Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
System Modeling
Загружено:
kaladevi21Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
System Modeling
Загружено:
kaladevi21Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 1
Question 1
System planning can be carried out in number of ways SWOT (Strengths,
Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats), VCM (Value Chain Model), BPR (Business
Process Reengineering) and ISA (Information System Architecture). Discuss any of the
TWO (2) ways mentioned above.
1.1 System Planning
System planning also called as system analysis is a test and appraising of an operation
or task in order to identify and implement more efficient methods, usually through the use of
computers. Systems planning can be categories into three main areas which is the production
of a statement of objectives, determination of the methods of best achieving these objectives
in a cost-effective and efficient way and the preparation of a feasibility study.
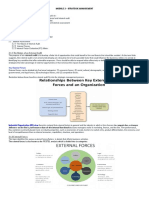
1.2 SWOT Analysis
SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) the Strengths (S) and
Weaknesses (W) are considered as an internal factors while Opportunities (O) and Threats
(T) are considered as an external factors. The purpose of SWOT Analysis identify the
strategies that will create a firm specific business model that will best align an organizations
resources and capabilities to the requirements of the environment in which the firm operates.
In simple words, it is the foundation for evaluating the internal potential and limitations and
the probable or likely opportunities and threats from the external environment. Understanding
of SWOT can study of the environment in which the firm operates helps in forecasting or
predicting the changing trends. Besides that, it is helps in the decision-making process of an
organization.
Environmental Scanning
Internal Analysis
Strengths
Weaknesses
External Analysis
Opportunities
Threats
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 2
The first factor from SWOT Analysis is Strength. The Strength competence us to
achieve the organizations mission. Strength can be either tangible or intangible. These are
what we learned in or what we have expertise in, the traits and qualities the employees
possess either individually and as a team and the distinct features that give the organization
its firmness. Strengths are the beneficial or capabilities of an organization, which includes
human competencies, process capabilities, financial resources, products and services,
customer goodwill and brand loyalty. Examples of organizational strengths are huge financial
resources, broad product line, no debt and committed employees.
The second is Weaknesses. It is qualities that prevent us from achieving our mission
and our full potential. These weaknesses deteriorate influences on the organizational success
and growth. It is a factor which does not meet the standards we feel they should meet.
Weaknesses in an organization may be depreciating machinery, narrow product range, poor
decision-making, insufficient research and development facilities. Weaknesses are
controllable and must be minimized and eliminated. For instance, to overcome obsolete
machinery, new machinery can be purchased. Other examples of organizational weaknesses
are high employee turnover, huge debts, narrow product range, complex decision making
process and large wastage of raw materials.
The next is Opportunities. Opportunities are presented by the environment within
which an organization operates. These arise when an organization can take benefit of
conditions in its environment to plan and execute strategies that enable it to become more
profitable. Organizations can gain competitive advantage by making use of opportunities.
Organization should be careful and recognize the opportunities and grasp whenever it arises.
Selecting the targets that will best serve the clients while getting desired results is a difficult
task. Opportunities may arise from market, competition, industry or government and
technology. Increasing demand for telecommunications accompanied by deregulation is a
great opportunity for new firms to enter telecom sector and compete with existing firms for
revenue.
And the last is Threats. Threats appear when conditions in external environment at the
risk reliability and profitability of the organizations business. It compounds the vulnerability
when they relate to the weaknesses. Threats are uncontrollable. When a threat comes, the
stability and survival can be at stake. Examples of threats are unrest among employees, ever
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 3
changing technology and increase competition leading to excess capacity, price wars and
reducing industry profits.
External
SWOT Analysis is a strategy formulation and selection. It is strong tool, but it
involves a great subjective element. It is best when used as a guide, and not as a prescription.
Successful businesses build on their strengths, correct their weakness and protect against
internal weaknesses and external threats. It is also a view on their overall business
environment and recognizes and exploits new opportunities faster than its competitors.
