Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Electrochemistry
Загружено:
Gokul NathАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Electrochemistry
Загружено:
Gokul NathАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Electrochemistry Neeraj Swarnkar
SAMCQ
1. H
2
(g) and O
2
(g), can be produced by the electrolysis of water. What total volume (in
L) of O
2
and H
2
are produced at STP when a current of 30 A is passed through a
K
2
SO
4
(aq) solution for 193 min.?
(a) 20.16 (b) 40.32 (c) 60.48 (d) 80.64
2. The standard EMF of Mn | Mn
2+
electrode is +1.18 V at 25C. The
2
Mn(s)|Mn(OH) (s)|OH
E
is (Given
Mn(OH)
2
sp
K = 2 10
13
and log 2 = 0.3)
(a) 1.56 V (b) 1.18 V (c) 0.805 V (d) none of these
3. The standard reduction potential of a silver chloride electrode is 0.2 V and that of a
silver electrode is0.79V. The maximum amount of AgCl that can dissolve in 10
6
L of
a 0.1 M AgNO
3
solution is
(a) 0.5mmol (b) 1.0 mmol (c)2.0mmol (d) 2.5mmol
4. Twolitre solution of a buffer mixture containing 1.0 MNaH
2
PO
4
and 1.0 M Na
2
HPO
4
is placed in two compartments (one litre in each) of an electrolytic cell. The platinum
electrodes are inserted in each compartment and 1 .25 A current is passed for 212
min. Assuming electrolysis of water only at each compartment, what will be the sum
of pH in both compartment after passage of above charge? pK
a
for H
2
PO
4
- = 2.15.
(a) 4 (b) 4.3 (c) 4.6 (d) 4.9
5. In an analytical determination of arsenic, a solution containing arseneous acid,
H
3
AsO
4
, KI and a small amount of starch is electrolysed. The electrolysis produces
free I
2
from I
-
ions and the I
2
immediately oxidises the arseneous acid to hydrogen
arsenate ion, HAsO
4
2-
.
I
2
+ H
3
AsO
3
+ H
2
O
2I
-
+ HAsO
4
2-
+ 4H
+
When the
oxidation of arsenic is complete, the free iodine combines with the starch to give a
deep blue colour. If during a particular run, it takes 65.3 s for a current of 10.5 mA to
give an end point (indicated by the blue colour), how many gram of arsenic are
present in the solution? (As = 75)
(a) 0.266 mg (b) 0.0266 g (c) 0.1266 g (d) 0.1266 mg
6. KCl cannot be used as a salt bridge for the cell
Cu(s) | CuSO
4
(aq) || AgNO
3
(aq) | Ag(s)
because
(a) CuCl
2
gets precipitated (b) Cl
2
gas is evolved
(c) AgCl gets precipitated (d) none of the above
7. The reduction potential for the metal M in following species is given below :
M M MO MO MO
dV cV bV
2
aV
3
Here d > c > b > a
Which of the following is correct :
(a)
3
MO
will not disproportionate (b)
2
MO
will disproportionate.
(c)M will disproportionate. (d)All are correct.
8. Conducting power of an electrolyte depends on
(a) nature of electrolyte (b) Concentration of solution
(c) Temperature (d)All are correct
MAMCQ
9. The values of E
0
of some reactions are given
I
2
+ 2e
2I
E
0
= 0.54 volts
Sn
+4
+ 2e
Sn
2+
E
0
= 0.152 volts
Cl
2
+ 2e
2Cl
E
0
= 1.36 volts
Fe
+3
+ e
Fe
2+
E
0
= 0.76 volts
Ce
+4
+ e
Ce
3+
E
0
= 1.6 volts
Hence
(a) Fe
3+
oxidizes Ce
+3
(b) Ce
4+
can oxidize Fe
2+
(c) Sn
2+
will reduce Fe
3+
to Fe
2+
(d) Cl
2
will be liberated from KCl by passing I
2
.
