shall be set every time the Field Device [Radio + AP] suffered a configuration
modification.
- When the Radio sends the response to the Gateway master, the Device Status byte reflects both the
Radio and AP statuses
- In order for the Configuration Changed status flag to be reset, the Master [Gateway in this example]
shall send WHART command 38 to the Field Device. For the FULL API flavour, this command is
executed by the Radio, which is correct, since it has the Device Status from the AP. If the Master
does not send command 38, then the Configuration Changed status bit is not reset by the Radio.
- The AP processor shall clear the Configuration Changed bit after sending the Device Status
to the Radio. This operation is needed in order to avoid an erroneous incrementation of the
Configuration Changed counter [handled by the Radio] at the next transaction.
- According to the WHART requirements, there are multiple WHART commands that, on execution,
should also set the Configuration Changed status bit, to signal that the device’s configuration was
changed. For example, WHART commands that set-up a burst message [CMD103, 104, 107, 108,
109] shall set this status bit. For the complete list of commands, please refer to the WHART spec.
- For more information regarding the Configuration Changed bit and counter , as well as WHART
command 38, please check the HCD_SPEC-127 document.
3.8.6 Device Status: More Status Available (MSA) flag handled by the Radio
- The Radio stores two instances of the Device Status bytes :
o One which reflects the actual status of the Radio
o One which reflects the actual status of the AP
- As a result, when the Radio wants to clear the MSA bit [i.e. condition disappeared], only the flag
associated with the Radio’s Device Status byte is reset.
- There are two ways for the MSA bit to be cleared:
o The condition/defect disappears, so the Radio/AP clears this flag
o The Master sends WHART command 48
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 39/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
Application
Network Manager Gateway VN310 radio
Processor
CMD 109 Req – enable burst
Forward (Radio DevStatus byte + CMD 109 Req) [DS = 0x00]
ServiceRequest via FULL API
ServiceResponse via FULL API [RC33]
SrvcRequest (Radio+AP DevStatus byte + CMD 799 Req) [DS = 0x10]
1
SrvcResponse [CMD799 Resp – RC33]
Response (AP DevStatus byte + CMD 109 Resp) [DS = 0x40]
2
Forward (Radio+AP DevStatus byte + CMD 109 Resp) [DS = 0x50]
3
SrvcRequest (Radio+AP DevStatus byte + CMD 799 Req) [DS = 0x50]
4
SrvcResponse [CMD799 Resp – RC0]
5
CMD 109 Req – enable burst
Forward (Radio DevStatus byte + CMD 109 Req) [DS = 0x50]
ServiceRequest via FULL API
ServiceResponse via FULL API [RC0]
Response (AP DevStatus byte + CMD 109 Resp) [DS = 0x00]
6
Forward (Radio+AP DevStatus byte + CMD 109 Resp) [DS = 0x40]
- The Radio shall ask for the Service Request to the NM, so the Radio shall set
the MoreStatusAvailable (MSA) flag within the DeviceStatus byte
- In addition, the Radio shall set the “Bandwidth AllocationPending” flag within - Because the AP executed CMD109, the Configuration Changed flag is set
1 2
the StandardisedStatus3 byte - Send the response via FULL API
- The MSA bit will be reset if (CMD48 is issued by the Master) or (the
“Bandwidth AllocationPending” condition disappears)
- Read the AP DevStatus byte; ConfigChanged bit is set => increment the
ConfigChanged counter - The status bits are maintained by the Field Device for each Master [Gateway,
4
3 - The current DevStatus byte value = Radio DevStatus + AP DevStatus Network Manager, Maintenance Port]
- Send the response to the Gateway together with the current DevStatus
- Bandwidth negotiation successfully finished, so clear the
5 6 -Burst is active now; send the CMD109 response to the Radio
MoreStatusAvailable and Bandwidth AllocationPending flags
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 40/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
3.8.7 Device Status: More Status Available (MSA) flag handled by the AP
- Since most WHART Masters issue command 48 [Read Additional Device Status] when the MSA flag
is set, thus decreasing available communication bandwidth, the designers of the Filed Device must
carefully consider which diagnostics must set this Device Status flag.
- There are two methods to clear the MSA bit on the App Processor side:
A) The Master issues commands 48
Application
Gateway VN310 radio
Processor
Request : WHART cmd
Forward (Radio DevStatus byte + WHART cmd Req) [DS = 0x00]
Response (Radio DevStatus byte+WHART cmd Resp) [DS = 0x10]
1
Forward (Radio+AP DevStatus byte + WHART cmd Resp) [DS = 0x10]
2
Request : WriteAdditionalDeviceStatus via FULL API
3
Response : ACK via FULL API
Request : CMD48
Response : CMD48 payload [DS = 0x00]
4
Request : ClearMSA via FULL API
5
Response : ACK via FULL API
- The AP is responsible to track its specific DeviceStatus Flags
1 - When the AP sets one of the specific DeviceStatus Flags, it shall also set the - The Radio reads the AP Device Status and sets the MSA bit, which will be sent
2
MoreStatusAvailable(MSA) status bit within the AP DeviceStatus byte, which to the Master
will be sent to the Radio.
