Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
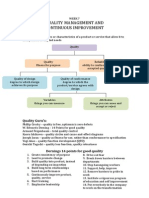
Quality Management History of Quality
Загружено:
Hirenkumar ShahОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Quality Management History of Quality
Загружено:
Hirenkumar ShahАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
35A00210
Operations Management
Lecture 10
Quality management
History of quality
Definition of quality
Cost of qual ity
Total quality management
Quality awards
Lecture 10
Quality management
History of quality
OM2013 - 10
Development of quality
3 OM2013 - 10
The three main gurus of quality
W. Edwards Deming
- quality is continuous improving and minimizing
variation
- the biggest reason for low quality is bad
management
- 14 points, plan-do-check-act cycle, removing
fear, long term focus, training employees, fact-
based management
Joseph M. Juran
- quality is fitness for use(functionality)
- strongest customer point of view
- importance of management, planning, training,
annual quality breakthroughs, focus on chronic
problems, quality has a price
4
OM2013 - 10
The three main gurus of quality
Phil ip Crosby
- quality is production according to specifications
- Quality is free, Zero defects
- prevention of errors/faults is important
- there is no trade-off in quality
- Increased publicity of quality tremendously
5 OM2013 - 10
Walter Shewhart
- statistical process control (SPC) already in
1930s
Other important persons related to
quality
Genichi Taguchi
- product and production design as a base for quality and
costs
- Quality loss -function (even a small deviation from
optimal cost money), Robust design -ideology
Armend Feigenbaum
- everybody is responsible for quality
(TQM in 1950s), Total Quality
Control
6
Other important persons related to
quality
OM2013 - 10
Kaoro Ishikawa
- quality circles, customershipwithin the organization
- Ishikawa-diagrams (cause-effect) and graphical
presentation of quality
Yoki Akao
- QFD (quality function deployment/House of Quality) as
tool for product design
Shigeo Shingo
- Poka-Yoke (mistake-proofing) -design, redesign of
processes
7
Lecture 10
Quality management
Definition of quality
OM2013 - 10
Quality is remembered
long after the price has
been forgotten Gucci family slogan
9
Importance of quality - case
Firestone -
OM2013 - 10 10
174 dead, 700 injured, 13 million recalled tires
and $2,5 billion bill!
OM2013 - 10
What is quality really?
The degree of excellence of a thing (Webster)
Excellence
The totality of features and characteristics that satisfy needs
How customer and potential customers view the product
Meeting and exceeding customer expectations
Value for the price
Fitness for use
Neither mind or matter, but a third entity independent of the
two...even though it cannot be defined, you know what it is
Psychological impressions
Specifications as to how product should be made
How well each unit of product meets specifications
Conformance to specifications
Quality is hard to define or even notice. On the other hand,
bad quality can be seen far away
12
Many ways to define quality
Production orientati on
- quality is measured by the faults in the product
Product ori entation
- the features of the product define its quality
Value ori entation
- value in relation to price
Competition ori entation
- value that customer gives to product in comparison to others
Customer ori entation
- ability to satisfy customer needs
Environmental orientati on
- total impact on society and environment
OM2013 - 10 13
Two main ways to look at quality
Meeting standards
and specifications
- quality of production
- costs, regulations
Difference in quali ty
leads to deviati on
from agreed
properties
Ability to meet
customer needs and
expectations
- quality of design
- price, features, user
friendliness, functionality,...