SWOT Analysis helps in strategic planning in various ways which are:
Opportunities Threats
Strength
How do you leverage
your strength to benefit
from opportunities?
How do you use your
strength to minimize the
impact of threats?
Weaknesses
How do you ensure your
weaknesses will not stop
you from opportunities?
How will you fix
weaknesses that can
make threats have a real
impact?
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 4
It is a source of information for strategic planning.
Builds organizations strengths.
Reverse its weaknesses.
Maximize its response to opportunities.
Overcome organizations threats.
It helps in identifying core competencies of the firm.
It helps in setting of objectives for strategic planning.
It helps in knowing past, present and future so that by using past and current data, to
make correction for future plans.
It provide information that helps in synchronizing the firms resources and
capabilities with the competitive environment in which the firm operates.
1.3 The Value Chain
The term value chain is to understand the activities through which a firm develop a
competitive advantage and create shareholder value, it is useful to separate the business
system into a series of value-generating activities. The value chain can be used or applied for
the process views of organisations, the method of looking at a product manufacturing (or
service) organisation as a system, develop of subsystems each with inputs, transformation
processes and outputs. Inputs, transformation processes, and outputs involve the possession
and destruction of resources which is labour, money, materials, buildings, land, equipment,
administration and management.
Most organisations engage thousands of activities in the process of converting inputs to
outputs. These activities can be classified generally as either primary or support activities that
all businesses must undertake in some form.
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 5
According to Porter (1985), the primary activities are:
Inbound Logistics.
It is involve relationships with suppliers and include all the activities required to receive,
store, and disseminate inputs.
Operations.
All of these activities required to transform inputs into outputs (products and services).
Outbound Logistics.
These include all the activities required to collect, store, and separate the output.
Marketing and Sales.
In these part activities inform buyers about products and services, lead buyers to purchase
them, and to assist the progress o
Service.
These includes all the activities required to keep the product or service working to
accomplish the purpose for the buyer after it is sold and delivered.
Secondary activities are:
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 6
Firm Infrastructure.
This part serves the company's needs and ties its various parts together; it consists of
functions or departments such as accounting, finance, legal, public affairs, government
relations, quality assurance and general management.
Human Resource Management.
These consists of all activities involved in recruiting, hiring, training, developing,
compensating and if necessary dismissing or laying off personnel.
Technological Development.
It is relation to the equipment, hardware, software, procedures and technical knowledge
brought to bear in the firm's transformation of inputs into the outputs.
Procurement.
It is a gaining possession of inputs, or resources, for the firm.
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 7
Question 2
The School is considering a new system that will speed up the registration process. As a
system analyst, you asked to develop a plan for fact-finding.
a. List all the possible techniques that you might use.
The possible techniques that can use to develop a plan for fact-finding:
Interviewing
Interviewing is the technique that used the collection of data by asking targeted
groups questions and following up or probing their answers. It also an important
technique as interviewing involving interactive processes.
Observation
Observation is involving the active acquisition of information. It includes the primary
source data collection technique. Observation also the evaluation of the current
system operations that will verify the project statements and use for documentation
references
Research
Research is a systematic technique to investigate the project info and study the
collected data materials and sources deliver the project facts and find the new
solution. The research involved the finding of project background, data materials
collection and analysis and etc.
Document review
Document review is the process where every individual to the project sorts through
and analyzes the project document and collected data to identifying which are
sensitive or otherwise relevant to the case. Document review also provides the better
understanding about the project and work it supposed to works.
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 8
Surveys and Questionnaires
Survey is the technique to examine the project as to the condition, situation or value.
It also used to collect data for the project analysis of aspect of area in project by
query. It involves a question or set of questions that being developed in order to
collect information to measure and analysis.
b. Describe an advantage for each technique.
