Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Biologi Modul 1 (P1 & P2)
Загружено:
shazy7Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Biologi Modul 1 (P1 & P2)
Загружено:
shazy7Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
MODUL KERTAS 1 & 2
MODUL 1
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
2
1 Diagram 1 shows a type of muscle tissue found in the human body. Where is the
tissue found?
Diagram 1
A Heart C Biceps
B Pancreas D Small intestine
2 The plasma membrane consists of molecules arranged in a double layer as
shown in Diagram 2
Diagram 2
The part labelled I and II are
A hydrophobic and hydrophilic respectively
B hydrophilic and hydrophobic respectively
C both hydrophobic
D both hydrophilic
3. Diagram 3 shows the net flow of water molecules from a dilute solution
to a concentrated solution through a semi-permeable membrane.
Diagram 3
What is this process called?
A Osmosis
B Active transport
C Simple diffusion
D Facilitated diffusion
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
3
4 Diagram 4 is a graph which shows the changes in mass of potato strips immersed in
different concentrations of sucrose solution.
Diagram 4
Based on the graph, which of the following concentrations of sucrose solution should
be used so that a flaccid potato strip regains its turgidity?
A 1.5 g per 100 ml
B 2.5 g per 100 ml
C 3.5 g per 100 ml
D 4.5 g per 100 ml
5. Lipid is needed to build substance X while cellulose is needed to build substance Y.
What are substances X and Y?
Substance X Substance Y
A Protoplasm Cell wall
B Plasma membrane Cell wall
C Cell wall Protoplasm
D Cell wall Plasma membrane
6 . Haemoglobin is an example of a
A. primary structure of protein
B. secondary structure of protein
C. tertiary structure of protein
D. quarternary structure of protein
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
4
7 Which of the following graph shows the effect of pH on the metabolic rate of the
enzyme pepsin?
8 Diagram 5 shows the phases in a cell cycle.
Diagram 5
Y
phase
X phase
Rate of
reaction Rate of
reaction
Rate of
reaction Rate of
reaction
X phase
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
5
Which of the following represents V ?
A mitosis C stage S
B cytokinesis D stage G
1
9 Diagram 6 shows a phase in mitosis of a plant cell.
Diagram 6
Which of the following is true about the cell in Diagram 6 ?
Stage of mitosis Number of chromosomes in the
mother cell
A Anaphase 4
B Telophase 4
C Anaphase 8
D Telophase 8
10. Crossing over is an important process in meiosis. It results in variations in the daughter
cells. At which stage of meiosis does crossing over take place?
A Prophase I
B Prophase II
C Metaphase II
D Anaphase I
11 Lack of vitamin D in the diet will cause the disease
A scurvy.
B beri-beri.
C rickets.
D pellagra.
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
6
12 Diagram 7 shows the molecular structure of three food classes
Diagram 7
Which food classes do X, Y and Z belong to ?
X Y Z
A Carbohydrate
B Protein
C Protein
D Lipid
Protein
Lipid
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate
Lipid
Carbohydrate
Lipid
Protein
13 Diagram 8 shows part of the human alimentary canal.
Diagram 8
A person who has structure P removed must regulate his dietary intake of
A. fats C protein
B. carbohydrate D. water
14 In the absence of oxygen the skeletal muscles contract using energy from the
breakdown of glucose and glycogen to
A ethanol and water
B energy and water
C ethanol and lactic acid
D lactic acid and energy
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
7
15 Which of the following is not involved in the transportation of carbon dioxide by the
blood.
A Carbonic acid
B Carbaminohaemoglobin
C Hydrogen carbonate ion
D Carbon monoxide
16 Table shows the biomass of a few types of organisms in a community.
Organism Total Biomass of all the
organisms at each
trophic level(kg)
P 1200
Q 30
R 150
S 670
T 100
U 2700
Which of the following is a possible food chain in this community?
A P U S T C P S T Q
B Q R S P D U S P Q
17 Which of the following organisms is a parasite ?
A C
B D
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
8
18 Diagram 9 is a graph which shows changes in the population of two species of
beetles, T and U, over a period of time. Both species feed on the same food source.
Diagram 9
What is the interrelationship between species T and U?
A Symbiosis C Parasitism
B Predation D Competition
19 Diagram 10 shows a cross section of a young dicotyledon root consisting of a few
main tissues.
Diagram 10
What is Y ?
A Phloem B Xylem
C Cortex D Cambium
20 Diagram 11 shows some human bones .
Diagram 11
Population
T U
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
9
Which bones are part of the axial skeleton ?
A P and S
B Q and R
C P , Q and R
D Q , R and S
21 Diagram 12 below shows a motor neuron.
Diagram 12
Which one of the following A, B, C or D in the table below names the labelled parts
correctly?
1 2
A
B
C
D
Cell body
Axon
Dendrite
Synapse
Axon
Dendrite
Myelin sheath
Dendrite
22 Diagram 13 shows a plant with soft stem .
Which of the following support structures helps the plant climb to obtain sunlight ?
Diagram 13
A Clasping roots B Twining stems
C Tendrils D Thorns.
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
10
23 Diagram 14 shows a nerve pathway involved in a reflex action. Which structure is the
efferent neurone?
Diagram 14
24 Some cucumber slices are immersed in 0.1% sucrose solution. After 3 hours, the
slices are found to be turgid and hard.
Which of the following statements explains this phenomenon?
A The cucumber cell wall prevents it from shrinking
B The cell sap is hypotonic towards the sucrose solution
C The high concentration of the cell sap in the vacuole causes water to
diffuse into the cell
D The cucumber cell wall allows the sucrose molecules to diffuse into the
cell
25 Diagram 15 shows the four-chambered stomach of a ruminant.
Diagram 15
Which of the following is not a correct match about each chamber and its function?
A. S- Rumen, mutualistic bacteria digest cellulose.
B. V- Reticulum, the partially digested food is formed into balls and regurgitated into the
mouth for chewing
C. U- Omasum, the regurgitated food in the mouth is passed into the omasum
D. T- Duodenum, the digested products are absorbed.
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
11
26 What substances are dissolved in the fuid which passes along the ureter to the
bladder of a healthy person?
Glucose Protein Salts Urea
A. Absent Absent Absent Present
B. Absent Absent Present Present
C. Present Absent Present Present
D. Present Present Absent Absent
27 Diagram 16 shows the female reproductive system. In which parts are the eggs and
the zygote formed?
Diagram 16
Eggs Zygote
A
B
C
D
1
1
2
2
2
3
1
3
28 Diagram 17 shows sex determination in human.
Ovary cell Testis cell
Gametes
Diagram 17
1
2
P Q
R
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
12
If a couple have a son, what is the cell composition in P, Q and R?
P Q R
A 44 + X 44 + Y 44 + XY
B 22 + Y 22 + X 44 + XY
C 22 + X 22 + X 44 + XX
D 22 + X 22 + Y 44 + XY
29 Which of these genetically inherited disease is dangerous and can cause death
at a young age?
A. Albino
B. Haemophilia
C. Short-sightedness
D. Down syndrome
30 Table 1 shows a Punnet square which represents the gametes and progeny
from a dihybrid cross. Alphabets a to p represent the daughter cells from this
cross.
male gamete
female gamete
HK Hk hK hk
HK a b c d
Hk e f g h
hK I j k l
hk m n o p
Table 1
Which of the following daughter cells have the same genotype as the parent ?
A a, f, k, p C d, g, j, m
B b, c, e, I D e, f, h, l
31 Diagram 18 shows the development of a pollen tube and its entry into the ovule.
Which part develops into the testa after fertilisation?
Diagram 18
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
13
32 Contraceptive pills contain a combination of
A. estrogen and luteinising hormone.
B. progesterone and prolactin
C. estrogen and follicle stimulating hormone
D. progesterone and estrogen.
33. Which of the following shows the differences between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis Meiosis
I Involves one stage of cell division Involves two stages of cell division
II Produces two diploid daughter cells Produces four haploid daughter
cells
III Synapsis and crossing over takes
place between homologous
chromosomes
Synapsis and crossing over does
not take place
IV Chromosomes are not in pairs Homologous chromosomes are in
pairs at prophase I
A I and II only
B I and III only
C I, II and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
34 Diagram 19 is a graph which represents a type of variation found in students.
Diagram 19
This variation may be
I height II weight
III type of ear lobe IV dimple
A I and II only C III and IV only
B I and III only D I, II, III and IV
Variation
Number of
individuals
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
14
35 Which of the following is not a cause of variation?
A. Radiation B. Gene mutation
C. Asexual reproduction D. Meiosis
36 Diagram 20 shows the structure of a villus in the ileum
Diagram 20
Which vessels P, Q, R, and S carry the largest amounts of glucose, amino acids, lipid
droplets or fat-soluble vitamins?
Glucose Amino
acids
Lipid
droplets
Fat soluble
vitamins
A P Q R S
B Q P R S
C R R S S
D S S R R
37 Diagram 21 shows a plastic quadrat used to determine the percentage coverage of
bread mould on a piece of bread. The shaded area shows the presence of mould.
Diagram 21
Based on the result obtained in Diagram 21, calculate the percentage coverage of
the bread mould , taking the area of each small square to be 1 cm
A 32 % C 56%
B 40% D 80%
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
15
38 Diagram 22 below shows equipment that can cause the thinning of the ozone layer.
Diagram 22
How can this problem be solved?
I Stop using chlorofluorocarbon
II Replace CFCs with HCFCs
III Patching holes in the ozone layer
IV Produce less electrical goods
A I and II
B II and IV
C I, II and III
D I, II, III and IV
39 The following statement is about eutrophication.
What is the correct sequence of the eutrophication process ?
A O, L, M and N C L, M, O and N
B L, N, M and O D O, M, L and N
L : Excess fertilisers from agriculture lands flow into lakes
M : Bacteria grow rapidly
N : Algae grow rapidly and covers the surface of the lake
O : The value of BOD increase
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
16
40. An experiment was carried out to investigate the rate of water loss from a plant in a
day.The wind and relative humidity factors were kept constant. Diagram 23 is a graph
which shows the result obtained from 0600 to 1300 hours .Which of the curves A,B,C
or D is expected to show the rate of water loss in the plant after 1300 hours ?
Diagram 23
41 Diagram 24 shows a human arm .
Diagram 24
If tendon X was torn off,what happens to the arm ?
