Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Equipments
Загружено:
Muhammad Arshad Jawad0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
30 просмотров4 страницыSubstation Equipments
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документSubstation Equipments
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
30 просмотров4 страницыEquipments
Загружено:
Muhammad Arshad JawadSubstation Equipments
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 4
SURGE ARRESTOR:
A protective device for limiting surge voltages by
discharging or bypassing surge current, and it also
prevents the flow of follow current while remaining
capable of repeating these functions.
CAPACTIOR VOLTAGE TRANSFORMER:
Both coupling capacitors and coupling capacitor voltage
Transformers are single-phase devices that utilize one or more
capacitor units, usually mounted on a base, to Couple a
communication signal to a high voltage Power line. Coupling
capacitors (CCs) are used in conjunction with Line Traps and line
tuners for power line carrier (PLC) communication over high-
voltage power lines.
A CC with an electromagnetic unit is called a Coupling Capacitor
Voltage Transformer (CCVT). CCVTs can be used to supply
voltage for metering and protection applications similar to a
voltage transformer.
LINE TRAP:
Line trap also is known as Wave trap. Trapping the high frequency
communication signals sent on the line from the remote substation and
diverting them to the telecom/teleprotection panel in the substation
control room (through coupling capacitor and LMU)
The Line trap offers high impedance to the high frequency
communication signals thus obstructs the flow of these signals in to the
substation busbars. If there were not to be there, then signal loss is
more and communication will be ineffective/probably impossible
Disconnecting Switch:
Isolators are provided for isolation from live parts for the purpose of
maintenance. Isolators are located at either side of the circuit breaker.
Isolators are operated under no load. Isolator does not have any rating
for current breaking or current making. Isolators are interlocked with
circuit breakers
Types of Isolators are
1. Central rotating, horizontal swing
2. Centre-Break
3. Vertical swing
4. Pantograph type
Circuit Breaker:
Circuit Breaker is used for Switching during normal and abnormal
operating conditions. It is used to interrupt the short circuit currents. It is
used to interrupt short circuit currents. Circuit Breaker operations
include.
1. Closing
2. Opening
3. Auto reclosing
Circuit Breaker is located near every switching point and also located at
the both ends of every protection zone.
Current Transformer:
Current transformers are used for Stepping down current for
measurement, protection and control. Current transformers are of
two types
1. Protective CT
2. Measuring CT
Current transformers can be included in two general categories:
metering service and relay service. As a rule, current transformers
designed for metering service should not be used for relay applications or system protection.
Likewise, current transformers designed for relay service should not be used for high accuracy
metering applications.
Voltage Transformer:
Voltage transformers are used to step down the voltage for
measurement, protection and control. Voltage transformers are of two
types.
1. Electromagnetic type
2. Capacitive VT located on the feeder side of the Circuit Breaker.
Power Transformers:
Power Transformers are used to step up or step down a.c.
voltages and to transfer electrical power from one voltage level to
another. Tap changers are used for voltage control.
Auto Transformer:
Auto transformer is kind of electrical transformer where
primary and secondary shares same common single
winding. In Substation where transfer ratio is less the 2 it is
preferable to use autotransformer because it is less
expensive then the two winding transformer.
Bus Bar:
Various incoming and outgoing circuits are connected to busbars. Busbars receive power from
incoming circuits and deliver power to outgoing circuits.
One and Half breaker Busbar scheme:
Two circuits are connected between the three circuit breakers.
Hence one and half breaker name was coined for this type of
arrangement. Under normal operating conditions all the
breakers are closed and both the busbars are energized.
Advantages:
1. Most flexible operation possible
2. High reliability
3. Bus failure will not remove any circuit from service
Disadvantages:
1. High cost
2. Relaying is somewhat complicated since the middle breaker must responsible for both the
circuits on either direction and should operate
Double bus & single breaker Scheme:
Normally in double main busbar scheme each circuit is connected to
both the buses. In double main busbar arrangement one or two
breakers can be provided for each circuit. Double main busbar and
double breaker scheme provides high reliability in the case of fault
or outage of one of the breaker.
