Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Frequently Asked Questions About The 2000 CDC Growth Charts
Загружено:
Montu Chakma0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
19 просмотров3 страницыCDC growth chart 2000-FAQ
Оригинальное название
Frequently Asked Questions About the 2000 CDC Growth Charts
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документCDC growth chart 2000-FAQ
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
19 просмотров3 страницыFrequently Asked Questions About The 2000 CDC Growth Charts
Загружено:
Montu ChakmaCDC growth chart 2000-FAQ
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
Frequently Asked Questions About the
2000 CDC Growth Charts
How can I get copies of the growth charts?
The clinical charts are available from the Clinical Growth Charts page and
can be downloaded and copied. PowerPoint files of the growth charts,
which can be modified with different logos, are also available on
the PowerPoint Presentations of the Clinical 2000 CDC Growth Charts
page. Growth charts formatted for the Women, Infants, and Children
(WIC) program are available from the WIC website . In addition, The
American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) is selling copies of the growth
charts and some pharmaceutical companies are distributing them.
What is a percentile?
Percentiles are the most commonly used clinical indicator to assess the
size and growth patterns of individual children in the United States.
Percentiles rank the position of an individual by indicating what percent of
the reference population the individual would equal or exceed. For
example, on the weight-for-age growth charts, a 5-year-old girl whose
weight is at the 25th percentile, weighs the same or more than 25
percent of the reference population of 5-year-old girls, and weighs less
than 75 percent of the 5-year-old girls in the reference population.
What is a z-score?
A z-score is the deviation of the value for an individual from the mean
value of the reference population divided by the standard deviation for
the reference population. Because z-scores have a direct relationship with
percentiles, a conversion can occur in either direction using a standard
normal distribution table. Therefore, for every z-score there is a
corresponding percentile and vice versa.
My child is at the 5th percentile on a chart, what should I do?
If you are concerned about your childs growth, talk with your child's
health care provider.
What growth charts are appropriate to use with exclusively
breastfed babies?
In the United States, the WHO growth standard charts are recommended
to use with both breastfed and formula fed infants and children from birth
to 2 years of age (CDC, 2010). The WHO growth charts reflect growth
patterns among children who were predominantly breastfed for at least 4
months and still breastfeeding at 12 months. These charts describe the
growth of healthy children living in well-supported environments in sites
in six countries throughout the world including the United States. The
WHO growth charts show how infants and children should grow rather
than simply how they do grow in a certain time and place and are
therefore recommended for all infants (Dewey, 2004; WHO Multicentre
Growth Reference Study Group, 2006).
The WHO growth charts establish the growth of the breastfed infant as
the norm for growth. Healthy breastfed infants typically put on weight
more slowly than formula fed infants in the first year of life (Dewey,
1998). Formula fed infants gain weight more rapidly after about 3 months
of age. Differences in weight patterns continue even after complementary
foods are introduced (Dewey, 1998).
What charts should be used for special populations?
The CDC has not evaluated the use of the WHO growth charts in
premature or very low-birth weight infants. The 2000 CDC growth charts
for the United States include data on low birth weight infants but do not
include data on very low birth weight infants (VLBW; less than 1,500
grams). Alternate charts are available to assess the growth of VLBW
infants. The most recent charts are those developed from data collected
in the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
Neonatal Research Network Centers (Ehrenkranz, 1999). These charts
extend to about 120 days uncorrected postnatal age or until a body
weight of 2,000 grams is reached. A specific growth reference available
for VLBW infants is the Infant Health and Development Program (IHDP)
reference (Guo, 1996; Guo, 1997; Roche, 1997). The IHDP growth charts
are an option for assessing the growth of VLBW infants from an age
corrected for gestation of 40 weeks to 36 months. However, a limitation
of the IHDP charts is that they are based on data collected in 1985,
before current medical and nutritional care practices were being used.
See the training module: Growth Charts for Children with Special Health
Care Needs for information on assessing growthof low birth weight and
premature infants.