- The CMD48 response payload reflects both the Radio and AP Device Status
- After the AP sets the MSA bit, it shall send a request to the Radio which bytes.
contains the additional device status bytes that are managed by the AP - If there is a match between the Request and Response payloads of CMD 48,
3 - If the Radio correctly receives this request, it will update the current 4
then the Radio resets the MSA flag.
DeviceStatus bytes [this data will be sent to the Master] and send an ACK on - The AP must be notified by this action, so after the MSA flag is cleared, the
FULL API interface Radio shall send the ClearMSA request via FULL API interface.
- The AP is informed that the MSA bit was cleared, which means that the
Master received the actual Status Bytes and, therefore, knows about the
5 current conditions of the Field Device.
- It is recommended that, upon receiving this command, the AP clears its
internal MSA bit if no other change occurred
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 41/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
- For example, due to an EEPROM failure, the AP sets the Non-volatile Memory Defect bit within the
Standardised Status 0. As a result, the AP also sets the MSA bit within the Device Status byte.
- The new value of the AP’s Status Byte is received by the Radio, which then, on behalf of AP, informs
the Master about the current Field Device Status.
- It is the AP’s responsibility to send to the Radio the latest values of the additional status bytes via the
Stack Specific command “HART_WRITE_ADDITIONAL_DEVICE_STATUS”
- When the Master issues command 48, the Radio returns also the Additional Device Status Bytes
received from the AP
- If the MSA flag is cleared upon reception of Command 48, the Radio notifies the AP about this using
the HART_CLEAR_MSA Stack Specific command.
B) The fault/condition disappears
Application
Gateway VN310 radio
Processor
Request : WHART cmd
Forward (Radio DevStatus byte + WHART cmd Req) [DS = 0x00]
Response (Radio DevStatus byte+WHART cmd Resp) [DS = 0x10]
1
Forward (Radio+AP DevStatus byte + WHART cmd Resp) [DS = 0x10]
2
Request : WriteAdditionalDeviceStatus via FULL API
3
Response : ACK via FULL API
Request : WHART cmd
Forward (Radio DevStatus byte + WHART cmd Req) [DS = 0x10]
Response (AP DevStatus byte+WHART cmd Resp) [DS = 0x00]
4
Forward (Radio+AP DevStatus byte + WHART cmd Resp) [DS = 0x00]
5
Request : WriteAdditionalDeviceStatus via FULL API
6
Response : ACK via FULL API
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 42/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
- The AP is responsible to track its specific DeviceStatus Flags
1 - When the AP sets one of the specific DeviceStatus Flags, it shall also set the - The Radio reads the AP Device Status and sets the MSA bit, which will be sent
2
MoreStatusAvailable(MSA) status bit within the AP DeviceStatus byte, which to the Master
will be sent to the Radio.
- After the AP sets the MSA bit, it shall send a request to the Radio which
contains the additional device status bytes that are managed by the AP
3 - If the Radio correctly receives this request, it will update the current 4 - When all the defects/conditions disappeared, the AP shall clear the MSA bit.
DeviceStatus bytes [this data will be sent to the Master] and send an ACK on
FULL API interface
- After the AP clears the MSA bit, it shall send a request to the Radio which
contains the values of the additional device status bytes that are managed by
- The Radio reads the AP Device Status and clears the MSA bit. the AP [i.e. defects disappeared so the updated values must be sent]
5 6 - If the Radio correctly receives this request, it will update the current
- The Master received the updated Device Status byte.
DeviceStatus bytes [this data will be sent to the Master] and send an ACK on
FULL API interface
- It may happen that, even if the MSA status bit is set, the Master does not acknowledge it by issuing
Command 48;
- If the MSA bit was set and if the AP does not have the fault/condition anymore [i.e. the EEPROM
error disappeared], the AP must clear the associated flag within the Additional Device Status Bytes
and, in addition, it must also reset the MSA bit if all faults have disappeared.
- Therefore, the AP shall send to the Radio the “HART_WRITE_ADDITIONAL_DEVICE_STATUS”
Stack Specific command, with a payload that reflects the latest values of the Device Status Byte and
the Additional Bytes. Upon reception of this command, the Radio will clear the MSA bit and will
update the Additional Bytes accordingly. As a result, even if the Master did not query the Field
Device about the Device Status, it will be informed that there is no condition/fault.
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 43/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
4 Examples
4.1 Hart Wireless Command Forwarding (command 1)
4.1.1 Request
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
STX 1 0xF1 This is the start character for every message.
Message Header 1 70 USER_BOARD Request
Message Type 1 01 DAQ_FW_WIRELESS
Message ID 1 8B MessageID
Data Size 1 03 Data Size
Data 3 00 01 00 00 01 Command (as per HART standard)
00 Byte Count (as per HART standard)
CRC 2 56 CD CRC
4.1.2 Response
Field Size Values Comments
(Bytes)
STX 1 0xF1 This is the start character for every message.