Quality enables
satisfying customer
needs
OM2013 - 10 14
Customer
point of view
Producer
point of view
OM2013 - 10
The characteristics of quality
Functionality
Reliability
Appearance
Recovery
Contact
Overall
quality
Durability
15
OM2013 - 10
Responsiveness Reliability
Credibility
Competence
Timeliness
and speed
Performance
Ten dimensions of service quality
Service
quality
Tangibles
Communi-
cation
Empathy
Assurance
16
Service Quality Gap Model
Lecture 10
Quality management
Cost of quality
OM2013 - 10
OM2013 - 10
Mr. Biv gives managers grey hair
Mistakes
Rework
Breakdown
Inefficiency
Variation
19
OM2013 - 10
Costs of quality assurance
Design of quality
systems and control
- both management and
control
Implementation of
quality system
- training and teaching
- product, process and
machine design
- checking processes
- supplier relationships
- information gathering and
analyzing
Quality control and
inspection
- material, production
process, finished product,
installation etc. inspections
Maintenance of test
equipment
External approval
costs
Control Prevention
20 OM2013 - 10
Costs of low quality
Guarantees and
liability costs
Repairing costs
Return and recall
costs
Discounts
Customer complaints
Bad reputation
Lost sales
Legal costs
Reproduction
Retesting
Scrap costs
Downtime
Lower yield
Extra capacity,
inventory, work time
Extra scheduling
Internal failure External failure
21
OM2013 - 10
Different costs are not linear!
C
o
s
t
s
f
o
r
f
i
n
d
i
n
g
a
n
d
f
i
x
i
n
g
t
h
e
p
r
o
b
l
e
m
Prevention Customer Process Final inspection
22 OM2013 - 10
C
o
s
t
p
e
r
p
r
o
d
u
c
e
d
u
n
i
t
100%
wrong
Quality level 100%
good
Cost of
quali ty assurance
Cost of
low quality
Total
Quality
Costs
Optimal level
Minimum cost level
Traditional view on quality costs
24
OM2013 - 10
Optimal level
More current view on quality costs
Minimum cost level
100%
wrong
Quality level 100%
good
C
o
s
t
p
e
r
p
r
o
d
u
c
e
d
u
n
i
t
Cost of
quali ty assurance
Cost of
low quality
Total
Quality
Costs
Cost of quality assurance
does not increase
exponentially with quality
level when its build into
the system!
25
Other remarks of quality costs
Its been estimated that costs of low quality are
even 20-30% of sales
Great amount of quality costs are created in
design phase
- 95% of quality costs are fixed after design phase
The sooner the fai lure is found the lower is the
cost it causes
- inspection is 100 times cheaper than sending repairperson
- unfortunately, most of the quality costs still come from failure
Sometimes good enough -poli cy is optimal
- on the other hand, in some cases its not acceptable to produce
quality lower than 100%
OM2013 - 10 26
Lecture 10
Quality management
Total quality management
OM2013 - 10
What is Total Quality Management
(TQM)?
Qual ity philosophy concerning the whole
organi zation
Managing the whole organization so that it can
fulfil l customer expectations
- quality (in broad sense) is the most important success factor
In TQM all persons in organizati on influence i n
quality, not just quality control or inspection
department
15% of all quality problems are related to a particul ar worker or
tool. The other 85% arise from faults in the companys system
and will continue until the system is changed.
W. Edwards Deming
29
OM2013 - 10
Principles of TQM
TQM
Scientific
quali ty control
Principle of
continuous
improvement
and commitment
Customer focus
and commitment
for quality
Involvement of
whole
organization
30
Principles of TQM
Customer specifies quality standards
Management commits to quality and manages
improving of quality
Employees are responsible for quality
- e.g. quality circles (group focus), training
Design of processes to maintain quality
Doing things right in the first time
Continuous improvement
- plan - do - check - act, benchmarking
Observing quality and immediate reactions
- e.g. prevention and statistical quality control
- improvements are based on facts
Involvement of suppliers in quality programs etc.
OM2013 - 10 31
Implementing TQM
Prerequisites and requirements...
- commitment of top management
- training and empowerment of employees
- strong customer focus and broad quality concept
- continuous process improvement
Implementation...
- process differs from one company to another
- begins and ends with training
- training of management, composition of steering group
- quality improvement plans, goals, responsibilities, priorities
- recognizing core processes, information gathering
- communication, training of lower level employees
- finding causes and solutions for problems
- from problem solving to managing processes
OM2013 - 10 32 OM2013 - 10
Why do TQM programs usually
fail?
Lack of commitment of top management
- organization structure, rewards, lack of resources
Concentrating on one technique instead of whole
process
- e.g. quality circles TQM is process, not a formula/technique
- all departments can influence quality (human resources, purchasing...)