10. Which of the following cell(s) can act as concentration cell:
(a)Pt, H
2
(P
1
)|HCl(aq.)|H
2
(P
2
), Pt
(b)Ag|AgCl(s), KCl(aq.)||Ag
+
(aq.)
|Ag
(c)Pt, H
2
(P
1
)| OH
(aq.)
||H
+
(aq)
|H
2
(P
1
), Pt
(d)PtH
2
(P
1
)|H
+
(aq)
|O
2
(P
2
), Pt
11. The metal(s) which can not be obtained by electrolysis of its aqueous solution is
(a) Au (b) Al (c) Cu (d) Zn
12. Molar conductivity of an electrolyte increases with increase in temperature due to
(a) Increase in average kinetic energy of solution
(b) Increase in effective degree of ionization.
(c) Weakening of interionic attraction so ions become more free to move
(d) Decrease in viscosity of solution
13. For a solution of an electrolyte at a particular concentration and temperature, which
of the following is not the function of cell constant?
(a) Specific conductance (b) Molar conductance
(c) Equivalent conductance (d) Conductance
14. A test for completeness of electrodeposition of Cu from a solution of
( )
2
Cu aq
+
is to
add
3
NH
( ) aq . A blue colour signifies the formation of the complex ion
Cu NH
3
( )
4
2+
K
f
=1.110
13
( )
. 250mLof
( )
4
0.1MCuSO aq is electrolysed with a
3.512 A current for 1368 s. A sufficient quantity of
( )
3
NH aq is added to complex
any remaining
2
Cu
+
and to maintain a free
| |
3
NH 0.10M = .
NOTE :
Cu NH
3
( )
4
+2
is detectable at concentration greater than
5
1 10 M
,
(a) Blue colour will appear
(b) In the solution conc. of complex is
4 10
4
M
(c) In the solution
Cu
+2
= 3.6x10
13
(d) No blue colour will appear
INTEGAR TYPE
15. The potential of Pt, Hg
(l)
Hg(I) nitrate (0.01M) Hg(I) nitrate (0.1M) Hg
(l)
, Pt
is y x 10
-2
V.The value of y is--------------------
given,
RT
2.303 0.06
F
=
16. For following cell, calculate value of E
cell
in multiple of
10
2
volts
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
2 4 4 3 2
Pt s H 1atm NH Cl 0.2M , NH OH 0.1M NaHCO 0.1M H 1atm Pt s
Also given
k 4
b
P of NH OH 4.7 = for
2 3
H CO
6 10
a a
1 2
K 10 , K 10
= =
14
w
K 10
=
10
log 2 0.3 =
RT
2.303 0.06
F
=
COMPREHENSION-1
A hydrogen electrode, Pt, H
2
( 1atm) 30 ml HA (weak acid) is set up at 298k. The
electrolyte solution is titrated with a strong base BOH and the potential of the
electrode is measured at different volumes of BOH added. The following data is
observed
BURETTEREADING (in mL) E of hydrogen electrode (in Volts)
(volume of BOH added)
10 -0.4068
15 -0.4356
30 -0.7620
(Take 2.303RT/F = 0.06; log2 = 0.3; log3 = 0.48; log5 = 0.7)
17. The initial pH of (before addition of BOH) of HA solution is
(a) 4.74 (b) 3.65 (c) 3.74 (d) 3.89
18. The potential of hydrogen electrode at equivalence point of titration is
(a) -0.5958V (b) -0.6024V (c)-0.5934V (d)-0.42V
COMPREHENSION-2
The overvoltage is a polarization potential associated with the electrochemical
processes occurring at the electrode surface. This effect is particularly important
when the product of electrolysis is a gaseous one. The difference between the voltage
actually required for an electrode half reaction to occur, and that expected
theoretically is termed as over voltage.
