Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
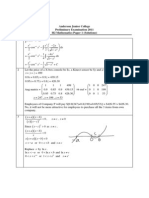
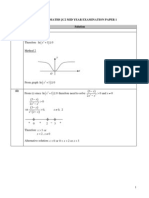
Further Differentiation - Solutions
Загружено:
wolfretonmathsАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Further Differentiation - Solutions
Загружено:
wolfretonmathsАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AQA Core 2 Calculus
1 of 4 15/01/13 MEI
Section 1: Further differentiation
Solutions to Exercise
1. (i)
3
3
1
f( ) x x
x
= =
4
4
3
f ( ) 3 x x
x
' = =
(ii)
1
3 3
f( ) x x x = =
2
3 1
3
f ( ) x x
' =
(iii)
1 2
2
2 3
f( ) 2 3 x x x
x x
= =
2 3
2 3
2 3
f ( ) 2 3 2
2 6
2 6
x x x
x x
x x
' =
= +
= +
(iv)
1 1
2 2
3
f( ) 4 4 3 x x x x
x
= =
( )
1 3
2 2
1 3
2 2
1 1
2 2
3
2
3
f( ) 4 3
2
2 3
2
x x x
x x
x
x
=
= +
= +
(v)
5 7
f( ) 3 2 x x x
=
6 8
6 8
6 8
f ( ) 3 5 2 7
15 14
15 14
x x x
x x
x x
' =
= +
= +
(vi)
2 2
3 3
f( ) 2 5 x x x
=
1 5
3 3
1 5
3 3
2 2
3 3
4 10
3 3
f ( ) 2 5 x x x
x x
' =
= +
(vii)
2
1 2
1 3
2 2
2
2 3
f( )
2
x x
x x x
x
+
= = +
AQA C2 Calculus 1 Exercise solutions
2 of 4 15/01/13 MEI
2 3
3
2
2 3
2 3
f ( ) ( 1) 2
3
1 3
x x x
x x
x x
' = +
=
=
(viii)
( )
5 1
2 2
2
f( ) 2 2 x x x x x = =
3 1
2 2
3 1
2 2
5 1
2 2
5
2
f ( ) 2 x x x
x x
' =
=
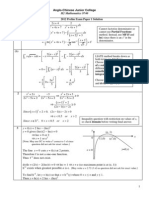
2. (i)
1
1
2 2 y x x x
x
= =
2
2
d
1
2 ( ) 2
d
y
x
x x
= = +
When x = 1, gradient
2
1
2 3
1
= + =
(ii)
1
2
3 3 y x x = =
1
2 1
2
d
1
d 2
y
x
x x
= =
When x = 4, gradient
1 1
2 4 4
= =
(iii)
5
2
2
y x x x = =
3
2 5
2
d
d
y
x
x
=
When x = 1, gradient
3
2 5 5
2 2
1 = =
3. (i)
= =
2
2
4
4 y x x x
x
= + = +
3
3
d
8
1 8 1
d
y
x
x x
At turning points,
d
0
d
y
x
=
3
3
3
8
1 0
8
1
8
2
x
x
x
x
+ =
=
=
=
When x = -2, = = =
2
4
2 2 1 3
( 2)
y
so (-2, -3) is a turning point.
AQA C2 Calculus 1 Exercise solutions
3 of 4 15/01/13 MEI
= =
2
4
2 4
d
24
24
d
y
x
x x
When x = -2, = <
2
2 4
d
24
0
d ( 2)
y
x
, so (-2, -3) is a maximum point.
(ii)
= + = +
1 1
2 2
1
y x x x
x
= =
1 3
2 2 1 1
2 2
3
d
1 1
d 2
2
y
x x
x x
x
At turning points, =
d
0
d
y
x
=
3
1 1
0
2
2
x
x
=
=
=
=
+ =
= = =
3
3
3
2
0
( 1) 0
( 1)( 1) 0
0 or 1 or 1
x x
x x
x x
x x
x x x
x x x
Since the curve is not defined at x = 0 or at x = -1, the only turning
point is at x = 1.
When x = 1, = + = + =
1
1 1 1 2
1
y , so (1, 2) is a turning point.