Message 1 78 USER_BOARD Response
Header
Message 1 01 DAQ_FW_WIRELESS
Type
Message ID 1 8B MessageID
Data Size 1 08 Data Size
Data 9 00 01 05 00 41 40 00 00 00 01 Command (as per HART standard)
05 Byte Count (as per HART standard)
00 Response code (as per HART standard)
41 40 00 00 Primary variable
CRC 2 0B 02 CRC
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 44/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
4.2 Hart Wired Command Forwarding (command 105)
4.2.1 Request data
40 69 01 00
meaning:
40 - Device Status
69 - Command Id
01- Byte Count
00 – Burst Message
4.2.2 Response data
69 1f 00 40 02 1f f6 f5 f4 f7 f5 f4 f7 f6 00 03 00 09 00 03 e8 00 06 dd d0 00 00 40 20 41 e8 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00
meaning:
69 - Command Id
1e - Byte Count
00 - Response Code
And command data:
02 - Burst Mode (enabled)
1f - Command Number
f6 f5 f4 f7 f5 f4 f7 f6 – Burst Variables
00 – Burst Message
03 – Maximum number of burst messages supported by the device
00 09 – Extended Command Number
00 03 e8 00 – Update Time (=8 sec)
06 dd d0 00 – Maximum Update Time (=3600 sec)
00 – Burst Trigger Mode (=Continuous Mode)
40 – Device Variable Classification for Trigger ( = Temperature)
20 – Units Code (= Degrees Celsius)
41 e8 00 00 – Trigger Value (=29)
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 45/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
5 Annexes
5.1 Annex A - Command Implementation Reference
Starting with field device firmware version 1.5.7, the implementation supports all mandatory HART and
WirelessHART commands, and a subset of the recommended and optional commands as listed in the table
below. For each command, the Decoder & Responder column will specify which module (radio module or
application processor) is responsible for implementing the command.
In general, the VersaNode forwards to the application processor all device specific and variable related
commands, whether mandatory or not. The implementation of such commands will be the decision of the
application processor’s implementer.
All the commands can be executed on both Wireless and maintenance (wired) interfaces. The VersaNode
will forward to the application processor the commands received on the maintenance port that are
application processor’s responsibility.
Command Type Certification Decoder & Responder
U = Universal Command M = HCF Mandatory VN = VN220/VN310 Radio module
CP = Common Practice Command R = HCF Recommended AP = Application processor
W = Wireless Command O = Optional (neither M nor R) VN + I = VN + info to AP
NR = HCF Not Recommended AP + I = AP + info to VN
N/A = Not applicable
* = Not implemented
Cmd Certification HCF Ref Decoder &
Wireless Maint
Type Command Interface Port Doc # Responder
U C000_ReadUniqueIdentifier M M [1] VN
U C001_ReadPrimaryVariable M M [1] AP
U C002_ReadLoopCurrentAndPercentOfRange M M [1] AP
U C003_ReadDynamicVariablesAndLoopCurrent M M [1] AP
U C006_WritePollingAddress M M [1] VN
U C007_ReadLoopConfiguration M M [1] VN
U C008_ReadDynamicVariableClassifications M M [1] AP
U C009_ReadDeviceVariablesWithStatus M M [1] AP
U C011_ReadUniqueIdentifierAssociatedWithTag M M [1] VN
U C012_ReadMessage M M [1] VN
U C013_ReadTagDescriptorDate M M [1] VN
U C014_ReadPrimaryVariableTransducerInformation M M [1] AP
U C015_ReadDeviceInformation M M [1] AP
U C016_ReadFinalAssemblyNumber M M [1] VN
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 46/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
U C017_WriteMessage M M [1] VN
U C018_WriteTagDescriptorDate M M [1] VN
U C019_WriteFinalAssemblyNumber M M [1] VN
U C020_ReadLongTag M M [1] VN
U C021_ReadUniqueIdentifierAssociatedWithLongTag M M [1] VN
U C022_WriteLongTag M M [1] VN
CP C033_ReadDeviceVariables O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C034_WritePrimaryVariableDampingValue O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C035_WritePrimaryVariableRangeValues O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C036_SetPrimaryVariableUpperRangeValue O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C037_SetPrimaryVariableLowerRangeValue O O [2] [3] [4] AP
U C038_ResetConfigurationChangedFlag M M [2] [3] [4] VN