A The elbow joint loosens up
B The fingers cannot grip
C The arm connot be bent
D The lower arm cannot twist.
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
17
42 Diagram 25 is a graph which shows the changes in the glucose concentration in the
blood of a person over a period of two hours.
Diagram 25
Which of the following best explains the shape of the graph after X?
A. The person has eaten a meal that is high in sugar .
B. The person has had an insulin injection.
C. The person is suffering from diabetes mellitus.
D. The person starts some vigorous physical exercise.
43 Which characteristics of the glomerulus enhances the efficiency of ultrafiltration ?
I. The diameter of the afferent arteriole is larger than that of the efferent arteriole.
II. The afferent arteriole divides further into a dense network of capillaries.
III. The high hydrostatic pressure of the blood entering the glomerulus.
IV. The Bowmans capsule is made up of only two layers of cells.
A. I, II and III only
B. I, II and IV only
C. II, III and IV only
D. I, II, III and IV
44 A womans menstrual period started on 23
rd
March. In which week was an egg most
likely to have been released?
Week March
Sun Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat
A - - - 1 2 3 4
B 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
C 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
D 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
26 27 28 29 30 31
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
18
45 What is true about the importance of secondary growth in plants?
I. It increases the diameters of the plant stems and roots for mechanical support.
II. It allows plants to increase in length to achieve maximum height.
III. It produces new phloem and xylem tissues to replace the old and damaged ones.
IV. It produces a thick bark which reduces the evaporation of water from the surface
of the stem.
A. I, II and III only B. I, III and IV only
C II, III and IV only D. I, II, III and IV.
46 A woman with blood group A claims that a man with blood group AB is the
father of her baby. The babys blood is tested. Which of the following could be the
babys blood group?
I Group A
II Group B
III Group O
IV Group AB
A I and II only
B I and IV only
C I, II and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
47 Which of the following shows the difference between continuous variation and
discontinuous variation?
Continuous Variation Discontinuous Variation
A Controlled by dominant genes. Controlled by recessive genes.
B Caused by mutation. Not caused by mutation.
C Occurs in animals. Occurs in plants.
D Can be measured. Cannot be measured.
48 The Hydrangea plant produces blue flowers when grown on acidic soil, and red
flowers when grown on alkaline soil. What conclusion can be made from this
observation?
A. The colour of the Hydrangea flower is a continuous variation
B. The environment affects the colour of the flowers
C. The pH of the soil causes mutation
D. The colour of the flower is affected by the genetic factor only
4551/1 LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
19
49 I - Homologous chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell.
II - Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles
III Sister chromatids separate and move to different poles
IV Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disintegrate.
I, II, III and IV shows the processes which occur in meiosis. Among the following
events, which occur in anaphase I ?.
A I only
B II only
C III and IV only
D II and IV only
50 Diagram 26 shows an organ system.
Diagram 26
What are the functions of the organ system shown above?
I To transport oxygen to the body cells
II To defend the body against diseases
III To remove metabolic wastes
IV To help regulate the volume and composition of blood
A I and II only
B I and III only
C II and IV only
D III and IV only
END OF QUESTION PAPER
KERTAS SOALAN TAMAT
4551/2 - 2 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
Section A
[ 60 marks ]
Answer all questions from this section.
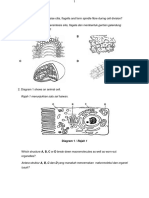
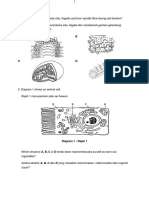
1. Diagram 1 shows cell organisation in plant. Cells J undergo differentiation and
specialisation to form several tissues in a leaf of a green plant.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan organisasi sel dalam satu tumbuhan. Sel-sel J mengalami
pembezaan dan pengkhususan untuk membentuk beberapa tisu dalamsatu
tumbuhan hijau.
Cell Specialisation
DIAGRAM 1
(a) Name tissue K and tissue L.
Namakan tisu K dan L
K :
L:
[2 marks]
Cells J
Sel-sel J
Cross-section
of a leaf
Keratan
rentas sehelai
daun
K
L
Xylem
tissue
Tisu
xilem
M
4551/2 - 3 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
(b) State the function of cells K and M in a leaf.
Nyatakan fungsi sel K dan M dalam sehelai daun
K : .
M: ...
[2 marks]
(c) (i) Explain the differentiation of cells J to form the xylem tissue.
Terangkan pembezaan sel J dalam membentuk tisu xilem.
[2 marks]
(ii) During the formation of the xylem tissue, the plant was unable to synthesise lignin.
Explain the effect on the function of the leaf.
Sewaktu pembentukan tisu xylem, satu tumbuhan gagal mensistesis lignin.
Terangkan kesannya keatas fungsi daun tumbuhan tersebut.
[2 marks]
(d) Based on diagram 1, state the meaning of cell specialization.
Berdasarkan rajah 1, nyatakan maksud pengkhususan sel.
[2 marks]
(e) Leaf is the main photosynthetic organ of a plant.
Explain the adaptation of tissue L to enable the leaf to carry out its function.
Daun adalah organ utama fotosintesis sesuatu tumbuhan
Terangkan adaptasi tisu L untuk membolehkannya menjalankan fungsinya
[2 marks]
TOTAL
4551/2 - 4 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
2. Diagram 2.1 shows the cell cycle of an organism.
Diagram 2.1
(a) Name phase U in Diagram 2.1.
.
U:
[1 mark]
(b) Phase U is further divided into three sub phases, X, Y and Z. Describe what
happens at sub phases X, Y and Z.
X:
Y:
Z:
[3 marks]
(c) The number of chromosomes present in the nucleus of a somatic cell is 6.
Diagram 2.2 shows a stage of cell division to produce gametes.
Diagram 2.2
Mitotic cell
division
Phase U
4551/2 - 5 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
Complete the diagram to show the chromosomes for a daughter cell produced
at the end of sub-phase Q.
[2 marks]
( d ) Explain how radiotherapy affected cell cycle in cancer treatment.
[2 marks]
(e)(i) A farmer wants to breed a good variety of banana plants for commercial
production. Suggest a suitable method to be used and explain how the method
named can increase the crop yield.
[3 marks]
(ii) State a problem that can occur when using this method..
[1 mark]
TOTAL
4551/2 - 6 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
3. Diagram 3 shows part of a nitrogen cycle.
Rajah 3 menunjukkan sebahagian kitar nitrogen.
DIAGRAM 4
DIAGRAM 3
a) Name P, Q and R
Namakan P, Q dan R.
P: .........................................................................................................................
Q: ........................................................................................................................
R: .........................................................................................................................
[3marks]
Nitrogen in the atmosphere
Nitrogen dalam atmosfera
Nitrogen fixation by
microorganisms in plant P
Pengikatan nitrogen oleh
mikroorganisma dalam
tumbuhan P
Nitrogenous
compounds in plants
Sebatian nitrogen
dalam tumbuhan
Nitrogenous compounds
in animals
Sebatian nitrogen dalam
haiwan
Organism R
Organisma R
Process Y
Proses Y
Substance Q
Bahan Q
Ammonium compounds
Sebatian ammonium
Nitrites
Nitrit
4551/2 - 7 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
(b) (i ) Name the microorganism that is involved in the nitrogen cycle and lives in plant
P.
Namakan mikroorganisma yang terlibat dalam kitar nitrogen dan tinggal dalam
tumbuhan P.
..........................................................................................................................................
[ 1 mark]
(ii) Besides nitrogen fixation by microorganisms, name a natural phenomenon which is
also able to convert nitrogen in the atmosphere to substance Q.
Selain daripada pengikatan nitrogen oleh mikroorganisma, namakan satu
fenomena semulajadi yang boleh menukarkan nitrogen dalam atmosfera kepada
bahan Q.
..........................................................................................................................................
[ 1 mark]
(c) Microorganisms are involved in process Y.
Mikroorganisma terlibat dalam proses Y.
(i) Name one type of microorganism which is involved in process Y.
Namakan sejenis mikroorganisma yang terlibat dalam proses Y.
..........................................................................................................................................
[ 1 mark]
(ii) Explain the role of the microorganism in ( c)(i)
Terangkan peranan mikroorganisma dalam (c)(i)
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
[ 3 marks]
(d) Explain how a deficiency of Q in the soil affects the growth of the plants.
Terangkan bagaimana kekurangan Q dalam tanah memberi kesan terhadap
pertumbuhan tumbuhan.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
[ 3 marks]
TOTAL
4551/2 - 8 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
4 Two individuals P and Q were given injections to acquire immunity. The level of antibodies
in the blood of individual P and Q is shown in Diagram 4.1 and 4.2 respectively.
DIAGRAM 4.1
DIAGRAM 5.2
DIAGRAM 4.2
(a) What is the substance injected into the blood of individual P and individual Q ?
P :
Q :
1
st
injection 2
nd
injection
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
C
o
n
c
e
n
t
r
a
t
i
o
n
o
f
a
n
t
i
b
o
d
i
e
s
i
n
t
h
e
b
l
o
o
d
(
a
r
b
i
t
r
a
r
y
u
n
i
t
)
Immunity level
Increase
immediately
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
1
st
vaccination 2
nd
vaccination Time (weeks)
Immunity level
C
o
n
c
e
n
t
r
a
t
i
o
n
o
f
a
n
t
i
b
o
d
i
e
s
i
n
t
h
e
b
l
o
o
d
(
a
r
b
i
t
r
a
r
y
u
n
i
t
)
Booster dose (2
nd
)
stimulates a faster and
larger lasting
response.
Individual P
1
st
Injection 2nd Injection
Time (weeks)
Individual Q
4551/2 - 9 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
[ 2 marks ]
(b) State the type of immunity obtained by individual P and individual Q.
P : ..
Q : ..
[ 2 marks ]
(c) Using your biological knowledge, describe how you could save this boy.
...
[ 4 marks ]
(d) Table 4.1 shows a schedule of immunisation given for every new born Malaysian until the
age of two.
Age Types of Immunity
New born
Tuberculosis (B.C.G)
Hepatitis B ( First dose )
1 month Hepatitis B ( Second dose )
3 month
Triple Antigen
Polio ( First dose )
5 month
Triple Antigen
Polio ( Second dose )
Hepatitis B ( Third dose )
9 24 month Germans measles
1 - 2 year
Triple Antigen
Polio ( Third dose )
TABLE 4.1
A boy was bitten by a snake. He was unconscious
and he was hospitalised.
