Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Of Enterprise Growth Showing Advantages of Each With Clear References
Загружено:
Adroit Writer0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
21 просмотров8 страницsolutions to the ird assignments
Оригинальное название
final ird
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документsolutions to the ird assignments
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
21 просмотров8 страницOf Enterprise Growth Showing Advantages of Each With Clear References
Загружено:
Adroit Writersolutions to the ird assignments
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 8
QUESTION: WITH USE OF RELEVANT EXAMPLES EXAMINE VARIOUS STRATEGIES
OF ENTERPRISE GROWTH SHOWING ADVANTAGES OF EACH WITH CLEAR
REFERENCES.
SOLUTION
WHAT IS BUSINESS GROWTH?
Simply stated, business growth means an increase in the size or scale of operations of a firm
usually accompanied by increase in its resources and output.
This are the various things such as increase in the total sales volume per annum, an increase in
the production capacity, increase in employment, an increase in production volume , an
increase in the use of raw material and power. They indicate growth but do not provide a
specific meaning of growth.
NEED FOR GROWTH
Growth is precondition for the survival of a business firm. An enterprise that does not grow
may, in course of time have to be closed down because of its obsolete products. i.e. pagers
company closed due to introduction of cell phones.
Reasons for growth include:
Survival: due to the companies dorminating and introducing monopoly and
monopolistic markets its vita for the companies to grow tentatively increasing their
chance of survival.
Economies of Scale: Growth of a firm may provide several economies in production,
purchasing, marketing, finance, management.
Owners mandate: Capable management may on its own like to take carefully
calculated risk and expand the size of the company.
Expansion of the market Business firms grow to meet the increasing demand.
Expanding markets provide opportunity for business growth.
Latest Technology Some business firms invest in research and development activities
to create new products and new techniques others try to acquire latest technology from
the market.
Prestige and Power The more the size of the business firm increase the more is the
prestige and power of the firm.
Self-sufficiency Some firms grow to become self sufficient in terms of marketing of
raw material or marketing of products. Growth in either or both of these forms reduces
the dependency of the firm over other firms.
WHAT IS GROWTH STRATEGY
Growth Strategy refers to a strategic plan formulated and implemented for expanding firms
business. For smaller businesses, growth plans are especially important because these
businesses get easily affected even by smallest changes in the marketplace. Changes in
customers, new moves by competitors, or fluctuations in the overall business environment can
negatively impact their cash flow in a very short time frame.
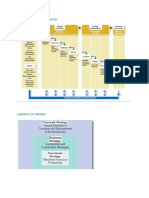
TYPES OF GROWTH STRATEGIES
The following are the main growth strategies available to firms:
1. Intensive Growth Strategy (Expansion)
2. Diversification
3. Modernization
4. Mergers
5. Joint Ventures
1) INTENSIVE GROWTH STRATEGY
Intensive growth strategy or expansion involves raising the market share, sales revenue and
profit of the present product or services. The firm slowly increases its production and so it is
called internal growth strategy. It is a good strategy for firms with a smaller share of the
market. Three alternative strategies are available in this regard.
These are:
(a) Market Penetration: This strategy aims at increasing the sale of present product in the
presented market through aggressive promotion.
(b) Market Development : It implies increasing sales by selling present products in the new
markets. For example selling electronic goods in rural areas or sale of chocolates to middle aged
and old persons.
(c) Product Development: In this, the firm tries to grow by developing improved products for
the present market. For example, A.C. with remote control.
Advantages
Growth is slow and natural. Therefore, it can be handled easily.
Capital required for expansion can be taken from the firm's own funds.
Existing resources can be better utilized
The growing firm is in a better position to face competition in the market.
Only a few changes are required in the organisation and management systems of
business.
Expansion provides economics of large-scale operations.
Limitations
Growth is very slow and it takes a long time for growth to actually happen.
A business firm loses the possibility of exploiting many business opportunities by
restricting its operations to the present products and markets.
It is not always possible to grow in the present product market.
2) DIVERSIFICATION
Diversification is a much talked about and widely used strategy for growth. Many companies
have opted for this. For example, LIC, an insurance concern initially, diversified into mutual
funds. State Bank of India diversified into merchant banking and mutual funds. Similarly, Larsen
and Toubro, an engineering company diversified into cement.