The advantage for the above techniques is:
Interviewing
The advantages of the interviewing technique is providing more accurate data
collection compared to other methods as it is involve face-to-face interaction between
interviewer and interviewee. So it is good and easy technique to getting information
about complex, emotionally laden subjects.
Observation
The observation technique allows the development of new patterns and theories as
multiple observations are conducted with different times and locations, the observer is
able to detect certain patterns of behavior across participants. Observation provides
chances for the observer to discover what is really happening in observing the project
or system.
Research
The advantage of research is to provide a systematic and clear data collection and
analysis where it provide each aspect in detail and clear information overall about the
project.
Document review
The advantage of document review is the information contained in the extant
documents is independently verifiable and the process can be done independently
without needing to solicit extensive input from other sources. It is a less expensive
data collection technique.
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 9
Surveys and Questionnaires
Survey and questionnaires have its own separate advantage. Survey is an effective
method to collect information of a large number of people where it can be many
questions to ask over a given topic. Questionnaire also similar to survey as it is easily
and quickly to complete.
c. Suppose the development budget is tight. How might that affect the fact finding
process?
The effect of tight budget in development to the fact finding process is the fact finding
process could not able to use Joint Application Development (JAD) techniques because JAD
techniques requires an expensive budget. For example, conducting interview cause an
expensive cost which is include the preparing time, conducting cost, and documentation
preparation. From the above techniques, surveys and questionnaires used low cost budget in
conducting. It could be an effective technique to use when the budget is tight to the fact
finding process.
d. What are FIVE (5) important questions to use during fact-finding?
WHAT
Used as an interrogative expressing inquiry about the identity, nature, or value of an
object or matter. The "what" is the primary subject, the reason the information is
being gathered and presented and it might be stated in a title and in a purpose statement. The
"what" may need to be defined, a process that may comprise the remainder of a document.
Often used to ask for repetition of an utterance or part an utterance not properly heard or
understood.
WHO
What or which person or persons used as an interrogative used by speakers on all education
level and by many reputable writers, though disapproved by some grammarians, as the object
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 10
of a verb or a following.. The "who" may be part of the lead, and the user of the system or
developers.
HOW
How as an verb (introducing a direct or indirect question): How do you spell your last name?
Talking about the way that someone behaves or the way that something happens. It
description the step that involving. A considerable appetite for understanding how to do
something can be found across users. Sometimes effort focuses on the "what" when more
work might be devoted to explaining the "how."
WHEN
When a conjunction (connecting two clauses ): When he saw me, he waved . As a question
adverb (introducing a direct or indirect question): When shall we meet? When is process
performed? Could they be performed more efficiently elsewhere? Answering the "when"
indicates any time-sensitivity related to the "what." It may be part of an instruction regarding
the proper point at which an action should be taken. Sometimes it may be part of an
"If...then" scenario of conditional action.
WHERE
Where are operations being performed? Why? Where could they be performed? Could they
be performed more efficiently elsewhere? In or at what place, position or circumstance, what
particular respect, to what place point and for what source. The "where" describes a
geographical or physical location of importance to the "what." At times, the where may be
less important than other factors.
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 11
Question 3
What might be effect of using an inappropriate development methodology?
Software Development Methodology
A software development methodology or system development methodology in
software engineering is a framework that is used to structure, plan, and control the process of
developing an information system.
There are certain types of software development methodology. Which are waterfall
mode, spiral model, rational unified process, agile software development and so on.
Waterfall Model.
The waterfall model is a popular version of the systems development life cycle model
for software engineering. Often considered the classic approach to the systems development
life cycle, the waterfall model describes a development method that is rigid and linear.
Waterfall development has distinct goals for each phase of development where each phase is
completed for the next one is started and there is no turning back.
Disadvantage of waterfall, no early feedback (prototyping), slow to respond to
change, high cost for missed or unclear requirements, it is optimized for hardware, thereby
neglecting the essential characteristics of software.
