Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Spaulding Daniel Lesson Three Newtons Laws
Загружено:
api-2643706740 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
20 просмотров26 страницОригинальное название
spaulding daniel lesson three newtons laws
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
20 просмотров26 страницSpaulding Daniel Lesson Three Newtons Laws
Загружено:
api-264370674Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 26
Chapter 19
Force and Newtons Laws
Newtons Three Laws of Motion
Newtons First Law
If the net force acting on an object is zero, the object remains at rest, or if the
object is already moving, continues to move in a straight line with constant
speed.
Newtons Second Law
Connects force, acceleration, and mass. An object acted upon by a force will
accelerate in the direction of the force. Force equals mass times acceleration (F =
ma).
Newtons Third Law
For every action there is an equal but opposite reaction.
Newtons First Law of Motion
Newtons First Law of Motion states that an object in motion stays in
motion and an object at rest stays at rest until acted upon by an
unbalanced force.
The first law is also referred to as The Law of Inertia
Law of Inertia
Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its velocity:
whether in motion or motionless.
An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in
motion at constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced
force.
These pumpkins will not move unless acted on
by an unbalanced force.
What Causes Motion?
An object moves if a force makes it move.
A force is a push or a pull.
When forces make something move, we say that forces are acting
on the object.
Forces that act on objects are either balanced or unbalanced.
Balanced Forces
Balanced forces two or more forces whose effects cancel each
other out and do not change the motion of the object
All the objects on
your desk have
balanced forces
acting on them.
The objects do not
move.
Unbalanced Forces
Unbalanced forces two or more forces acting on an object that do
not cancel, and cause the object to accelerate
Objects move when unbalanced forces act on them.
The dolly carrying the cases of bottles does not move until the boy
pushes it.
The toy wagon does not move until the girl pulls it.
Push
Pull
Net Force
Net Force combination of all forces acting on an object
If forces act on the object in the same direction, add the forces
together.
If forces act on the object in the opposite directions, subtract the
forces.
Objects will always move in the direction of the greater force.
Calculating Net Force
If forces act on the object in the same direction, add the forces
together. In this example, two forces are acting on the box in the
same direction.
50 N + 50 N = 100 N to the left
Calculating Net Force
If forces act on the object in the opposite direction, subtract the
forces. In this example, two forces are acting on the box in opposite
directions. The net force will always take the direction of the greater
force.
75 N - 50 N = 25 N to the right
Calculating Net Force
If forces act on the object in the opposite direction, subtract the
forces. In this example, two forces are acting on the box in the
opposite direction with the same amount of force in each direction.
50N - 50 N = 0 Newtons
When an object has a force of zero Newtons,
it is balanced.
Friction
Friction force that acts to oppose sliding between two surfaces that
are touching.
Sliding Friction type of friction that slows down an object that
slides.
Due to the microscopic roughness of two surfaces
Friction
Static Friction type of friction that prevents an object from moving
when a force is applied.
Caused by the attraction between the atoms on the two surfaces that are in
contact
As the surfaces gets rougher and the objects heavier the force of static friction
will be larger.
Friction
Rolling Friction type of friction needed to make a wheel or tire turn.
Occurs between the ground and the part of the tire touching the ground
Prevents tire from slipping
Newtons Second Law of Motion
Newtons Second Law of Motion states that objects will move in the
direction of the force.
Force is measured in units called Newtons (named for Sir Isaac
Newton)
1 N = 1 kgm/s
2
The formula used to calculate force is Force = mass x acceleration, or
F=ma
Weight
The force of gravity causes all objects near Earths surface to fall with
an acceleration of 9.8 m/s
2
.
According to Newtons second law the gravitational force on any
object near Earths surface is:
F = ma = m X (9.8 m/s
2
)
Weight your weight on Earth is the gravitational force between you
and Earth.
Mass
Mass is the amount of matter in an object, and doesnt depend on
location
Weight will vary with location but mass will remain constant
Ex. a book with a mass of 1 kg has a mass of 1 kg on Earth or on Mars.
However, the weight of the book would be different on Earth and
Mars.
Why? Weight is a force just like the push of your hand is a force. When
standing on a bathroom scale, you are measuring the pull of Earths
gravity.
Center of Mass
The point in an object that moves as if all the objects mass were
concentrated at that point.
Circular Motion
Centripetal Force means center seeking force; any motion in a
curved path represents accelerated motion, and requires a force
directed toward the center of the path and is always perpendicular to
the motion.