Electrode Overvoltage Electrode Overvoltage
Pt (platinized) 0.00 Ni 0.21
Pt (smooth) 0.09 Cd 0.48
Au 0.02 Sn 0.53
Ag 0.15 Pb 0.64
Cu 0.23 Zn 0.70
Fe 0.08 Hg 0.78
19. Overvoltage depends on
(a) Nature & physical state of electrode employed
(b) The physical state of the substance deposited
(c) Current density employed
(d) All of these
20. Potential difference required for liberation of
2
H at cathode (platinised- platinum
electrode) is from 1M
2 4
H SO solution is 0.48 V. The discharge potential of
2
H for
same solution at Zn electrode
(a) 0.48 V (b) 1.08 V (c) 0.7 V (d) 1.18 V
21. Given
0
Na Na
E 2.71V
+
=
0
Cl Cl
2
E 1.36V
= +
0
H O,OH H
2 2
E 0.83V
=
0
O H , H O
2 2
E 1.23V
+
= +
In electrolysis of aq. NaCl, water gets reduced at cathode and from
0
E values
given here it appears water will get oxidize at anode. But Cl
-
gets oxidize at anode
hence value of over potential of oxygen evolution should be greater than
(a) 1.23 V (b) 0.1 V (c) 0.13 V (d) 1.36 V
COMPREHENSION-3
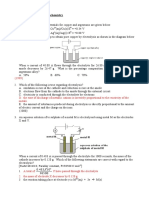
For the next four questions refer to the following illustrations in which 1.0 M
solution and strips of metal shown below:
(I) A strip of metal D was inserted into each solution. Reactions occurred
in solutions containing A
2+
and C
2+
ions.
(II) Metal B reacted with solutions containing D
2+
and E
3+
ions. It was not
tested in other solutions.
(III) Metal C does not react with any of the solutions.
22. If metal A were placed in each solution, a reaction would be expected in
(A) solutions containing C
2+
ions only
(B) solutions containing B
+
, C
2+
and D
2+
only
(C) solutions containing C
2+
, D
2+
and E
3+
only
(D) solutions containing B
+
, D
2+
and E
3+
ions only
3 3
E(NO ) (aq)
23. For the metal A to E, a possible decreasing order of their oxidizing strength is
(A) A > B > C > D > E (B) C > A > E > D > B
(C) E > D > C > B > A (D) B > E > D > A > C
24. If the answer of the above question is assumed to be perfectly correct, all of the
following combinations of metal-metal-ion solution represents non-spontaneous
conditions except
(A) E D(NO
3
)
2
(B) A E(NO
3
)
3
(C) A C(NO
3
)
2
(D) C E(NO
3
)
2
25. Assuming that none of the metals A E produces H
2
(g) when dissolved in HCl, if the
above mentioned beakers are connected in series, molar ratio in which metals A E
deposited respectively.
(A) 1 : 1 : 1 : 1 : 3 (B) 2 : 2 : 2 : 2 : 3 (C) 3 : 3 : 3 : 3 : 2 (D) 3 : 3 : 3 : 3 : 1
COMPREHENSION-4
The next three questions relate to the illustrated apparatus below:
Half-cell E
o
(V at 25
o
C) Molar masses
Ni
2+
+ 2e
-
Ni 0.25 V Ni = 60
Pb
2+
+ 2e
-
Pb 0.13 V Pb = 207
Ag
+
+ e
-
Ag + 0.80 V Ag = 108
26. When the voltmeter is connected between Ni and Pb electrodes, it reads 0.12 V. After
0.10 mol of electrons have passed through the voltmeter, the mass of Ni electrodes
will be
(A) 6 grams greater (B) 3 grams greater (C) 6 grams less (D) 3 grams less
27. Based on the information above, in which cases would a spontaneous reaction be
expected to take place between the metal and the solution paired with it?
(I) Pb(s) Ag
+
(aq) (II) Ag(s) Ni
2+
(aq) (III) Pb(s) Ni
2+
(aq)
(IV) Ag(s) Pb
2+
(aq) (V) Ni(s) Pb
2+
(aq)
(A) I and II only (B) I and V only (C) II and V only (D) I, III and IV
28. If Ni/Ni(NO
3
)
2
and Ag/AgNO
3
half-cells are connected to a battery, what minimum
voltage would be required to reverse the cell reaction
Also given : At 25
o
C
2H
2
O + 2e
-
H
2
(g) + 2OH
-
; E
o
= 0.828 V
4OH
-
O
2
+ 2H
2
O + 4e
-
; E
o
= 0.40 V
(A) 1.05 V
(B) less than 1.05 V
(C) greater than 1.05 V
(D) the cell is not reversible i.e., water oxidizes before Ag start oxidizing
MATRIX MATCH
29. If following solution electrolysed using the inert electrodes gases liberated are
Column I Column - II
A
2 4
Na SO
P
2
Cl
B
4
ZnSO
Q
2
O
C HCl R
2
H
D
2 4
Ag SO
S
2
SO
30. Match Matrix
+
o
-10
Ag /Ag E = 0.8, Ksp(AgCl) = 10
| |
|
\ .