Trying to implement procedures that dont fit into
organization (e.g. statistical process control)
Lack of involvement of employees
- no interest, no commitment (middle management usually problem)
Support ends with training
- TQM needs continuous contribution
Lack of long term interest
- trying everything expecting immediate results
34
Lecture 10
Quality management
Quality standards and
awards
OM2013 - 10 36
ISO -standards
International quality certification system
- founded in 1987, used in over that 100 countries
- International Organization for Standardization
Prerequisite for i nternati onal competi tion?
- Common language for different parties, minimum requirement
Five different series; ISO 9000-9004
- 9000 and 9004 basically just instructions and guidelines
OM2013 - 10 37
Desing Purchasing Productions Testing Installation Service
ISO 9001
ISO 9002
ISO 9003
OM2013 - 10
ISO -standards
Mainly quality improvement tool
- how is quality assured in a company? (=prevention)
- organization must document everything related to quality and then
operate according to documents
- firms apply due to internal improvements and external credibility
Concentrates on quality and control of
processes
- systematic policies and processes
- dont take innovations in account
Does not provide solution for probl ems but
suggestions how to improve quality system
Does not guarantee quali ty of operati ons
- having a standard and using one are different things!
40
ISO beyond quality
OM2013 - 10 41
Quality awards
Basic idea is to improve appreciation of quality and
award successful companies
- gather information, experiences and implementation advices from winners -
and sell it
Many different awards around the world
- Deming (J apan), Baldrige (USA), European Quality Award, Finnish quality
award etc.
- different categories (e.g. production, service, SMEs, public organizations)
Application processes long and expensive
- lots of documentation, focus on other things in organization may disappear
TQM variables often stressed
- enablers (processes of TQM) have been more important than real results
- now the balance is 50% vs. 50%
Is there advantage in taking part?
OM2013 - 10 42
OM2013 - 10
European Foundation for Quality
Management
43
10%
10%
10%
10%
10%
10%
10%
15% 15%
Complementary methods with different kinds of
objectives
- both are based on commitment to quality
OM2013 - 10
Internal focus
Process oriented quality
No continuousness
required
Standards
Standards and awards
Awards
External focus
Customer oriented quality
Supports continuous
development
45
Вам также может понравиться
- Role of QA&QC in Manufacturing - PresentationДокумент32 страницыRole of QA&QC in Manufacturing - Presentationimran jamilОценок пока нет
- Keepa ApiДокумент55 страницKeepa ApiQazi Sohail AhmadОценок пока нет
- PESTEL AnalysisДокумент2 страницыPESTEL AnalysisSayantan NandyОценок пока нет
- Quality Management Iso9001:2015 Changes: A Guide to ImplementationОт EverandQuality Management Iso9001:2015 Changes: A Guide to ImplementationРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Pega DevOps Release Pipeline OverviewДокумент200 страницPega DevOps Release Pipeline OverviewArun100% (1)
- Quality Management and Continuous ImprovementДокумент6 страницQuality Management and Continuous ImprovementautumntaitОценок пока нет
- Value ChainДокумент6 страницValue ChainSyed NazrulОценок пока нет
- Quality: Presented By: Mohd Saiful Izwaan Bin Saadon Lecturer (Quality Engineering Dept.)Документ40 страницQuality: Presented By: Mohd Saiful Izwaan Bin Saadon Lecturer (Quality Engineering Dept.)Khairul ZaimОценок пока нет
- TQMДокумент10 страницTQMpartech206752Оценок пока нет