CP C040_EnterExitFixedCurrentMode O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C041_PerformSelfTest M M [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C042_PerformDeviceReset M M [2] [3] [4] VN
CP C043_SetPrimaryVariableZero O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C044_WritePrimaryVariableUnits O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C045_TrimLoopCurrentZero O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C046_TrimLoopCurrentGain O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C047_WritePrimaryVariableTransferFunction O O [2] [3] [4] AP
U C048_ReadAdditionalDeviceStatus M M [2] [3] [4] VN
CP C049_WritePrimaryVariableTransducerSerialNumber O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C050_ReadDynamicVariableAssignments O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C051_WriteDynamicVariableAssignments O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C052_SetDeviceVariableZero R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C053_WriteDeviceVariableUnits R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C054_ReadDeviceVariableInformation M M [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C055_WriteDeviceVariableDampingValue R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C056_WriteDeviceVariableTransducerSerialNo O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C059_WriteNumberOfResponsePreambles M M [2] [3] [4] VN
CP C060_ReadAnalogChannelAndPercentOfRange O O [2] [3] [4] AP
C061_ReadDynamicVariablesAndPrimaryVariableAnal
CP O O [2] [3] [4] AP
ogChannel
CP C062_ReadAnalogChannels O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C063_ReadAnalogChannelInformation O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C064_WriteAnalogChannelAdditionalDampingValue O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C065_WriteAnalogChannelRangeValues O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C066_EnterExitFixedAnalogChannelMode O O [2] [3] [4] AP
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 47/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
CP C067_TrimAnalogChannelZero O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C068_TrimAnalogChannelGain O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C069_WriteAnalogChannelTransferFunction O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C070_ReadAnalogChannelEndpointValues O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C071_LockDevice R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C072_Squawk R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C073_FindDevice R R [2] [3] [4] N/A
CP C074_ReadIOSystemCapabilities O O [2] [3] [4] N/A
CP C075_PollSubDevice O O [2] [3] [4] N/A
CP C076_ReadLockDeviceState R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C077_SendCommandToSubDevice O O [2] [3] [4] N/A
CP C078_ReadAggregatedCommands M M [2] [3] [4] VN
CP C079_WriteDeviceVariable M M [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C080_ReadDeviceVariableTrimPoints R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C081_ReadDeviceVariableTrimGuidelines R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C082_WriteDeviceVariableTrimPoint R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C083_ResetDeviceVariableTrim R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C084_ReadSubDeviceIdentitySummary O O [2] [3] [4] N/A
CP C085_ReadIOChannelStatistics O O [2] [3] [4] N/A
CP C086_ReadSubDeviceStatistics O O [2] [3] [4] N/A
CP C087_WriteIOSystemMasterMode O O [2] [3] [4] N/A
CP C088_WriteIOSystemRetryCount O O [2] [3] [4] N/A
CP C089_SetRealTimeClock O O [2] [3] [4] VN
CP C090_ReadRealTimeClock M M [2] [3] [4] VN
CP C091_ReadTrendConfiguration R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C092_WriteTrendConfiguration R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C093_ReadTrend R R [2] [3] [4] AP
C094_ReadIOSystemClientSideCommunicationStatisti
CP O O [2] [3] [4] N/A
cs
CP C095_ReadDeviceCommunicationsStatistics R R [2] [3] [4] VN
CP C096_ReadSynchronousAction R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C097_ConfigureSynchronousAction R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C098_ReadCommandAction R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C099_ConfigureCommandAction R R [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C101_ReadSubDeviceToBurstMessageMap O O [2] [3] [4] N/A