.
COLUMN I COLUMN - II
(A) Pt|H
2
(0.1 bar)| H
+
(0.1 M)|| H
+
(1 M) | H
2
(0.01 bar)| Pt P. Concentration cell
(B) Ag |AgCl (KCl, 0.1 M) ||Ag
+
(0.01M) | Ag Q. E
cell
> 0
(C) Cu| Cu
2+
(0.1 M)|| Cu
2+
(0.01 M)| Cu R. E
0
cell
= 0 but cell is
working
(D) Pt|Cl
2
(1 bar) | HCl (0.1 M)|| NaCl (0.1 M) Cl
2
(1 bar) | Pt S. non working condition
ANSWER KEY
Que. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Ans. c a b b a c d
Que. 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Ans. d bc abc bd abcd abc abc
Que. 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
Ans. 3 6 c a d d c
Que. 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
Ans. a b c c d b d
29.
AQ, R; BQ, R;CP, R; DQ
30. A P, Q, R; B Q; C P,S; D P,S
Вам также может понравиться
- 10 - Yang H. Huang 1983 Stability Analysis of Earth Slopes PDFДокумент307 страниц10 - Yang H. Huang 1983 Stability Analysis of Earth Slopes PDFLuis VélezОценок пока нет
- 01-SAMSS-043 2018 ASTM Carbon Steel and Low Alloy Pipes For On-Plot ApplicationsДокумент18 страниц01-SAMSS-043 2018 ASTM Carbon Steel and Low Alloy Pipes For On-Plot ApplicationsWHWEN100% (1)
- National Building Code of India 2005Документ1 178 страницNational Building Code of India 2005Sonmoy Chatterjee82% (39)
- Inspection and Test Plan (ITP) PDFДокумент4 страницыInspection and Test Plan (ITP) PDFSAIIN khodirОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Question Bank For HiighschoolДокумент221 страницаChemistry Question Bank For HiighschoolsakuraleeshaoranОценок пока нет
- Unit 8B AP Chem - ElectrochemistryДокумент11 страницUnit 8B AP Chem - ElectrochemistryAnivia12100% (1)
- D1149Документ4 страницыD1149ABe MustofaОценок пока нет
- Bumper Systems - An IntroductionДокумент25 страницBumper Systems - An IntroductionMichaelОценок пока нет
- Topical Test Echem 2014Документ1 страницаTopical Test Echem 2014irnihafizan6812Оценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Din 8077-8078 & Iso 15874-2Документ7 страницDin 8077-8078 & Iso 15874-2Filip100% (4)
- Chemistry Paper 3 TZ2 HLДокумент36 страницChemistry Paper 3 TZ2 HLJuan Camilo VargasОценок пока нет
- Electro ChemДокумент27 страницElectro ChemTori RodriquezОценок пока нет
- 2-5 Redox Reactions Practice Worksheet With AnswersДокумент9 страниц2-5 Redox Reactions Practice Worksheet With AnswersThanabalan MunuswamyОценок пока нет
- Day 2 Questions That Came Out in The ExamДокумент7 страницDay 2 Questions That Came Out in The ExamAdrian Joshua BernagaОценок пока нет
- Electro Chemistry Assignment For Iitjee PDFДокумент19 страницElectro Chemistry Assignment For Iitjee PDFggk20130% (2)
- Electrochemistry: 0 8 0 79 0 34 2 37 Ag / Ag - HG / HG - Cu / Cu - MG / MGДокумент11 страницElectrochemistry: 0 8 0 79 0 34 2 37 Ag / Ag - HG / HG - Cu / Cu - MG / MGAnikin Skywalker100% (1)
- Electro Chemistry AssaignmentДокумент9 страницElectro Chemistry AssaignmentGadde Gopala KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Final Revision Module For ChemistryДокумент8 страницFinal Revision Module For ChemistryVibhu MittalОценок пока нет
- Reduction-Oxidation Reactions and ElectrochemistryДокумент14 страницReduction-Oxidation Reactions and Electrochemistrykaushi123Оценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry MCQ SendДокумент7 страницElectrochemistry MCQ SendRajendra ChikkamathОценок пока нет
- LT Iit Che DPT - 15 - 21.02.2024Документ3 страницыLT Iit Che DPT - 15 - 21.02.2024Deena chemistОценок пока нет
