Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ammunition Russia 37-40mm
Загружено:
enrico100%(1)100% нашли этот документ полезным (1 голос)
837 просмотров5 страницAmmunition Russia
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документAmmunition Russia
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(1)100% нашли этот документ полезным (1 голос)
837 просмотров5 страницAmmunition Russia 37-40mm
Загружено:
enricoAmmunition Russia
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 5
THE RUSS!AN ANNUN!T!
ON PAGE - 37NN TO +0NN
Please note that these pages are no longer updated and contain partially obsolete data.
For comprehensive and up to date information, please refer to my new book "Soviet Cannon" at
www.russianammo.org.
Compared to this webpage with its 69 pages, the book and the enclosed CD-Rom offer a total of almost
900 pages.
37x94R 37mm Hotchkiss Revolver- and Rapid-Loading Gun
With the appearance of the first torpedoboats in the late 1870s the Navies of the world realized the need for a quick fireing gun against those
torpedo boats. The Hotchkiss cannons were developed and produced in France by Benjamin B. Hotchkiss and were later also licence built by
Armstrong in England. The 37mm Hotchkiss cannons spread all over the world, their use was documented at least in 28 different countries.
!n 1880 the French 37mm Hotchkiss revolver cannon was introduced to service in Russia. Later, the 37mm Hotchkiss rapid-loading cannon joined
service. !n 1918 about +000 37mm cannons were listed in the Russian army.
Sadly, no precise technical data is known about the Russian ammunition in this caliber, the projectiles all have a weight arround 500g and a muzzle
velocity of about +00mfs (estimated).
Russian rounds all have a destinctive brass driving band 12mm - 12,5mm wide. Some rounds have a second driving band 6,5mm wide and spaced
12,5mm in front of the lower band.
Ammunition used in the Hotchkiss revolver gun and Hotchkiss rapid-loading gun:
USSR Designation US Abbreviation Bullet Weight [g| Nuzzle velocity [mfs| Description
Common Shell APHE ~ 500 ~ +00
APHE shell with brass base fuze (right hand thread) and black
powder charge. l= 9+mm (without fuze)
Steel Shell APHE ~ 500 ~ +00
APHE shell with two driving bands and steel base screw (right hand
thread). !nternal fuze inserted in base screw. l=92mm (without base
screw)
Armour Piercing AP ~ 500 ~ +00 Solid AP shot with two driving bands, l=82mm
Explosive Shell HE ~ 500 ~ +00
HE shell with time fuze. The time fuze has a knurled ring for time
adjustment. l=95mm (including fuze)
Partial cutaway drawings of the rounds listed above. Drawings from ECRA special bulletin 1990, cortesy of the German "Wehrtechnikmuseum" in
RoethenbachfPegnitz.
Picture of the first round with brass base fuze. l=93,6mm, m=+17g (without charge and without base fuze) ol=166,8mm, headstamp: 0,311 1 { !.Z.
anchor { G T { 2 1916
!mprinted in the projectile base: G S 17 1+ (5)
37x155 37mm N-37 aircraft cannon
The short recoil operated N-37 aircraft cannon was based on the wartime NS-37 but considerably reduced in powder and weight. !t was introduced
in 19+6 to replace the older NS-37 because the task of destroying mainly tanks and ground targets was obsolete and propper air to air combat
probabilities with higher rate of fire were needed.
The rate of fire of the N-37 is +00-+50rpm, ammunition is fed in linked steel belts. The gun weights 103kg without ammunition load and was
1 of 5 15f08f2013 10:57
2+60mm long, barrel length was 1310mm. The NiG-15 and -17 carried one gun each with +0 rounds of ammunition load, the N-37 may still be in
use today in underwing gun-pods.
Cartridge cases are brass and filled with 127g of +f1 FL propellant, they use the same percussion primer as the +5mm antitank rounds use.
Naximum armor penetration of the AP shell was 50mm.
20 cartridges of older manufacture were packed in a wooden box and separated by wooden spacers, these boxes weighted +0kg. Later, 10
cartridges were packed in a sealed metal container and 3 of those containers were overpacked in a wooden box weighting 56kg. Cartridge belt
links are packed in +00 pieces separately in a wooden box that weighted 60kg.
Ammunition was manufactured by the Czech Republic, Poland and Russia.