Situations that may lead to diversification
When diversification promises greater profitability than expansion.
When the firm cannot attain its growth target by the strategy of expansion alone.
When the financial resources of the firm are much in excess of the requirements of
expansion.
Advantages
Better use of its resources. By adding up related products to its existing product
portfolio, a company can more effectively utilize its managerial personnel, marketing
network, research and development facilities.
Reduce the decline in sales. By developing new products the sales revenue and earnings
can be maintained or even increased.
More competitive With greater resources, more products and higher profits, the
diversified firm is more competitive than a single product firm.
Minimize risk. When one line of business faces recession, another line may be in high
growth stage. For example, a well-diversified engineering firm like Larsen and Toubro
did well even when the engineering industry was facing recession.
Use of cash surplus of one business to finance another business having good potential
for growth.
Economies of scale Diversification adds to size of business which improves the
competitiveness of a firm. It offers a lot of economy in operations because common
facilities can be used for several products.
Limitations
Huge funds are required for diversification. The internal savings of the business may not
be sufficient to finance growth.
(ii) The functions and responsibilities of top executives increase because of need to
handle new product, technology and markets. They may find problems in coordination
which may lead to inefficient operations.
(iii) Diversification may involve new technology and new markets and the present staff
may face problems in adjusting to this growth pattern.
(iv) Diversification may lead to unknown products and markets leading to more risk.
Types of Diversification
Horizontal Integration.
Vertical Integration.
Concentric.
Conglomerate.
Horizontal Integration: involves addition of parallel new products to the
existing product line. This may happen internally or externally, internally, a company may
decide to enter a parallel product market in addition to the existing product line.
Externally, a company combines with a competing firm.
Vertical Integration: In vertical integration new products or services are added which are
complementary to the present product line or service. New products fulfill the firms own
requirements by either supplying inputs or by serving as a customer for its output. In vertical
integration the firm moves backward or forward from the present product or service.
Concentric Diversification: When a firm diversifies into some business which is related with its
present business in terms of marketing, technology, or both, it is called concentric
diversification. When in concentric diversification new product or service is provided with the
help of existing or similar technology it is called technology-related concentric diversification.
Conglomerate Diversification: When a firm diversifies into business which is not related to its
existing business both in terms of marketing and technology it is called conglomerate
Diversification
3) MODERNISATION
A firm may use the strategy of modernization to achieve growth. Modernization basically
involves upgradation of technology to increase production, to improve quality and to reduce
wastages and cost of production. The worn-out and obsolete machines and equipment are
replaced by the modern machines and equipment.
Implications
A firm may go for modernization at a low pace to maintain its position in the market.
Thus, it may be considered a stability strategy.
Modernization may be used with full strength to achieve internal growth. Thus, it is used
as an internal growth strategy.
Advantages
Modernization improves the productivity and efficiency of the firm.
The profitability of the firm goes up because of increased efficiency and reduced
wastages.
It makes available better quality products to the customers.
The firm becomes more competitive in the long-run because of modernization.
The growth is systematic and does not affect the normal functioning of the firm.
The workers acquire modern skills because of which their wages go zup.
Limitations
The accumulated savings of the business may not be sufficient to Finance modernization
of plant and machinery.
The responsibilities of top executives would increase because of need to handle new
product, technology and markets.
The existing staff may face problems in adapting to the new technology.
4) MERGER
When different companies combine together into new corporate organizations, such a process
is known as mergers.
Merger can occur in two ways:
Acquisition of takeover
Amalgamation.
Takeover or acquisition takes place when a company offers cash or securities in exchange for
the majority shares of another company. It involves one company taking over control of
another.
Amalgamation takes place when two or more companies of equal size or strength formally
submerge their corporate identities into a single one in a friendly atmosphere.
Advantages
A merger provides economies of large-scale operations.
Better utilization of funds can be made to increase profits.
There is possibility of diversification.
More efficient use of resources can be made.
Sick firms can be rehabilitated by merging them with strong and efficient concerns.
It is often cheaper to acquire an existing unit than to set up a new one.
It is possible to gain quick entry into new lines of business.
It can provide access to scarce raw materials and distribution network and managerial
expertise.