How do satellites stay in orbit?
Satellites are being pulled down toward the Earth just like a thrown baseball.
However, they are at such a distance from Earth and traveling so fast
horizontally that Earths surface curves downward at the same rate that the
satellites are falling downward.
The speed at which a satellite must move to go into orbit near Earths surface is
about 8 km/s, or about 29,000 km/h.
Circular Motion
Circular Motion
http://glencoe.mcgraw-
hill.com/sites/0078617707/student_view0/chapter2/concept_animati
ons.html#
Newton Explains
http://www.sciencewithmrnoon.com/projectarise/physics1st/newton2law.swf
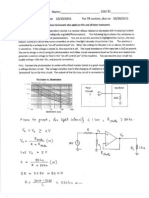
Lets Practice
How much force is needed to accelerate a 1400 kilogram car 2 m/s
2
?
Write the formula
F = m x a
Fill in given numbers and units
F = 1400 kg x 2 m/s
2
Solve for the unknown
2800 kg- m/s
2
or 2800 N
More Practice
What acceleration will result when a 12 N net force applied to a 3 kg
object? A 6 kg object?
A net force of 16 N causes a mass to accelerate at a rate of 5 m/s
2
.
Determine the mass.
How much force is needed to accelerate a 66 kg skier 1 m/s
2
?
What is the force on a 1000 kg elevator that is falling freely at 9.8
m/s
2
?
More Practice
What acceleration will result when a 12 N net force applied to a 3 kg
object? A 6 kg object?
12 N = 3 kg x 4 m/s
2
A net force of 16 N causes a mass to accelerate at a rate of 5 m/s
2
.
Determine the mass.
16 N = 3.2 kg x 5 m/s
2
How much force is needed to accelerate a 66 kg skier 1 m/s
2
?
66 kg-m/sec/sec or 66 N
What is the force on a 1000 kg elevator that is falling freely at 9.8
m/s
2
?
9800 kg-m/s
2
or 9800 N
Newtons Third Law of Motion
Newtons Third Law of Motion states that every
action has an equal and opposite reaction.
Every action occurs in equal but opposite pairs.
This basketball will hit the floor because of the
downward force of gravity, but the floor will also
exert a force on the ball and it will bounce in the
opposite direction.
Newtons Third Law of Motion
Action and reaction forces DO NOT cancel!
The forces exerted by two objects on each other are often called an
action-reaction force pair.
Either force can be considered the action force or the reaction force.
Just because action reaction forces are opposite and equal does not mean they
cancel creating zero net force.
Why? Because they act on different objects! Forces can only cancel
when acting on the same object.
Ex. two boys pushing on the same door from opposite directions can cancel each
other creating zero net force.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- End Winding Vibration Hydro GeneratorДокумент5 страницEnd Winding Vibration Hydro Generatorpatel chandramaniОценок пока нет
- The Ball Piston EngineДокумент13 страницThe Ball Piston EnginedhairyashilОценок пока нет
- Choosing Between Resistor and Reactor For Neutral Ground ImpedanceДокумент3 страницыChoosing Between Resistor and Reactor For Neutral Ground ImpedanceJeya KannanОценок пока нет
- Corona EffectДокумент22 страницыCorona EffectCharneth Noe Cate PanchoОценок пока нет
- Academic TranscriptДокумент10 страницAcademic Transcriptapi-264370674Оценок пока нет
- Resume Daniel SpauldingДокумент2 страницыResume Daniel Spauldingapi-264370674Оценок пока нет
- Spaulding Daniel Teaching License Oct 2016Документ2 страницыSpaulding Daniel Teaching License Oct 2016api-264370674Оценок пока нет
- Educational Mission StatementДокумент1 страницаEducational Mission Statementapi-264370674Оценок пока нет
- Educational Philosophy StatementДокумент2 страницыEducational Philosophy Statementapi-264370674Оценок пока нет
- Spaulding Daniel Lesson Two Writing PromptДокумент7 страницSpaulding Daniel Lesson Two Writing Promptapi-264370674Оценок пока нет
- Improved Ear JeopardyДокумент33 страницыImproved Ear Jeopardyapi-264370674Оценок пока нет