In practice, waterfall development often falls short of expectations as it does not
embrace the inevitable changes and revisions that become necessary with most projects. Once
an application is in the testing stage, it is very difficult to go back and change something that
was not thought of in the concept stage. Alternatives to the waterfall model include joint
application development (JAD), rapid application development (RAD), sync and stabilize,
build and fix, and the spiral model.
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 12
Spiral Model
The spiral model is a software development process combining elements of both
design and prototyping-in-stages, in an effort to combine advantages of top-down and
bottom-up concepts. Also known as the spiral lifecycle model (or spiral development), it is a
systems development method (SDM) used in information technology (IT). This model of
development combines the features of the prototyping model and the waterfall model. The
spiral model is intended for large, expensive and complicated projects.
Spiral model help risks, risk analysis requires expertise and costly model. Used most
often in large projects and need constant review to stay on target. The interaction represented
as a cycle in spiral. Disadvantages of spiral model, costly model, risk analysis requires
expertise and doesnt work well for smaller project.
Rational Unified Process
There are two dimensional terms which are horizontal and vertical. Horizontal
dimensional represent successive phases of each iteration, such as inception, elaboration,
construction, transition. For vertical dimension represent process workflow and supporting
activities.
Disadvantages of RUP Software Development
The team members need to be expert in their field to develop software under this
methodology. The development process is too complex and disorganized. On cutting edge
projects which utilize new technology, the reuse of components will not be possible. Hence
the time saving one could have made will be impossible to fulfill.
Integration throughout the process of software development, in theory sounds a good
thing. But on particularly big projects with multiple development streams it will only add to
the confusion and cause more issues during the stages of testing
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 13
Agile Software Development
Key points of agility in software production are individuals and interactions over
processes and tools. Second, working software over comprehensive documentation. Third,
customer collaboration over contract negotiation. Lastly, responding to change over
following a plan.
The best known representatives:
i) Extreme programming (XP)
ii) Aspect Oriented Software Development
iii) Feature- Driven Development
iv) Lean Development
An iterative approach is attempting to minimize risk. It can performed in a highly
collaborative manner by self-organizing cross functional teams. Third, produces high quality
software in a cost effective and timely manner. In addition, capable to release new software at
the end of each iteration. Lastly, prefer work face-to-face and provide little written
documentation.
Disadvantages of Agile Methodology
In case of some software deliverables, especially the large ones, it is difficult to assess
the effort required at the beginning of the software development life cycle. There is lack of
emphasis on necessary designing and documentation. The project can easily get taken off
track if the customer representative is not clear what final outcome that they want. Only
senior programmers are capable of taking the kind of decisions required during the
development process. Hence it has no place for newbie programmers, unless combined with
experienced resources.
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 14
4.0 References
4.1 Question 1
http://www.businessballs.com/swotanalysisfreetemplate.htm
http://forlearn.jrc.ec.europa.eu/guide/4_methodology/meth_swot-analysis.htm
http://ctb.ku.edu/en/table-of-contents/assessment/assessing-community-needs-and-
resources/swot-analysis/main
http://www.strategicmanagementinsight.com/tools/value-chain-analysis.html
http://www.quickmba.com/strategy/value-chain/
http://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMC_10.htm
4.2 Question 2
http://www.cdc.gov/healthyyouth/evaluation/pdf/brief18.pdf
http://www.evalued.bcu.ac.uk/tutorial/4c.htm
Lusthaus C, Adrien M, and Anderson G, Carden F. Enhancing Organizational
Performance: A Toolbox for Self-Assessment. International Development Research
Centre. 1999. Available at http://www.idrc.ca/openebooks/870-8/#page_31.
Evaluation Handbook. W.K. Kellogg Foundation. January 1998. Available at
http://www.wkkf.org/Pubs/Tools/Evaluation/Pub770. Pdf
http://www.ask.com/question/what-is-observation
http://serve.mt.gov/wp-content/uploads/2010/02/Data-Collection-Methods-cbi.pdf
http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/questionnaire.html
http://www.chegg.com/homework-help/definitions/sampling-methods-31
http://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/sampling.asp
Finn, J., & Jacobson, M. (2008). Just Practice: A Social Justice Approach to Social
Work. Peosta, IL: Eddie bowers publishing.