Disadvantages
The combined enterprise may be unwieldy. Effective co-ordination and control becomes
difficult. As a result efficiency and profitability may decline.
Mergers give rise to monopoly and concentration of economic power which often
operate against the interest of the society and the country.
5) JOINT VENTURE
When two or more firms mutually decide to establish a new enterprise by participating in
equity capital and in business operations, it is known as joint venture. A joint venture is a
business partnership between two or more companies for a specific business operation.
Joint venture can be with a firm in the same country or a foreign country.
REFERENCES
Alternative growth strategies for small business by Sonia Sabharwal
Вам также может понравиться
- Cash CallsДокумент7 страницCash CallseddiemedОценок пока нет
- Offshore Company Formation For More Than 40 Offshore Jurisdictions.Документ31 страницаOffshore Company Formation For More Than 40 Offshore Jurisdictions.Offshore Company Formation100% (1)
- Copia de COLOMBIA, US Commercial Service, Doing Business In..., 2015Документ139 страницCopia de COLOMBIA, US Commercial Service, Doing Business In..., 2015Rita Mitacc SaraviaОценок пока нет
- Griffin - 8e - PPT - ch02 The Environment of Organizations and The ManagersДокумент38 страницGriffin - 8e - PPT - ch02 The Environment of Organizations and The ManagersKrisangel AbletesОценок пока нет
- Redefining Business Growth: New Products, Markets & RevenueДокумент27 страницRedefining Business Growth: New Products, Markets & RevenueJasvinder Singh67% (3)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)От EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (25)
- Top US stocks by market cap and floatДокумент34 страницыTop US stocks by market cap and floatAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Strategic MGMT Unit 4Документ7 страницStrategic MGMT Unit 4PrannoyChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- Mckinsey Growth Pyramid: Name: Ravi Chevli Batch: ITBM 2009-11 PRN: 9030241026 Topic: Growth StrategyДокумент6 страницMckinsey Growth Pyramid: Name: Ravi Chevli Batch: ITBM 2009-11 PRN: 9030241026 Topic: Growth Strategyravi_29_08Оценок пока нет
- Luna Pen NegotiationДокумент9 страницLuna Pen NegotiationJoanne Ferrer100% (1)
- Grand StrategiesДокумент5 страницGrand StrategiesNawab Ali100% (1)
- MABUHAY v. SEMBCORPДокумент3 страницыMABUHAY v. SEMBCORPitsmesteph60% (5)
- Bba Iv TH Semester Business Policy & Stratergic Analysis Module - Iv NotesДокумент74 страницыBba Iv TH Semester Business Policy & Stratergic Analysis Module - Iv NotesShivaniОценок пока нет
- Joint Venture AgreementДокумент4 страницыJoint Venture AgreementTariq Hussain KhanОценок пока нет
- Narra Nickel Mining and Development CorpДокумент4 страницыNarra Nickel Mining and Development CorpGillian Alexis ColegadoОценок пока нет
- Types of Growth StrategiesДокумент35 страницTypes of Growth StrategiesYash MittalОценок пока нет
- Principles of The Contract Farming AgreementДокумент2 страницыPrinciples of The Contract Farming AgreementAlexОценок пока нет
- MCom Types of StrategiesДокумент63 страницыMCom Types of StrategiesViraj BalsaraОценок пока нет
- FDI Benefits of GlobalizationДокумент10 страницFDI Benefits of GlobalizationTommy MonteroОценок пока нет
- Unit 4-Diversification & MergersДокумент8 страницUnit 4-Diversification & MergersnagamaniОценок пока нет
- Successful Joint Ventures in TheДокумент14 страницSuccessful Joint Ventures in TheQuỳnh NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Global M&A Diversification StrategiesДокумент9 страницGlobal M&A Diversification StrategiesJebin JamesОценок пока нет
- Strategic ManagementДокумент49 страницStrategic Managementnoorkalif89% (18)
- HRM On PantaloonsДокумент32 страницыHRM On PantaloonsHarish Kumar Shakya38% (8)
- Expansion Growth StrategiesДокумент20 страницExpansion Growth StrategiesButtercupОценок пока нет
- Meaning of Expansion StrategyДокумент31 страницаMeaning of Expansion StrategybhagyashreemohiteОценок пока нет
- First AssignmentДокумент5 страницFirst Assignmentমুহম্মদ কামরুল ইসলামОценок пока нет