Ammunition used in the N-37:
USSR Designation US Abbreviation Bullet Weight [g| Nuzzle velocity [mfs| Description
OZT HE!-T 735 670
Conventional HE!-T shell filled with 37g of HE!, self-destruction nose
fuzes A-37, A-37U or B-37 fitted
OFZ HE! 729 670 As above but without tracer and filled with +9g of HE!
BR APHE 73+ 670 Base fuzed APHE shell filled with 36,1g of HE, AD-37 base fuze
BZT AP-T 735 670
Pointed AP shell with ballistic windshield cap (no incendiary!), tracer
element is sometimes not fitted
This type is also used as TP-T training round
UB-37 TP Airburst 726 670
As HE! shell but with self destruction fuze without impact action, light
blue colored fuze tip. For aerial target practice, self destructs
between 9 and 12 sek.
Left picture:
37x155 Czech OZSv (HE-T) shell, m=735g, l=175mm, ol=288mm, vo=670mfs, 127g of 7f1 FL smokeless powder, high explosive: 25g TNT,
Narkings on fuze: A-37 18-56 fut 23-56 evr, Narkings on shell: 27-fut-12-57-O
!n black on the case: SvED OZSv, headstamp: hsu { 3 { 57 { 57
37x155 Czech AP-T shell, m=735g, l=165mm, ol=285mm, vo=670mfs, 127g of F+f1 smokeless powder, tracer is not fitted. Narkings on shell:
22-fut-53 . < 13
Brass cartridge case, headstamp: hsu { 8 { 56 { 56,
!n black on the case (wrong case, this case is from a HET shell):
Nk
37 LK
OZSv
Nc tp 2,6x1,0f32 - F+f1
nma 2f55
1+ 56 - evr
cartridge
Czech designation of caliber
type of shell (HET)
type and measurements of powder
manufacturer, Lot-No.fyear of powder
Lot-No., year - assembler of round
Right picture: 3 different Russian, one Czech and one East-German inert drill round.
37x198 37mm NS-37 aircraft cannon
This cartridge was developed for the Shpitalny Sh-37 cannon, but this cannon was very unreliable and only a small test batch was fitted to LaGG-3
and !l-2 fighters for trials.
The experimental Sh-37 was replaced by the more reliable NS-37 in 19+2, the gun was mainly developed by A. Nudelman and A. Suranov at the
"Precision Engineer Design Bureau" called "OKB-16" later on.
As ammunition for the Sh-37 with cartridge case dimension 37x198 was readily developed and in production that time, the NS-37 adopted this
caliber.
The NS-37 was called 11-P-37 in prototype state, it had a rate of fire of 250-260rpm and weighted 150kg.
The recoil operated cannon was intended to engage German tanks and armored vehicles, as well as to destroy hostile aircraft with a single hit. The
AP shells were belt fed and could penetrate +0mm up to an angle of +5;
2 of 5 15f08f2013 10:57
the NS-37 cannon was 3+10mm long and had a barrel length of 2300mm.
!t was fixed to the LaGG-3 in the engine vee and on the !l-2 in underwing pods, and on the Su-8 in underbelly mounts. But most NS-37 cannons
were mounted between the cylinder banks of the engine of the Yak-9T fighter, ammunition load was 32 rounds. !t was used in air to air and air to
ground combat successfully, about 8000 cannons were built. Rate of fire was quite low for air combat and recoil was so violent that pilots were
trained to fire only three-round bursts. So no wonder that this gun was soon replaced by the N-37 with less powerful ammunition as described
above.
Ammunition used in the NS-37:
USSR Designation US Abbreviation Bullet Weight [g| Nuzzle velocity [mfs| Description
OFZ HE or HE! 735 900
Similar in shape to early N1939 HE-T shells (ogive body) but without
tracer.
BT AP-T 760 880 Penetrated 50mm of armor at 200m
Probably, target practice and drill rounds were used.
A special tungsten carbide core AP projectile has been developed, however none has been discovered so far, so it may not have been itroduced to
service.
37x252SR 37mm Russian M1939 AAA
This caliber was developed from the Swedish 25mm Bofors AA gun sold to Russia in the 1930s. The design was a joint task by L. A. Loktev and N.