4551/2 - 10 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM
2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
(d) (i) Based on Table 4.1, state the type of pathogen which cause the diseases.
...................................................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
(ii) Explain why there is a need for second and third doses for the immunisation.
[ 3 marks ]
TOTAL
4551/2 - 11 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
5. Figure 5 shows various types of fingerprints.
Rajah 5 menunjukkan bebrapa jenis cap jari
Composite Whorl Curves Loops
Komposit Pusar Lengkung Gelung
FIGURE 5
(a) (i) Based on Figure 5, name the type of fingerprints of students X and Y below.
Berdasarkan Rajah 5, namakan jenis cap jari bagi pelajar X dan Y di bawah.
Student X Student Y
Type of fingerprint: Type of fingerprint:
Jenis cap ibu jari: Jenis cap ibu jari:
.
[2 marks]
(ii) State one factor that causes variation in the fingerprints of students X and Y.
Nyatakan bagaimana faktor di (a)(ii) menghasilkan variasi.
.... ..
[1 mark]
(iii) State how the factor in (a) (ii) causes variation.
Nyatakan bagaimana faktor di (a)(ii) menghasilkan variasi.
[1 mark]
4551/2 - 12 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
(b) (i) What is the type of variation shown in Figure 5?
Apakah jenis variasi yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 5?
[1 mark]
(ii) State two traits, other than fingerprint, which show the same type of variation as
in (b)(i).
Nyatakan dua trait selain cap jari yang menunjukkan variasi yang sama seperti
(b)(i).
Trait 1 :
Trait 2 :
[2 marks]
(c) Height is a type of variation.
Explain the differences between the type of variation shown by fingerprints and
height.
Trait ketinggian merupakan sejenis variasi
Huraikan perbezaan antara variasi yang ditunjukkan oleh trait jenis cap jari dengan
trait ketinggian pelajar.
[2 marks]
(d) Explain how variation can ensure the survival of a species.
Terangkan bagaimana variasi boleh menjamin kemandirian suatu spesies
[3 marks]
TOTAL
4551/2 - 13 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
SECTION B
[ 40 marks ]
Answer two questions from this section.
6. Diagram 6.1 shows a respiratory structure of an insect.
Rajah 6.1 menunjukkan struktur respirasi satu serangga
DIAGRAM 6.1
(a) (i) Explain the gases exchange between tracheol and body cell.
Terangkan pertukaran gas antara trakeol dan sel-sel badan
[4 marks]
(ii) Chitin is a polysaccharide on the outer surface of structure P. Due to the change in
the environment, the insect is unable to form the polysaccharide.
Explain how the absence of chitin affects inhalation and the energy production.
Kitin adalah polisakarida yang terdapat pada permukaan struktur P. Disebabkan
perubahan dalam persekitaran, serangga tidak dapat menghasilkan polisakarida.
Terangkan bagaimana ketiadaan kitin memberi kesan keatas proses tarikan nafas
dan penghasilan tenaga .
[6 marks]
P
Tracheol
Trakeol
Body cells
Sel-sel
Badan
4551/2 - 14 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
(b) Diagram 6.2 shows the rate of oxygen intake before, during and after a vigorous
exercise of an athlete.
Rajah 6.2 menunjukkan kadar pengambilan oksigen sebelum, semasa dan selepas
satu latihan intensif seorang atlit.
Time (min)
DIAGRAM 6.2
(i) Based on the graph, compare the respiration before and during the vigorous
exercise.
Berdasarkan graf diatas, bezakan proses respirasi sebelum dan semasa
latihan tersebut.
[4 marks]
(ii) Explain how the oxygen intake by the athlete returns to the normal level at the 25th
minute.
Terangkan bagaiman pengambilan oksigen oleh atlit tersebut kembali ke asal
selepas minit ke 25
[6 marks]
Vigorous exercise
Oxygen intake
(litre/minute)
4551/2 - 15 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
(7) (a) Figure 7 shows development of the follicle in the female ovary, thickening
of uterine endometrium and the hormones involved.
Rajah 7 menunjukkan perkembangan folokel dalam ovari seorang perempuan,
penebalan endometrium uterus dan hormonphormon yang terlbat.
FIGURE 7
Explain the relationship between development of the follicle , changing of the
respective hormonal level in the blood and the thickening of the uterine
endometrium in a female.
Terangkan hubungan antara perkembangan folikel, perubahan aras hormon-
hormon masing-masing dalam darah dan penebalan endometrium uterus pada
seorang perempuan.
(10marks)
Time (Day)
Estrogen
4551/2 - 16 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
(b) Graph 7(a) and 7(b) show the growth curve of human and insect.
Based on the graph , compare the growth process in human and insect.
Graf 7 (a) dan 7 (b) menunjkkan lengkuk pertumbuhan manusia dan serangga
Berdasarkan graf, bandingkan proses pertumbuhan pada manusia dan serangga.
(10marks)
GRAPH 7(a) : Growth curve for human
GRAPH 7(b) : Growth curve for insect
Heigh
t (cm)
Time (year)
Length
(cm)
Time(day)
4551/2 - 17 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
8 (a) Diagram 8 shows the blood groups of a married couple, Encik Ahmad and
Puan Amalina and their children.
Rajah 8 menunjukkan kumpulan darah bagi pasangan suami isteri Encik
Ahmad dan Puan Amalina serta anak-anaknya.
Parents
Ibu bapa
0ffspring
Anak
blood group 0 blood group 0 blood group 0 blood group AB
kumpulan darah O kumpulan darah O kumpulan darah O kumpulann darah AB
Diagram 8
Diagram 8 shows the variation of blood groups in En Ahmads family. Explain why
there is a variation in blood groups of the offspring.
Rajah 8 menunjukkan variasi kumpulan darah dalam keluarga En Ahmad. Terangkan
mengapa adanya variasi dalam kumpulan darah anak-anaknya.
[ 10 marks]
(b) Genetic engineering is widely used in the field of agriculture and medicine.
Justify the impact of genetic engineering on humans and the environment.
Kejuruteraan genetik digunakan secara meluas dalam bidang pertanian dan
perubatan.
Beri wajaran tentang impak kejuruteraan genetik terhadap manusia dan
persekitaran.
[ 10 marks]
E En Ahmad
Blood group A
Kumpulan darah A
darahBloogroup A
EPn Amalina
Blood group B
Kumpulan darah B
Blood group A
4551/2 - 18 - LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
Biodiversity is the variety of plants, animals and microorganisms living on Earth.
These organisms live in different ecosystems and are important to our lives.
Biodiversiti ialah kepelbagaian jenis tumbuhan, haiwan dan Mikroorganisma yang
hidup di bumi. Organisma ini hidup dalam berbagai ekosistem dan penting kepada
kehidupan kita.
9.(a)(i) Based on the statement discuss the importance of biodiversity.
Berdasarkan pernyataan di atas bincangkan kepentingan biodiversiti.
[4 marks]
(ii) Diagram 9 shows an ecosystem in Malaysia.
Rajah 9 menunjukkan satu ekosistem di Malaysia
Diagram 9
Discuss the importance of the ecosystem shown in Diagram 8 to the environment
and economy of our country.
Bincangkan kepentingan ekosistem di Rajah 8 kepada persekitaran dan ekonomi
negara kita.
[6 marks]
(b)
Biotechnology is the application of organisms or microorganisms or their biological
processes in the production of materials for use in medicine and industry.
Biotechnology ialah aplikasi organisma atau microorganism atau proses biologi
dalam penghasilan bahan-bahan untuk kegunaan bidang perubatan dan
perindustrian.
Discuss the uses of microorganisms in
Bincangkan pengunaan microorganisma dalam
(i) the waste treatment process.
proses rawatan kumbahan.
(ii) food processing
pemprosesan makanan
[10 marks]
END OF QUESTION PAPER
PPD MELAKA TENGAH
LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009
JAWAPAN - BIOLOGY PAPER 1
1. A 11. C 21. C 31. C 41. C
2. B 12. C 22. C 32. D 42. A
3. A 13. A 23. C 33. D 43. A
4. A 14. D 24. C 34. C 44. B
5. B 15. D 25. D 35. C 45. B
6. D 16. C 26. B 36. C 46. C
7. C 17. B 27. C 37. C 47. D
8. B 18. D 28. D 38. C 48. B
9. A 19. A 29. B 39. B 49. B
10. A 20. C 30. C 40. D 50. D
PPDMT LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009 BIOLOGY P2
2
MARKING SCHEME - BIOLOGY PAPER 2
QUESTION 1
No Criteria Marks
(a)
Able to name tissue K and tissue L.
Answer:
K: Upper epidermis (cells / tissue)
L: Palisade mesophyll (cells / tissue)
1
1 2
(b)
Able to state the function of cells K and M in a leaf.
Sample answer:
K: Protect the inner tissues. // Allows light to penetrate.
M: Controls the size of stoma / transpiration / gaseous exchange
// Allows gaseous exchange through the stoma.
1
1
2
(c) (i)
Able to explain the differentiation of cells J to form the xylem tissue.
Sample answer:
Cells J join end to end, / the wall of cells J at the joints dissolved,
to form a hollow tube / continuous tube (from root to leaves).
The wall of xylem vessel is thickened by lignin. (Any 2)
1
1
1 2
(ii)
Able to explain the effect on the function of the leaf when the plant
unable to synthesise lignin during the formation of the xylem tissue.
Sample answer:
Xylem cannot be strengthened / cannot uphold leaf.
Less sunlight received / absorbed.
Slow down the rate of photosynthesis / less glucose produced
Or (Any 2)
Xylem vessels collapsed.
Less water supplied to leaves.
Slow down the rate of photosynthesis / less glucose produced
(Any 2)
1
1
1
1
1
1 2
(d) Able to state the meaning of cell specialisation.
Sample answer:
Cells grow, change shape / differentiate.
To carry out / perform specific function.
1
1 2
(e) Able to explain the adaptation of palisade mesophyll tissue to enable
the leaf to carry out its function.
Sample answer:
Upright and closely packed.
Contains large number of chloroplast.
All cells receive maximum amount of sunlight.
// Absorb maximum amount of sunlight // energy.