- Grand StrategyДокумент6 страницGrand StrategyEma AkhterОценок пока нет
- First AssignmentДокумент5 страницFirst Assignmentkhang gamingОценок пока нет
- EED Note 2Документ34 страницыEED Note 2Shem HaElohim EjemОценок пока нет
- Meaning of Corporate Strategy: Strategic Management Kmbn301 Unit IiiДокумент32 страницыMeaning of Corporate Strategy: Strategic Management Kmbn301 Unit IiiANKUR CHOUDHARYОценок пока нет
- SM Unit 3Документ34 страницыSM Unit 3ANKUR CHOUDHARYОценок пока нет
- Diversification strategies risks rewardsДокумент8 страницDiversification strategies risks rewardsSheila Mae AramanОценок пока нет
- BUSINESS-PLANNINGДокумент60 страницBUSINESS-PLANNINGVishwa NatarajОценок пока нет
- Bussiness Chapter 7Документ8 страницBussiness Chapter 7Bethelhem YetwaleОценок пока нет
- Chapter Seven 7. Growth Strategies For Small BusinessДокумент8 страницChapter Seven 7. Growth Strategies For Small BusinessDamto BirhanuОценок пока нет
- Presentation On Topic: Concentration and Integration StrategiesДокумент19 страницPresentation On Topic: Concentration and Integration StrategiesMalmarugan DОценок пока нет
- Growth Strategies Small FirmsДокумент12 страницGrowth Strategies Small FirmsAtaklti TekaОценок пока нет
- Latest CH 3Документ29 страницLatest CH 3Berhe GebrezgiabherОценок пока нет
- Parenting (The Building of Corporate Synergies Through Resource Sharing andДокумент8 страницParenting (The Building of Corporate Synergies Through Resource Sharing andMalikОценок пока нет
- Balanced Scorecard: Introduction of The Types of StrategiesДокумент13 страницBalanced Scorecard: Introduction of The Types of StrategiesnellОценок пока нет
- Mergers and Acquisitions Types and Value CreationДокумент10 страницMergers and Acquisitions Types and Value CreationSoorajKrishnanОценок пока нет
- Business Policy & Strategy: Unit 4Документ73 страницыBusiness Policy & Strategy: Unit 4Harsh y.Оценок пока нет
- Strategies in Action: 13 Options for Growth and StabilityДокумент66 страницStrategies in Action: 13 Options for Growth and StabilitySemira muradОценок пока нет
- Strategies and ConceptsДокумент23 страницыStrategies and ConceptsSagar PanditОценок пока нет
- STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT UNIT 3 NCEДокумент28 страницSTRATEGIC MANAGEMENT UNIT 3 NCEBorish LiffinОценок пока нет
- Grand StrategiesДокумент8 страницGrand StrategiesGautam Krishna50% (2)
- Internal Growth StrategyДокумент17 страницInternal Growth StrategysiesarooОценок пока нет
- Strategic Management: Business Strategies and Corporate StrategiesДокумент22 страницыStrategic Management: Business Strategies and Corporate StrategiesRajat ShettyОценок пока нет
- Corporate Level StrategiesДокумент20 страницCorporate Level StrategiessaiОценок пока нет
- Diversification, Venturing and Corporate Restructuring For National and International BusinessДокумент12 страницDiversification, Venturing and Corporate Restructuring For National and International BusinessShubh GuptaОценок пока нет
- Strategies in ActionДокумент66 страницStrategies in ActiontibebuОценок пока нет
- Grand StrategiesДокумент7 страницGrand Strategiesgauravkumar100% (4)
- DiversificationДокумент3 страницыDiversificationahamd aslamОценок пока нет
- Maryland International College Strategies in ActionДокумент66 страницMaryland International College Strategies in ActionAbdurehman AliОценок пока нет
- Corporate-Level Strategy:: Integration: Vertical IntegrationДокумент5 страницCorporate-Level Strategy:: Integration: Vertical IntegrationkriteshjayswalОценок пока нет
- ENT 202 - Note 9Документ5 страницENT 202 - Note 9Akinyemi IbrahimОценок пока нет
- Strategic Financial Management: Individual AssignmentДокумент11 страницStrategic Financial Management: Individual AssignmentSoorajKrishnanОценок пока нет
- New AssignementДокумент4 страницыNew AssignementMUQADAR RajpootОценок пока нет
- Diversification Strategy GuideДокумент15 страницDiversification Strategy GuideMandeep Singh Birdi100% (1)
- Strategic ManagementДокумент14 страницStrategic ManagementAmin JasaniОценок пока нет