N. Loginov in the Design Bureau of Artillery Plant No. 8 at Kaliningrad. The N1939 had certain similarities with the later +0mm Bofors Lf60 AA gun
like clip feeding and a similar carriage. The N1939 was introduced in Autumn 1939 and is a AA cannon of 2,1 tons weight (without optional shield)
and fitted with a barrel 27+0mm long. Rate of fire was 160 to 180rpm, its ammunition was fed in 5-round charger clips. Naximum range was
9500m horizontally and effective vertical range 3000m, the AA gun was operated by 8 men and had a fire unit of ammunition of 200 rounds. The
N1939 was recoil operated and air cooled, it was also modified after the war to water cooled cannons designated 70-K as single barrel and v-11N
as double barrel cannon. Two Naval versions were also used in WW!!, a single and a twin barrel mounting designated 3,7cmf67 N1939.
The towed N1939 AA gun was still widely used after the war, as well in the Soviet Union, its associated states, Yugoslavia and China and it is still in
service. The twin barrel gun was also made for export and is still in service in Algeria and Egypt.
China built its own versions as single barrel Type 55, as twin barrel Type 65 and 7+ and as advanced twin barrel P793 anti aircraft gun with
modernized fire control system.
Cartridge cases are brass with a Kv-2U percussion primer screw, the powder charge is held in place by a cardboard assembly. The propellant
consists of 7f1+ nitrocellulose powder with a by-charge of black powder, the inner walls of the case are coated with waxed paper, that acts as
phlegmatiser. A piece of lead-tin wire is located inside the case to act as decoppering agent, because driving bands are copper.
!n Naval service 30 rounds are packed in a gray lacquered wooden box measuring 6+0x++0x230mm and weighting 50kg, that has various
descriptive letters painted on. 20 round boxes are known as well, they measure 925x355x185mm and weigh +2kg. The projectiles are identical with
the shells for the N-37 gun. AP shells are able to penetrate 37mmf60f500m or 28mmf90f1500m of RHA. The AP shell has two pronounced
grooves that help to control the compression of the shell on impact on hard armor.
Ammunition is manufactured by China, Egypt, Pakistan, Poland, Yugoslavia and Russia.
China and Poland also manufacture steel cartridge cases.
The ammunition used post WW!!:
USSR Designation US Abbreviation Bullet Weight [g| Nuzzle velocity [mfs| Description
UOR-167 HE-T 735 866 Old type, filled TNT with NG-37 fuze
UOR-167N HE-T 735 866 Filled 3+g A-!X-2, with B-37 fuze
UBR-167 AP-T 760 866 Old type with small tracer
UBR-167 AP-T 760 866 New type with larger tracer
UBU-167 TP SD 726 866
Airburst practice shell with UTSCH-37 self destruction fuze. Blue fuze
tip
UP-167 TP-T 735 866 !nert Bitumen filled shell, dummy fuze
!nert drill rounds are used as well.
3 of 5 15f08f2013 10:57
The above picture was kindly provided by Harry Galloway, it shows different live and inert drill rounds.
40mm GP-25 Kostyor grenade launcher
This caliber is no fixed cartridge, but it has a propelling section with percussion primer to the rear. Actually, two types of ammunition are used in te
GP-25 launcher, that may be attached underbarrel to the AKN and AK-7+ assault rifles. The launcher is similar to the US N203 launcher, but the
GP-25 is a rifeled muzzle loader, it is 280mm long, weights 1,2kg and maximum range is +00m. The grenade launcher is locked in position under
the assault rifle barrel behind the trigger guard and attached to the muzzle adaptor at the front. The GP-25 is now replaced by the improved GP-30
Obuvka launcher.
The GP-30 weights 1,5kg, fires with a double action trigger and has a sighting range of +00m.
Also developed is a six barrel grenade rifle 6GP-30 that has a extendable stock and a revolving breech that is preliminary wound by a spring to
achieve a firing rate of 15-18 rdsfmin. The grenade rifle is 510mm long, 680mm with extended stock and weights 6kg.