= = +
3 5 3 5
2 2 2 2
2
1 1 1 3 1 3
2 2 2 2 4 8
2
d
d
y
x x x x
x
When x = 1, = + >
2
1 3
4 8
2
d
0
d
y
x
, so (1, 2) is a minimum point.
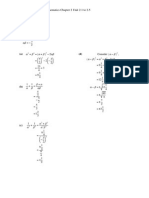
4.
= =
1
2
1
y x
x
=
3
2 1
2
d
d
y
x
x
When x = 1,
= =
3
2 1 1
2 2
d
1
d
y
x
When x = 1, = =
1
1
1
y
Tangent is straight line with gradient
1
2
passing through (1, 1).
Equation of tangent is =
=
= +
+ =
1
2
1 ( 1)
2( 1) ( 1)
2 2 1
2 3
y x
y x
y x
y x
AQA C2 Calculus 1 Exercise solutions
4 of 4 15/01/13 MEI
5.
= =
1 2
2
1 2
2 y x x
x x
= = +
2 3
2 3
d
1 4
2 2
d
y
x x
x x x
When x = 2, = + = + =
2 3
d
1 4 1 1 1
d 2 2 4 2 4
y
x
Gradient of tangent =
1
4
, so gradient of normal = -4.
When x = 2, = = =
2
1 2 1 1
0
2 2 2 2
y
Normal is straight line with gradient -4 passing through (2, 0)
Equation of normal is =
= +
0 4( 2)
4 8
y x
y x
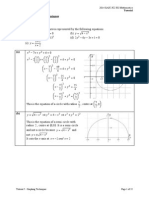
6. (i)
2
2
2
2000
2000
V r h
r h
h
r
t
t
t
=
=
=
(ii) Surface area S
2
2
2
2
2 2
2000
2 2
4000
2
r rh
r r
r
r
r
t t
t t
t
t
= +
= +
= +
(iii)
2 1
2 4000 S r r t
= +
2
d
4 4000
d
S
r r
r
t
=
At turning point,
2
2
3
3
4000
4 0
4000
4
1000
10
r
r
r
r
r
r
t
t
t
t
=
=
=
=
2
3
2
d
4 8000 0
d
S
r
r
t
= + > , so this is a minimum point.
The surface area is minimised when
3
10
r
t
= cm.
Вам также может понравиться
- 2013 - 2014 H2 Maths JJC Promo SolnsДокумент11 страниц2013 - 2014 H2 Maths JJC Promo SolnsLionel Torres LeeОценок пока нет
- Yjc h2 Math p1 SolutionsДокумент12 страницYjc h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- TJC h2 Math p1 SolutionДокумент12 страницTJC h2 Math p1 SolutionjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Mi h2 Math Solutions p1Документ10 страницMi h2 Math Solutions p1jimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Answers Are You Ready For CalculusДокумент6 страницAnswers Are You Ready For CalculusKevin HsiehОценок пока нет
- PJC h2 Math p1 SolutionsДокумент13 страницPJC h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- JC2 Prelim H2 Math Solution Paper 1Документ10 страницJC2 Prelim H2 Math Solution Paper 1Huixin LimОценок пока нет
- 2006 AJC H2 MY SolnДокумент9 страниц2006 AJC H2 MY Solnjunie9201Оценок пока нет
- BT2 Revision Package Solutions (2008 Prelims)Документ111 страницBT2 Revision Package Solutions (2008 Prelims)gerwynngОценок пока нет
- ACJC 2014 H2 Maths Supp Exam (Solution For Students)Документ9 страницACJC 2014 H2 Maths Supp Exam (Solution For Students)RaymondZhangОценок пока нет
- 2007 YJC Paper 1solДокумент12 страниц2007 YJC Paper 1solYudi KhoОценок пока нет
- Ajc h2 Math p1 SolutionsДокумент15 страницAjc h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- AJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Документ12 страницAJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Sajc 2010 Prelim Math p1 SolnДокумент10 страницSajc 2010 Prelim Math p1 SolnAh XiuОценок пока нет
- 2013 HCI C1 Block Test H2 Mathematics Revision Package SolutionsДокумент80 страниц2013 HCI C1 Block Test H2 Mathematics Revision Package SolutionsGabriel Francis ChuaОценок пока нет
- QN Solution 1: H2 Math Paper 1Документ11 страницQN Solution 1: H2 Math Paper 1Alex SoonОценок пока нет
- Dhs h2 Math p1 SolutionДокумент11 страницDhs h2 Math p1 SolutionjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Solutions To Home Practice Test-5/Mathematics: Differential Calculus - 2 HWT - 1Документ12 страницSolutions To Home Practice Test-5/Mathematics: Differential Calculus - 2 HWT - 1varunkohliinОценок пока нет
- Advanced Inequations Exercise - 3Документ19 страницAdvanced Inequations Exercise - 3Atul KumarОценок пока нет
- Solutions To Home Practice Test/Mathematics: Differential Equation HWT - 1Документ7 страницSolutions To Home Practice Test/Mathematics: Differential Equation HWT - 1varunkohliinОценок пока нет