- Merger As A Strategy of Growth: Manita Jindal 133 Sweta Aggarwal Sumit Lakra 102 Himansu KumarДокумент21 страницаMerger As A Strategy of Growth: Manita Jindal 133 Sweta Aggarwal Sumit Lakra 102 Himansu KumarHimanshu KumarОценок пока нет
- Strategy Notes - Comb MhmDEДокумент34 страницыStrategy Notes - Comb MhmDEMohamad AbrarОценок пока нет
- Diversification Strategy: Diversification in The Context of Growth StrategiesДокумент7 страницDiversification Strategy: Diversification in The Context of Growth StrategiesZainab ChitalwalaОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 4Документ4 страницыTutorial 4Aminath AzneeОценок пока нет
- Mergers and AcquisitionsДокумент6 страницMergers and AcquisitionsVishnu RajeshОценок пока нет
- Growth Strategies in BusinessДокумент4 страницыGrowth Strategies in BusinessShweta raiОценок пока нет
- Corporate and acquisition strategies for competitive advantageДокумент13 страницCorporate and acquisition strategies for competitive advantageRegional SwamyОценок пока нет
- Corporate - Level StrategiesДокумент27 страницCorporate - Level Strategiescoolth2Оценок пока нет
- Advantages of DiversificationДокумент4 страницыAdvantages of DiversificationbijayОценок пока нет
- Diversification Strategy Unit - IVДокумент20 страницDiversification Strategy Unit - IVKavya GuptaОценок пока нет
- ANOVACorrelation RegressionДокумент4 страницыANOVACorrelation RegressionAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Week 4 Anova Human Behaviors Assignment 1Документ21 страницаWeek 4 Anova Human Behaviors Assignment 1Adroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Wk11 Assignments Due Jun 19, 2020: Discussion Board Topic 1Документ2 страницыWk11 Assignments Due Jun 19, 2020: Discussion Board Topic 1Adroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Week3 Quiz Q1Документ6 страницWeek3 Quiz Q1Adroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Running Head: Should Welfare Applicants Be Drug Tested 1Документ6 страницRunning Head: Should Welfare Applicants Be Drug Tested 1Adroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Weekly QuestionДокумент2 страницыWeekly QuestionAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Week 4 Chi Square AssignmentДокумент1 страницаWeek 4 Chi Square AssignmentAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Deliverable 05 - Worksheet: Instructions: The Following Worksheet Describes Two Examples - One Is An Example ForДокумент6 страницDeliverable 05 - Worksheet: Instructions: The Following Worksheet Describes Two Examples - One Is An Example ForAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Key Words: Occupational Health, Safety, COVID 19, Corona Virus, Construction, EngineeringДокумент13 страницKey Words: Occupational Health, Safety, COVID 19, Corona Virus, Construction, EngineeringAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Send A Message With Your Answer Spreadsheet To The ProfessorДокумент2 страницыSend A Message With Your Answer Spreadsheet To The ProfessorAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Job TitleДокумент18 страницJob TitleAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Envy, CWB, and Leadership Moderation in Public vs Private OrgsДокумент8 страницEnvy, CWB, and Leadership Moderation in Public vs Private OrgsAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Factors That Determine Appropriate Demands Made On EmployeesДокумент5 страницFactors That Determine Appropriate Demands Made On EmployeesAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- 323660653Документ3 страницы323660653Adroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Running Head: Interpretation of Graphs in Excel and Spss 1Документ7 страницRunning Head: Interpretation of Graphs in Excel and Spss 1Adroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Brief Introduction About Orthogonal Design (OD)Документ8 страницBrief Introduction About Orthogonal Design (OD)Adroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Subject Before After 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12Документ2 страницыSubject Before After 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12Adroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Running Head: DISCUSSION HOMEWORK 1Документ2 страницыRunning Head: DISCUSSION HOMEWORK 1Adroit WriterОценок пока нет