CP C102_MapSubDeviceToBurstMessage O O [2] [3] [4] N/A
CP C103_WriteBurstPeriod M M [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C104_WriteBurstTrigger M M [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C105_ReadBurstModeConfiguration M M [2] [3] [4] AP
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 48/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
CP C106_FlushDelayedResponses M M [2] [3] [4] VN
CP C107_WriteBurstDeviceVariables M M [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C108_WriteBurstModeCommandNumber M M [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C109_BurstModeControl M M [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C110_ReadAllDynamicVariables NR NR [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C111_TransferServiceControl R R [2] [3] [4] VN*
CP C112_TransferService R R [2] [3] [4] VN*
CP C113_CatchDeviceVariable O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C114_ReadCaughtDeviceVariable O O [2] [3] [4] AP
CP C115_ReadEventNotificationSummary M M [2] [3] [4] VN
CP C116_WriteEventNotificationBitMask M M [2] [3] [4] VN
CP C117_WriteEventNotificationTiming M M [2] [3] [4] VN
CP C118_EventNotificationControl M M [2] [3] [4] VN
CP C119_AcknowledgeEventNotification M M [2] [3] [4] VN
CP * C120_Configure Synchronous Sampling R R [2] [3] [4] N/A
CP * C121_Configure Delayed Command Exection R R [2] [3] [4] N/A
CP * C512_Read Country Code O O [2] [3] [4] VN
CP * C513_Write Country Code O O [2] [3] [4] VN
W C768_WriteJoinKey M M [5] [6] VN
W C769_ReadJoinStatus M M [5] [6] VN
W C770_RequestActiveAdvertise M M [5] [6] VN
W C771_ForceJoin M M [5] [6] VN
W C772_ReadJoinModeConfiguration M M [5] [6] VN
W C773_WriteNetworkId M M [5] [6] VN
W C774_ReadNetworkId M M [5] [6] VN
W C775_WriteNetworkTag M M [5] [6] VN
W C776_ReadNetworkTag M M [5] [6] VN
W C777_ReadWirelessDeviceInformation M M [5] [6] VN
W C778_ReadBatteryLife M M [5] [6] VN
W C779_ReportDeviceHealth M M [5] [6] VN
W C780_ReportNeighborHealthList M M [5] [6] VN
W C781_ReadDeviceNicknameAddress M M [5] [6] VN
W C782_ReadSessionEntries M M [5] [6] VN
W C783_ReadSuperframeList M M [5] [6] VN
W C784_ReadLinkList M M [5] [6] VN
W C785_ReadGraphList M M [5] [6] VN
W C786_ReadNeighborPropertyFlag M M [5] [6] VN
W C787_ReportNeighborSignalLevels M M [5] [6] VN
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 49/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
W C788_AlarmPathDown M N/A [5] [6] VN
W C789_AlarmSourceRouteFailed M N/A [5] [6] VN
W C790_AlarmGraphRouteFailed M N/A [5] [6] VN
W C791_AlarmTransportLayerFailed M N/A [5] [6] VN
W C793_WriteUTCTime M N/A [5] [6] VN
W C794_ReadUTCTime M M [5] [6] VN
W C795_WriteTimerInterval M N/A [5] [6] VN
W C796_ReadTimerInterval M M [5] [6] VN
W C797_WriteRadioPower M M [5] [6] VN
W C798_ReadRadioPower M M [5] [6] VN
W C799_RequestService [5] [6] N/A
W C800_ReadServiceList M M [5] [6] VN
W C801_DeleteService M N/A [5] [6] VN
W C802_ReadRouteList M M [5] [6] VN
W C803_ReadSourceRoute M M [5] [6] VN
W C804_ReadRadioCCAMode M M [5] [6] VN
W C805_WriteRadioCCAMode M N/A [5] [6] VN
W C806_ReadHandheldSuperframe M M [5] [6] VN
W C807_RequestHandheldSuperframeMode M M [5] [6] VN
W C808_ReadTimeToLive M M [5] [6] VN
W C809_WriteTimeToLive M M [5] [6] VN
W C810_ReadJoinPriority M M [5] [6] VN
W C811_WriteJoinPriority M N/A [5] [6] VN
W C812_ReadPacketReceivePriority M M [5] [6] VN
W C813_WritePacketReceivePriority M N/A [5] [6] VN
W C814_ReadDeviceListEntries M M [5] [6] VN
W C815_AddDeviceListTableEntry M M [5] [6] VN
W C816_DeleteDeviceListTableEntry M M [5] [6] VN
W C817_ReadChannelBlacklist M M [5] [6] VN
W C818_WriteChannelBlacklist M N/A [5] [6] VN
W C819_ReadBackOffExponent M M [5] [6] VN
W C820_WriteBackOffExponent M N/A [5] [6] VN
W C821_WriteNetworkAccessMode [5] [6] N/A
W C822_ReadNetworkAccessMode [5] [6] N/A
W C823_RequestSession [5] [6] N/A
W C64512_ReadWirelessModuleRevision M M [5] [6] VN
HCF Specification Documents
[1] Universal Command Specification ( HCF_SPEC-127 Rev 7.1 May 10, 2008 )