The grenade launchers fire vOG-25 and vOG-25P standard fragmentation rounds. The latter model is provided with an expelling charge which
ensures the rebound of the grenade on impact and its airburst to effectively defeat a screened target. !n addition, a special purpose Gvozd gas
grenade can also be used to enhance the weapon versatility. The first type of shell is the vOG-25, a steel shell with outer obturations that look like
a driving band, but these are actually the fragmentation grooves. This body is filled with +8g of high explosive and closed with an impact nose fuze,
a light alloy cap covers the fuze except from the tip. The impact fuze remains sensitive even on snow, bog and water surface. A short cylinder
protrudes out of the base, this is the propelling section, filled with P-200 propellant. A central percussion cap is surrounded by ten small nozzle
holes that provide a highflow pressure boost. This grenade uses the vNG-N or vNG-K nose fuze.
The second shell is the vOG-25P, it has a larger obturated steel body filled with 37g of explosive and has a rebated truncated cone as front
assembly. On impact, this assembly makes the shell jump up into the air again, detonating in a height between 1 and 2 meters, producing a lethal
radius of 5m. This grenade uses the vNG-P nose fuze. All fuze types self destruct after a time period of 1+ - 19 sec.
Ammunition is manufactured by Russia.
USSR Designation US Abbreviation Bullet Weight [g| Nuzzle velocity [mfs| Description
vOG-25 HE FRAG 250 76,5
Grooved steel body filled with +8g of HE, vNG-N or vNG-K nose fuze
partly covered by sheet metal cap
vOG-25P HE Airburst 278 75
Rebounding fragmentation shell filled with 37g of HE and fitted with
vNG-P nose fuze
GRD-+0 Smoke 250 75 Smoke shell (Probaly the same as a reported "Gvozd" gas grenade?)
? TP 250 76,5 !nert practice shell
Drill rounds exist as well, of course.
+ of 5 15f08f2013 10:57
Four drill grenades and one vOG-25P, the cap has been removed on the third grenade from the right.
40.6mm Djakonoff rifle grenade
This WW!! caliber consists of only one type of shell that is projected by the Djakonoff 30 rifle grenade assembly that could be fixed to the muzzle
of all standard 7.62mm rifles. The shell, type "vGD" consists of a steel envelope that may have fragmentation grooves or not. The envelope is
closed on the top with an ogive cap and to the rear with the driving band and fuze assembly. A central tube leads through the entire shell, to allow
the use of standard ball ammunition for projecting. Three studs on the driving band located on the lower third of the shell transmit the spin of the
grenade projector. Below the driving band is a ring with imprinted numbers for adjustment of the delay
time of the powder burning fuze. The base of the shell is recessed to act as seal against the powder gases, this recess also takes an optional
additional powder charge for greater range. The detonator cap reaches deep inside the shell, between the outer wall and the central tube.
Technical data:
The shell is 115mm long and weights 350g, it has a HE filling of 50g of TNT. !f other types of HE are used, the gray cap is painted in other colors.
The muzzle velocity is 5+mfs with a standard 7,62 Nosin Nagant ball rifle cartridge, with an additional powder charge of 2,5g of smokeless powder
in a silk bag, the muzzle velocity was 110mfs. The according maximum ranges were 300m and 900m. The powder delay time fuze could be
adjusted between 3 and 12 sec., the fuze is ignited by the hot powder gases. The shell produces about 3+0 fragments on detonation, that form a
deadly radius of about 50m.
Each shell is single packed in a sealed metal container, 32 or 50 of these containers are overpacked in a wooden box, the weight of the larger box
was 30kg.
Legend: m= mass of projectile, om= mass of complete round, pm=mass of propellant, l= length of projectile, ol= overall length of complete round, Vo= muzzle
velocity, cartridge case headstamps are given in the clockwise system, the clock-sections divided by "|" for better reading. The "|" does not mean an imprinted line
in the headstamp. Example: symbol at 12 oclock | 3 oclock | 6 oclock | 9 oclock
Please note that these pages are no longer updated and contain partially obsolete data.
For comprehensive and up to date information, please refer to my new book "Soviet Cannon" at
www.russianammo.org.
Compared to this webpage with its 69 pages, the book and the enclosed CD-Rom offer a total of almost
900 pages.