- 322847353Документ2 страницы322847353Adroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Deliverable 01 Worksheet: Answer and ExplanationДокумент5 страницDeliverable 01 Worksheet: Answer and ExplanationAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Topic: Text Messaging And/or Instant Messaging Is Time-Consuming Topic Description: Text Messaging Is About Twenty-Seven Years Old (Eveleth), AndДокумент14 страницTopic: Text Messaging And/or Instant Messaging Is Time-Consuming Topic Description: Text Messaging Is About Twenty-Seven Years Old (Eveleth), AndAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Deliverable 05 - Worksheet: Instructions: The Following Worksheet Describes Two Examples - One Is An Example ForДокумент6 страницDeliverable 05 - Worksheet: Instructions: The Following Worksheet Describes Two Examples - One Is An Example ForAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Trigonometry and The Area of A Triangle: Course ActivityДокумент9 страницTrigonometry and The Area of A Triangle: Course ActivityAdroit Writer100% (1)
- 322847353Документ2 страницы322847353Adroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Deliverable 01 Worksheet: Answer and ExplanationДокумент5 страницDeliverable 01 Worksheet: Answer and ExplanationAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Interpreting Statistics WorksheetДокумент4 страницыInterpreting Statistics WorksheetAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Job TitleДокумент18 страницJob TitleAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Question One: Surname 1 Name of Student Instructor's Name Course Name Date Questions and AnswersДокумент3 страницыQuestion One: Surname 1 Name of Student Instructor's Name Course Name Date Questions and AnswersAdroit WriterОценок пока нет
- Subject Before After 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12Документ2 страницыSubject Before After 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12Adroit WriterОценок пока нет
- TitagarhДокумент94 страницыTitagarhdhruvfeedbackОценок пока нет
- International Trade PDFДокумент302 страницыInternational Trade PDFsaravanan_mcОценок пока нет
- PQ CP-305 System Doc 31.05.2016Документ89 страницPQ CP-305 System Doc 31.05.2016sahil4INDОценок пока нет
- EPCC For New Boil Off Gas Compressor Project - ITT DocumentДокумент253 страницыEPCC For New Boil Off Gas Compressor Project - ITT Documenteasysapphire007Оценок пока нет
- IJV MARLEY AutomotiveДокумент6 страницIJV MARLEY AutomotiveUmer HamidОценок пока нет
- CIT Calcutta v. Burlop Dealers Ltd.Документ3 страницыCIT Calcutta v. Burlop Dealers Ltd.anilaumesh100% (1)
- Legislation on Joint Ventures in EthiopiaДокумент2 страницыLegislation on Joint Ventures in EthiopiaVinse Milan100% (2)
- Thailand Legal System OverviewДокумент41 страницаThailand Legal System Overviewempty87Оценок пока нет
- 28th Annual Report-2022Документ165 страниц28th Annual Report-2022titu_1552Оценок пока нет
- SMEs in Msia - Ebook ISBN 978-3-659-52051-8Документ189 страницSMEs in Msia - Ebook ISBN 978-3-659-52051-8Pok Wei FongОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9: Strategic Alliances 16Документ27 страницChapter 9: Strategic Alliances 16Michelle LindsayОценок пока нет
- Executive SummaryДокумент36 страницExecutive SummarySuchitaSalviОценок пока нет
- Northern Railway - Tender DocumentДокумент52 страницыNorthern Railway - Tender Documentabhi_1mehrotaОценок пока нет
- Doing Business in Indonesia Guide for U.S. CompaniesДокумент113 страницDoing Business in Indonesia Guide for U.S. CompaniesFerdy Fer DОценок пока нет
- Davao Water Treatment Plant Design and ConstructionДокумент217 страницDavao Water Treatment Plant Design and ConstructionBert EngОценок пока нет
- Vol-I Basti Zone PDFДокумент248 страницVol-I Basti Zone PDFSagarОценок пока нет
- Kinds of TaxpayersДокумент7 страницKinds of TaxpayersRZ ZamoraОценок пока нет
- Defence Offset PolicyДокумент8 страницDefence Offset PolicyMahim SharmaОценок пока нет