1
1
1
2
TOTAL 12
PPDMT LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009 BIOLOGY P2
3
QUESTION 2
No Criteria Marks
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)(i)
(e)(ii)
Able to name the phase U.
Sample answer:
U : Interphase
Able to describe the processes at sub phases X, Y and Z during
phase U
Sample answer :
X : Cell synthesises protein / new orgenelles formed
Y : DNA is synthesized / is replicated / 2 sister chromatids
formed
Z : Cell accumulates energy / synthesise energy / prepare for
cell division
Able to draw a daughter cell based on the following criteria:
No. of chromosomes are haploid / 3 chromosomes
Types of chromosomes/ non homologous
New genetic combination
Able to explain how radiotherapy can treat cancer.
Sample answer :
F : Radiotherapy uses radiation / high energy rays
E1 : destroy the nucleus of cancerous cells
E2 : cancerous cells die / cannot divide mitotically
E3 : cell cycle stops
Able to name the method and explain the advantages of the
method in increasing crop yield.
Sample answer :
T : Tissue culture / Cloning
E1 : Large numbers of clones can be produced
E2 : Within a short period of time / any time
E3 : Clones inherited good characteristics/ resistance to diseases
/ fast growth rate / large fruit / good genetic traits
Able to state one problem :
Clones can be destroyed completely if they do not have the
resistance to new diseases / pest.//
No variation
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Any 2
1
1
1
1
Any
1E = 1
1
1
1
1
T=1m
Any
2E
Marks
Any 1
1
3
2
2
3
1
TOTAL 12
PPDMT LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009 BIOLOGY P2
4
QUESTION 3
No Criteria Marks
3 a
b(i)
(ii)
c(i)
(ii)
d
Able to name P,Q and R
Suggested answer
P: leguminous plant / example of a leguminous plant
Q: nitrates
R: denitrifying bacteria
Able to state the name of the microorganism
Suggested answer
Rhizobium sp /nitrogen fixing bacteria
Able to name the natural phenomenon that can convert atmospheric
nitrogen to substance Q
Suggested answer
Lightning
Able to suggest the type of the microorganism that is involved in
process Y.
Suggested answer
saprophytic bacteria / fungi // putrefying bacteria / fungi
Able to explain the role of the microorganism in the nitrogen cycle
Suggested answer
1. Saprophytic bacteria / fungi decompose protein in the dead
plants and animals / excretory products of animals
2. to ammonium/ simpler nitrogenous compounds/ ammonia which
is eventually converted to nitrates.
3. This increases the nitrate / nitrogen content of the soil.
Able to explain how a deficiency of Q in the soil affects plant growth.
Suggested answer
1 Root hairs absorb less Q/nitrates/nitrogen
// less Q/nitrates/nitrogen is available to be absorbed by plants.
2. Less chlorophyll / protein is synthesized.
3 Rate of photosynthesis decreases.
4 Plant growth is slow / retarded.
Any 3
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
3
1
1
1
3
3
TOTAL 12
PPDMT LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009 BIOLOGY P2
5
QUESTION 4
No Criteria Marks
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)(i)
(ii)
Able to state the substances injected into the blood of individual
P and individual Q.
Sample answer:
P : Dead or weakened bacteria / viruses / antigens// vaccine
Q : Serum containing antibodies // antiserum
Able to explain the type of immunity obtained by individual P and
individual Q.
Sample answer :
P : Artificial active immunity
The body produces its own antibodies to fight against
infections by pathogens.
Q : Artificial passive immunity
The body receives antibodies produced from outside sources
to fight against infections by pathogens.
Able to describe how could save that boy.
Sample answer :
F1: Snake venom / toxin acts as antigen to our body
F2: Injection of serum which contains instant antibodies /
antiserum / anti-toxin must be given to the patient.
F3: Antibody-antigen action occured very fast
F4: Antitoxin/ antibody reacts with toxin / snake venom/ antigen
and neutralize it / he is saved.
Able to state the types of pathogen which cause the diseases
Answer:
Virus / bacteria
Able to explain why there is a need for second and third doses
for the immunisation
Sample answer :
F1: Immunisation is given to prevent infection from pathogens
that caused diseases like Tuberculosis, Hepatitis B, Polio,
diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus. German measles ( state at
least 2 example )
F2: New born are injected with vaccines to get Artificially Active
Immunity
F3: First dose are given to induce baby lymphocytes to produce
antibodies which are specific against the antigens / bacteria /
virus
F4: 2
nd
and 3
rd
dose are booster dose to increase the production
of antibodies at a faster rate.
F5: Achieved immunity level // antibodies remained in the blood
for a long time and provide permanent immunity / protect them
from the next infection.
Any 3
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
4
3
TOTAL 12
PPDMT LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009 BIOLOGY P2
6
QUESTION 5
No Criteria Marks
(a) (i)
( ii)
(iii)
(b) (i)
(ii)
(c)
(d)
Able to name the type of fingerprints of students X and Y
Answer:
X - Loop ; Y- Composite
Able to state one factor that causes variation in the fingerprints
of students X and Y.
Answer:
Genetic factor
Able to state how the factor in (a) (ii) causes variation
Answer:
Genetic recombination during crossing over
results in the formation of different
Able to state the type of variation
Answer:
Continuos variation
Able to state two traits, other than fingerprint, which show the
same type of variation as in (b)(i)
Answer:
The ability to roll tongue
Types of hair
Able to explain the differences between the type of variation
shown by fingerprints and height.
Sample answer:
Height Types of fingerprint
- Shows normal distribution Shows discrete distribution
- Affected by environmental Not affected by
Factors environmental factor
Able to explain how variation can ensure the survival of a species
Sample answer:
- Can differentiate from one individual to another / no one is the
same
- Able to adapt to a new environment
- Able to camourflage to run away from any predators
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
1
1
2
2
3
TOTAL 12
PPDMT LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009 BIOLOGY P2
7
SECTION B
QUESTION 6
No Criteria Marks
(a) (i)
Able to explain the exchange of gases between tracheole and body
cell.
Sample answer:
Partial pressure/concentration of oxygen in the tracheole is higher
than partial pressure/concentration of oxygen in body cell .
Oxygen diffuse from tracheole to body cell
Partial pressure/concentration of carbon dioxide in the body cell is
higher than partial pressure/concentration of carbon dioxide in
tracheole .
Carbon dioxide diffuse from tracheole to body cell
1
1
1
1 4
(ii)
Able to explain how the absent of chitin affect the process of
inhalation and energy production of the insect.
Sample answer:
The function of chitin is to prevent trachea from collapsing/sustain
the air pressure
During inhalation high pressure air moves into the trachea.
The absent of chitin will cause the trachea / P to collapse / burst /
rupture.
Air with oxygen cannot reach tracheal.
Body cell cannot get enough oxygen for cellular respiration
The insect does not produce enough energy and respire
anaerobically.
Less energy produced. (Any 6)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
6
b (i)
Able to compare and explain the respiration before and during
vigorous exercise.
Sample answer:
Before (A) During (B) Explanation (E)
1
.
Aerobic
Respiration
Anaerobic
Respiration
Before - oxygen intake is
low/the same as oxygen
required/enough oxygen
is supplied to the cell
During oxygen required
is more than oxygen
intake
2
.
The
muscles are
in normal
condition
The muscles
are in the state
of oxygen debt
Before oxygen is
sufficient
During oxygen is
insufficient / oxygen
supplied is less than
oxygen supplied.
3
.
Energy
produced is
Energy
produced is
Before complete break
down of glucose (produce
PPDMT LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009 BIOLOGY P2
8
more/38
ATP
less / 2 ATP more energy)
During incomplete break
down of glucose (produce
less energy)
4
.
No/less
accumulatio
n of lactic
acid in the
muscles
High
accumulation
of lactic acid in
the muscles
Before complete break
down of glucose produce
carbon dioxide and water
During Incomplete
breakdown of glucose
produce lactic acid
A + B = 1m
E=1m (Any one E)
8
(b) (ii)
Able to explain how the oxygen intake by the athlete returns to the
normal level at the 25
th
minute.
Sample answer:
Lactic acid has been removed from the muscles
The lactic acid has been converted to energy/ convert to glucose
1
1 2
TOTAL 20
PPDMT LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009 BIOLOGY P2
9
QUESTION 7
No. Criteria Mark Remark
7(a) Able to explain the relationship between development of
the follicle , changing of the respective hormonal level in
the blood and the thickening of the uterine
endometrium.
Suggested answer:
Day 0 7
Follicle
very small
start to develop when receive FSH from pituitary
the wall of follicle will produce estrogen
FSH
- pituitary start to release FSH, FSH will go
to the ovary
- FSH stimulate development of follicle
Endometrium
- stimulate by estrogen; undergo thickening / repairing
Day 8 14
Follicle
- become larger, develop to form follicle Graaf
FSH / LH/ Estrogen/progesterone
- FSH decrease, LH at maximum level , estrogen at
maximum level
- LH stimulate ovulation / completion of meiosis I,
estrogen stimulate the thickening of endometrium
- Progesterone level very low
Endometrium
- endometrium become very thick (ready to
implantation (of embryo))
-
Day 15 - 21
Follicle
- Follicle undergoes ovulation/ released oocyte II
- The remaining follicle tissue / corpus luteum
secreted small amount of estrogen but large
amount of progesterone
FSH/ LH/ Estrogen/ Progesterone
- Progesterone stimulated the thickening of
endometrium , halted the secretion of FSH/LH
- Development of new follicle and ovulation stop.
Endometrium
- more thicker and highly vascular
- ready for implantation of embryo
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max 3
marks for
each stage
- 9 marks
At least the
answer
shows the
relationship
between 3
parameter
i.e follicle,
hormone
and
endometriu
m
- 1 mark
PPDMT LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009 BIOLOGY P2
10
Day 22 28
Corpus luteum
- if no fertilisation, corpus luteum become
disintegrate
FSH/ LH/ Estrogen / Progesterone
- FSH, LH and estrogen at minimum level;
progesterone level also drop
Endometrium
- endometrium become breakdown & disintegrate
- blood and tissue are shed / lining of uterus
discharge through vagina as menstrual flow.
1
1
1
1 Max 10
7(b) Able to compare the growth process in human and
insect.