- 2009 Mathematics Advanced Higher Finalised Marking InstructionsДокумент10 страниц2009 Mathematics Advanced Higher Finalised Marking InstructionsQwaAlmanlawiОценок пока нет
- AJC H2 Math 2013 Prelim P1 SolutionsДокумент15 страницAJC H2 Math 2013 Prelim P1 Solutionsnej200695Оценок пока нет
- 2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math SolnДокумент15 страниц2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math Solnckhowh_23284524667% (3)
- Inequation & Equation Solutions FinalДокумент67 страницInequation & Equation Solutions FinalAkshay PatelОценок пока нет
- Recitation 5: Sections 12.1-12.3Документ40 страницRecitation 5: Sections 12.1-12.3Oğuzhan ÖzdemirОценок пока нет
- 2009 NJC SH2 H2 Mathematics Prelim Paper 2 SolutionsДокумент21 страница2009 NJC SH2 H2 Mathematics Prelim Paper 2 SolutionsNicholas ChoyОценок пока нет
- Inxhapter Exercise SolutionДокумент16 страницInxhapter Exercise SolutionAkshay PatelОценок пока нет
- HCI H2 Maths 2012 Prelim P1 SolutionsДокумент12 страницHCI H2 Maths 2012 Prelim P1 Solutionsnej200695Оценок пока нет
- Secondary 3 Additional Mathematics Chapter 2 Unit 2.1 To 2.5Документ10 страницSecondary 3 Additional Mathematics Chapter 2 Unit 2.1 To 2.5sqhaaОценок пока нет
- 2007 Ajc h2 Prelims Paper 1 SolutionsДокумент9 страниц2007 Ajc h2 Prelims Paper 1 Solutionsvincesee85Оценок пока нет
- 2010-H2 Maths-Integration and Its Applications (Tut 3) - Int Applications Solutions)Документ13 страниц2010-H2 Maths-Integration and Its Applications (Tut 3) - Int Applications Solutions)Anita Yun Chu PengОценок пока нет
- 4ACh01Quadratic Equations in One UnknownДокумент32 страницы4ACh01Quadratic Equations in One UnknownPrecious GaJaОценок пока нет
- Edexcel C3 June 2005 To June 2011 All Questions Mark SchemeДокумент44 страницыEdexcel C3 June 2005 To June 2011 All Questions Mark SchemeOrhan AtestemurОценок пока нет
- Dhs h2 Math p2 SolutionДокумент14 страницDhs h2 Math p2 SolutionjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Module Tests AnswersДокумент28 страницUnit 2 Module Tests AnswersashtigosineОценок пока нет
- II Sem (Csvtu) Mathematics Unit 2 (Linear Differential Equation) SolustionsДокумент31 страницаII Sem (Csvtu) Mathematics Unit 2 (Linear Differential Equation) SolustionsMrityunjoy DuttaОценок пока нет
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm AДокумент8 страницAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremОценок пока нет
- NJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsДокумент10 страницNJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Rvhs h2 Math p1 SolutionsДокумент13 страницRvhs h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Paper B SolutionДокумент11 страницPaper B SolutiontimchanymОценок пока нет
- NYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Документ10 страницNYJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- 2011 IJC Prelims P1 SolnДокумент15 страниц2011 IJC Prelims P1 Solnmath3matics3Оценок пока нет
- Tutorial 6 Graphing Techniques SolutionsДокумент22 страницыTutorial 6 Graphing Techniques SolutionsLawrenceJGLimesaОценок пока нет
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Документ22 страницыMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Chapter 13 AnswersДокумент8 страницUnit 2 Chapter 13 AnswersashtigosineОценок пока нет
- Nyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionДокумент10 страницNyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm AДокумент9 страницAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremОценок пока нет
- Section G: Integer Answer Type: X FX F XДокумент10 страницSection G: Integer Answer Type: X FX F XsatwiksmОценок пока нет
- (3x) (1+ 1 3x) 1 2 3x + 1 2 (1 2 1) 2 (1 3x) + ...... ) (3x) + 1 2 (3x) 1 8 (3x) + ......Документ10 страниц(3x) (1+ 1 3x) 1 2 3x + 1 2 (1 2 1) 2 (1 3x) + ...... ) (3x) + 1 2 (3x) 1 8 (3x) + ......Matthew ShiaОценок пока нет