- Electro Chemistry AssaignmentДокумент11 страницElectro Chemistry AssaignmentGadde Gopala KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Fall Semester Review KEYДокумент8 страницFall Semester Review KEYbangtanswifue -Оценок пока нет
- Sample Questions - Chapter 15Документ6 страницSample Questions - Chapter 15Rasel IslamОценок пока нет
- Electrochem AДокумент1 страницаElectrochem AAman9692Оценок пока нет
- This Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingДокумент16 страницThis Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingvarunkohliinОценок пока нет
- RedoEqui 3 2 12Документ3 страницыRedoEqui 3 2 12Huzeyfa Hassan LatheefОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 ElectrolysisДокумент8 страницChapter 4 ElectrolysisPremОценок пока нет
- C 2 Amal 1 Galvanic 2017Документ16 страницC 2 Amal 1 Galvanic 2017kjjkimkmkОценок пока нет
- JEE Main Sample PaperДокумент15 страницJEE Main Sample PaperAnweshaBose100% (1)
- AP Chemistry: Electrochemistry Multiple Choice: Which of The Above Occurs For Each of The Following Circumstances?Документ5 страницAP Chemistry: Electrochemistry Multiple Choice: Which of The Above Occurs For Each of The Following Circumstances?Mohammed AbdelhakeemОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry Worksheet 2: Done in FigДокумент8 страницElectrochemistry Worksheet 2: Done in Figrezwanur rahmanОценок пока нет
- 12TH Grade Electrochemistry Worksheet-1Документ3 страницы12TH Grade Electrochemistry Worksheet-1Amen RaipurОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 3 ElectrochemistryДокумент6 страницTutorial 3 ElectrochemistrymunirahОценок пока нет
- DPP 17Документ1 страницаDPP 17Saiprasad K. MalekarОценок пока нет
- واجب شامل للمقررДокумент30 страницواجب شامل للمقررOsama AlkinaneОценок пока нет
- Ejercicios QuímicaДокумент3 страницыEjercicios QuímicaAndreaForteRuizОценок пока нет
- The Advanced Placement Examination in Chemistry: ElectrochemistryДокумент21 страницаThe Advanced Placement Examination in Chemistry: ElectrochemistrySreeyaОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry MCQ With Ans. NeetДокумент7 страницElectrochemistry MCQ With Ans. NeetDheeraj YadavОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry Past Papers 2022-14Документ4 страницыElectrochemistry Past Papers 2022-1410 A Pratyush Dubey0% (1)
- Electrochemistry Past Papers 2022-14Документ4 страницыElectrochemistry Past Papers 2022-14Venugopal JujhavarappuОценок пока нет
- SCH4U Exam ReviewДокумент3 страницыSCH4U Exam Reviewtaya guyОценок пока нет
- Module 7 Problem Set Answer KeyДокумент3 страницыModule 7 Problem Set Answer KeyPauline Grace CadusaleОценок пока нет
- Electro Kinetics Coordination Set OДокумент2 страницыElectro Kinetics Coordination Set OShivam SahuОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry: E° (Cathode) - E° (Anode) G - nFE F 96,485J/ V X Mols G GДокумент15 страницElectrochemistry: E° (Cathode) - E° (Anode) G - nFE F 96,485J/ V X Mols G GandrewОценок пока нет
- RT Solutions-30!01!2012 XII ABCD Part Test IIДокумент12 страницRT Solutions-30!01!2012 XII ABCD Part Test IIvishal27042233Оценок пока нет
- Soal ElectrochemistryДокумент3 страницыSoal ElectrochemistryHerlinda OktaОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry Ch20bДокумент13 страницElectrochemistry Ch20bSiti Aisyah RuzelanОценок пока нет
