Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Sulfur Recovery Units (SRU)
Загружено:
Splish SplashАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Sulfur Recovery Units (SRU)
Загружено:
Splish SplashАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Sulfur Recovery Units (SRU)
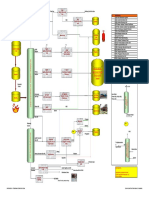
1. Proses Claus
Proses Claus merupakan proses kimia katalitik yang dimanfaatkan untuk mengkonversi
gas hydrogen sulfide (H
2
S) menjadi elemental sulfur (S).Proses ini sering disebut sebagai
Sulfur Recovery Unit (SRU) dan sangat sering digunakan untuk menghasilkan sulfur dari
hydrogen sulfide yang terdapat pada gas alam mentah dan sour gas yang mengandung
hydrogen sulfide yang berasal dari pengilangan minyak bumi, minyak mentah dan
fasilitas industry lainnya.
[1]
Deskripsi proses :
[2]
The basic Claus unit comprises a thermal stage and two stage or three catalyst stages.
Typical sulfur recoveries efficiencies are in the range 95-98% depending upon the feed
gas composition and plant configuration.
The basic chemical reactions occurring in a Claus process are represented by the
following reactions :
Some of the H
2
S in the feed gas is thermally converted to SO
2
in the reaction furnace of
the hermal stage according to reaction (1). The remaining H
2
S is then reacted with the
thermally produced SO
2
to form elemental sulphur in the thermal stage and the
subsequent catalytic stages according to reaction (2). Claus reaction (2) is
thermodynamically limited and has a relatively low equilibrium constant for reaction (2)
over the catalytic operation region.
As the feed acid gas normally contains other compounds, which could include carbon
dioxid, hydrocarbons, mercaptants and ammonia, the actual chemistry in the furnace is
very complex. The latest analysis of this has been presented by Borsboom and Clark.
Simplified Process Description
The hot combustion products from the furnace at 100-1300
o
C enter the waste heat
boiler and are partially cooled by generating steam. Any steam level from 3 to 45 bar
g can be generated
The combustion products are further cooled in the sulphur condenser, usually by
generating LP steam at 3-5 bar g. This cools the gas enough to condense the sulphur
formed in the furnace, which is then separated from the gas and drained to a
collection pit.
In order to avoid sulphur condensing in the downstream catalyst bed, the gas leaving
the sulphur condenser must be heated before entering the reactor.
The heated stream enters the first reactor, containing a bed of sulphur conversion
catalyst. About 70% of the remaining H
2
S and SO
2
in the gas will react to form
sulphur, which leaves the reactor with the gas as sulphur vapour.
The hot gas leaving the first reactor is cooled in the second sulphur condenser, where
LP steam is again produced and the sulphur formed in the reactor is condensed
A further one or two more heating, reaction, and condensing stages follow to react
most of the remaining H
2
S and SO
2
The sulphur plant tail gas is routed either to a Tail Gas treatment Unit for further
processing, or to a Thermal Oxidiser to incinerate all the sulphur compounds in the
tail gas to SO
2
before dispersing the effluent to the atmosphere.
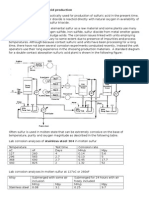
2. Proses LO-CAT
Proses LO-CAT bersifat aqueous (basah), bertemparatur rendah yang menggunakan
regenerasi katalis besi. Katalis besi digunakan untuk mengkonversi hydrogen sulfide
menjadi unsur yang tidak berbahaya, sulfur. Proses ini tidak menggunakan bahan kimia
beracun dan tidak menghasilkan produk sampingan berupa limbah berbahaya. Katalis
yang tersedia akan terus mengalami regenerasi dalam proses, sehingga penggunaan
katalis lebih sedikit dan penghematan juga dilakukan.
[1]
Deskripsi proses :
[1]
Intensitas proses adalah mengoksidasi ion-ion hydrosulfide (HS
-
) menjadi unsur sulfur
dengan mereduksi ion ferik (Fe
3+
) menjadi ion ferrous (Fe
2+
) dan tahapan reoksidasi ion
ferrous menjadi ferik melalui kontak dengan udara. Proses kimia adalah sebagai berikut :
Absorpsi H
2
S
()
()
()
()
Ionisasi H
2
S
()
Oksidasi Sulfida
Absorpsi Oksigen
()
()
()
()
Oksidasi Besi
()
Reaksi keseluruhan
()
()
3. Shell-Paques/THIOPAQ
TM
Proses Shell-Paques/THIOPAQ
TM
dapat menghilangkan H
2
S pada aliran gas alam
tekanan rendah, sedang ataupun tinggi. Pada proses ini aliran gas yang mengandung H
2
S
dikontakkan dengan larutan air soda yang mengandung bakteri Thiobacillus pada
absorber. Soda mengabsorp H
2
S dan sialirkan ke aerated atmospheric tank dimana secara
biologi bakteri mengubah H
2
S menjadi sulfur.