- MGT311 Assignment 1Документ7 страницMGT311 Assignment 1Hut MutОценок пока нет
- Product QualityДокумент17 страницProduct QualityMalkeet SinghОценок пока нет
- Total Quality Management: FACULTY: Dr. Mossa. Anisa KhatunДокумент21 страницаTotal Quality Management: FACULTY: Dr. Mossa. Anisa KhatunArup SahaОценок пока нет
- TQM QA Unit1Документ9 страницTQM QA Unit1akhshayamОценок пока нет
- Chapter - V: Managing QualityДокумент27 страницChapter - V: Managing Qualityak5775Оценок пока нет
- TQM Resource MaterialДокумент86 страницTQM Resource Materialj80164309Оценок пока нет
- Unit 1&2Документ34 страницыUnit 1&2AbinayaОценок пока нет
- Management of Quality The Quest For QualityДокумент12 страницManagement of Quality The Quest For QualityKelvin mwai100% (1)
- TQM 2&16 Mark With AnswerДокумент25 страницTQM 2&16 Mark With AnswerJaga Deesh100% (1)
- Total Quality Management: Mudassar SalmanДокумент51 страницаTotal Quality Management: Mudassar SalmanJuan M. Reyes Jr.Оценок пока нет
- TQM Unit 1Документ24 страницыTQM Unit 1bhuvansparksОценок пока нет
- L4 Quality ManagementДокумент7 страницL4 Quality Managementaiswaria 03Оценок пока нет
- TQM & Om: TQM Customer-Driven Quality ManagementДокумент24 страницыTQM & Om: TQM Customer-Driven Quality ManagementsadfiziaОценок пока нет
- TQM FinalДокумент27 страницTQM FinalSamyak Swastik SahooОценок пока нет
- Part 2 SatisfactionДокумент53 страницыPart 2 SatisfactioncharithОценок пока нет
- Compiled by Ramdziah Md. NasirДокумент46 страницCompiled by Ramdziah Md. NasirWei HuaiОценок пока нет
- TQM Questions and AnswersДокумент19 страницTQM Questions and AnswersYogeesha HCОценок пока нет
- Joy Degobaton - OMTQ Topic 6Документ4 страницыJoy Degobaton - OMTQ Topic 6Joy DegobatonОценок пока нет
- Total Quality Management Unit I GE2022Документ52 страницыTotal Quality Management Unit I GE2022standalonembaОценок пока нет
- Quality and ReliabilityДокумент32 страницыQuality and ReliabilitymaheshОценок пока нет
- TQM Question Bank Final 1Документ36 страницTQM Question Bank Final 1menakadevieceОценок пока нет
- QM 0010Документ12 страницQM 0010Mrinal KalitaОценок пока нет
- Operations Management: William J. StevensonДокумент67 страницOperations Management: William J. StevensonaprianОценок пока нет
- Basic of Quality, SPC, Process CapabilityДокумент110 страницBasic of Quality, SPC, Process CapabilityminionОценок пока нет
- Cost of Quality - 3 September, 2010 - Dr. Paramjit KaurДокумент52 страницыCost of Quality - 3 September, 2010 - Dr. Paramjit KaurArushi ...Оценок пока нет
- Total Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsДокумент35 страницTotal Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key Elementsronski17Оценок пока нет
- TQM Mod-1Документ4 страницыTQM Mod-1baluranmissy29Оценок пока нет
- Module 6 - Quality and Its Importance in An OrganizationДокумент28 страницModule 6 - Quality and Its Importance in An OrganizationalexОценок пока нет
- QTДокумент17 страницQTuiddcguzОценок пока нет
- Total Quality Management WordДокумент9 страницTotal Quality Management WordEbru KolacanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Introduction and Fundamental of QC PDFДокумент28 страницLecture 1 Introduction and Fundamental of QC PDFWoon HowОценок пока нет
- Quality - IntroductionДокумент7 страницQuality - IntroductionvmktptОценок пока нет
- LSS U1 2020Документ23 страницыLSS U1 2020Kamal KannanОценок пока нет
- BUMAДокумент11 страницBUMAElaine Ü LubianoОценок пока нет
- Airports Total Quality ManagementДокумент87 страницAirports Total Quality ManagementmuhamadmomtazОценок пока нет