- UPSEE Sample Papers 2 (UPSEE Chemistry Questions Paper 2)Документ6 страницUPSEE Sample Papers 2 (UPSEE Chemistry Questions Paper 2)Firdosh KhanОценок пока нет
- 1 ElectrochemistryДокумент18 страниц1 ElectrochemistryPriyaranjanОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry Board Questions 2010Документ4 страницыElectrochemistry Board Questions 2010amone nОценок пока нет
- Solutions To Problem Set 2Документ5 страницSolutions To Problem Set 2Andy Nguyen100% (1)
- Physical Chemistry OBJECTIVEДокумент188 страницPhysical Chemistry OBJECTIVEGadde Gopala Krishna100% (2)
- Past Year Question: ElectrochemistryДокумент3 страницыPast Year Question: ElectrochemistryLuk HKОценок пока нет
- Chemistrynht Examrep17Документ12 страницChemistrynht Examrep17KLОценок пока нет
- Acs Local Exam 1990Документ10 страницAcs Local Exam 1990kateexdОценок пока нет
- Class-Xii (Chemistry) Sumit Sir SirДокумент2 страницыClass-Xii (Chemistry) Sumit Sir Sirmanyag1605Оценок пока нет
- Assignment 4 StudДокумент4 страницыAssignment 4 StudutpОценок пока нет
- Worksheet Chemo G 12 Unit Tu 22 2016Документ9 страницWorksheet Chemo G 12 Unit Tu 22 2016Dagim YenenehОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Assignment Electro GGДокумент4 страницыChemistry Assignment Electro GGyashОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry FДокумент8 страницElectrochemistry FAshwin Balaji100% (1)
- 20 Petrucci10e CSMДокумент66 страниц20 Petrucci10e CSMAlexОценок пока нет
- Chemistry (Theory) : General InstructionsДокумент8 страницChemistry (Theory) : General InstructionsDeepali SinghОценок пока нет
- IMP Question Bank Class XIIДокумент8 страницIMP Question Bank Class XIIeshani0706Оценок пока нет
- AP 02 Multiple ChoiceДокумент16 страницAP 02 Multiple ChoiceKat TomasОценок пока нет
- STD 12 - Chemistry - AssignmentДокумент2 страницыSTD 12 - Chemistry - AssignmentHetalben PatelОценок пока нет
- 10 FullДокумент4 страницы10 FullroobanОценок пока нет
- Endohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideОт EverandEndohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideОценок пока нет
- E Ticket: Itinerary and Reservation DetailsДокумент2 страницыE Ticket: Itinerary and Reservation DetailsGokul NathОценок пока нет
- You, The IIT Aspirant Captain: Sunday, The 5th of May April RevisionДокумент4 страницыYou, The IIT Aspirant Captain: Sunday, The 5th of May April RevisionGokul NathОценок пока нет
- Index Sequential SearchДокумент3 страницыIndex Sequential SearchGokul NathОценок пока нет
- List of TINFC-PAN Centre Biometric 08122017Документ34 страницыList of TINFC-PAN Centre Biometric 08122017Gokul NathОценок пока нет
- XIIth Maths Practice Questions 2014-15Документ10 страницXIIth Maths Practice Questions 2014-15Gokul NathОценок пока нет
- Donation AcknowledgementДокумент1 страницаDonation AcknowledgementGokul NathОценок пока нет
- Exercise 1 (C) : DX DyДокумент7 страницExercise 1 (C) : DX DyGokul NathОценок пока нет
- Private Sector Banks 2014Документ2 страницыPrivate Sector Banks 2014Gokul Nath0% (1)
- Conic Section DPPДокумент3 страницыConic Section DPPGokul Nath0% (2)
- DPP 6Документ4 страницыDPP 6Gokul Nath100% (1)
- NL CQ 6 SSPДокумент4 страницыNL CQ 6 SSPGokul NathОценок пока нет
- Limits of FunctionДокумент12 страницLimits of FunctionGokul NathОценок пока нет
- Newton's Laws of Motion.Документ2 страницыNewton's Laws of Motion.Gokul Nath100% (1)