Jacobson, M., Pruitt Chapin, K., & Rugeley, C. (2009). Toward Reconstructing
Poverty Knowledge: Addressing Food Insecurity through Grassroots Research Design
and Implementation. Journal of Poverty, 13(1), 1-19.
Russ-Eft, D., & Preskill, H. (2001). Evaluation in Organizations. New York: Basic
Books.
http://urp.ucsd.edu/for-students/what-is-research.html
5505TECYPC- SYSTEM MODELING AND REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS | 15
4.3 Questions 3
Segue Technologies Inc., 2014. SEGUE Technologies. [Online] Available at:
http://www.seguetech.com/blog/2013/07/05/waterfall-vs-agile-right-development-
methodology [Accessed 30 May 2014].
WebFinance,Inc., 2014. BusinessDictionary. [Online] Available at:
m.businessdictionary.com/ [Accessed 30 May 2014]
Levin, J.R. & Levin, M.E. (1993). Methodological problems in research on
academic retention programs for at-risk minority college students. Journal of
College Student Development, 34, 118-124
Вам также может понравиться
- SM Module 2Документ14 страницSM Module 2Nikhat ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Swot Def, Av PDFДокумент8 страницSwot Def, Av PDFCaty TudoseОценок пока нет
- Strategic Analysis and SWOT for Effective Decision Making (38Документ3 страницыStrategic Analysis and SWOT for Effective Decision Making (38Fathi FathuОценок пока нет
- Competitive Advantage and Internal Organizational AssessmentДокумент12 страницCompetitive Advantage and Internal Organizational AssessmentArturo González MaldonadoОценок пока нет
- Competitive Advantage and Internal Organizational AssessmentДокумент12 страницCompetitive Advantage and Internal Organizational AssessmentVish VicОценок пока нет
- S Wort ProjectДокумент37 страницS Wort ProjectPari SavlaОценок пока нет
- Module 2 - Strat ManДокумент4 страницыModule 2 - Strat ManElla MaeОценок пока нет
- Strategic Planning (Unit-2)Документ14 страницStrategic Planning (Unit-2)jalaja munirajuОценок пока нет
- SM 2 UnitДокумент27 страницSM 2 UnitANKUR CHOUDHARYОценок пока нет
- Unit 2Документ43 страницыUnit 2Atul KumarОценок пока нет
- Strategic Planning vs Strategic ManagementДокумент4 страницыStrategic Planning vs Strategic ManagementKashfmmОценок пока нет
- Pionner Internatinal CollegeДокумент6 страницPionner Internatinal CollegeRoy Kimathi MwikaОценок пока нет
- Internal Analysis and SWOT Analysis BenefitsДокумент11 страницInternal Analysis and SWOT Analysis BenefitsSagar PanditОценок пока нет
- SWOT Analysis - Definition, Advantages and LimitationsДокумент2 страницыSWOT Analysis - Definition, Advantages and LimitationsmackОценок пока нет
- Strategic EvaluationДокумент54 страницыStrategic EvaluationanviОценок пока нет
- NEO AXEL M. BMEC1 ASSIGNMENTSДокумент4 страницыNEO AXEL M. BMEC1 ASSIGNMENTSAxel NeoОценок пока нет
- Strategy ManagementДокумент17 страницStrategy Managementsubin100% (2)
- CMI (2011) - Performing A SWOT AnalysisДокумент5 страницCMI (2011) - Performing A SWOT AnalysisAhmed OladayoОценок пока нет
- Internal Assessment PDFДокумент18 страницInternal Assessment PDFAngela de MesaОценок пока нет
- Fme5 Written ReportДокумент7 страницFme5 Written ReportIngrid NavarroОценок пока нет
- SM Module 1Документ10 страницSM Module 1Jeevan ManjunathОценок пока нет