- The Cost of QualityДокумент41 страницаThe Cost of QualityKundan Kumar SinghОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 5 - Quality ManagementДокумент21 страницаCHAPTER 5 - Quality ManagementJohn TuahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 ClassroomДокумент62 страницыChapter 9 Classroompreetam sapreОценок пока нет
- Operation Management Chapter 12Документ70 страницOperation Management Chapter 12Ahmad Izzat HamzahОценок пока нет
- 6 Quality Management-Ch-9 (Stevenson)Документ53 страницы6 Quality Management-Ch-9 (Stevenson)tahmid quayum50% (2)
- Prevention Costs Are All Costs Incurred in The Process of Preventing Poor Quality From Occurring. They Include QualityДокумент7 страницPrevention Costs Are All Costs Incurred in The Process of Preventing Poor Quality From Occurring. They Include Qualitymreenal kalitaОценок пока нет
- Unit-5 Quality Control - New For PDFДокумент49 страницUnit-5 Quality Control - New For PDFMubin Shaikh NooruОценок пока нет
- Handouts by Total Quality ManagementДокумент18 страницHandouts by Total Quality ManagementRheymar PaguioОценок пока нет
- Chapter Five Quality Management and Control 5.1. Overview of Total Quality Management and Quality SpecificationДокумент7 страницChapter Five Quality Management and Control 5.1. Overview of Total Quality Management and Quality SpecificationGebrekiros ArayaОценок пока нет
- Group 1 Foundation of TQMДокумент9 страницGroup 1 Foundation of TQMSweetMikanОценок пока нет
- Otal Uality AnagementДокумент143 страницыOtal Uality AnagementJohn Rex PanestanteОценок пока нет
- MT 14 - Total Quality ManagementДокумент43 страницыMT 14 - Total Quality ManagementRuíz Figueroa, Jean E.Оценок пока нет
- OM M9 TQM HandoutДокумент64 страницыOM M9 TQM HandoutChandan SainiОценок пока нет
- CBMEДокумент41 страницаCBMEJocelle IgosОценок пока нет
- DCM 222/quality Management Introduction and Implementation of Total Quality Management (TQM)Документ6 страницDCM 222/quality Management Introduction and Implementation of Total Quality Management (TQM)johnОценок пока нет
- The Challenge of QualityДокумент22 страницыThe Challenge of QualitytungquacertОценок пока нет
- Wheels BusДокумент2 страницыWheels BusHirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет
- Humpty Dumpty CompleteДокумент25 страницHumpty Dumpty CompleteSvetik RotaruОценок пока нет
- Feathers For LunchДокумент34 страницыFeathers For LunchHirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет
- Jolly Good HockeyДокумент20 страницJolly Good HockeyHirenkumar Shah100% (2)
- Emergency Vehicles WheelДокумент2 страницыEmergency Vehicles WheelHirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет
- G1V1 U1 T1Документ37 страницG1V1 U1 T1Hirenkumar Shah100% (2)
- Animal SensesДокумент14 страницAnimal SensesHirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет
- English Language Arts Test: Book 1Документ16 страницEnglish Language Arts Test: Book 1Lena KovalenkoОценок пока нет
- Activity Book KДокумент325 страницActivity Book KManuel Antonio Lazo Velasquez100% (1)
- Clever JohnДокумент20 страницClever JohnHirenkumar Shah100% (1)
- Scholasticnews Indepth War-Iraq Militaryquestions PDFДокумент1 страницаScholasticnews Indepth War-Iraq Militaryquestions PDFHirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет
- Expert Answers: A Child Psychologist Helps You Field The Tough Questions Your Students May AskДокумент1 страницаExpert Answers: A Child Psychologist Helps You Field The Tough Questions Your Students May AskHirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет
- Scholasticnews Indepth Space Space3Документ1 страницаScholasticnews Indepth Space Space3Hirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет
- Scholasticnews Indepth Special Olympics SpecialolympicsДокумент1 страницаScholasticnews Indepth Special Olympics SpecialolympicsHirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет
- Scholasticnews Indepth War-Iraq Expert AdviceДокумент1 страницаScholasticnews Indepth War-Iraq Expert AdviceHirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет
- Scholasticnews Indepth War-Iraq Brodkin12Документ1 страницаScholasticnews Indepth War-Iraq Brodkin12Hirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет
- Scholasticnews Indepth Shuttle PiecesДокумент1 страницаScholasticnews Indepth Shuttle PiecesHirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет
- Scholasticnews Indepth Space Space2Документ1 страницаScholasticnews Indepth Space Space2Hirenkumar ShahОценок пока нет
- Demand Management in Global Supply Chain - Disertasi S3Документ166 страницDemand Management in Global Supply Chain - Disertasi S3Ahmad BuchoriОценок пока нет
- Statistics For EconomicsДокумент58 страницStatistics For EconomicsKintu GeraldОценок пока нет
- 3500 Ha027988 7Документ384 страницы3500 Ha027988 7Gigi ZitoОценок пока нет
- Pre-Colonial Philippine ArtДокумент5 страницPre-Colonial Philippine Artpaulinavera100% (5)
- The USP AdvantageДокумент30 страницThe USP AdvantageGabriel A. RamírezОценок пока нет
- Kalsi P S - Organic Reactions and Their Mechanisms 5eДокумент26 страницKalsi P S - Organic Reactions and Their Mechanisms 5eeasy BooksОценок пока нет
- Fruit Brearing CropsДокумент177 страницFruit Brearing CropsJoshua G. Sapin100% (1)
- A Guide To Energy Efficiency ComplianceДокумент16 страницA Guide To Energy Efficiency ComplianceOARIASCOОценок пока нет
- A Cultura-Mundo - Resposta A Uma SociedДокумент7 страницA Cultura-Mundo - Resposta A Uma SociedSevero UlissesОценок пока нет
- Paper 5Документ4 страницыPaper 5hbyhОценок пока нет
- Confirmation 2Документ11 страницConfirmation 2حمزة دراغمةОценок пока нет
- Ecological Pyramids WorksheetДокумент3 страницыEcological Pyramids Worksheetapi-26236818833% (3)
- Revised Implementing Rules and Regulations Ra 10575Документ79 страницRevised Implementing Rules and Regulations Ra 10575Rodel D. LuyaoОценок пока нет
- Akebono NVH White PaperДокумент4 страницыAkebono NVH White Paperapi-3702571100% (1)
- Soil ResistivityДокумент6 страницSoil ResistivityAnonymous EP0GKhfОценок пока нет
- PCI20107, Overview of Boiler Commissioning and Startup PDFДокумент17 страницPCI20107, Overview of Boiler Commissioning and Startup PDFMarc AnmellaОценок пока нет
- Check To Make Sure You Have The Most Recent Set of AWS Simple Icons Creating DiagramsДокумент48 страницCheck To Make Sure You Have The Most Recent Set of AWS Simple Icons Creating DiagramsarunchockanОценок пока нет
- AI LabДокумент17 страницAI LabTripti JainОценок пока нет
- Linberg V MakatiДокумент2 страницыLinberg V MakatiChimney sweepОценок пока нет
- Effect of Water On Quality and Preservation of FoodДокумент10 страницEffect of Water On Quality and Preservation of FoodrupinisinnanОценок пока нет
- Grade 8 Mock 1Документ11 страницGrade 8 Mock 1yutika GhuwalewalaОценок пока нет
- SAP HR and Payroll Wage TypesДокумент3 страницыSAP HR and Payroll Wage TypesBharathk Kld0% (1)
- Cell Signaling - The ComponentsДокумент7 страницCell Signaling - The Componentsk10 Lớp Dinh DưỡngОценок пока нет
- Jibachha's Textbook of Animal Health Volume-IIДокумент16 страницJibachha's Textbook of Animal Health Volume-IIjibachha sahОценок пока нет
- Pressuremeter TestДокумент33 страницыPressuremeter TestHo100% (1)
- (FORD) Manual de Propietario Ford Ranger 1998Документ160 страниц(FORD) Manual de Propietario Ford Ranger 1998Marly Salas GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Krunker SettingsДокумент2 страницыKrunker SettingsArsyad DanishОценок пока нет