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics Solutions (2-4 2-7&2-10)Документ26 страницAdvanced Engineering Mathematics Solutions (2-4 2-7&2-10)Fa VelizОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 1 - 2 - To - 1 - 6 - Polynomials - and - Partial - Fractions - Solutions 2Документ19 страницChapter - 1 - 2 - To - 1 - 6 - Polynomials - and - Partial - Fractions - Solutions 2sqhaaОценок пока нет
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm AДокумент5 страницAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremОценок пока нет
- 2010 TJC SolДокумент12 страниц2010 TJC SolPooja KapurОценок пока нет
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageОт EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageОценок пока нет
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsОт EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsОт EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Using Graphs - Solutions PDFДокумент5 страницUsing Graphs - Solutions PDFwolfretonmaths100% (1)
- Using Graphs Exercise PDFДокумент4 страницыUsing Graphs Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Friction Exercise PDFДокумент1 страницаFriction Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Using Vectors - Solutions PDFДокумент5 страницUsing Vectors - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Projectile Motion - Solutions PDFДокумент6 страницProjectile Motion - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise PDFДокумент2 страницыNewton's Laws of Motion Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Using Vectors Exercise PDFДокумент2 страницыUsing Vectors Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Forces & Equilibrium Exercise PDFДокумент2 страницыForces & Equilibrium Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Projectile Motion Exercise PDFДокумент2 страницыProjectile Motion Exercise PDFwolfretonmaths100% (2)
- Constant Acceleration Exercise PDFДокумент2 страницыConstant Acceleration Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Forces & Equilibrium - Solutions PDFДокумент5 страницForces & Equilibrium - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Friction - Solutions PDFДокумент3 страницыFriction - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Newton's Laws of Motion - Solutions PDFДокумент6 страницNewton's Laws of Motion - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Constant Acceleration - Solutions PDFДокумент6 страницConstant Acceleration - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Conservation of Momentum CPДокумент1 страницаConservation of Momentum CPwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Conservation of Momentum - Solutions PDFДокумент3 страницыConservation of Momentum - Solutions PDFwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Connected Particles - Solutions PDFДокумент6 страницConnected Particles - Solutions PDFwolfretonmaths67% (3)
- Connected Particles Exercise PDFДокумент2 страницыConnected Particles Exercise PDFwolfretonmaths100% (1)
- Newton's Laws of Motion CPДокумент1 страницаNewton's Laws of Motion CPwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Conservation of Momentum Exercise PDFДокумент1 страницаConservation of Momentum Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Using Vectors CPДокумент1 страницаUsing Vectors CPwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Using Graphs CPДокумент1 страницаUsing Graphs CPwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Connected Particles CPДокумент1 страницаConnected Particles CPwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Constant Acceleration CPДокумент1 страницаConstant Acceleration CPwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Constant AccelerationДокумент5 страницConstant AccelerationwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Forces & Equilibrium CPДокумент1 страницаForces & Equilibrium CPwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Projectile Motion CPДокумент1 страницаProjectile Motion CPwolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Connected ParticlesДокумент4 страницыConnected ParticleswolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- Using VectorsДокумент3 страницыUsing VectorswolfretonmathsОценок пока нет
