Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Azfar Afandi Phonetic. No 10
Загружено:
Azfar Afandi Nazri0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
11 просмотров2 страницыo
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документo
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
11 просмотров2 страницыAzfar Afandi Phonetic. No 10
Загружено:
Azfar Afandi Nazrio
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
SHORT ESSAY
QUESTION 10: Explain in articulatory terms the features of the following
consonants: affricate.
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) was designated in the year 1886 to
devise a universal phonetic alphabet. It consists of the vowels and the consonants
as a whole and complements the everyday communication in a way to have the
accurate pronunciation. From the topic chosen, the focus is on the consonants of
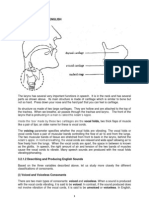
affricates. What is consonant in the phonological system? It is actually a terms of
where the constriction is made, how it is made, and what kind of phonation it
supports.(John Clark & Collin Yallop, 1990). Other than that,(Finegan, 2008) states
that consonants are sounds produced by partially or completely blocking of air in its
passage from the lung through the vocal tract. This means that, human makes
consonant sounds through the blockage of air in their vocal tract. In the consonants
chart, there is the place of articulation which is placed from the left side to the right
side (from the front of the vocal tract to the back) of the chart. It is then combined
with the manners of articulation which is placed from the top until the bottom of the
chart (from stops to semi-vowel) and they are also categorised into the voiceless
and the voicedway of sounding.
Next after that, what is it actually the affricate? It is the degree of air
turbulence and friction at the release of the stops(John Clark & Collin Yallop, 1990).
While on the other hand, (Finegan, 2008) states that in the pronunciation of affricate,
air is built up by a complete closure of the oral tract. It can be clearly seen that, the
production of affricate sound involves air friction due the blockage in the vocal tract.
This affricate manner of articulation consists of the voiceless affricate (t )and voice
affricate (d)that comes with the combination of place of articulation of alveolar.So,
what is the definition of alveolar? It refers to the gum ridge; the thick membranous
covering on the bone structure which joins the tooth-bearing bone of the upper jaw
and the arched bone structure of the hard palate(John Clark & Collin Yallop, 1990). It
is the articulation place right after the teeth that produce voiceless [t] and [s] with
voiced [d], [z] and [n].The affricate is normally a short duration that counts as the
release burst of the stop itself. For example, the initial sounds of chin and ginand
the final sounds of batch and badge. If the sound is pronounced slowly enough, we
can recognize it as the stop-fricatives, which are more accurately called as
affricates. In the pronunciation of affricate, air is built up by a complete closure of
the oral tract and at some place of articulation, then released (something like a stop)
and continued (like a fricative). The sound of chin earlier is the combination of the
stop [ t ] and the fricative [ ]and is then represented as (t ). The sound at the
beginning and the end of judge is a combination of the stop [ d ] and the fricative
[ ], represented as(d). In English, there is only this type of affricates and they are
called alveo-palatal affricates in order to capture their place of articulation. In addition,
as they share the phonetic property of constricting the airflow through the vocal tract,
fricatives, stops, and affricates are together referred as obstruentwhich is a fricative
or plosive speech sound.
Вам также может понравиться
- Phonology SeptemberДокумент10 страницPhonology SeptemberaladeobashinaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Linguistics: Phonetics: July 27, 2017Документ17 страницIntroduction To Linguistics: Phonetics: July 27, 2017zyanmktsdОценок пока нет
- Summary GimsonДокумент6 страницSummary GimsonsgambelluribeiroОценок пока нет
- Phonetic and PhonologyДокумент22 страницыPhonetic and PhonologyloganzxОценок пока нет
- Linguistics - Unit 3Документ5 страницLinguistics - Unit 3Appas SahaОценок пока нет
- Eng 323 Lect 3Документ6 страницEng 323 Lect 3maryjames ikebunaОценок пока нет