Suggested answers:
Similarities
- height of man / length of instar increases by time
- both show horizontal line / constant growth during
adult
Difference
- Form of graph Sigmoid form for human and like
series of steps in insect
- Age of organism the height measured yearly,
but in insect used day for measuring the length
- Caused of different human have endoskeleton
but insect have exoskeleton
- Stages involve in human, the curve has three
different phases, but there are five steps in insect
// nymphal stages
- Vertical and horizontal line : curve for human did
not shows different line (only the curve from
continuous points), but there are five different
horizontal and vertical lines each
- Zero growth no point to show zero growth in
human, but there are 5 time of zero growth (at
horizontal line)
- Sudden growth : no sudden growth for human,
but there are sudden growth in insect (at vertical
line)
- Ecdysis : no ecdysis in human but ecdysis
occurred in insect
- Mitosis : the cells in human undergo mitosis all
the time, but in insect, mitosis only occurred at
certain time (during ecdysis)
- Absorption of air : in human, there are no
absorption of air, but in insect, during ecdysis
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max 10
marks
*2 marks
for
similarities,
8 marks for
differences
TOTAL 20
PPDMT LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009 BIOLOGY P2
11
QUESTION 8
No Criteria Marks
8(a) Able to explain why there is a variation of blood groups in the
offspring
1. The ABO blood group in humans is controlled by three alleles
I
A,
, I
B
and I
o.
2 Alleles I
A
and I
B
are codominant but allele I
o
is recessive.
3 Ahmad is heterozygous for blood group A // Genotype of
Ahmad is I
A,
I
O,
4 Amalina is heterozygous for blood group B // Genotype of
Amalina is I
B,
I
O
5 Ahmad produces two types of sperms, one containing allele I
A
and the other containing allele I
O
.
6 Amalina produces ovum containing allele I
O
or allele I
B
7 When the sperm containing allele I
O
fertilizes with the ovum
containing allele I
O
the offspring produced will have the
genotype I
O
I
O
8 and the phenotype is blood group O.
9 Three of the children who have the blood group O are
produced this way and they have the genotype I
O
I
O
10 When the sperm containing the I
A
allele fertilizes with the
ovum containing allele I
B
then the offspring produced will
have the genotype I
A
I
B
11 and the phenotype is blood group AB.
12 One of the children who have the blood group AB is produced
this way and has the genotype I
A,
I
B.
Any 10 points
Genetic diagram:
Parents Ahmad x Amalina
Genotype I
A
I
O
I
B
I
O
PT 3,4
PT 5., 6
Gametes
Fertilisation
Offspring
Genotype I
A
I
B
I
O
I
O
PT7.10
Phenotype blood group AB blood group B
Pt 8, 11
(If answer using schematic diagram - only maximum 7 marks)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1 10
No Criteria Marks
I
A
I
O
I
B
I
O
PPDMT LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009 BIOLOGY P2
12
8b Able to explain the effect of genetic engineering on man and the
environment
Suggested answer
Good effects
Agriculture
F1 Genetic engineering used to produce disease resistant/ pest resistant
plants
e.g legumes, peas and beans
P : Less pesticides are used
- less pollution to the environment
- better health for consumers.
P : increase yield of crops
- better livelihood for farmers.
- help to solve problems of insufficient food.
F2 : create crops with better nutrition value e.g tomatoes with higher
vitamin A content
- help to solve problems of malnutrition.
F3: create crops with longer shelf lives e.g tomato
- less food wastage
F4 : genetically modified livestock e. g cows
- produce meat with less fat / more milk.
Medicine
F5 : genetically modified bacteria produce insulin
P ; for treatment of diabetis mellitus
F6: Genetically modified yeast to produce vaccine for hepatitis
P: for prevention of diseases.
F7: Gene therapy for treatment of genetic disorders/ diseases e.g
muscular dystrophy, rheumatoid arthritis, sickle cell anaemia
P: Defective gene removed and normal gene inserted.
Any 2F and P for agriculture,
any 1F and P for medicine Max : 6m
Bad effect
F1 Pest resistant genes may be transferred to weeds
P: may be difficult to control growth of weeds.
F2: Some transgenic crops may have animal genes
P : this may not be acceptable to certain groups for religious reasons.
F3: Genetically modified foods may be harmful to health
P: may activate human genes to cause cancer.
F4: Transgenic organisms may affect the survival of other organisms
in the ecosystem.
P: may cause the imbalance of nature / ecosystem
F5: Gene therapy used for the treatment of genetic disorder has its
limitations.
P : may not be acceptable because of religious and moral values.
: very costly
Any 2F and P
Max 4m
6
4
10
TOTAL 20
QUESTION 9
PPDMT LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009 BIOLOGY P2
13
No Criteria Marks
9 (a)(i)
(ii)
Able to discuss the importance of Biodiversity
Suggested answer:
F- it provides humans with necessities of life
P- is a resource for food/timber to build shelter/as a fuel/fibres
for clothing.
F- many plant species are original sources of pharmaceutical
drugs/medicines.
P- new commodities, for example, new crop plants or medicinal
materials could be developed using the gene pool from wild
species in the forests.
F- allow for biological control to maintain stable population
P- regulate climatic conditions, biogeochemical cycles, prevent
flooding
F- Natural ecosystems and species in the wild are beautiful
P- there is much pleasure to be derived from unspoilt natural
environment
F- ecotourism
P- could provide income for some countries
Any 4 points
Able to discuss the Importance of mangrove swamps.
Sample answer:
- F: resource for timber used in building industry
- P : has many varieties of species of mangrove trees
- F: Mangroves protect the coastlines and prevent
- coastal erosion.
- P: The roots of mangrove trees act as wave
- breakers which stabilise the coastlines.
- F:: Mangrove swamps are good breeding grounds
- for fish and crustaceans/ prawns, crabs etc.
- Important for fishermen
- P: The calm water and prop roots shelter the
- spawns from predators
- F: Serve as habitat for many species of birds,
- amphibians and reptiles.
- P: The habitat provides food, shelter, living space,
- nesting and breeding sites for these animals.
- F: Serve as natural barriers against torrential
- storms and tsunamis
- P: The trees block the water from flooding the
land during a storm.
Any 6 ponts
Max 4
Max 6
PPDMT LONJAKAN SAUJANA SPM 2009 BIOLOGY P2
14
(b)(i)
(ii)
Able to discuss the uses of microorganisms in ;
Waste treatment
- rich in organic matters, bacteria and microorganisms
- (in oxidation pond)the sewage is decomposed
by(millions) of aerobic bacteria(in the presence of
oxygen)
- Decomposed sewage/sludge settled to the bottom of the
pond
- fermentation takes place at sedimentation tanks
- using anaerobic bacteria
- produce methane/carbon dioxide/minerals
- digested sludge use as fertilizers
Any 5 points
Food processing
- F: Use of yeast in making of bread and cake
- P: Fermentation by yeast produces carbon dioxide
- which makes dough rise.
- F: Beer brewed from barley/ wine from grape juice
- P: Yeast fermentation of the sugar in barley/ grape
- produces ethanol
- F: Yoghurt is made from fermentation of milk by
- bacteria / Lactobacillus sp. / Streptooccus
- thermophillus
- P: Bacteria converts sugar into lactic acid which
- coagulates the milk to / form yoghurt
- F: Cheese made by adding bacteria and rennin to
- milk.
- P: Milk separates into curd and whey/ coagulates
- F: Soya sauce made from fermentation of soya
- bean by fungi
- P: Yeast fermentation breaks down soya bean and
- gives it flavour
Any 5 points
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max 5
Max 5
TOTAL 20
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
j*k
MARKING SCHEME
PAPER 1
TRIAL KEDAH 2010
1. C 26. A
2. A 27. A
3. C 28. B
4. D 29. C
5. C 30. C
6. B 31. C
7. A 32. B
8. D 33. A
9. D 34. C
10. B 35. D
11. C 36. A
12. D 37. A
13. D 38. A
14. D 39. D
15. B 40. A
16. D 41. A
17. C 42. C
18. A 43. B
19. D 44. B
20. C 45. A
21. B 46. B
22. D 47 D
23. A 48. A
24. B 49. C
25. C 50. B
j*k
2
BIOLOGY
SECTION A
PAPER 2 [4551/2]
No.
Marking Criteria / Sample Answers Marks
1 (a) (i) Gills
1
(ii) Tracheal system
1
(b) P : Filaments
Q: Spiracles
1
1
2
(c) (R is ring of chitin which) support the tracheal / prevent the tracheal
from collapsing.
1
(d) Diagram 1.1(b):
P1: The filament have numerous thin-walled lamellae to maximise
the surface area for gaseous exchange.
P2: The gill filaments have thin membrane and covered by a net
work of capillaries to transport respiratory gases.
P3: The surface of the gills is moist which allows the gases to be
dissolved.
Any 1P
1
Diagram 1.2(b)
P1: The large number of tracheoles provides a large surface for the
diffusion of gases.
P2: Tip of tracheoles have thin permeable walls and contain fluid in
which respiratory gases can dissolve.
P3:Terminal ends of the tracheol remains moist which allows the
gases to be dissolved.
Any 1P
1
(e) (i) P1:( The gaseous exchange process occurs over the whole body
surface in an Amoeba sp) through simple diffusion.
P2:Higher concentration of oxygen in the water surrounding causes
oxygen to diffuse into the Amoeba.
P3:Higher concentration of carbon dioxide in the cell causes carbon
dioxide to diffuse out of the Amoeba.
Any 2P
1
1
1
2
(ii) S: Contractile vacuole
1
(iii) P1: Freshwater is hypotonic to the cytoplasmic fluid of Amoeba sp .
P2: Water diffuses into the cell and fill the contractile vacuole by
osmosis
P3: When the contractile vacuole is filled with water to its maximum
size, it contracts to expel its content from time to time.
Any 2P
1
1
1
2
j*k
3
No.
Marking criteria/ Sample answers Mark
2 (a) (i) Osmosis
1
(ii) P1 : Sucrose solution is hypertonic / more concentrated.
P2 : Water diffuse from distilled water into the sucrose solution
P3 : The level of sucrose solution in the capillary tube stop rising
at the equilibrium stage / the concentration inside and outside
of the visking tubing is the same / the amount of water
diffuse into and out from the visking tubing is the same.
Any 2 Ps
1
1
1
2
(b)
F- Sucrose molecules are too large
E- The visking tubing is a semi permeable membrane/
which only allows certain substances to pass through.