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 50/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
[2] Common Practice Command Specification ( HCF_SPEC-151 Rev 9.1 May 21, 2008 )
[3] 6.0 WirelessHART Field Devices - HCF Spec "WirelessHART Device Specification (HCF_SPEC-
290)" May 22, 2008 p26-27
[4] HCF Spec "Addendum To Wireless Command Specification (HCF_SPEC-151)" May 21, 2008 p10-12
[5] Wireless Command Specification ( HCF_SPEC-155 Rev 1.1 May 28, 2008 )
[6] HCF Spec "Addendum To Wireless Command Specification (HCF_SPEC-155)" May 28, 2008 p27-30
5.2 Annex B - Country Codes and radio maximum output power
Maximum
Country Output
Country
Codes Power in
dBm
4 AFG - AFGHANISTAN 9
8 ALB - ALBANIA 19
10 ATA - ANTARCTICA 9
12 DZA - ALGERIA (El Djazaïr) 9
16 ASM - AMERICAN SAMOA 9
20 AND - ANDORRA 9
24 AGO - ANGOLA 9
28 ATG - ANTIGUA AND BARBUDA 9
31 AZE - AZERBAIJAN 9
32 ARG - ARGENTINA 9
36 AUS - AUSTRALIA 30
40 AUT - AUSTRIA 19
44 BHS - BAHAMAS 9
48 BHR - BAHRAIN 9
50 BGD - BANGLADESH 9
51 ARM - ARMENIA 9
52 BRB - BARBADOS 9
56 BEL - BELGIUM 19
60 BMU - BERMUDA 9
64 BTN - BHUTAN 9
68 BOL - BOLIVIA 9
70 BIH - BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA 9
72 BWA - BOTSWANA 9
74 BVT - BOUVET ISLAND 9
76 BRA - BRAZIL 9
84 BLZ - BELIZE 9
86 IOT - BRITISH INDIAN OCEAN TERRITORY 9
90 SLB - SOLOMON ISLANDS 9
92 VGB - VIRGIN ISLANDS, BRITISH 9
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 51/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
96 BRN - BRUNEI DARUSSALAM 9
100 BGR - BULGARIA 19
104 MMR - MYANMAR (formerly Burma) 9
108 BDI - BURUNDI 9
112 BLR - BELARUS 9
116 KHM - CAMBODIA 9
120 CMR - CAMEROON 9
124 CAN - CANADA 20
132 CPV - CAPE VERDE 9
136 CYM - CAYMAN ISLANDS 9
140 CAF - CENTRAL AFRICAN REPUBLIC 9
144 LKA - SRI LANKA (formerly Ceylon) 9
148 TCD - CHAD (Tchad) 9
152 CHL - CHILE 9
156 CHN - CHINA 9
158 TWN - TAIWAN 9
162 CXR - CHRISTMAS ISLAND 9
166 CCK - COCOS (KEELING) ISLANDS 9
170 COL - COLOMBIA 9
174 COM - COMOROS 9
175 MYT - MAYOTTE 9
178 COG - CONGO, REPUBLIC OF 9
180 COD - CONGO, THE DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE (formerly Zaire) 9
184 COK - COOK ISLANDS 9
188 CRI - COSTA RICA 9
191 HRV - CROATIA (Hrvatska) 19
192 CUB - CUBA 9
196 CYP - CYPRUS 9
203 CZE - CZECH REPUBLIC 19
204 BEN - BENIN 9
208 DNK - DENMARK 19
212 DMA - DOMINICA 9
214 DOM - DOMINICAN REPUBLIC 9
218 ECU - ECUADOR 9
222 SLV - EL SALVADOR 9
226 GNQ - EQUATORIAL GUINEA 9
231 ETH - ETHIOPIA 9
232 ERI - ERITREA 9
233 EST - ESTONIA 9
234 FRO - FAEROE ISLANDS 9
238 FLK - FALKLAND ISLANDS (MALVINAS) 9
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 52/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
239 SGS - SOUTH GEORGIA AND THE SOUTH SANDWICH ISLANDS 9
242 FJI - FIJI 9
246 FIN - FINLAND 9
248 ALA - ÅLAND ISLANDS 9
250 FRA - FRANCE 19
254 GUF - FRENCH GUIANA 19
258 PYF - FRENCH POLYNESIA 19
260 ATF - FRENCH SOUTHERN TERRITORIES 19
262 DJI - DJIBOUTI 9
266 GAB - GABON 9
268 GEO - GEORGIA 9
270 GMB - GAMBIA, THE 9
275 PSE - PALESTINIAN TERRITORIES 9
276 DEU - GERMANY (Deutschland) 19
288 GHA - GHANA 9
292 GIB - GIBRALTAR 9
296 KIR - KIRIBATI 9
300 GRC - GREECE 19
304 GRL - GREENLAND 19
308 GRD - GRENADA 9
312 GLP - GUADELOUPE 9
316 GUM - GUAM 9
320 GTM - GUATEMALA 9
324 GIN - GUINEA 9
328 GUY - GUYANA 9
332 HTI - HAITI 20
334 HMD - HEARD ISLAND AND MCDONALD ISLANDS 9
336 VAT - VATICAN CITY (Holy See) 19
340 HND - HONDURAS 9
344 HKG - HONG KONG (Special Administrative Region of China) 9
348 HUN - HUNGARY 19
352 ISL - ICELAND 9
356 IND - INDIA 9
360 IDN - INDONESIA 9
364 IRN - IRAN (Islamic Republic of Iran) 9
368 IRQ - IRAQ 9
372 IRL - IRELAND 9
376 ISR - ISRAEL 9
380 ITA - ITALY 19
384 CIV - CÔTE D'IVOIRE (Ivory Coast) 9
388 JAM - JAMAICA 9
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 53/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
392 JPN - JAPAN 9
398 KAZ - KAZAKHSTAN 9
400 JOR - JORDAN (Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan) 9
404 KEN - KENYA 9
408 PRK - KOREA (Democratic Peoples Republic of [North] Korea) 9
410 KOR - KOREA (Republic of [South] Korea) 9
414 KWT - KUWAIT 9
417 KGZ - KYRGYZSTAN 9
418 LAO - LAO PEOPLE'S DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC 9
422 LBN - LEBANON 9