- SWOT AnalysisДокумент4 страницыSWOT AnalysisNishu KatiyarОценок пока нет
- Organizational Change and Innovation at British AirwaysДокумент12 страницOrganizational Change and Innovation at British AirwaysFEKEDE JOTEОценок пока нет
- Environmental Scanning and Strategic Planning ToolsДокумент5 страницEnvironmental Scanning and Strategic Planning ToolsMA. FRANCHESKA BALTAZARОценок пока нет
- 5 - Resource Audit and Strategic Advantage AnalysisДокумент16 страниц5 - Resource Audit and Strategic Advantage AnalysisMansi GoelОценок пока нет
- Planning: Foundation of Strategy: Reporter: Chiara Mari S. Manalo Subject: BA 108 - Business PolicyДокумент34 страницыPlanning: Foundation of Strategy: Reporter: Chiara Mari S. Manalo Subject: BA 108 - Business PolicyChiara Mari ManaloОценок пока нет
- Analyze Internal Environment Using Porter's Value Chain ModelДокумент30 страницAnalyze Internal Environment Using Porter's Value Chain Modeleliza ChaleОценок пока нет
- Analyzing Internal EnvironmentДокумент15 страницAnalyzing Internal EnvironmentjmhdeveОценок пока нет
- Strength Weakness Opportunity & Threat - SWOT AnalysisДокумент3 страницыStrength Weakness Opportunity & Threat - SWOT AnalysisSurabhi Kapadekar100% (3)
- Strategic Management Tools and TechniquesДокумент22 страницыStrategic Management Tools and TechniquesRaj ThakurОценок пока нет
- Environmental Analysis LessonДокумент10 страницEnvironmental Analysis LessonApril Joy DelacruzОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 The Internal Environment: Analysing Strategic CapabilityДокумент4 страницыUnit 5 The Internal Environment: Analysing Strategic CapabilityPiyal HossainОценок пока нет
- CS AssignmentДокумент14 страницCS AssignmentSamrin KhanОценок пока нет
- CHA2 - Strategic MGMTДокумент20 страницCHA2 - Strategic MGMTAbdoul Shakour NeyaОценок пока нет
- Seedrox Case Analysis ToolsДокумент21 страницаSeedrox Case Analysis ToolsMahua Adak MandalОценок пока нет
- Dissertation On Performance Management System PDFДокумент6 страницDissertation On Performance Management System PDFPayToWriteAPaperUKОценок пока нет
- Jomo Kenyatta University Strategic ManagementДокумент12 страницJomo Kenyatta University Strategic ManagementRedemptah Mutheu Mutua100% (1)
- Risk and Crisis Assig 2Документ11 страницRisk and Crisis Assig 2sanjevaanОценок пока нет
- Manage Opportunities with SWOT AnalysisДокумент11 страницManage Opportunities with SWOT AnalysissanjevaanОценок пока нет
- MM5012 Business Strategy: Emba 52 ClassДокумент11 страницMM5012 Business Strategy: Emba 52 ClassWahyudi AnugrahОценок пока нет
- IT and The Executive: Value Chain Analysis: Question: What Is A Strategy (1) ?Документ10 страницIT and The Executive: Value Chain Analysis: Question: What Is A Strategy (1) ?Kim SoonОценок пока нет
- Swot - STMДокумент3 страницыSwot - STMrajeeevaОценок пока нет
- Introduction of The Topic: SWOT Analysis (Alternatively SWOT Matrix) Is An Acronym For Strengths, WeaknessДокумент59 страницIntroduction of The Topic: SWOT Analysis (Alternatively SWOT Matrix) Is An Acronym For Strengths, WeaknessStarОценок пока нет
- Data Collection and DiagnosisДокумент20 страницData Collection and DiagnosisJohn AlbateraОценок пока нет