< Previous Page < Home > Next Page >
5 of 5 15f08f2013 10:57
Вам также может понравиться
- German Explosive Ordnance PDFДокумент281 страницаGerman Explosive Ordnance PDFX20XER94% (16)
- British Grenades - Section 2Документ32 страницыBritish Grenades - Section 2cockybundooОценок пока нет
- Subcourse Edition FA 3117 B Us Army Field Artillery School Field Artillery Cannon AmmunitionДокумент153 страницыSubcourse Edition FA 3117 B Us Army Field Artillery School Field Artillery Cannon AmmunitionVicente VelezОценок пока нет
- 03 ProjectileДокумент132 страницы03 Projectilemwiweko2013100% (1)
- US Army Experimental Cartridges T NumbersДокумент13 страницUS Army Experimental Cartridges T Numbersenrico100% (1)
- Base Lining of The 40mm Family of AmmunitionДокумент31 страницаBase Lining of The 40mm Family of AmmunitionWilliam James Abercrombie100% (1)
- TM - 43-0001-47 Ammunition Disassymbly ToolsДокумент10 страницTM - 43-0001-47 Ammunition Disassymbly ToolslygoreОценок пока нет
- Handbook of Ammunition Used in Irak and Surrounding AreasДокумент319 страницHandbook of Ammunition Used in Irak and Surrounding Areasmalone6993% (15)
- FM 3-23.25 Shoulder-Launched MunitionsДокумент192 страницыFM 3-23.25 Shoulder-Launched MunitionsGasMaskBob0% (1)
- TM 43-0001-30 (Rockets)Документ144 страницыTM 43-0001-30 (Rockets)jbart252100% (4)
- IATG 01.40 Ammunition ReferenceДокумент44 страницыIATG 01.40 Ammunition Referenceenrico100% (1)
- Vietnam ProjosДокумент271 страницаVietnam Projosjbart252Оценок пока нет
- 15mm MG 151 MunitionДокумент16 страниц15mm MG 151 MunitionAncarion100% (1)
- 40mm AmmunitionДокумент50 страниц40mm AmmunitionjwsoldatОценок пока нет
- TM 9-1900 1942 AMMUNITION GENERALДокумент214 страницTM 9-1900 1942 AMMUNITION GENERALAdvocateОценок пока нет
- SAS Research Note 55Документ4 страницыSAS Research Note 55John ThomasОценок пока нет
- The Munitions Handbook Specifications and Informations For The Use of Munitions Albania 1983Документ381 страницаThe Munitions Handbook Specifications and Informations For The Use of Munitions Albania 1983arnoldvv100% (2)
- TM 43-0001-39 (Cads)Документ239 страницTM 43-0001-39 (Cads)jbart2520% (1)
- Albanian Munitions Manual PDFДокумент381 страницаAlbanian Munitions Manual PDFMihalache Radu Catalin100% (2)
- FM 3-50 Chemical Smoke Generator Company, Jan 1959Документ262 страницыFM 3-50 Chemical Smoke Generator Company, Jan 1959Hauke Krapf100% (2)
- Ammunition Types and FunctionДокумент15 страницAmmunition Types and FunctionVikas Chandra100% (1)
- OP 1415 RKT AssyДокумент152 страницыOP 1415 RKT Assyjbart252100% (1)
- Department of The Navy Naveod Projectile GuideДокумент211 страницDepartment of The Navy Naveod Projectile GuideEOD987654321Оценок пока нет
- TM 9-1330 GrenadeДокумент5 страницTM 9-1330 GrenadeYHonglee YhongleeОценок пока нет
- Operator Information On m829 (Apfsds-T), M829a1 (Apfsds-T), m830 (Heat-Mp-T), m831 (TP-T) m865 (TPCSDS-T)Документ34 страницыOperator Information On m829 (Apfsds-T), M829a1 (Apfsds-T), m830 (Heat-Mp-T), m831 (TP-T) m865 (TPCSDS-T)Cameron Farquhar100% (1)
- Belgian Projectile Fuze, BD, NR 2 490Документ0 страницBelgian Projectile Fuze, BD, NR 2 490jan_petras7247Оценок пока нет
- Chinese AmmunitionДокумент98 страницChinese AmmunitionFrancesco100% (7)
- 40mm Low-Velocity GrenadesДокумент46 страниц40mm Low-Velocity Grenadesroberto portoОценок пока нет
- Fdocuments - in - Introduction To FuzeДокумент36 страницFdocuments - in - Introduction To FuzeBui Duc ManhОценок пока нет