- INPHO Solved Paper 2013Документ31 страницаINPHO Solved Paper 2013Pankaj MishraОценок пока нет
- DPP 12Документ11 страницDPP 12Gokul Nath50% (2)
- 21 FDДокумент6 страниц21 FDKool PrashantОценок пока нет
- If N Is Even Positive Integer Then The Smallest Integer Greater ThanДокумент4 страницыIf N Is Even Positive Integer Then The Smallest Integer Greater ThanGokul NathОценок пока нет
- Functions Ex.2 (B)Документ20 страницFunctions Ex.2 (B)Gokul NathОценок пока нет
- Electrostatics For JEEДокумент7 страницElectrostatics For JEEGokul NathОценок пока нет
- Formal-5Документ44 страницыFormal-5Tamzidul AlamОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bath DepositionДокумент6 страницChemical Bath DepositionJune AlapaОценок пока нет
- 11 Chemistry Sample PapersДокумент10 страниц11 Chemistry Sample PapersPc xoixaОценок пока нет
- NCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 14 Semiconductors ElectronicДокумент14 страницNCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 14 Semiconductors ElectronicVidyakulОценок пока нет
- Dyes NotesДокумент3 страницыDyes NotesArianne BatallonesОценок пока нет
- XNEM-program: Photo Lithography Sequence For Developing Micro Structure & Rie (Reactive Ion Etching)Документ7 страницXNEM-program: Photo Lithography Sequence For Developing Micro Structure & Rie (Reactive Ion Etching)baraniinstОценок пока нет
- Influence Height Lattice Work Contribution Shear Resistance Reinforced ConcretДокумент10 страницInfluence Height Lattice Work Contribution Shear Resistance Reinforced ConcretGuillermo AragonОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law: Systems, States, and Energy (Sections 6.1-6.8)Документ12 страницChapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law: Systems, States, and Energy (Sections 6.1-6.8)MostafaRock100% (2)
- Xii Worksheet No.1 SolutionsДокумент2 страницыXii Worksheet No.1 SolutionsD4RKwizОценок пока нет
- EP7 3.2.1 Glass Containers For Pharmaceutical Use PDFДокумент5 страницEP7 3.2.1 Glass Containers For Pharmaceutical Use PDFRany BanaОценок пока нет
- Dielectric ConstantsДокумент3 страницыDielectric Constantsleandroperao5374Оценок пока нет
- Submersible Wastewater Pumps With Single Vane Impeller 3" Discharge - 2" SolidsДокумент2 страницыSubmersible Wastewater Pumps With Single Vane Impeller 3" Discharge - 2" SolidsAdemir JúniorОценок пока нет
- The Density of Liquids and An Introduction To Graphing PDFДокумент5 страницThe Density of Liquids and An Introduction To Graphing PDFEric BirdОценок пока нет
- Self-Gripping Gasketing: Program 1011Документ1 страницаSelf-Gripping Gasketing: Program 1011Sofyan HadiОценок пока нет
- Shell Morlina S2 B 220 - TDSДокумент4 страницыShell Morlina S2 B 220 - TDSFandemen AdintaОценок пока нет
- ResourceДокумент2 страницыResourceSHAISTA AFREEN TEACHERОценок пока нет
- The Tile Industry in KeralaДокумент40 страницThe Tile Industry in KeralaNazanin SabetОценок пока нет
- Abstrak GranitДокумент2 страницыAbstrak GranitAhmad Alam Faizal HasibuanОценок пока нет
- Nsec 2013 PaperДокумент15 страницNsec 2013 PaperShivamGuptaОценок пока нет
- Performance Evaluation of A Small Scale Palm Fruit PDFДокумент6 страницPerformance Evaluation of A Small Scale Palm Fruit PDFAliaОценок пока нет
- Cyclic Pile Load Test On Large Diameter Piles, A Case Study PDFДокумент5 страницCyclic Pile Load Test On Large Diameter Piles, A Case Study PDFhardik sorathiyaОценок пока нет