1
1
2
(c) (i) Y : crenation
Z : haemolysis
1
1
2
(ii) P1- Solution Z is hypotonic compare to red blood cell.
P2- Osmosis occur
P3- water leaves/ diffuses into the cell
P4- Red blood cell expand/ swell and burst.
Any 3P
1
1
1
1
3
(iii) F : No
P1 : Plant cell consists of cell wall
P2 : Cell wall is made up of cellulose
// Cell wall able to withstand the pressure.
Any 2
1
1
1
2
Total
12
j*k
4
No.
Marking criteria/ Sample answers Mark
3 (a) (i) Absorption / Simple diffusion / facilitated diffusion
1
(ii) F1 thin wall/ one cell thick
E1 increase rate of diffusion of digested food/ nutrients
F2 large surface area/ has microvilli
E2 increase rate of absorption of digested food/ nutrient
F3 has a network of capillaries/ blood vessels
E3 to transport the absorbed nutrients
Any F + E
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
(b)
P: hepatic portal vein
Q: lymphatic/lymph vessel/ duct
1
1
2
(c) P1: Deamination.// The amino group is removed (from amino acid)/
converted to ammonia .
P2: (Ammonia) is converted to urea.
P3: urea will be excreted through the kidneys.
Any 2 Ps
1
1
1
2
(d) L1: A major energy reserve in the body//
L2: (phospholipids are) components of the plasma membrane//
L3: Lipids is used as a respiratory substrate//
L4: Excess fats are stored in adipose tissues (under the skin, around
internal organs)
Any 1L
A1:Amino acids are used in protein synthesis//
A2:For repair and production of new protoplasm/growth and repair//
A3:Used in the formation of enzymes/ some hormones/protein part of
haemoglobin/ antibodies
Any 1A
G1:Glucose is used as the main respiratory substrate// It is oxidised to
release energy (water and carbon dioxide)//
G2:Excessive glucose is converted to glycogen
// Blood glucose level rise / increase.
Any 1 G
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
3
(e) P1: Diabetes mellitus // Blood sugar level increases// Hyperglycemia
P2: Excess glucose cannot be converted to glycogen.
1
1
2
Total 12
j*k
5
No.
Marking criteria/ Sample answers Mark
4 (a)
Both arrows correct
1
(b) A Pulmonary artery
B Pulmonary vein
1
1
2
(c)
F : Contraction of ventricle / heart
E1: generates a (high) pressure
E2 : (to) propel/ force / pump the blood flow from the heart/ ventricle to
vessel A
Any two
1
1
1
2
(d)(i)
Coronary artery
1
1
(ii) P1: Cut the supply of O
2
/ nutrients to the heart muscle
P2: causing chest pain / angina / heart attack / myocardial infarction
Reject Heart problem
1
1
2
(e) (i)
(ii)
P1: platelets break down and release chemicals
P2: to cause platelets to stick to each other
P3: platelets clump together to form a plug to prevent blood loss .
P4: released thrombokinase and other clotting factors
Any 2P
P1 : Fibrinogen is soluble, fibrin is insoluble / not soluble
P2 : Fibrin able to form fibres / meshwork / thread to trap
blood cells, fibrinogen is not able to do so.
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
Total 12
j*k
6
No.
Marking Criteria / Sample Answers Marks
5 (a) (i) (Transfer/flow of) energy
1
(a) (ii) F : Phytoplankton is an autotrophic organism.
P1 : Able to absorb light energy / consists of chloroplast.
P2 : synthesis their own food / carry out photosynthesis
Any 2
1
1
1
2
(b) F1 : population of small fish increases
P1 : no shark feed on small fish // shark is the predator
F2 : population of plankton decreases
P2 : more small fish feed on the plankton
F3 : Eventually the population of small fish decreases
Any 3
1
1
1
1
1
3
(c) F : Commensalism
P1 : Shark is the host / neither gain any benefit nor harmed.
P2 : Remora benefits
P3 : Remora obtain protection / food / transport from the shark.
Any 3
1
1
1
1
3
(d) P1 : Fertilizer washed away by rain water into the lake
P2 : Nutrient / minerals content in the lake increase.
P3 : alga bloom / alga grow rapidly in the lake.
P4 : eutrophication occur.
P5 : Oxygen content in the lake decrease / drop
P6 : Fishes die / population decrease
Any 3 P
1
1
1
1
1
1
3
Total
12
j*k
7
BIOLOGY
SECTION A
PAPER 2 [4551/2] - ESSAY
No.
Marking Scheme Mark
6(a) (i)
Continuous variation : body weight, height
Discontinuous variation : types of earlobe, types of finger print.
1
1
2
(a)(ii) Continuous Variation Discontinuous variation
P1 The changes of
characteristics among
individual are gradual
The differences among
individuals are distinct.
P2 Continuous variation is
quantitative // characteristics
can be measured.
Discontinuous variation is
qualitative // characteristic
is either present or absent.
P3 The graph shows the normal
distribution curve.
The graph shows the
discrete distribution.
P4 The character is determined
by many genes
The character is determined
by a single genes
P5 The characteristic is
influenced by the
environmental factor and
genetic factor.
The characteristic is
influenced by the genetic
factor.
P6 Exhibits a range of
phenotype with intermediate
characters.
There are no intermediate
groups.
Any 4
pair
Max
4 m
(b) Albinisme
F : Albinisme is caused by the change in gene // mutation
P1 : Body / skin unable to produce black pigment (melanin)
P2 : The skin and hair of albinos are white // their eyes are pink.
Any 2
Sickle cell anaemia
F : Sickle cell anaemia is caused by the change in the genes //
mutation.
P1 : haemoglobin produced is not normal / abnormal
P2 : Abnormal haemoglobin unable to bind / transport / carries
with oxygen efficiently.
P3 : The patient will always feel weak / cannot carries out
vigorous activities.
Any 2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max
2 m
Max
2m
j*k
8
6(c) (i) Abiotic factors that cause variation between the two sets of ginger plants
are:
F1: Sun light
P1: Plants need light energy to carry out photosynthesis for
growth
P2: Set A, plants are obtain more / exposed to sunlight
// Plants in set B obtain less sunlight / not exposed to Sunlight.
P3 : Growth rate of plants in Set A is higher than plants in Set B.
1
1
1
1
F2: Space
P4: Plants need (space) to grow a large root system / leaves
P5: Plants able to absorb sufficient water and minerals/sunlight.
P6: Set A, plants have larger space for the root and leaves to
Grow // Plants in set B have smaller space for the root and
leaves to grow.
1
1
1
1
F3: Soil / minerals
P7: Plants need mineral for (healthy) growth.
P8: Loam soil provides more minerals in Set A.
// Sandy loam soil in Set B contains less minerals.
P9: Loam soil able to trap / store water better than sandy loam soil.
Any 8
1
1
1
1
max
8
6(c) (ii) F1 : Plantlets from tissue culture have the same genetic material.
P1 : This is to show /ensure/proof the differences of plants in
Set A and Set B are not caused by genetic factor / have the same
genetic material.
// This is to show /ensure/proof the differences of plants in
Set A and Set B are caused by abiotic factors.
1
1
2
Total 20
No.
Marking Scheme Mark
7(a) P1 : Nerve impulses arrive at the axon terminal of
(presynaptic) neurone.
P2 : Causes the synaptic vesicles to move towards the
(presynaptic) membrane and fuse with the membrane.
P3 : Neurotransmiters /acetylcoline (examples) molecules
are released from synaptic vesicles.
P4 : (The neurotransmitter molecules) diffuse across the
synaptic cleft into the postsynaptic knob / dendrite
/ cell body of neighbouring neurone..
P5 : The neurotransmitter molecules bind to specific
receptor sites in the postsynaptic knob.
P6 : The binding triggers / generates new nerve Impulses.
P7 : The impulses then move along the postsynaptic neurone.
P8 : The release of neurotransmitter is in one direction,
from the synaptic knob to the postsynaptic neurone.
P9 : Mitochondria in the synaptic knob generate ATP
/ energy to synthesis neurotransmitter molecules.
Any 6
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max
6
j*k
9
No.
Marking Scheme Mark
7 (b) P1 : The receptor at the terminal of X stimulated by the heat.
P2 : The receptor generates a nerve impulse.
P3 : The nerve impulse travels along X / afferent neurone
To the spinal cord.
P4 : In the spinal cord, the nerve impulse is transmitted to
an interneurone.
P5 : From the interneurone, the nerve impulse is
transmitted to an efferent neurone/ neurone Y.
P6 : Nerve impulse travels along efferent neurone / Y and
reach the effector / muscle tissue / fingers.
P7 : Muscles contract to withdraw the hand / finger.
Any 4
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max 4
7 (c) P1 : The receptors in the eyes detect the dog.
P2 : Nerve impulses are generated and transmitted to the
brain via the afferent neurone.
P3 : The hypothalamus in the brain is stimulated.
P4 : It actives the sympathetic nervous system to generate
nerve impulses.
P5 : Nerve impulses are transmitted to the adrenal medulla
to stimulate secretion of adrenaline.
P6 : Adrenaline carried / transported by blood circulatory
system to the targeted organs.
P7 : Adrenaline promotes the breakdown of glycogen to
glucose.
P8 : (Adrenaline) increases the breathing rate.
P9 : More oxygen will be taken into the body
P10 : (Adrenaline) increases the rate of heartbeat/ blood
pressure.
P11 : Rate of the blood flow increase.
P12 : More glucose and oxygen will be supplied to the muscles.
P13 : More energy produced by the muscles.
// metabolic rate increase.
P14 : Body has enough energy to face the fight or flight
situation.
Any 10
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max 10
Total 20
j*k
10
No. Marking Scheme Mark
8 (a)(i) P1 fish have streamline shapes // the anterior of the fish is
smooth and rounded // the body is long and tapers
towards the end.
P2 the body of a fish is covered with scales that have a
slimy coating
1
1
2
(a)(ii) P1 myotomes muscles are arranged in both side of the body
P2 the vertebral column of the fish is flexible and can bent
from side to side
P3 myotome muscles act antagonistically in fish./ carry out
opposite action in a fish
P4 when the muscles on right side contract, the muscle on
the left side relax
P5 the tail/body will be bent to the right.
P6 when the muscles on left side contract, the muscle on
the right side relax
P7 the tail/body will be bent to the left.