- M256 120mm Smoothbore GunДокумент23 страницыM256 120mm Smoothbore GunjfmanОценок пока нет
- 20-11M Automatic Gui 1111 An D 20-Mm Alacran Automatic Gun An-112Документ138 страниц20-11M Automatic Gui 1111 An D 20-Mm Alacran Automatic Gun An-112ENAK9000100% (1)
- Dinamit Nobel DefenceДокумент59 страницDinamit Nobel DefenceNash7777Оценок пока нет
- Weapons & Sensors NATOДокумент20 страницWeapons & Sensors NATOPtolomeoyloKagoОценок пока нет
- Ammunition GeneralДокумент243 страницыAmmunition GeneralPlainNormalGuy2100% (4)
- Bazalt 2008Документ68 страницBazalt 2008DiskoElmОценок пока нет
- Fuze PDM 572 c1 Animation 1Документ10 страницFuze PDM 572 c1 Animation 1Vikas Chandra67% (3)
- Browning Machine Gun Cal .30 - MIL-G-13665 Military Specification, Gun, Machine, Browning, Caliber 30, M1919A6 - 1954Документ13 страницBrowning Machine Gun Cal .30 - MIL-G-13665 Military Specification, Gun, Machine, Browning, Caliber 30, M1919A6 - 1954ab212amisarОценок пока нет
- Aviation Bomb DatabaseДокумент39 страницAviation Bomb Databasezix013100% (1)
- British Grenades Color PDFДокумент62 страницыBritish Grenades Color PDFEnriquenfОценок пока нет
- FM 23-30 1969 - Grenades and Pyrotechnic SignalsДокумент90 страницFM 23-30 1969 - Grenades and Pyrotechnic Signalsjack49100% (2)
- 20mm AMR - New Use For Unused AmmoДокумент48 страниц20mm AMR - New Use For Unused Ammosergey62100% (2)
- Weapon and Ammunition Technical Manual Infantry Regiment ParachuteДокумент55 страницWeapon and Ammunition Technical Manual Infantry Regiment ParachuteKa Lay Thar100% (1)
- Laos PDF Files From RobbyДокумент314 страницLaos PDF Files From RobbyeodmatОценок пока нет
- Excalibur OverviewДокумент10 страницExcalibur Overviewjarod437Оценок пока нет
- CW 11-1 Ammo, 4.2 Mortar, 1945Документ16 страницCW 11-1 Ammo, 4.2 Mortar, 1945richardwb1Оценок пока нет
- Pergolizzi PDFДокумент22 страницыPergolizzi PDFaftetОценок пока нет
- Practical Guide to the Operational Use of the M79 Grenade LauncherОт EverandPractical Guide to the Operational Use of the M79 Grenade LauncherОценок пока нет
- Practical Guide to the Operational Use of the PPSh-41 Submachine GunОт EverandPractical Guide to the Operational Use of the PPSh-41 Submachine GunРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Tiger 2 Ausf.B Battle TankДокумент11 страницTiger 2 Ausf.B Battle TankMeor Amri100% (5)
- SAFN 49 Venezuala DevelopmentДокумент3 страницыSAFN 49 Venezuala Developmentp317Оценок пока нет
- German Anti-Tank GunsДокумент66 страницGerman Anti-Tank GunsAdi Antonescu100% (9)
- Artillery Ammunition GeneralДокумент14 страницArtillery Ammunition Generalenrico0% (1)
- Browning Machine Gun Cal .30 - Technical Air Intelligence Report 21 - Examination of Japanese Browning Machine Gun - 1944Документ15 страницBrowning Machine Gun Cal .30 - Technical Air Intelligence Report 21 - Examination of Japanese Browning Machine Gun - 1944ab212amisarОценок пока нет
- University of Nebraska - LincolnДокумент52 страницыUniversity of Nebraska - LincolnSrg KshvОценок пока нет
- Panzerkampfwagen Tiger: Germany's White ElephantДокумент19 страницPanzerkampfwagen Tiger: Germany's White ElephantEnsignExpendable100% (4)
- Anti-Tank Rifles of The Second World WarДокумент4 страницыAnti-Tank Rifles of The Second World WarTimia TalashekОценок пока нет
- Electrolytic Rust RemovalДокумент15 страницElectrolytic Rust RemovalenricoОценок пока нет