- The Human Speech ApparatusДокумент2 страницыThe Human Speech ApparatusClou Clou Peña100% (2)
- English ConsonantsДокумент10 страницEnglish ConsonantsallocishОценок пока нет
- English Phonetics - ConsonantsДокумент15 страницEnglish Phonetics - ConsonantsJandelineОценок пока нет
- The Human Speech ApparatusДокумент10 страницThe Human Speech ApparatusRunato Basanes100% (1)
- Handout Chapter 2 Phonetics Spring Semester 2023Документ11 страницHandout Chapter 2 Phonetics Spring Semester 2023mhmddhwyb8Оценок пока нет
- The Sounds of EnglishДокумент11 страницThe Sounds of EnglishNicole Calisay VerzosaОценок пока нет
- Makalah Phonology Kelompok 2Документ11 страницMakalah Phonology Kelompok 2meldianto manugalaОценок пока нет
- Sounds ClassificationДокумент4 страницыSounds ClassificationSantiago Etcheverry FeelyОценок пока нет
- Psycholinguistics Chapter 2Документ7 страницPsycholinguistics Chapter 2Syah AgusОценок пока нет
- English ConsonantsДокумент28 страницEnglish ConsonantsIzzati AzmanОценок пока нет
- Phonetics and Phonology at A Glance 1: Articulatory PhoneticsДокумент6 страницPhonetics and Phonology at A Glance 1: Articulatory PhoneticsIva BasarОценок пока нет
- Linguistics 2Документ45 страницLinguistics 2Bani AbdullaОценок пока нет
- Phonetics NotesДокумент5 страницPhonetics NotesYaya CasablancaОценок пока нет
- الثاني صوتДокумент13 страницالثاني صوتg7j85hvb52Оценок пока нет
- 4 Phonetics: Speech OrgansДокумент8 страниц4 Phonetics: Speech OrgansLorz CatalinaОценок пока нет
- Classification and Description. Acoustic CorrelatesДокумент3 страницыClassification and Description. Acoustic CorrelatescalluraОценок пока нет
- Phonetics Study MaterialДокумент5 страницPhonetics Study MaterialSoumini BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- Vocal TractДокумент16 страницVocal TractniroelОценок пока нет
- Manner of Articulation: ExercisesДокумент1 страницаManner of Articulation: ExercisesHomero Apeña CarranzaОценок пока нет
- Phonetics Book LING 372 Chapter 2Документ5 страницPhonetics Book LING 372 Chapter 2Rachida Al FakirОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2. ConsonantsДокумент8 страницLecture 2. ConsonantsEl Joumaili SimoОценок пока нет
- Ibn Tofail University LevelДокумент23 страницыIbn Tofail University LevelImad Es SaouabiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 (H06)Документ11 страницChapter 4 (H06)Jãşmíńë ØrtizОценок пока нет
- PHONETICS: The Sounds of LanguageДокумент5 страницPHONETICS: The Sounds of LanguageMayMay Serpajuan-SablanОценок пока нет
- Speech ChainДокумент6 страницSpeech ChainNatalia Correa GuerreroОценок пока нет
- Phonetic Handout 1Документ14 страницPhonetic Handout 1Wisten MárquezОценок пока нет
- I Year B. Tech. Lab NotesДокумент39 страницI Year B. Tech. Lab Notesbalajichakilam2012Оценок пока нет
- Manner of ArticulationДокумент6 страницManner of ArticulationDian Hadi NurrohimОценок пока нет
- Topic 8: Phonological System of The English Language Ii: Consonants. Phonetic SymbolsДокумент8 страницTopic 8: Phonological System of The English Language Ii: Consonants. Phonetic SymbolsLaura Irina Lara SánchezОценок пока нет
- Handout DFI 1. S1-2022Документ23 страницыHandout DFI 1. S1-2022andrea rojasОценок пока нет
- Phonetic and PhonologyДокумент8 страницPhonetic and PhonologyIzha AshariОценок пока нет
- Types of Phonemes Definitions PDFДокумент3 страницыTypes of Phonemes Definitions PDFLovely FinuliarОценок пока нет
- Chapter Five: (The Sounds of Language) : Articulation: Voiced and VoicelessДокумент2 страницыChapter Five: (The Sounds of Language) : Articulation: Voiced and VoicelessSara AHОценок пока нет
- Manner of ArticulationДокумент3 страницыManner of Articulationlalila melikaОценок пока нет
- Resume FonologiДокумент24 страницыResume FonologiEndang Tri RahayuОценок пока нет
- Articulatory Phonetics: 1) VoiceДокумент3 страницыArticulatory Phonetics: 1) VoiceDorepeОценок пока нет
- ENGLISH PHONOLOGY Materi 2Документ12 страницENGLISH PHONOLOGY Materi 2Agnes Nopita WidianiОценок пока нет
- Airstream Mechanisms: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchДокумент11 страницAirstream Mechanisms: Jump To Navigation Jump To Searchz9sps8fzbxОценок пока нет
- Phonetics and PhonologyДокумент41 страницаPhonetics and PhonologyAli MahdiОценок пока нет
- Phonetics and Phonology PDFДокумент62 страницыPhonetics and Phonology PDFCarlos Rojas CamachoОценок пока нет
- Manner of ArticulationДокумент8 страницManner of ArticulationSyafiq ImanОценок пока нет
- GHL #02Документ8 страницGHL #02esha khanОценок пока нет