A variety of health conditions affect growth status and there are
specialized charts that may be considered for use with children affected
by these conditions. See the training module:Growth Charts for Children
with Special Health Care Needs for a discussion of these charts. These
specialized growth charts provide useful growth references, but may have
some limitations. Generally, they were developed from relatively small
homogeneous samples and data used to develop the charts may have
been obtained from inconsistent measuring techniques. For example, in
some cases, chart reviews were used to collect data; in other cases, the
measurement techniques were not clearly defined. In most cases, Body
Mass Index (BMI)-for-age charts are not available for special conditions
and have not been validated to use with children whose body composition
might differ from that of typical children. For children aged 2 to 20 years,
the CDC BMI-for-age growth charts would provide a useful reference to
monitor weight in relation to stature.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Use of the World Health
Organization and CDC growth charts for children aged 0-59 months in the
United States. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2010;59(RR-9);1-
15. http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr5909a1.htm.
Accessed November 26, 2012.
Dewey KG, Cohen RJ, Nommsen-Rivers LA, Heinig MJ, for the WHO Multicenter Growth Reference
Study Group. Implementation for the WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study in the United
States. Food Nutr Bull. 2004;25(suppl1):S84-S89.
WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group. Assessment of differences in linear growth
among populations in the WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study. Acta
Paediatr Suppl.2006;450:56-65.
Dewey KG. Growth characteristics of breastfed compared to formula-fed infants. Biol
Neonate.1998;74(2):94-105.
Ehrenkranz RA, Younes N, Lemons JA, Fanaroff AA, Donovan EF, Wright LL, Katsikiotis V, Tyson JE,
Oh W, Shankaran S, Bauer CR, Korones SB, Stoll BJ, Stevenson DK, Papile L. Longitudinal growth
of hospitalized very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 1999;104:280-289.
Guo SS, Wholihan K, Roche AF, Chumlea WC, Casey PH. Weight-for-length reference data for
preterm, low birth weight infants. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1996;150:964-970.
Guo SS, Roche AF, Chumlea WC, Casey PH, Moore WM. Growth in weight, recumbent length, and
head circumference for preterm low-birthweight infants during the first three years of life using
gestation-adjusted ages. Early Hum Dev. 1997;47:305-325.
Roche AF, Guo SS, Wholihan K, Casey PH. Reference data for head circumference-for-length in
preterm low-birth-weight infants. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 19
Вам также может понравиться
- Tripura Gazette: Extraordinary IssueДокумент39 страницTripura Gazette: Extraordinary IssueMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Scrub TyphusДокумент2 страницыScrub TyphusMontu Chakma100% (1)
- Classification of Raga by Time of The DayДокумент4 страницыClassification of Raga by Time of The DayMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- DNB 2013 JuneДокумент1 страницаDNB 2013 JuneMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Seven CCHDsДокумент1 страницаSeven CCHDsMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- A Newly Identified Protein Could Be A New Drug Target To Control The Toxoplasmosis ParasiteДокумент1 страницаA Newly Identified Protein Could Be A New Drug Target To Control The Toxoplasmosis ParasiteMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Café Au Lait SpotsДокумент1 страницаCafé Au Lait SpotsMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- International NewsДокумент1 страницаInternational NewsMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Newborn Screening - Dr. T. GhoshДокумент32 страницыNewborn Screening - Dr. T. GhoshMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Department of Paediatrics Agmc & GBP Hospital: PG Academic ScheduleДокумент1 страницаDepartment of Paediatrics Agmc & GBP Hospital: PG Academic ScheduleMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Agartala Medical College Pediatrics Patient RecordДокумент1 страницаAgartala Medical College Pediatrics Patient RecordMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Drugs of ChoiceДокумент1 страницаDrugs of ChoiceMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Bangla ConsentДокумент1 страницаBangla ConsentMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Emergency DrugsДокумент2 страницыEmergency DrugsMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Case Record FormДокумент5 страницCase Record FormMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Comparative efficacy of Quinine and ArtesunateДокумент4 страницыComparative efficacy of Quinine and ArtesunateMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Lumber Puncture NeedleДокумент2 страницыLumber Puncture NeedleMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Materials and Methods-ProtocolДокумент5 страницMaterials and Methods-ProtocolMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Antiviral DrugsДокумент1 страницаAntiviral DrugsMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- Important ValuesДокумент1 страницаImportant ValuesMontu ChakmaОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Standard Treatment: Guidelines 2022Документ10 страницStandard Treatment: Guidelines 2022LijoeliyasОценок пока нет
- Summer Eval IДокумент4 страницыSummer Eval Iapi-632827798Оценок пока нет
- Anna Giuliani - Assisted Peritoneal Dialysis - Ren Replace Ther 2022Документ7 страницAnna Giuliani - Assisted Peritoneal Dialysis - Ren Replace Ther 2022francescoОценок пока нет
- PharmacistДокумент2 страницыPharmacistcrisjavaОценок пока нет
- OphthalmologyДокумент69 страницOphthalmologyjatavОценок пока нет
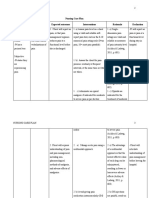
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Expected Outcomes Interventions Rationale EvaluationДокумент7 страницNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Expected Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluationلمى الشهريОценок пока нет
- Ido PPT 2020Документ47 страницIdo PPT 2020Vikas SinhmarОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Health Information Systems (HISДокумент36 страницIntroduction to Health Information Systems (HISmariel santosОценок пока нет
- Sas 2 HaДокумент1 страницаSas 2 HaKristinelou Marie N. ReynaОценок пока нет
- Mental health impacts of COVID-19 on childrenДокумент3 страницыMental health impacts of COVID-19 on childrenMj RagucosОценок пока нет
- Dispensing Medications During Off-Hours StrategiesДокумент14 страницDispensing Medications During Off-Hours StrategiesHamza Ali100% (2)
- Perioperative Preparation and Management: Pre-OperativeДокумент14 страницPerioperative Preparation and Management: Pre-OperativeRed StohlОценок пока нет
- HRM Case Study-PatelДокумент11 страницHRM Case Study-PatelHumaira ShafiqОценок пока нет
- OPAT WebinarДокумент2 страницыOPAT Webinarshafiq0abdullahОценок пока нет
- Resume Aug2014Документ1 страницаResume Aug2014api-260643635Оценок пока нет
- NPCDCSДокумент3 страницыNPCDCSPankaj KhatriОценок пока нет
- Therapeutic Drug Monitoring-FinalДокумент49 страницTherapeutic Drug Monitoring-FinalSaiesh PhaldesaiОценок пока нет
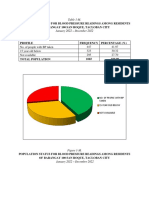
- Community Diagnosis HPN BmiДокумент10 страницCommunity Diagnosis HPN BmiFiel Andrei BorataОценок пока нет
- Pengetahuan Ibu Tentang Mobilisasi Dini Pasca Persalinan Normal Pervaginam Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Labuhan Rasoki Kecamatan Padangsidimpuan Tenggara Tahun 2018Документ6 страницPengetahuan Ibu Tentang Mobilisasi Dini Pasca Persalinan Normal Pervaginam Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Labuhan Rasoki Kecamatan Padangsidimpuan Tenggara Tahun 2018Geuman ChajgoОценок пока нет
- OPD Schedule of Faculty of Dental Sciences BHUДокумент1 страницаOPD Schedule of Faculty of Dental Sciences BHUG HhОценок пока нет
- FCD Ethical and Legal IssuesДокумент6 страницFCD Ethical and Legal Issuesnicholas51292Оценок пока нет
- Peer Support Workers Theory and PracticeДокумент16 страницPeer Support Workers Theory and PracticeSimple FaceОценок пока нет
- Full Version in PDF (Pashto/Dari & English) : DVD University Author Name of The Book No I. P.C.BДокумент4 страницыFull Version in PDF (Pashto/Dari & English) : DVD University Author Name of The Book No I. P.C.BDrMohib Habibzai100% (1)
- Nurse Patient Ratio PDFДокумент7 страницNurse Patient Ratio PDFSafrina WaldiniОценок пока нет
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesДокумент11 страницDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesRogen VigilОценок пока нет
- 1883 - 17 E GamesДокумент22 страницы1883 - 17 E GamesMohamed Rikarz Ahamed Rikarz100% (1)
- 2019 Guide For ImmunizationДокумент195 страниц2019 Guide For ImmunizationReigner paul DavidОценок пока нет
- IGI Insurance Provides Comprehensive Healthcare SolutionsДокумент6 страницIGI Insurance Provides Comprehensive Healthcare SolutionsadnanakhtarhrpОценок пока нет
- Grade 10-Health-Quarter 1 Lesson 3Документ40 страницGrade 10-Health-Quarter 1 Lesson 3eric manuevo100% (1)
- PGI Opd at GlanceДокумент18 страницPGI Opd at Glancevirk_70100% (2)