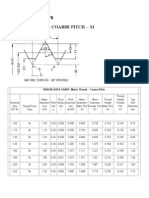
- Metric Thread - Coarse Pitch - MДокумент3 страницыMetric Thread - Coarse Pitch - MenricoОценок пока нет
- How Do I Set Up My TIG Welder?: Owner's ManualДокумент2 страницыHow Do I Set Up My TIG Welder?: Owner's ManualenricoОценок пока нет
- Procedures - Copper WeldingДокумент6 страницProcedures - Copper WeldingenricoОценок пока нет
- Procedures - Copper WeldingДокумент6 страницProcedures - Copper WeldingenricoОценок пока нет
- Drill & Tap SizesДокумент2 страницыDrill & Tap SizesenricoОценок пока нет
- Garmin Map Converter InstructionsДокумент3 страницыGarmin Map Converter InstructionsenricoОценок пока нет
- ODN 784 Handbook On Trench Mortar Fuzes 1918Документ16 страницODN 784 Handbook On Trench Mortar Fuzes 1918enricoОценок пока нет
- Amm 3.7cm BK LDV 4000 10 COL 1944Документ21 страницаAmm 3.7cm BK LDV 4000 10 COL 1944enricoОценок пока нет
- Garmin Maps TutorialДокумент6 страницGarmin Maps TutorialenricoОценок пока нет
- Amm 0.303 British HeadstampsДокумент14 страницAmm 0.303 British Headstampsenrico100% (2)
- Ammunition TablesДокумент7 страницAmmunition Tablesenrico100% (1)
- Amm 0.303 BritishДокумент9 страницAmm 0.303 Britishenrico0% (1)
- Amm 105mm x617 TK L7 CN105F1 MecarДокумент4 страницыAmm 105mm x617 TK L7 CN105F1 MecarenricoОценок пока нет
- Amm 25mm Apfsds Mecar m935Документ1 страницаAmm 25mm Apfsds Mecar m935enricoОценок пока нет
- French Guns Technical Data 1940Документ4 страницыFrench Guns Technical Data 1940enrico100% (1)
- Tank Ammunition: 105mm Tk. HE M1010Документ1 страницаTank Ammunition: 105mm Tk. HE M1010enricoОценок пока нет
- Amm 105mm x617 TK M1056Документ1 страницаAmm 105mm x617 TK M1056enricoОценок пока нет
- Amm 90mm x580 Mk8 Mecar M690Документ1 страницаAmm 90mm x580 Mk8 Mecar M690enricoОценок пока нет
- Amm 105mm x617 TK M1060Документ1 страницаAmm 105mm x617 TK M1060enricoОценок пока нет
- Amm 105mm x617 TK M1057Документ1 страницаAmm 105mm x617 TK M1057enricoОценок пока нет
- Italian Artillery Tables of Characteristics Artillery in The DesertДокумент2 страницыItalian Artillery Tables of Characteristics Artillery in The DesertEnrico959Оценок пока нет
- Amm 3.7cm x264 BK Stuka PDFДокумент8 страницAmm 3.7cm x264 BK Stuka PDFenricoОценок пока нет
- FM 4-30.16 - EOD - Multi-Service Tactics, Techniques and Procedures For Explosive Ordnance Disposal in A Joint Environment (2005)Документ96 страницFM 4-30.16 - EOD - Multi-Service Tactics, Techniques and Procedures For Explosive Ordnance Disposal in A Joint Environment (2005)defendercc130100% (2)
- BIOS 365 Paint of German AircraftsДокумент29 страницBIOS 365 Paint of German AircraftsenricoОценок пока нет
- MIL-STD-1168B (Ammunition Lot Numbering and Amm. Data Card) PDFДокумент50 страницMIL-STD-1168B (Ammunition Lot Numbering and Amm. Data Card) PDFzorlon1Оценок пока нет
- Captured and Converted French Vehicles in German ServiceWWIIДокумент14 страницCaptured and Converted French Vehicles in German ServiceWWIIaxiswarlordhcv100% (2)
- Amm 3cm Mk108 Komet CannonДокумент9 страницAmm 3cm Mk108 Komet CannonenricoОценок пока нет
- Amm 4.5inch British HowitzerДокумент6 страницAmm 4.5inch British HowitzerenricoОценок пока нет
- Amm 12.7mm x81 JapaneseДокумент8 страницAmm 12.7mm x81 JapaneseenricoОценок пока нет
- Summary For Shuhadah CompensationДокумент9 страницSummary For Shuhadah CompensationMuhammad NadeemОценок пока нет