P8 alternate contraction of the right and left myotome block
enable its tail to move left and right
P9 to produce a force that propel the fish forward.
[ any 6]
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max
6
(b)(i) Similarities:
F1 Both Joint S and Joint T has a cavity filled with
svnovial fluid // lined with synovial membrane
El Synovial fluid acts as lubricant to reduce friction
between bones // absorbs shock of the movement.
F2 The end surfaces of the humerus bone of Joint S and
Joint T are covered with cartilage
E2 To protect the bone / reduce friction between the bones
F3 Both Joint S and T are connected with ligaments
E3 to absorb shock // strengthen the articulation of bones/ joint.
Differences:
D1 Joint S is hinge joint
E4 Joint S allows the movement of bones in one plane /
direction
D2 Joint T is ball-and-socket joint.
E5 Joint T allows rotational movement of bones in
all directions.
[ any 8 ]
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max
8
8 (b)(ii) Osteoporosis
P1 : the bone become thinner / more brittle / porous / fragile.
P2 : Loss of bone mass.
P3 : Lack of calcium / phosphorus / vitamin D
Arthritis
P4 : Cartilage between bones become thinner.
P5 : Ligaments become shorter / loss elasticity
P6 : Less production of synovial fluid.
P7 : The joints become swollen / stiff / painful
[ any 4 ]
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max
4
Total 20
j*k
11
No.
Marking Scheme Mark
9 (a)
(b)
The tree
F1 : Less tree will be chopped / felled
P1 : More CO
2
absorbed by the trees for photosynthesis
P2 : Avoid the increasing of CO
2
in the atmosphere.
P3 : Reduce the impact of Green house effect // global warming
P4 : Less habitat of fauna and flora will be destroyed.
P5 : Reduce / avoid the extinction of fauna and flora.
P6 : To maintain / preserve the biodiversity.
The oil / fuel // Save Energy
F2 : Reduce the burning of oil / fuel
P7 : More fuel/energy can be preserved for future.
P8 : Less green house gases / acidic gases released.
P9 : Reduce / avoid the impact of green house effect / acid rain.
The Landfill
F3 : Less landfill will be opened
P10 : Landfill cause leaching / ground water pollution.
P11 : Less diseases / health problem caused by the improper managed
landfill.
The Water
F4 : Less used water / effluent / untreated sewage released into river.
P12 : Reduce / avoid the impact of water pollution / avoid the
extinction of aquatic organisms.
Any 10
Good Effect
G1 : Generate hydropower electricity
G2 : As reservoir / to store water / supply fresh water
G3 : Supply water for agricultural / industries.
G4 : Place/site for recreation / tourism
G5 : Reduce the flood problem at the downstream.
Bad Effect
B1 : Flooded / submerge trees / habitat of the fauna and flora
B2 : Less tree / plants to carry out photosynthesis
// Less CO
2
absorbed for photosynthesis
B3 : Amount of CO
2
in the atmosphere increase
B4 : Increase the impact of green house effect / global warming.
B5 : Many species of fauna and flora extinct
// Reduce the biodiversity.
B6 : Reduce the flow of water at the downstream.
B7 : Cause the population of aquatic life at the downstream reduce.
B8 : Reduce the land used for residential / agricultural
B9 : Flooded / destroy / loss of historical building / site.
Any 10
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
max
10
max
10
Total 20
j*k
SULIT 4551/1
1. Which organ consists of cells which has the highest densit of rough endo!lasmic
reticulum "
%rgan mana!ah mengandungi sel-sel yang mempunyai !epadatan alinan
endoplasmi! !asar paling tinggi&
# Stomach $ Brain
#erut %ta!
B %eart & Kidne
Jantung 'inal
2. &iagram 1 shows three t!es of cells.
Raah ( menunu!!an tiga enis sel.
P / R
&iagram 1
'o which sstems do the cells shown abo(e belong"
Kepada system mana!ah sel-sel di atas dipadan!an &
P / R
#. &igesti(e sstem
Sistem pen"ernaan)
)es!irator sstem
Sistem respirasi
*er(ous sstem
Sistem sara$
B. *er(ous sstem
Sistem sara$
)e!roducti(e sstem
Sistem pembia!an
$irculator sstem
Sistem peredaran
$
.
)es!irator sstem
Sistem respirasi
$irculator sstem
Sistem sara$
&igesti(e sstem
Sistem pen"ernaan
&
.
)e!roducti(e sstem
Sistem pembia!an
&igesti(e sstem
Sistem pen"ernaan
*er(ous sstem
Sistem sara$
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
SULIT 4551/1
+. &iagram 2 shows a unicellular organism li(ing in freshwater !ond.
Raah 2 menunu!!an seenis organisma unisel yang hidup di dalam !olam air tawar.
Which !rocess in(ol(es in the mo(ement of water "
*pa!ah proses yang terlibat dalam pergera!an air.
# &iffusion $ #cti(e trans!ort
Resapan #engang!utan a!ti$
B ,smosis & -acilitated diffusion
%smosis Resapan berbantu
.. &iagram + shows a cross section of a leaf.
Raah 3 menunu!!an !eratan rentas daun
&iagram +
Which of the cell labelled A/ B/ C and * does not contain chloro!last"
*ntara sel yang berlabel *+ ,+ - dan . yang mana!ah tida! mengandungi !loroplas&
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
*i$g!$m 2
Water
#ir
A
B
C
*
SULIT 4551/1
0. &iagram . shows a t!e of !lant tissue.
Raah / menunu!!an seenis tisu tumbuhan.
&iagram .
What is the im!ortance of the thickening of substance 1 to the !lant tissue"
*pa!ah !epentingan penebalan bahan 0 terhadap tisu tersebut &
A 'o transfer !hotosnthesis !roducts
1ntu! memindah!an hasil $otosintesis
B 'o gi(e turgidit to the tissues
1ntu! memberi!an !esegahan !epada tisu
C 'o transfer water and mineral salts
1ntu! memindah!an air dan garam mineral
* 'o gi(e su!!ort and mechanical strength
1ntu! memberi!an so!ongan dan !e!uatan me!ani!al
2. Which of the following se3uence of organelles in(ol(ed in the snthesis of
e4tracellular en5mes is 0o!!e0t"
Mana!ah di antara urutan beri!ut betul yang melibat!an organel dalam sintesis en2im
luar sel&
# 6olgi a!!aratus7)ibosomes 7)ough endo!lasmic reticulum
*lat 'olgi - Ribosom Jalinan endoplasmi! !asar
B )ough endo!lasmic reticulum7)ibosomes76olgi a!!aratus
Jalinan endoplasmi! !asar Ribosom *lat 'olgi
$ )ibosomes76olgi a!!aratus7)ough endo!lasmic reticulum
Ribosom *lat 'olgi Jalinan endoplasmi! !asar
& )ibosomes7)ough endo!lasmic reticulum76olgi a!!aratus
Ribosom Jalinan endoplasmi! !asar *lat 'olgi)
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
SULIT 4551/1
8. $arrot slices are immersed in 9.1: sucrose solution. #fter . hours/ the slices are
found to be turgid and hard.
3irisan loba! merah direndam di dalam larutan su!rosa 0.(4. Selepas / am+ hirisan
itu didapati segah dan !eras.
Which of the following statement e4!lains this !henomenon"
*ntara pernyataan beri!ut+ yang mana!ah menerang!an $enomena ini &
# 'he carrot cell wall !re(ent it from shrinking .
.inding sel !arot menghalangnya dari menge"ut.
B 'he high concentration of the cell sa! in the (acuole causes water to diffuse. .
Kepe!atan yang tinggi dalam sap sel 5a!uol menyebab!an air meresap !e dalam
Sel.
$ 'he cell sa! is h!otonic towards the sucrose solution.
Sap sel adalah hipotoni! !epada larutan su!rosa.
& 'he carrot cell wall allows the sucrose molecules to diffuse into the cell.
.inding sel !arot membenar!an mole!ul selulosa meresap !e dalam sel.
;. &iagram 0 shows a cell after immersed into a !articular solution.
Raah 5 menunu!!an sel yang telah direndam!an !e dalam larutan
tertentu.
&iagram 0
Which is e4!erienced b the cell"
*pa!ah yang dialami oleh sel itu &
# $renation $ &e!lasmolsis
Krenasi .eplasmolisis
B <lasmolsis & %aemolsis
#lasmolisis 3emolisis
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
SULIT 4551/1
9. &iagram 2 shows the action of an en5me on a substrate.
Raah 6 menunu!!an tinda!an en2im !e atas suatu substrat.
What is re!resented b K"
*pa!ah yang diwa!ili oleh K&
# =n5me $ <roducts of reaction
=n2im 3asil tinda! balas
B =n5me>substrate com!le4 & Substrate
Komple!s-en2im substrat Substrat
19. Based on the information below/ name the en5me that can be used.
,erdasar!an ma!lumat di bawah+ nama!an en2im yang sesuai diguna!an.
=4tracting agar ?ell from seaweeds
Mengasing!an agar-agar daripada laut.)
)emo(ing the seed coats from cereal grains
Mengeluar!an !ulit dari biirin
# @mase $ $elulase
7imase Selulosa
B #mlase & <rotease
*milase #rotease
11. &iagram 8 shows a gra!h between the rate of reaction at different substrate
concentration when factor A is changed.
Raah 8 menunu!!an gra$ diantara !adar tinda! balas dan !epe!atan substrat
apabila $a!tor 9 diubah.
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
&iagram 2
K
SULIT 4551/1
&iagram 8
What is factor A "
*pa!ah $a!tor 9 &
# !% $ Bnhibitor
p3 #eren"at
B 'ime & =n5me concentration
Masa Kepe!atan en2im
12. 'he following information shows starch molecules undergoing !rocess M.
Ma!lumat beri!ut menunu!!an mole!ul !ani melalui proses M.
P!o0e++ M P!o0e++ M
Starch >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> Maltose >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 6lucose
:Kan) Maltosa 'lu!osa
What is !rocess M "
#!akah !roses M &
# <hotosnthesis $ $ondensation
;otosintesis Kondensas)
B %drolisis & <olmerisation
3idrolisis #empolimeran
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
1$0to! /
Faktor Q
SULIT 4551/1
1+. &iagram ; shows a cell ccle of an organism.
Raah < menunu!!an !itar sel bagi suatu organisma.