- (Made Simple Books) William R. Gondin, Bernard Sohmer - Advanced Algebra and Calculus Made Simple (1959, Doubleday) - Libgen - LiДокумент228 страниц(Made Simple Books) William R. Gondin, Bernard Sohmer - Advanced Algebra and Calculus Made Simple (1959, Doubleday) - Libgen - LiRodrigoОценок пока нет
- Ajith Sir - Differentiation HWДокумент12 страницAjith Sir - Differentiation HWNiel AntonyОценок пока нет
- Topic 5. Calculus PDFДокумент137 страницTopic 5. Calculus PDFJuan Gustavo SerranoОценок пока нет
- CE 411 Lecture 03 - Moment AreaДокумент27 страницCE 411 Lecture 03 - Moment AreaNophiОценок пока нет
- Deleuze Matma 1Документ13 страницDeleuze Matma 1Wojtek RosolowskiОценок пока нет
- 2 - Shear and Moment Using Short MethodДокумент10 страниц2 - Shear and Moment Using Short MethodShanen CruzОценок пока нет
- G C A 2 ChordsSecantsandTangents8Документ7 страницG C A 2 ChordsSecantsandTangents8Klevin Lloyd100% (1)
- MESL - Analytic Geometry 1Документ7 страницMESL - Analytic Geometry 1Mark-Lorie Duculan NonesОценок пока нет
- 01 02 Circles 2 PDFДокумент21 страница01 02 Circles 2 PDFrohit kumarОценок пока нет
- Mathematics B: Pearson Edexcel International GCSEДокумент28 страницMathematics B: Pearson Edexcel International GCSEMir Sameen HasnatОценок пока нет
- MATH226 Hand in Hw4Документ1 страницаMATH226 Hand in Hw4wizbizphdОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Letter 101/3/2020: Mathematics 1 (Engineering)Документ30 страницTutorial Letter 101/3/2020: Mathematics 1 (Engineering)ger pingОценок пока нет
- Day 3 Reviewer 50 Questions Ver 1Документ5 страницDay 3 Reviewer 50 Questions Ver 1Darwin EugenioОценок пока нет
- Multiple ChoiceДокумент121 страницаMultiple ChoicecathyОценок пока нет
- 950/1, 954/1 STPM (Trial) 2012: Mathematics S Mathematics TДокумент32 страницы950/1, 954/1 STPM (Trial) 2012: Mathematics S Mathematics TNormal MdiОценок пока нет
- ActionДокумент83 страницыActionprabs20069178Оценок пока нет
- Ial Maths Pure 4 CR5Документ10 страницIal Maths Pure 4 CR5nasehaОценок пока нет
- 11 Secant AnglesДокумент4 страницы11 Secant AnglesTravis TothОценок пока нет
- MAT051 Midterm To FinalДокумент38 страницMAT051 Midterm To FinalJulpae PirisОценок пока нет
- Application of DerivativesДокумент53 страницыApplication of DerivativesTushar PalОценок пока нет
- Design & Analysis of Shell Structures - M. FarshadДокумент422 страницыDesign & Analysis of Shell Structures - M. FarshadAamirShabbir100% (9)
- Route TD For All Student Learner's Highway EngineeringДокумент25 страницRoute TD For All Student Learner's Highway Engineeringkrishy19sОценок пока нет
- Calc 1 Practice Problems Midterm ExamДокумент9 страницCalc 1 Practice Problems Midterm ExamDestiny AllenОценок пока нет
- AWS90 Structural Nonlin Ch03 ContactДокумент78 страницAWS90 Structural Nonlin Ch03 ContactPatrick SilvaОценок пока нет
- M323 Exam 3 Prac KeyДокумент7 страницM323 Exam 3 Prac Keyikechukwujoel8Оценок пока нет
- P1 - Algebra: Past Papers QuestionsДокумент50 страницP1 - Algebra: Past Papers QuestionsJumanaAsimОценок пока нет
- Parametric CurvesДокумент8 страницParametric Curvessiva_ksrОценок пока нет
- 3 Curvilinear MotionДокумент9 страниц3 Curvilinear MotionPercival ArcherОценок пока нет
- Abhinay Muthoo-Bargaining Theory With Applications (1999)Документ373 страницыAbhinay Muthoo-Bargaining Theory With Applications (1999)D. KОценок пока нет
- MATH MELCs Grade 10Документ3 страницыMATH MELCs Grade 10Jaylord Tayum100% (3)