- JLPT Shiken Mondai To Seikai 3-4 Kyuu 2005Документ120 страницJLPT Shiken Mondai To Seikai 3-4 Kyuu 2005Alexey YankovetskyОценок пока нет
- Spyder Victor 2012Документ36 страницSpyder Victor 2012William HernándezОценок пока нет
- NSTPДокумент3 страницыNSTPVia Mariz BalmocenaОценок пока нет
- German Type VII SubmarineДокумент10 страницGerman Type VII SubmarineOliverChrisLudwigОценок пока нет
- The Plans and Programs GuideДокумент130 страницThe Plans and Programs GuideMatt Stankey100% (2)
- High-Explosive Incendiary:armor-Piercing Ammunition - WikipediaДокумент9 страницHigh-Explosive Incendiary:armor-Piercing Ammunition - Wikipediapincer-pincerОценок пока нет
- Manifest DestinyДокумент16 страницManifest Destinyapi-367477549100% (2)
- Chapter 2Документ5 страницChapter 2MeconОценок пока нет
- Mil STD 1911Документ23 страницыMil STD 1911jwsiglerОценок пока нет
- Marriage and Family HindiДокумент216 страницMarriage and Family HindiapcwoОценок пока нет
- Ir. Sekarno Moh. Hatta Ahmad Yani Jendral Sudirman Pangeran AntasariДокумент3 страницыIr. Sekarno Moh. Hatta Ahmad Yani Jendral Sudirman Pangeran AntasariIrman AminudinОценок пока нет
- ARL-TR-2074 - Analysis Fuze Configurable Range CorrectionДокумент71 страницаARL-TR-2074 - Analysis Fuze Configurable Range CorrectionIndiodyc69Оценок пока нет
- The Ira WarДокумент679 страницThe Ira WarLucian Dragos100% (1)
- Book of Cannon Patent DrawingsДокумент478 страницBook of Cannon Patent DrawingsToz Koparan100% (8)
- Marking VishayДокумент14 страницMarking Vishayramon navaОценок пока нет
- Crossman sp02Документ2 страницыCrossman sp02Andre Rodriguez SpirimОценок пока нет
- C2 Lab: Michael Koester Interoperability Test Director C2 Systems Branch/JITC (520) 538-4230 Michael - Koester@disa - MilДокумент35 страницC2 Lab: Michael Koester Interoperability Test Director C2 Systems Branch/JITC (520) 538-4230 Michael - Koester@disa - MilrewritingОценок пока нет
- Rekap To NasionalДокумент52 страницыRekap To NasionalMelisawiОценок пока нет
- Reading D Đoán Pic 100 Roman Shipbuilding and NavigationДокумент11 страницReading D Đoán Pic 100 Roman Shipbuilding and NavigationMinh ThuОценок пока нет
- Washington Post EXPRESS - 12032010Документ40 страницWashington Post EXPRESS - 12032010Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- The Ottoman Coinage of Tilimsan / Michael L. BatesДокумент15 страницThe Ottoman Coinage of Tilimsan / Michael L. BatesDigital Library Numis (DLN)100% (1)
- WD 0017 - Manual For The Medical Department (1898) PDFДокумент141 страницаWD 0017 - Manual For The Medical Department (1898) PDFDongelx100% (1)
- Ocampo 807 Scra 223Документ1 страницаOcampo 807 Scra 223Helen Grace M. BautistaОценок пока нет
- Liberation of DachauДокумент16 страницLiberation of DachauPaulDavis100% (2)
- Ganjgal ReportДокумент5 страницGanjgal ReportChristian LoweОценок пока нет
- Global Positioning System - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент27 страницGlobal Positioning System - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediajaved shaikh chaandОценок пока нет
- DB - Pregen - Adult Human KnightДокумент1 страницаDB - Pregen - Adult Human KnightMMKОценок пока нет
- M2 Browning HMG - 50 Cal - M2Hb: IdentificationДокумент4 страницыM2 Browning HMG - 50 Cal - M2Hb: IdentificationOsorio Luis0% (1)
- 10 Paces: Gunfights and Violence at The Saloon!Документ2 страницы10 Paces: Gunfights and Violence at The Saloon!Adrianna KellerОценок пока нет