[1]
Deskripsi proses :
[1]
Reaksi yang terjadi di absorber (pada tekanan feed gas)
Reaksi yang terjadi di bioreactor (pada tekanan atmosfer)
Note : (tambahan tentang Proses Claus)
[3]
This process includes two main section : the burner section with a reaction chamber
that does not have a catalyst, and a Claus reactor section. In the burner section, part of the
feed containing hydrogen sulfide and some hydrocarbons is burned with a limited amount
of air. The two main reactions that occur in this section are the complete oxidation of part
of the hydrogen sulfide (feed) to sulfur dioxide and water and the partial oxidation of
another part of the hydrogen sulfide to sulfur. The two reactions are exothermic :
In the second section, unconverted hydrogen sulfide reacts with the produced sulfur
dioxide over a bauxite catalyst in the Claus reactor. Normally more than one reactor is
available. In the Super-Claus process (Figure 4-3), three reactors are used. The last
reactor contains a selective oxidation catalyst of high efficiency. The reaction is slightly
exothermic :
Figure 4-3. The Super Claus process for producing sulfur. (1) main burner, (2,4,6,8)
condensers, (3,5) Claus reactors, (7) reactor with selective oxidation catalyst
After each reaction stage, sulfur is removed by condensation so that it does not collect on
the catalyst. The temperature in the catalyst converter should be kept over the dew point
of sulfur to prevent condensation on the catalyst, which reduces activity.
Due to the presence of hydrocarbons in the gas feed to the burner section, some
undesirable reaction occur, such as the formation of carbon disulfide (CS
2
) and carbonyl
sulfide (COS). A good catalyst has a high activity toward H
2
S conversion to sulfur and
reconversion of COS and CS
2
to sulfur and carbon oxides. Mercaptans in the acid gas
feed results in an increase in the air demand. For example, approximately 5-13% increase
in the air required is anticipated if about 2 mol% mercaptans are present. The increase in
the air requirement is essentially a fuction of the type of mercaptans present. The
oxidation of mercaptans could be represented as:
Sulfur dioxide is then reduced in the Claus Reactor to elemental sulfur.
REFERENCES :
1. Hidayat, Sungging. 2012. Perancangan dan Estimasi Biaya Sulfur Recovery Unit
metode Superclaus. Fakultas Teknik Departemen Teknik Kimia, Universitas
Indonesia, Depok.
2. Mahin Rameshni, P.E Sulfur Recovery Unit : Expansion Case Studies Worley
Parsons, resources & energy, UK
3. Sammi Matar and Lewis F. Hatch.1994.Chemistry of Petrochemical Processes
second edition; provides quick and easy access to hundreds of reaction, processes
and products, Texas. Hal 116-117
4.