426 LSO - LESOTHO 9
428 LVA - LATVIA 9
430 LBR - LIBERIA 9
434 LBY - LIBYA (Libyan Arab Jamahirya) 9
438 LIE - LIECHTENSTEIN (Fürstentum Liechtenstein) 19
440 LTU - LITHUANIA 9
442 LUX - LUXEMBOURG 19
446 MAC - MACAO (Special Administrative Region of China) 9
450 MDG - MADAGASCAR 9
454 MWI - MALAWI 9
458 MYS - MALAYSIA 9
462 MDV - MALDIVES 9
466 MLI - MALI 9
470 MLT - MALTA 19
474 MTQ - MARTINIQUE 9
478 MRT - MAURITANIA 9
480 MUS - MAURITIUS 9
484 MEX - MEXICO 9
492 MCO - MONACO 19
496 MNG - MONGOLIA 9
498 MDA - MOLDOVA 19
499 MNE - MONTENEGRO 9
500 MSR - MONTSERRAT 9
504 MAR - MOROCCO 9
508 MOZ - MOZAMBIQUE (Moçambique) 9
512 OMN - OMAN 9
516 NAM - NAMIBIA 9
520 NRU - NAURU 9
524 NPL - NEPAL 9
528 NLD - NETHERLANDS 19
530 ANT - NETHERLANDS ANTILLES (obsolete) 19
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 54/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
531 CUW - CURAÇAO 9
533 ABW - ARUBA 9
534 SXM - SINT MAARTEN 9
535 BES - BONAIRE, ST. EUSTATIUS, AND SABA 9
540 NCL - NEW CALEDONIA 9
548 VUT - VANUATU 9
554 NZL - NEW ZEALAND 30
558 NIC - NICARAGUA 9
562 NER - NIGER 9
566 NGA - NIGERIA 9
570 NIU - NIUE 9
574 NFK - NORFOLK ISLAND 9
578 NOR - NORWAY 9
580 MNP - NORTHERN MARIANA ISLANDS 9
581 UMI - UNITED STATES MINOR OUTLYING ISLANDS 20
583 FSM - MICRONESIA (Federated States of Micronesia) 9
584 MHL - MARSHALL ISLANDS 9
585 PLW - PALAU 9
586 PAK - PAKISTAN 9
591 PAN - PANAMA 9
598 PNG - PAPUA NEW GUINEA 9
600 PRY - PARAGUAY 9
604 PER - PERU 9
608 PHL - PHILIPPINES 9
612 PCN - PITCAIRN 9
616 POL - POLAND 19
620 PRT - PORTUGAL 19
624 GNB - GUINEA-BISSAU 9
626 TLS - TIMOR-LESTE (formerly East Timor) 9
630 PRI - PUERTO RICO 20
634 QAT - QATAR 9
638 REU - RÉUNION 9
642 ROU - ROMANIA 19
643 RUS - RUSSIAN FEDERATION 9
646 RWA - RWANDA 9
652 BLM - SAINT BARTHÉLEMY 9
654 SHN - SAINT HELENA 9
659 KNA - SAINT KITTS AND NEVIS 9
660 AIA - ANGUILLA 9
662 LCA - SAINT LUCIA 9
663 MAF - SAINT MARTIN (French portion) 9
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 55/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
666 SPM - SAINT PIERRE AND MIQUELON 9
670 VCT - SAINT VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES 9
674 SMR - SAN MARINO (Republic of) 9
678 STP - SAO TOME AND PRINCIPE 9
682 SAU - SAUDI ARABIA (Kingdom of Saudi Arabia) 9
686 SEN - SENEGAL 9
688 SRB - SERBIA (Republic of Serbia) 19
690 SYC - SEYCHELLES 9
694 SLE - SIERRA LEONE 9
702 SGP - SINGAPORE 9
703 SVK - SLOVAKIA (Slovak Republic) 19
704 VNM - VIET NAM 9
705 SVN - SLOVENIA 19
706 SOM - SOMALIA 9
710 ZAF - SOUTH AFRICA (Zuid Afrika) 9
716 ZWE - ZIMBABWE 9
724 ESP - SPAIN (España) 19
732 ESH - WESTERN SAHARA (formerly Spanish Sahara) 9
736 SDN - SUDAN 9
740 SUR - SURINAME 9
744 SJM - SVALBARD AND JAN MAYEN 9
748 SWZ - SWAZILAND 9
752 SWE - SWEDEN 19
756 CHE - SWITZERLAND (Confederation of Helvetia) 19
760 SYR - SYRIAN ARAB REPUBLIC 9
762 TJK - TAJIKISTAN 9
764 THA - THAILAND 9
768 TGO - TOGO 9
772 TKL - TOKELAU 9
776 TON - TONGA 9
780 TTO - TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO 9
784 ARE - UNITED ARAB EMIRATES 9
788 TUN - TUNISIA 9
792 TUR - TURKEY 19
795 TKM - TURKMENISTAN 9
796 TCA - TURKS AND CAICOS ISLANDS 9
798 TUV - TUVALU 9
800 UGA - UGANDA 9
804 UKR - UKRAINE 19
807 MKD - MACEDONIA (Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia) 19
818 EGY - EGYPT 9
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 56/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
826 GBR - GREAT BRITAIN (United Kingdom) 19
826 GBR - UNITED KINGDOM 19
830 - CHANNEL ISLANDS 9
833 IMN - ISLE OF MAN 9
834 TZA - TANZANIA 9
840 USA - UNITED STATES 20
850 VIR - VIRGIN ISLANDS, U.S. 20
854 BFA - BURKINA FASO 9
858 URY - URUGUAY 9
860 UZB - UZBEKISTAN 9
862 VEN - VENEZUELA 9
876 WLF - WALLIS AND FUTUNA 9
882 WSM - SAMOA (formerly Western Samoa) 9
887 YEM - YEMEN (Yemen Arab Republic) 9
894 ZMB - ZAMBIA (formerly Northern Rhodesia) 9
902 Nivis custom code 2
903 Nivis custom code 3
904 Nivis custom code 4
905 Nivis custom code 5
906 Nivis custom code 6
907 Nivis custom code 7
908 Nivis custom code 8
08-00029-02 WirelessHART Full API Integration Manual v2.1 57/57
Proprietary & Confidential – NIVIS LLC