- ManagementДокумент7 страницManagementbeshahashenafe20Оценок пока нет
- SWOTДокумент3 страницыSWOTSunita BasakОценок пока нет
- KMBN 301 Strategic Management Unit 2Документ15 страницKMBN 301 Strategic Management Unit 2Ashish DubeyОценок пока нет
- Balaji Institute of It and Management Corporate Parag Kulkarni It StrategyДокумент90 страницBalaji Institute of It and Management Corporate Parag Kulkarni It StrategyvijaykumarОценок пока нет
- Strategic NotesДокумент17 страницStrategic NotesSaurabh KumarОценок пока нет
- OMBC101 - Principles and Practices of ManagementДокумент3 страницыOMBC101 - Principles and Practices of ManagementSuraj ApexОценок пока нет
- The External Assessment: Strategic Management Concepts & CasesДокумент17 страницThe External Assessment: Strategic Management Concepts & CasesUlfa Fadilatul UlaОценок пока нет
- Business Information AnalysisДокумент14 страницBusiness Information Analysisthomasjjj54321Оценок пока нет
- BME02.HM3C.Chapter 2.roa - GiovanniДокумент8 страницBME02.HM3C.Chapter 2.roa - Giovannigiovanni roaОценок пока нет
- UNIT-2: Environmental AppraisalДокумент13 страницUNIT-2: Environmental AppraisalVIVEK KUMAR SINGH 13Оценок пока нет
- StrategyДокумент2 страницыStrategyHạ Thu DươngОценок пока нет
- Comprehensive Written Report in Strategic ManagementДокумент7 страницComprehensive Written Report in Strategic ManagementFLORENCE DE CASTROОценок пока нет
- Environmental ScanningДокумент6 страницEnvironmental ScanningCookie BusinessОценок пока нет
- Risk Management Within An OrganizationДокумент46 страницRisk Management Within An OrganizationAnonymous MFh19TBОценок пока нет
- POM Module1 Unit4Документ10 страницPOM Module1 Unit4KATHLYN ROSE OCAYОценок пока нет
- The SWOT Analysis: A key tool for developing your business strategyОт EverandThe SWOT Analysis: A key tool for developing your business strategyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (10)
- NewzaloraДокумент10 страницNewzalorakaladevi21Оценок пока нет
- Harvard Referencingfull GuideДокумент18 страницHarvard Referencingfull Guidekaladevi21Оценок пока нет
- Sample of Formal ReportДокумент15 страницSample of Formal Reportkaladevi21Оценок пока нет
- FinanceДокумент13 страницFinancekaladevi21Оценок пока нет
- Supply ChainДокумент13 страницSupply Chainkaladevi21Оценок пока нет
- How To Make A Good Presentation v2Документ32 страницыHow To Make A Good Presentation v2kaladevi21Оценок пока нет
- Atm Sequence Diagram With StepsДокумент3 страницыAtm Sequence Diagram With Stepskaladevi21Оценок пока нет
- DocumentationДокумент43 страницыDocumentationkaladevi21Оценок пока нет
- Behaviour of Bem Female Student Toward Purchasing BeautyДокумент24 страницыBehaviour of Bem Female Student Toward Purchasing Beautykaladevi21Оценок пока нет
- FYP Proposal SampleДокумент19 страницFYP Proposal Samplekaladevi21Оценок пока нет
- Essay of CybercrimeДокумент3 страницыEssay of Cybercrimekaladevi21Оценок пока нет
- SDLC Waterfall ModelДокумент3 страницыSDLC Waterfall Modelkaladevi21Оценок пока нет
- Atlas Copco XAS 375 JD6Документ2 страницыAtlas Copco XAS 375 JD6EngTamerОценок пока нет
- Vocational Training ProgramДокумент6 страницVocational Training ProgramolabodeogunОценок пока нет