Advantages:
1. Any circuit can be taken out of circuit for maintenance
2. Flexibility in connecting the feeder circuit to either of the busbars
Disadvantages:
1. Most expensive
2. Loose circuits connected to busbar when fault occurs on the busbar
Вам также может понравиться
- 500 KV Foundation Performa FrontДокумент1 страница500 KV Foundation Performa FrontMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- 500 KV Foundation Performa FrontДокумент1 страница500 KV Foundation Performa FrontMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
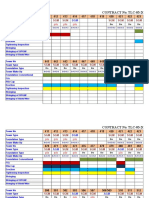
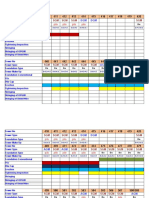
- CONTRACT No. TLC-03-2017 Lot-II: SGM SGM SGM SGM SGM SGM SGMДокумент8 страницCONTRACT No. TLC-03-2017 Lot-II: SGM SGM SGM SGM SGM SGM SGMMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- DPR TLC-14-2020 (21-09-2021)Документ1 страницаDPR TLC-14-2020 (21-09-2021)Muhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- 500 KV Foundation Performa BackДокумент1 страница500 KV Foundation Performa BackMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- TLC-14-2020 TLC-14-2020: (LOT-III) M/s Potential Engineers (LOT-II) M/s NPCC-Mecons (JV)Документ1 страницаTLC-14-2020 TLC-14-2020: (LOT-III) M/s Potential Engineers (LOT-II) M/s NPCC-Mecons (JV)Muhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- DPR September 20, 2021Документ1 страницаDPR September 20, 2021Muhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- CONTRACT No. TLC-03-2017 Lot-II: SGM SGM SGM SGM SGMДокумент11 страницCONTRACT No. TLC-03-2017 Lot-II: SGM SGM SGM SGM SGMMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- Scholorship FormДокумент2 страницыScholorship FormMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- Received Upto Nov & Dec-16 (SC&DC) (Sep-27-17)Документ3 страницыReceived Upto Nov & Dec-16 (SC&DC) (Sep-27-17)Muhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- ProgressДокумент18 страницProgressMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- IEEEP Membership FormДокумент2 страницыIEEEP Membership FormMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- ADB Progress Brief Dated 19-2-2019Документ6 страницADB Progress Brief Dated 19-2-2019Muhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
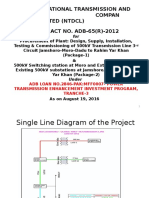
- ADB-65 (R) - 2012 Presentation As On Aug 19, 2016Документ38 страницADB-65 (R) - 2012 Presentation As On Aug 19, 2016Muhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- New LahoreДокумент2 страницыNew LahoreMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
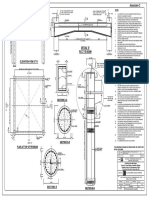
- Annexure-2-Single Pile Tie BeamДокумент1 страницаAnnexure-2-Single Pile Tie BeamMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- Adb 65r MPR March 2017Документ95 страницAdb 65r MPR March 2017Muhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- Alfalah Car Financing NMBRДокумент1 страницаAlfalah Car Financing NMBRMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- Advance Power System QualityTerm PaperДокумент8 страницAdvance Power System QualityTerm PaperMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- Asce Manual 74Документ5 страницAsce Manual 74Muhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- Leave Application Code No: Form: Casual Sick Earned DaysДокумент4 страницыLeave Application Code No: Form: Casual Sick Earned DaysMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- Wire CalculationsДокумент2 страницыWire CalculationsMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- Advance Power System QualityTerm Paper (Ph.d-009)Документ8 страницAdvance Power System QualityTerm Paper (Ph.d-009)Muhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- The University: Student Enrolled in Ms ProgrammeДокумент1 страницаThe University: Student Enrolled in Ms ProgrammeMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- List Sub ConДокумент1 страницаList Sub ConMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- Overhead LinesДокумент20 страницOverhead LinesMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- Application Form Procees-Prodaug14Документ1 страницаApplication Form Procees-Prodaug14محمد فصیح آفتابОценок пока нет