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Empowerment Technologies: Quarter 2 - Module 12: Multimedia and ICTДокумент26 страницEmpowerment Technologies: Quarter 2 - Module 12: Multimedia and ICTCheng Kie Odilao88% (43)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Communication Systems Engineering Proakis Solution Manual PDFДокумент2 страницыCommunication Systems Engineering Proakis Solution Manual PDFNatashaОценок пока нет
- Fundamental of Ict Lab Manual 2013Документ143 страницыFundamental of Ict Lab Manual 2013misss1230% (1)
- Centero VR910 DatasheetДокумент1 страницаCentero VR910 DatasheetraytangclОценок пока нет
- Centero VN220 HW Integration Application NoteДокумент46 страницCentero VN220 HW Integration Application NoteraytangclОценок пока нет
- Centero VersaNode 220 DatasheetДокумент1 страницаCentero VersaNode 220 DatasheetraytangclОценок пока нет
- FDA Solvent Based TC ApprovalДокумент1 страницаFDA Solvent Based TC ApprovalraytangclОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, IncДокумент33 страницыIntroduction To Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Incnhicole naguitОценок пока нет
- MCQs On Computer by Dr. Alok KumarДокумент151 страницаMCQs On Computer by Dr. Alok KumarGtxpreetОценок пока нет
- User Manual STM32F103 PDFДокумент655 страницUser Manual STM32F103 PDFSkvk0% (1)
- Measure in Minutes With Labview and The Daq AssistantДокумент2 страницыMeasure in Minutes With Labview and The Daq AssistantEdgar Mendoza GarcíaОценок пока нет
- Faa Swim User GuideДокумент24 страницыFaa Swim User GuideIonut ManeaОценок пока нет
- Y550-L03 V100R001ARGC25B249 - SLA - Claro (Argentina) - SW - Upgrade - Guide - +Ý+ + +ÂÍ©Á+-ÚДокумент7 страницY550-L03 V100R001ARGC25B249 - SLA - Claro (Argentina) - SW - Upgrade - Guide - +Ý+ + +ÂÍ©Á+-ÚZonia Lopez RОценок пока нет
- Project ReportДокумент13 страницProject ReportShoaib Nadeem0% (1)
- 0 640 sn755870Документ2 страницы0 640 sn755870lj41Оценок пока нет
- MD - Saidur Rahman's CV FullДокумент5 страницMD - Saidur Rahman's CV Fullsaidur182Оценок пока нет
- SSD1960 Application Note v1.3Документ32 страницыSSD1960 Application Note v1.3KrishОценок пока нет
- Detection of Fake Images Using Metadata Analysis and Error Level AnalysisДокумент28 страницDetection of Fake Images Using Metadata Analysis and Error Level Analysisutkarsh130896Оценок пока нет
- How To Use Your WiFi ADSL Modem Cum Router As A Wireless Access Point OnlyДокумент6 страницHow To Use Your WiFi ADSL Modem Cum Router As A Wireless Access Point OnlyKrishnamoorthy VijayalakshmiОценок пока нет
- PP 2000 01Документ132 страницыPP 2000 01franciscocampoverde8224100% (2)
- Dolby Surround Pro Logic OperationДокумент7 страницDolby Surround Pro Logic OperationavrelecОценок пока нет
- وظائف نظم المعلومات الجغرافيةДокумент30 страницوظائف نظم المعلومات الجغرافيةطه حافظ حسين 065Оценок пока нет
- 2700 Recetas ThermomixДокумент1 144 страницы2700 Recetas Thermomixgamusino007Оценок пока нет
- 3G RoadmapДокумент20 страниц3G RoadmapyurdumОценок пока нет
- Python For Serial Communication PDFДокумент21 страницаPython For Serial Communication PDFHelder PintoОценок пока нет
- ReadMe KMSpico PortableДокумент4 страницыReadMe KMSpico PortableRez ShahОценок пока нет
- Conference Proceedings Order Plan Spreadsheet 1998-2001Документ52 страницыConference Proceedings Order Plan Spreadsheet 1998-2001jkartheekОценок пока нет
- Dell PowerConnect Switch PWCNT VLAN InteroperabilityДокумент27 страницDell PowerConnect Switch PWCNT VLAN InteroperabilityHamish BowlyОценок пока нет
- CДокумент99 страницCDonna Mae SibayanОценок пока нет
- MC9500K User Manual From Barcode Datalink 11850101aДокумент258 страницMC9500K User Manual From Barcode Datalink 11850101amariusz87Оценок пока нет
- ROUTE v7 Chapter 1 Exam - CCNP v7 Exam Module Question & AnswerДокумент5 страницROUTE v7 Chapter 1 Exam - CCNP v7 Exam Module Question & AnswerJorge Lurbe Huertas83% (6)
- Synopsis of ProjectДокумент24 страницыSynopsis of Projectannu priya100% (1)
- Chapter 3: Arm Instruction Set: (Architecture Version: Armv4T)Документ32 страницыChapter 3: Arm Instruction Set: (Architecture Version: Armv4T)sunilbhimuОценок пока нет
- CHECKPOINT Appliance Comparison ChartДокумент12 страницCHECKPOINT Appliance Comparison ChartrtacconОценок пока нет