- Spaulding Daniel Field Placement Lesson Plan 3Документ10 страницSpaulding Daniel Field Placement Lesson Plan 3api-264370674Оценок пока нет
- Spaulding Daniel Field Placement Lesson Plan 3Документ10 страницSpaulding Daniel Field Placement Lesson Plan 3api-264370674Оценок пока нет
- Spaulding Daniel Lesson Plan One 1Документ12 страницSpaulding Daniel Lesson Plan One 1api-264370674Оценок пока нет
- Ear PulloutДокумент1 страницаEar Pulloutapi-264370674Оценок пока нет
- Educational Mission StatementДокумент1 страницаEducational Mission Statementapi-264370674Оценок пока нет
- Educational Philosophy StatementДокумент2 страницыEducational Philosophy Statementapi-264370674Оценок пока нет
- Ear Part IIДокумент37 страницEar Part IIapi-264370674100% (1)
- Forces and Friction: Sliding vs. Tipping ForcesДокумент8 страницForces and Friction: Sliding vs. Tipping ForcesmeeechersОценок пока нет
- The Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT) Position Sensor For Gravitational Wave Interferometer Low-Frequency ControlsДокумент19 страницThe Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT) Position Sensor For Gravitational Wave Interferometer Low-Frequency Controlsnikhilrane91_7522800Оценок пока нет
- Delta Vfdel Quickstart PDFДокумент25 страницDelta Vfdel Quickstart PDFHardikОценок пока нет
- Verify Ohm's Law ExperimentДокумент3 страницыVerify Ohm's Law ExperimentmohamadalfarОценок пока нет
- B3610 2 Design Considerations For Containment and Ventilation USДокумент15 страницB3610 2 Design Considerations For Containment and Ventilation USProveedora de servicios y suministros PSSОценок пока нет
- Arjuna - NLMДокумент11 страницArjuna - NLMGreat DeclamationsОценок пока нет
- Materials in Electrical EngineeringДокумент377 страницMaterials in Electrical Engineeringgiolgau01100% (1)
- Solution Manual For Engineering Mechanics, Statics - Sheri D. Sheppard, Thalia Anagnos, Sarah L. BillingtonДокумент24 страницыSolution Manual For Engineering Mechanics, Statics - Sheri D. Sheppard, Thalia Anagnos, Sarah L. BillingtonMaher MahmoodОценок пока нет
- Automatic Voltage Regulator Installation and Maintenance ManualДокумент75 страницAutomatic Voltage Regulator Installation and Maintenance ManualRobiОценок пока нет
- Debre Tabor University: Faculty of TechnologyДокумент101 страницаDebre Tabor University: Faculty of Technologyyoseph GetnetОценок пока нет
- A Lab Project Report On: "Simple Blinking Led"Документ14 страницA Lab Project Report On: "Simple Blinking Led"Sujee Reddy50% (2)
- Economy Force Sensor Manual CI 6746Документ6 страницEconomy Force Sensor Manual CI 6746scrusnОценок пока нет
- Conservation of MomentumДокумент19 страницConservation of MomentumwscienceОценок пока нет
- Electric Flux Density Gauss'S Law DivergenceДокумент26 страницElectric Flux Density Gauss'S Law Divergenceanon_360505511Оценок пока нет
- Electricity and Magnetism - Their HistoryДокумент8 страницElectricity and Magnetism - Their HistoryFrenzie Mae Vasquez RiveraОценок пока нет
- HW6 SolutionДокумент3 страницыHW6 SolutionDavid LhotakОценок пока нет
- VCAA 2006 Physics - Exam 2Документ19 страницVCAA 2006 Physics - Exam 2Sachin PathyОценок пока нет
- InTech-Ultra Wideband Antennas For High Pulsed Power ApplicationsДокумент31 страницаInTech-Ultra Wideband Antennas For High Pulsed Power ApplicationsprasenjitmailОценок пока нет
- Bird Flight AerodynamicsДокумент25 страницBird Flight AerodynamicsbooksforfunОценок пока нет
- CLS JEEAD-19-20 XII Phy Target-1 Level-2 Chapter-1 PDFДокумент28 страницCLS JEEAD-19-20 XII Phy Target-1 Level-2 Chapter-1 PDFShubhranshuОценок пока нет
- 11Документ38 страниц11yashittitaОценок пока нет
- Modelling Aircraft Performance on Contaminated RunwaysДокумент281 страницаModelling Aircraft Performance on Contaminated RunwaysSteven SullivanОценок пока нет
- Wound Rotor MotorДокумент6 страницWound Rotor MotorArun KumarОценок пока нет
- Module 5 IntroductionДокумент8 страницModule 5 IntroductionRAHUL NKОценок пока нет