Вам также может понравиться
- Water Gas Shift Reaction: Research Developments and ApplicationsОт EverandWater Gas Shift Reaction: Research Developments and ApplicationsОценок пока нет
- Lecture-10-Clous and Merox ProcessesДокумент43 страницыLecture-10-Clous and Merox ProcessesAnilKumar100% (2)
- Effect of Reaction Furnace and Converter Temperatures On Performance of Sulfur Recovery Units (SRUs)Документ3 страницыEffect of Reaction Furnace and Converter Temperatures On Performance of Sulfur Recovery Units (SRUs)SEP-PublisherОценок пока нет
- Sulfur Costs Vary With Process SelectionДокумент5 страницSulfur Costs Vary With Process Selectionbakhtiari_afОценок пока нет
- Look at Claus Unit DesignsДокумент11 страницLook at Claus Unit DesignsNacho MatosОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Sulfur Recovery by The Claus ProcessДокумент8 страницFundamentals of Sulfur Recovery by The Claus ProcessAram IbrahimОценок пока нет
- Sulfur Recovery PDFДокумент32 страницыSulfur Recovery PDFShaho Abdulqader Mohamedali0% (1)
- Merox SweeteningДокумент15 страницMerox Sweeteningajay7892Оценок пока нет
- MEROXДокумент8 страницMEROXZubyr AhmedОценок пока нет
- Gas Treatment Processes-1Документ17 страницGas Treatment Processes-1m sohailОценок пока нет
- Claus Process FundamentalДокумент45 страницClaus Process FundamentalIlham Hakim50% (2)
- Sulfur Magazine Ideas For Better Clean Up Jan 09Документ0 страницSulfur Magazine Ideas For Better Clean Up Jan 09Bharat VaajОценок пока нет
- Amine Gas Treating: Gases or Acid Gases in The Hydrocarbon Processing IndustriesДокумент4 страницыAmine Gas Treating: Gases or Acid Gases in The Hydrocarbon Processing IndustriesikatparОценок пока нет
- Sulphur Recovery UnitДокумент6 страницSulphur Recovery UnitsemОценок пока нет
- Amine Sweetening Process DesignДокумент12 страницAmine Sweetening Process Designswapnil2603100% (2)
- Cansolv TGT Plus FactsheetДокумент2 страницыCansolv TGT Plus FactsheetPe VandeОценок пока нет
- Section 22 - Sulfur RecoveryДокумент145 страницSection 22 - Sulfur RecoveryCHANADAS100% (1)
- Wet Air Oxidation of Refinery Spent Caustic Sept 2000Документ13 страницWet Air Oxidation of Refinery Spent Caustic Sept 2000DAN IN-MARОценок пока нет
- Sru TroubleshootingДокумент40 страницSru TroubleshootingGomathi Shankar100% (1)
- Introduction To Merichem TechnologyДокумент16 страницIntroduction To Merichem TechnologyNgoVietCuongОценок пока нет
- MEROXДокумент16 страницMEROXai_25109275% (4)
- Sulfur Recovery and Tail Gas Treating UnitДокумент4 страницыSulfur Recovery and Tail Gas Treating UnitSreenivas Guduru100% (1)
- Claus Tail Gas Treating Unit (TGTU)Документ3 страницыClaus Tail Gas Treating Unit (TGTU)eragornОценок пока нет
- Merox & HydrotreatmentДокумент18 страницMerox & HydrotreatmentLuis Acid100% (1)
- Equipment Analysis in Design of Sulphuric Acid Plant: Yogeesh Sharma B. Tech (Mechanical & Automation Engg.)Документ18 страницEquipment Analysis in Design of Sulphuric Acid Plant: Yogeesh Sharma B. Tech (Mechanical & Automation Engg.)yogeeshs123Оценок пока нет
- Desulfurization of Natural Gas FeedstockДокумент10 страницDesulfurization of Natural Gas FeedstockShalu Princess Diksh100% (1)
- GasSweetening WorkshopДокумент34 страницыGasSweetening Workshophrijucse100% (3)
- Sulfur RecoveryДокумент12 страницSulfur RecoverySrhosseini3100% (2)
- Pressure Drop Calculation in Sieve Plate Distillation ColumnДокумент15 страницPressure Drop Calculation in Sieve Plate Distillation ColumnAnoop Kumar GuptaОценок пока нет
- A Guide of Refinery ProcessДокумент1 страницаA Guide of Refinery ProcessSubramani DuraikannuОценок пока нет
- Caustic Scrubber Designs For h2s Removal From Refinery Gas Streams Afpm 2014Документ26 страницCaustic Scrubber Designs For h2s Removal From Refinery Gas Streams Afpm 2014Widya Isti AriantiОценок пока нет
- Hydrotreating FinalДокумент24 страницыHydrotreating FinalManuel Canelas67% (3)
- Rating of An Existing Absorption TowerДокумент9 страницRating of An Existing Absorption TowerKvspavan KumarОценок пока нет
- P10 Natural Gas - Removal of Acid GasesДокумент73 страницыP10 Natural Gas - Removal of Acid GasesWalid Ben Husein100% (2)
- Sulphur Recovery UnitДокумент30 страницSulphur Recovery UnitDevendra Sharma100% (3)
- Design of Bubble Cap TrayДокумент5 страницDesign of Bubble Cap TrayVirendra BhagatОценок пока нет
- Aminas - Iran IДокумент4 страницыAminas - Iran IJesus BcОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3. Acid Gas RemovalДокумент88 страницChapter 3. Acid Gas RemovalTu Dang TrongОценок пока нет
- SRU ExplainedДокумент5 страницSRU ExplainedRitu VarshneyОценок пока нет