- Consonant SoundsДокумент8 страницConsonant SoundsKhairul Nizam HamzahОценок пока нет
- Articulatory Phonetics 1Документ5 страницArticulatory Phonetics 1KhlifibrahimОценок пока нет
- English Lab NotesДокумент40 страницEnglish Lab Noteskgiridharreddy2022Оценок пока нет
- Variation in PlosiveДокумент2 страницыVariation in PlosiveRekar FazilОценок пока нет
- Manner of ArticulationДокумент1 страницаManner of ArticulationMeer BalochОценок пока нет
- Fricative and AffricateДокумент3 страницыFricative and AffricateShyamal Kanti Das100% (1)
- PhoneticsДокумент6 страницPhoneticsErica CacalОценок пока нет
- ngữ âm vị họcДокумент5 страницngữ âm vị họcThảo Min'ssОценок пока нет
- Uas Alrino Ode MasimuДокумент10 страницUas Alrino Ode MasimuArif FlouncxОценок пока нет
- Arif Hidayat English PhonologyДокумент54 страницыArif Hidayat English PhonologyArif FlouncxОценок пока нет
- Emerging QuestionsДокумент4 страницыEmerging QuestionsAllen MarcОценок пока нет
- SymphonyДокумент2 страницыSymphonyAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Modul Smart EnglishДокумент28 страницModul Smart EnglishAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Jadual U16 & U14 KysДокумент8 страницJadual U16 & U14 KysAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Pupil AДокумент4 страницыPupil AAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Week 23 - Unit 8 The RobotДокумент5 страницWeek 23 - Unit 8 The RobotAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Inuit People in CanadaДокумент4 страницыInuit People in CanadaAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Developing and Using Resources For The Primary Esl ClassroomДокумент25 страницDeveloping and Using Resources For The Primary Esl ClassroomKee Li LiОценок пока нет
- English Paper 1 Section B Year 4 - PPT 2016Документ8 страницEnglish Paper 1 Section B Year 4 - PPT 2016Azfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- DecklistДокумент1 страницаDecklistAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- School Based Oral Assessment English Language Student Achievement RecordДокумент4 страницыSchool Based Oral Assessment English Language Student Achievement RecordAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- School Based Oral Assessment English Language Student Achievement RecordДокумент5 страницSchool Based Oral Assessment English Language Student Achievement RecordAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Tugasan Projek Tamadun Islam Dan Tamadun Asia (WAJ3012) : Ipg Kampus Tun Hussein Onn Batu Pahat, JohorДокумент7 страницTugasan Projek Tamadun Islam Dan Tamadun Asia (WAJ3012) : Ipg Kampus Tun Hussein Onn Batu Pahat, JohorAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Daily Lesson Plan: Choose An ItemДокумент5 страницDaily Lesson Plan: Choose An ItemAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- TSL3113 Topic 3Документ17 страницTSL3113 Topic 3Kee Li LiОценок пока нет
- Anime LovequotesДокумент10 страницAnime LovequotesAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Tsl3111 - Brighton EducationДокумент120 страницTsl3111 - Brighton EducationChristina KiuОценок пока нет
- Course:: Developing and Using Resources For The Primary Esl ClassroomДокумент20 страницCourse:: Developing and Using Resources For The Primary Esl ClassroomAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Smart English Year 5Документ3 страницыFinal Exam Smart English Year 5Azfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- DividerДокумент2 страницыDividerAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Year 5 2016 RPT BiДокумент13 страницYear 5 2016 RPT BiAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Azfar Afandi Bin Ahmad NazriДокумент2 страницыAzfar Afandi Bin Ahmad NazriAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- List (Latest) 1502 WOMANДокумент5 страницList (Latest) 1502 WOMANAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Table 7.1: Holistic Scoring Scheme Source: S.S. Moya, Evaluation Assistance Center (EAC) - East, Georgetown University, WashingtonДокумент1 страницаTable 7.1: Holistic Scoring Scheme Source: S.S. Moya, Evaluation Assistance Center (EAC) - East, Georgetown University, WashingtonAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Tapak JadualДокумент3 страницыTapak JadualAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Poverty and Student PerformanceДокумент16 страницPoverty and Student Performancekitai123Оценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Unit 7Документ17 страницUnit 7Azfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Thanks Sorry StoryДокумент1 страницаThanks Sorry StoryAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Ever NoteДокумент3 страницыEver NoteAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan: Scientific Attitude & Noble Value Teaching & Learning ResourceДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan: Scientific Attitude & Noble Value Teaching & Learning ResourceAzfar Afandi NazriОценок пока нет