- Assig AssigДокумент1 страницаAssig AssigMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- Generated by CamscannerДокумент1 страницаGenerated by CamscannerMuhammad Arshad JawadОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- 1994 Impreza ECM PinoutДокумент2 страницы1994 Impreza ECM Pinoutguillermo6661Оценок пока нет
- EnduraLED - Bulkhead - Philips PDFДокумент2 страницыEnduraLED - Bulkhead - Philips PDFPaul JosephОценок пока нет
- ABB - Motor-StartersДокумент10 страницABB - Motor-StartersMac WaseemОценок пока нет
- Rebar Estimation Cover Sheet: Hampstead Heath Apartments Project NoДокумент92 страницыRebar Estimation Cover Sheet: Hampstead Heath Apartments Project NoDhatchina MoorthyОценок пока нет
- P4095 Faltplan Showroom enДокумент1 страницаP4095 Faltplan Showroom enwal1547Оценок пока нет
- 6m26 BaudouinДокумент149 страниц6m26 BaudouinMick VОценок пока нет
- Caterpillar CB 534D Serie FGH Sist. ElectricoДокумент6 страницCaterpillar CB 534D Serie FGH Sist. ElectricoCarlos Irabedra100% (1)
- Under & Over Current RelayДокумент2 страницыUnder & Over Current RelayRenghat RumahorboОценок пока нет
- AC Compressor Alternator PulleyДокумент3 страницыAC Compressor Alternator PulleyWayneОценок пока нет
- Toshiba Machine Co., Ltd. Die Cast Machine Engineering DivДокумент25 страницToshiba Machine Co., Ltd. Die Cast Machine Engineering DivmikeОценок пока нет
- Construction ArchitectureДокумент6 страницConstruction ArchitecturePranshu LondaseОценок пока нет
- LTR No.137 Water ReportДокумент2 страницыLTR No.137 Water ReportLACHMOLI BRIDGE NO. 8Оценок пока нет
- Chapter2 PDFДокумент18 страницChapter2 PDFshaik jaheerОценок пока нет
- Fa 249ex Ss SCH 01 - r1 Fa249ex Ss Marine Lantern SCH Sheet 3Документ1 страницаFa 249ex Ss SCH 01 - r1 Fa249ex Ss Marine Lantern SCH Sheet 3Omkumar KS100% (1)
- Window and Door Parts EstimationДокумент117 страницWindow and Door Parts EstimationAllen EspeletaОценок пока нет
- Capital Controls Series 2000Документ4 страницыCapital Controls Series 2000Bùi Công AnhОценок пока нет
- PNPN and Other Devices: Robert BoylestadДокумент53 страницыPNPN and Other Devices: Robert BoylestadTe Ng0% (1)
- 00054443020-Golf Vento - Basic Equipment From August 1995Документ484 страницы00054443020-Golf Vento - Basic Equipment From August 1995Bruno RedonОценок пока нет
- HGM 420Документ42 страницыHGM 420last730100% (1)
- Insert Changeable Flat Ratchet Screwdriver: Tmdb8Документ1 страницаInsert Changeable Flat Ratchet Screwdriver: Tmdb8AkmalОценок пока нет
- Diagrama Electrico 416FДокумент34 страницыDiagrama Electrico 416FPlstina RamsОценок пока нет
- Ac Machinery FormulasДокумент4 страницыAc Machinery FormulasNhilОценок пока нет
- WH21 Electric Water Heater Time Switch: WarningДокумент2 страницыWH21 Electric Water Heater Time Switch: WarningReinerio Praxedes Castillo CespedesОценок пока нет
- AC MotorsДокумент33 страницыAC MotorsAjitha SaktheesОценок пока нет
- STR BAJA 13102023 - Malika Kaylani - I0121090Документ7 страницSTR BAJA 13102023 - Malika Kaylani - I0121090Malika KaylaniОценок пока нет
- I. Lighting: Ambient Lighting (General Lighting)Документ11 страницI. Lighting: Ambient Lighting (General Lighting)Nikka TadejaОценок пока нет
- CB - Routine TestsДокумент15 страницCB - Routine Testsrpshvju100% (1)
- Eck - Engine Control System (k9k)Документ405 страницEck - Engine Control System (k9k)Eliecer Bayona100% (7)
- 40XMH'12 40XW'12: (67TN) (67TM)Документ51 страница40XMH'12 40XW'12: (67TN) (67TM)Carlos NetoОценок пока нет