- Basics of Hydrotreating Catalyst Sulfiding - Reactor Resources - Sulfiding Services, Alumina, Metal Reclamation, CatalystsДокумент5 страницBasics of Hydrotreating Catalyst Sulfiding - Reactor Resources - Sulfiding Services, Alumina, Metal Reclamation, Catalystsonizuka-t2263Оценок пока нет
- Simulation of Mechanical Vapor Recompression Process For Treatment of The Wastewater of Crude Oil Desalting Unit PDFДокумент10 страницSimulation of Mechanical Vapor Recompression Process For Treatment of The Wastewater of Crude Oil Desalting Unit PDFdesai sanketОценок пока нет
- MERICAT J: A New Kerosene Treating Technology To Meet Jet Fuel SpecificationsДокумент13 страницMERICAT J: A New Kerosene Treating Technology To Meet Jet Fuel SpecificationsRio RinaldiОценок пока нет
- Adsorbents and Adsorption Processes For Pollution ControlДокумент30 страницAdsorbents and Adsorption Processes For Pollution ControlJoao MinhoОценок пока нет
- Nickel Alloys For Sulfuric Acid ProductionДокумент5 страницNickel Alloys For Sulfuric Acid ProductionHeanjiaAlloysОценок пока нет
- SRU Training Module PDFДокумент161 страницаSRU Training Module PDFviettanct100% (22)
- Amine Rgeneration UnitДокумент88 страницAmine Rgeneration UnitsudhirОценок пока нет
- Theol Heat Transfer FluidДокумент3 страницыTheol Heat Transfer Fluidgautam_96948069Оценок пока нет
- PromaxДокумент20 страницPromaxehsan_sa405100% (1)
- Sulfur Plant Design ManualДокумент367 страницSulfur Plant Design ManualLuispajuelo73100% (8)
- Effect of Sodium Salts On Demercaptanization ProcessДокумент4 страницыEffect of Sodium Salts On Demercaptanization ProcessInternational Journal of Science and Engineering InvestigationsОценок пока нет
- Amine Recovery Unit (ARU) : E. BayanjargalДокумент12 страницAmine Recovery Unit (ARU) : E. BayanjargalBayanjargal ErdeneeОценок пока нет
- Design of Caustic Wash System For Light HydrocarboДокумент5 страницDesign of Caustic Wash System For Light HydrocarboWayne MonneryОценок пока нет
- Acid GasTreatment & Sulfur RecoveryДокумент28 страницAcid GasTreatment & Sulfur Recoveryzorro21072107100% (1)
- Claus Process: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент5 страницClaus Process: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAshish SutariyaОценок пока нет
- Sulfur - Sulfuric Acid IndustryДокумент18 страницSulfur - Sulfuric Acid IndustryS S S REDDY100% (1)
- Claus Process - WikipediaДокумент26 страницClaus Process - WikipediaTatenda SibandaОценок пока нет
- Contact ProcessДокумент19 страницContact ProcessLeela Santosh KumarОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 Inorganic Industries 2019Документ41 страницаLecture 2 Inorganic Industries 2019Mohamed AbdelaalОценок пока нет
- Claus ProcessДокумент6 страницClaus ProcessRafi AlgawiОценок пока нет
- The Claus Process Netl - Doe.govДокумент1 страницаThe Claus Process Netl - Doe.govezzo97 AlkhedrawyОценок пока нет
- Hydrogen SulfideДокумент26 страницHydrogen SulfideYassir HindiОценок пока нет
- Sulfur Recovery Units (SRU)Документ5 страницSulfur Recovery Units (SRU)Splish SplashОценок пока нет
- HTTPДокумент8 страницHTTPSplish SplashОценок пока нет
- Sulfur RecoveryДокумент96 страницSulfur RecoveryNirma Afrisanti KinasihОценок пока нет
- Chemical Engineering and Environmental EngineeringДокумент89 страницChemical Engineering and Environmental Engineeringpeyman_qz_coОценок пока нет
- My TestДокумент33 страницыMy TestqusaielnoorОценок пока нет
- BPA ProcessДокумент3 страницыBPA ProcessRahul Agrawal100% (1)
- KC and KP Exam QuДокумент3 страницыKC and KP Exam QuAriaNathan100% (1)
- Diffusion in Nano-Porous Materials: AngewandteДокумент2 страницыDiffusion in Nano-Porous Materials: AngewandteBrunoBarrosОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S1876107012000107 MainДокумент7 страниц1 s2.0 S1876107012000107 MainBUREAU VERITAS BLOQUESОценок пока нет
- Production of Biodiesel From Mixed Castor Seed andДокумент38 страницProduction of Biodiesel From Mixed Castor Seed andMohamed HalemОценок пока нет
- Astm UopДокумент5 страницAstm UopHamid Heidari50% (2)
- Project AcetoneДокумент19 страницProject AcetoneBhinitha ChandrasagaranОценок пока нет
- Biodiesel Production From Non Edible Plant OilsДокумент29 страницBiodiesel Production From Non Edible Plant OilsTeshome DengisoОценок пока нет
- Babs2244 Metabolic BiochemistryДокумент24 страницыBabs2244 Metabolic BiochemistryKhAi En33% (3)
- B.SC - .-Zoology SyllabДокумент19 страницB.SC - .-Zoology SyllabShanmugam DhanasekaranОценок пока нет
- Lucca 2008 PropilenoДокумент7 страницLucca 2008 Propilenoreclatis14Оценок пока нет
- Paintindia Sept2012Документ4 страницыPaintindia Sept2012Mamoon ShahidОценок пока нет