- Introduction to PowerMill Robot in Subtractive ManufacturingДокумент20 страницIntroduction to PowerMill Robot in Subtractive ManufacturingGauravОценок пока нет
- Slaa 116Документ21 страницаSlaa 116misaelrodrigoОценок пока нет
- Fishinger Road Transportation PlanДокумент89 страницFishinger Road Transportation Planapi-267404258Оценок пока нет
- PNG Standard Classification (Jan 09)Документ124 страницыPNG Standard Classification (Jan 09)Christian BarОценок пока нет
- Maa Rampyari Super Speciality Hospital Doc. No. E / Nabh / MRPSH / Fms / 1Документ4 страницыMaa Rampyari Super Speciality Hospital Doc. No. E / Nabh / MRPSH / Fms / 1tanishaОценок пока нет
- The 62443 Series OverviewДокумент4 страницыThe 62443 Series OverviewJuan RiveraОценок пока нет
- General Resume - NmuellerДокумент2 страницыGeneral Resume - Nmuellerapi-300000636Оценок пока нет
- ABB PS Range BrouchureДокумент12 страницABB PS Range BrouchureguigfsОценок пока нет
- Project Mercury A ChronologyДокумент255 страницProject Mercury A ChronologyBob Andrepont100% (1)
- Raees Ahmad: Total Experience: 5+ YearsДокумент2 страницыRaees Ahmad: Total Experience: 5+ YearsSamreenKhanОценок пока нет
- Anchor Bolt TolerancesДокумент3 страницыAnchor Bolt TolerancesRam BabuОценок пока нет
- BSNL Project Organization BehaviourДокумент32 страницыBSNL Project Organization BehaviourPrashantqmarОценок пока нет
- Lifting - Equipment - Matrix1 (Under Constrution)Документ1 страницаLifting - Equipment - Matrix1 (Under Constrution)PradeepОценок пока нет
- Blanking and PiercingДокумент5 страницBlanking and PiercingSatheesh Sekar100% (1)
- Cement Grinding OptimizationДокумент9 страницCement Grinding OptimizationFran JimenezОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 - ROLE of HUB PORT-note 4 CreditДокумент26 страницChapter 10 - ROLE of HUB PORT-note 4 CreditNishaliney NadarajanОценок пока нет
- Resume of Promila - MattuДокумент3 страницыResume of Promila - MattuKyle EmersonОценок пока нет
- Packing Instructions for Safe TransportДокумент50 страницPacking Instructions for Safe TransportDhaman A KokaОценок пока нет
- Block Plans: Block A (Typical Floor Plan)Документ7 страницBlock Plans: Block A (Typical Floor Plan)Manidipa SahaОценок пока нет
- Final Report Part IIДокумент127 страницFinal Report Part IIPatrisonОценок пока нет
- 2012 Conveyor Components CatalogДокумент53 страницы2012 Conveyor Components Catalogbandara123100% (1)
- A Guide To The Design of An Effective Low Pressure VAV Air Distribution SystemДокумент11 страницA Guide To The Design of An Effective Low Pressure VAV Air Distribution SystemAbdul RaheemОценок пока нет
- Exam 70 461 Microsoft SQL ServerДокумент10 страницExam 70 461 Microsoft SQL Serverjimmy_sam001Оценок пока нет
- Identity Theft Prevention: Protect Yourself and OthersДокумент4 страницыIdentity Theft Prevention: Protect Yourself and OtherscherryfooОценок пока нет
- OPM Batch ProcessДокумент494 страницыOPM Batch ProcessAmcy .SОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Layout Planning Model and Design Final FinalДокумент28 страницChapter 6 Layout Planning Model and Design Final Finaluser 123Оценок пока нет
- Essentials of Conversion Optimization by ConversionXLДокумент43 страницыEssentials of Conversion Optimization by ConversionXLJohn Sald100% (1)