- Employability Skills: (Class IX)Документ13 страницEmployability Skills: (Class IX)Chinna SamyОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER II FixДокумент15 страницCHAPTER II FixMike Nurmalia SariОценок пока нет
- Familiar Consonants, Part 1Документ4 страницыFamiliar Consonants, Part 1Harish Kumar JОценок пока нет
- LKM111 01 PDFДокумент27 страницLKM111 01 PDFcindy xieОценок пока нет
- Wishram Texts - Sapir and CurtainДокумент352 страницыWishram Texts - Sapir and Curtaindelphic78Оценок пока нет
- Segmental and Suprasegmental Sound - Cemink's VoicesДокумент3 страницыSegmental and Suprasegmental Sound - Cemink's VoicesJohnnyBernales0% (1)
- Intonation 120204031312 Phpapp02Документ48 страницIntonation 120204031312 Phpapp02Dayang Nur ZawaniОценок пока нет
- Giving A Hoot: Basic Countertenor Pedagogy For The Choral Conductor by Michael Hrivnak, August 2002Документ6 страницGiving A Hoot: Basic Countertenor Pedagogy For The Choral Conductor by Michael Hrivnak, August 2002JoeОценок пока нет
- Vowels, Diphtonɡs, ConsonantsДокумент3 страницыVowels, Diphtonɡs, ConsonantsKaolínka KručovskáОценок пока нет
- Grammaire de Référence de Tmazight de L'atlas (E.T Abd El Masih)Документ350 страницGrammaire de Référence de Tmazight de L'atlas (E.T Abd El Masih)Tasedlist100% (1)
- IntonationДокумент3 страницыIntonationPamKiteОценок пока нет
- EnunciationДокумент8 страницEnunciationHannah Sophia Gabrillo JimenezОценок пока нет
- Mal Phonetic Reader - RemovedДокумент66 страницMal Phonetic Reader - RemovedReshmi R NairОценок пока нет
- Bilabial Labiodental Dental Alveolar Post-Alveolar Palato-Alveolar Palatal Velar Glottal ConsonantsДокумент2 страницыBilabial Labiodental Dental Alveolar Post-Alveolar Palato-Alveolar Palatal Velar Glottal ConsonantsrockgasmОценок пока нет
- 48-Sounds Write Common Spellings of The Consonants and VowelsДокумент2 страницы48-Sounds Write Common Spellings of The Consonants and VowelsVictoriano Torres RiberaОценок пока нет
- Basic Korean Language For Bangladeshi StudentsДокумент139 страницBasic Korean Language For Bangladeshi StudentsArif HossainОценок пока нет
- SanskritGrammar2Sandhi PDFДокумент97 страницSanskritGrammar2Sandhi PDFKrish SaiОценок пока нет
- Larynx Muscles MCQSДокумент10 страницLarynx Muscles MCQSSalifyanji SimpambaОценок пока нет
- CockneyДокумент6 страницCockneyVivian Darkbloom100% (1)
- International Phonetic AlphabetДокумент1 страницаInternational Phonetic AlphabetAna Carolina DorofeiОценок пока нет
- Notes On Introduction To LinguisticsДокумент16 страницNotes On Introduction To LinguisticsMuhammad Tayyab Ahmad100% (1)
- Accentuation - Some Extra PracticeДокумент3 страницыAccentuation - Some Extra PracticeSoledad Alvarez ElgartОценок пока нет
- Phonological AwarenessДокумент8 страницPhonological AwarenessAnonymous rkioZUg8rОценок пока нет
- Pronpack Books 1 4 Mark Hancock Chester Hancock Mcdonald Elt 2017 Isbn 978-0-9957575 4 7Документ2 страницыPronpack Books 1 4 Mark Hancock Chester Hancock Mcdonald Elt 2017 Isbn 978-0-9957575 4 7MrCaju80100% (1)
- English Pronunciation ( Ɪŋglɪʃ Prənʌnsɪ Eɪʃn)Документ36 страницEnglish Pronunciation ( Ɪŋglɪʃ Prənʌnsɪ Eɪʃn)JAY CASIBANGОценок пока нет
- Popular Song and Music Theater Seth RiggДокумент5 страницPopular Song and Music Theater Seth Riggvikas kunduОценок пока нет
- M.Jegis Y.A - Analysis of Childhood Rhotacism in English Pronunciation Proposal, Chapter 1,2 &3Документ13 страницM.Jegis Y.A - Analysis of Childhood Rhotacism in English Pronunciation Proposal, Chapter 1,2 &3Mr Jeyz SMP PGIIОценок пока нет
- Hesitation Pauses in Conversational Interaction of The English Letters and Language Department's Students at The State Islamic University of MalangДокумент77 страницHesitation Pauses in Conversational Interaction of The English Letters and Language Department's Students at The State Islamic University of MalangSally Morgana RojasОценок пока нет
- Phonetics 2 Mock TestДокумент2 страницыPhonetics 2 Mock TestYoBishassОценок пока нет
- English Diphthongs and TriphthongsДокумент4 страницыEnglish Diphthongs and TriphthongsNorasiah100% (1)