- L3.2 Immobilized Enzyme KineticsДокумент98 страницL3.2 Immobilized Enzyme KineticsRalph Evidente100% (2)
- New Generation Ideation Contest - 2022Документ22 страницыNew Generation Ideation Contest - 2022Sandeep ChaurasiaОценок пока нет
- 1415 Exam 1 Answers (ICP) (EN)Документ8 страниц1415 Exam 1 Answers (ICP) (EN)김하은Оценок пока нет
- Catalitic FadingДокумент3 страницыCatalitic FadingJosé Iván Charry ZuluagaОценок пока нет
- Sterioselective Organic Reaction in WaterДокумент22 страницыSterioselective Organic Reaction in WaterAhsan MohdОценок пока нет
- Agritech LTD Internship ReportДокумент52 страницыAgritech LTD Internship ReportEngnrXaifQureshi50% (2)
- Pre-Lab 4: 1. What Is A Catalyst and A Catalysis Reaction?Документ4 страницыPre-Lab 4: 1. What Is A Catalyst and A Catalysis Reaction?Giao TranОценок пока нет
- About The Company: Central America Nickel (CAN) Is A Montreal-Based Company That HasДокумент4 страницыAbout The Company: Central America Nickel (CAN) Is A Montreal-Based Company That HasFerdiansyah FerdiansyahОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Structure, Classification and Mechanism of ActionДокумент18 страницEnzyme Structure, Classification and Mechanism of ActionFeblin VersiliantinaОценок пока нет
- Combustion of AlkanesДокумент12 страницCombustion of Alkaneszara_1692Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 9Документ18 страницChapter 9JeromeОценок пока нет
- CH 12Документ23 страницыCH 12filippo67% (3)
- Chemical Kinetics Study Material & QuestionsДокумент26 страницChemical Kinetics Study Material & QuestionsKRITHIKA .MОценок пока нет
- First-Principles Based Kinetic Model For The Hydrogenation of Toluene PDFДокумент10 страницFirst-Principles Based Kinetic Model For The Hydrogenation of Toluene PDFingbarragan87Оценок пока нет
- Modern Trends in BiothermokineticsДокумент484 страницыModern Trends in BiothermokineticsMarko BarićОценок пока нет
- I Sem B.pharmacy SyllabusДокумент14 страницI Sem B.pharmacy SyllabusSUMIT KUMAR PANDITОценок пока нет
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindОт EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindОценок пока нет
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarОт EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (19)
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonОт EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (103)
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldОт EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (58)
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellОт EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (81)
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsОт EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (242)
- The Knowledge: How to Rebuild Our World from ScratchОт EverandThe Knowledge: How to Rebuild Our World from ScratchРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (133)
- Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceОт EverandPale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (588)
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestОт EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (28)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldОт EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- The Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaОт EverandThe Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaОценок пока нет
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyОт EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyОценок пока нет
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerОт EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (122)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidОт EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1395)
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyОт EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (24)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastОт EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (31)
- Permaculture for the Rest of Us: Abundant Living on Less than an AcreОт EverandPermaculture for the Rest of Us: Abundant Living on Less than an AcreРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (33)
- Broken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterОт EverandBroken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerОт EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (54)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationОт EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (46)
- Dirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureОт EverandDirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (125)