.iagram <
Which of the following re!resent 1 and C "
=ang mana!ah di antara beri!ut mewa!ili 0 dan = &
<hase 1 <hase C
# Meiosis Bnter!hase
B Bnter!hase Mitosis
$ Mitosis Bnter!hase
& Bnter!hase Meiosis
1.. 'he di!loid chromosomes in a leaf cell of a mai5e !lant is 29. Bf one of the
homologous chromosome !air does not se!arate during the Meiosis 1/ how man
chromosomes can be found in the male nucleus of a !ollen grain of mai5e "
>ombor !romosom diploid dalam daun agung ialah 20. Ji!a satu daripada
#asangan !romosom homolog tida! terpisah semasa Meiosis (+ berapa!ah
bilangan !romosom yang mung!in didapati pada debunga daun agung &
# 9 B 19 $ 29 & 1;
15. Which of the following statements e4!lain the im!ortance of mitosis to cells"
=ang mana!ah di antara pernyataan beri!ut menerang!an !epentingan mitosis
!epada sel &
B . 'o ensure the chromosomal number is constant in all somatic cells.
1ntu! memasti!an bilangan !romosom adalah tetap dalam semua sel somati!.
BB 'o ensure the daughter cells ha(e the same number of chromosomes as the
!arent cell.
1ntu! memasti!an billangan !romosom adalah sama dengan biangan !romosom
sel indu!.
BBB 'o ensure that the genetic material in the daughter cells is the same as in the
!arent cell
1ntu! memasti!an bahan geneti! sel ana! dalah sama dengan sel indu!.
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
SULIT 4551/1
BD 'o contribute to the genetic (ariation in the daughter cells.
1ntu! menyumbang!an !epada 5ariasi geneti! dalam sel ana!.
# B and BB onl $ B / BB and BBB onl
B BB and BBB onl & B / BBB and BD onl
12. &iagram 9 shows the correct !ro!ortion for the (arious classes of food in the food
!ramid.
)aah ? menunu!!an nisbah yang betul bagi pelbagai !elas ma!anan dalam
piramid ma!anan.
Which of the following shows the correct classes of food in the !ramid"
=ang mana!ah di antara beri!ut menunu!!an !elas ma!anan yang betul dalam
piramid ma!anan di atas&
1 2 2 4
# -ats <roteins $arbohdrates Ditamins and
minerals
B $arbohdrates Ditamins and
minerals
<roteins -ats
$ <roteins $arbohdrate
s
-ats Ditamins and
minerals
& $arbohdrates -ats Ditamins and
minerals
<roteins
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
*i$g!$m 9
SULIT 4551/1
18. &iagram 19 shows the structure of the human alimentar canal.
Raah (0 menunu!!an stru!tur salur alimentari manusia.
&iagram 19
Which organ !roduces the en5me res!onsible for the breakdown of li!ids "
%rgan mana!ah merembes!an en2im yang bertanggungawab untu! peme"ahan
lipid&
A. S onl $ ) and S
B. < and A & A onl
1;. Which ada!tations hel! the (illi to absorb nutrients efficientl"
Cang mana!ah penyesuaian 5ilus untu! menyerap nutrien se"ara ber!esan&
B #bundant in number
,ilangan yang banya!
BB 'hin walls
.inding nipis
BBB %a(ing blood ca!illaries
Mempunyai !apilari darah
BD Lacteals to absorb fatt acids and glcerol
@a!teal untu! menyerap asid lema! dan gliserol
# B and BBB onl
B BB and BD onl
$ B/ BB and BBB onl
& B/ BB/ BBB and BD
19. When 9.. g of groundnut is com!letel burnt/ the tem!erature of 29 ml of water rise u!
from +9E$ to 89E$. $alculate the energ (alue of the groundnut.
FS!ecific heat ca!acit of water is ..2 Jg E$ G
,ila 0./g !a"ang tanah terba!ar dengan leng!ap+ suhu 20 ml air mening!at daripada
30A- !epada 80A-. 3itung nilai tenaga !a"ang tanah &
B Muatan haba tentu air ialah /.2 Jg A- C.
# 1.. kJgHI $ ;.. kJgHI
B +..kJg
>1
& 82.2 kJgHI
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
SULIT 4551/1
29. 6lucose J o4gen $arbon dio4ide J water J +; #'<
'lu!osa D o!sigen Karbon dio!sida D air D 3< *E#
'he abo(e e3uation shows
#ersamaan di atas menunu!!an
A. aerobic res!iration $ condensation reaction
respirasi aerobi! tinda!balas !ondensasi
B. anaerobic res!iration & hdroltic reaction
respirasi anaerobi! tinda!balas hidroliti!
21. Which of the following organelle in(ol(es in the gaseous e4change in *meoba sp"
*ntara organel beri!ut yang mana!ah terlibat dalam pertu!aran gas dalam *meoba
sp &
# $ell wall $ $ell membrane
.inding sel Membran sel
B *ucleus & Dacuole
>u!leus Fa!uol
22. &iagram 11 shows !arts of the tracheal sstem of insect.
Raah (( menunu!!an sebahagian daripada sistem tra!ea pada serangga.
&iagram 11
What !rocess occurs at 1 during the gas e4change of the insect"
*pa!ah proses yang berla!u di 0 semasa pertu!aran gas bagi serangga tersebut&
# &iffusion $ -acilitated diffusion
Resapan Resapan berbantu
B ,smosis & #cti(e trans!ort
%smosis <engang!utan a!ti$
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
bod
tissue
tracheoles
SULIT 4551/1
2+. &iagram 12 shows three different t!es of interaction between organisms.
Raah (2 menunu!!an tiga enis intera!si di antara organisma.
.
&iagram 12
Which of the following is t!,e about the interactions K/ L and M"
Mana!ah di antara beri!ut benar tentang intera!si K + @ dan M &
K L M
# Mutualism $ommensalism <arasitism
B Mutualism <arasitism Sa!ro!htism
$ Sa!ro!htism $ommensalism Mutualism
& <arasitism $ommensalism Mutualism
24. Which of the following chemical substance is used to kill or !re(ent the
multi!lication of microorganisms in the wound"
=ang mana!ah di antara sebatian !imia beri!ut+ diguna!an untu! membunuh atau
men"egah pembia!an mi!roorganisma dalam lu!a &
# #ntise!tic $ Daccine
*ntisepti! Fa!sin
B #ntibiotic & &isinfectant
*ntibioti! .isin$e!tan
20. *itrates and !hos!hates from farmland that flow into a lake caused ra!id growth
of algae .
What is described b the abo(e situation "
>itrat dan $os$at yang dialir!an dari ladang !e dalam tasi! telah menyebab!an
pertumbuhan alga yang mendada!.
*pa!ah yang diterang!an oleh situasi di atas &.
# =utro!hication $ -ertili5er accumulation
Gutro$i!asi #engumpulan baa
B <esticide !ollution & $olonisation
#en"emaran pestisid #eng!olonian
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
SULIT 4551/1
26. &iagram 1+ shows !lant cells.
Raah (3 menunu!!an sel tumbuhan.
Which of the following cell is the !roduct of meiosis"
Sel yang mana!ah di antara beri!ut adalah produ! pembahagian sel meiosis&
A B
C *
23 &iagram 1. shows a !art of a mangro(e !lant.
Raah (/ menunu!!an satu bahagian tumbuhan paya ba!au.
What is structure S"
*pa!ah stru!tur S&
*. Succulent lea(es
.aun su!ulen
B. <neumato!hores
#neumato$or
-. Di(i!ar seeds
,ii benih 5i5ipari
.. <ro! roots
*!ar ang!ang
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
Diagram 14
Diagram 13
SULIT 4551/1
2;. &iagram 10 shows a stage in the blood clotting mechanism.
Raah (5 menunu!!an satu pering!at di dalam me!anisme pembe!uan darah.
Which of the following statement e4!lains this stage"
*ntara pernyataan beri!ut+ yang mana!ah menerang!an pering!at ini&
#
B
$
&
'hrombo!lastin con(erts !rothrombin to thrombin
Eromboplastin menu!ar!an protrombin !epada trombin
'hrombin con(erts fibrinogen to meshwork of fibrin.
Erombin menu!ar!an $ibrinogen !epada aringan $ibrin
<latelets stimulate the formation of meshwork of fibrin.
#latlet meransang pembentu!an aringan $ibrin.
<latelets release the thrombo!lastin to form meshwork of fibrin.
#latlet membebas!an tromboplastin untu! membentu! aringan $ibrin.
29. &iagram 12 shows a cross>section through the car!el of a flower before fertili5ation.
Raah (6 menunu!!an !eratan rentas
melalui !arpel bunga sebelum
persenyawaan.
Where are the !osition of male and female
gametes before fertili5ation"
.i mana!ah !edudu!an gamet antan dan
betina sebelum persenyawaan &
Male gamete -emale gamete
# 1 0
B 1 .
$ 2 .
& + 0
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
Diagram 15
Diagram 16
SULIT 4551/1
+9. &iagram 18 shows !art of the !lacenta.
Raah (8 menunu!!an bahagian plasenta.
Bn which !arts do the blood contain the most o4gen and nutrients"
.i bahagian mana!ah darah mempunyai !andungan o!sigen dan nutrien yang
tinggi&
# 1 and + $ 2 and +
B 1 and . & 2 and .
+1. &iagram 1; shows the structure of a ne!hron.
Raah (< menunu!!an stru!tur ne$ron.
Which of the following acti(ities cause 1 to be more !ermeable to water "
=ang mana!ah di antara a!ti5iti beri!ut menyebab!an 0 lebih telap !epada air &
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
Diagram 17
Diagram 18
SULIT 4551/1
# < and ) $ A and )
B < and S & A and S
32. &iagram 19 shows the changes in the thickness of the uterus lining of a woman
during her menstrual ccle. #t which time is the woman most likel to be fertile"
:Raah (? menunu!!an perubahan !etebalan lapisan uterus seorang wanita semasa
!itar haid. #ada masa yang mana!ah wanita itu mengalami wa!tu paling subur&)
&iagram 19
++. 'he haemoglobin content of a !regnant mother is low. Which food should be taken
to increase the haemoglobin content in her blood "
Kandungan haemoglobin seorang ibu mengandung adalah rendah. Ma!anan
mana!ah yang perlu diambil untu! mening!at!an !andungan hemoglobin dalam
darahnya&
# S!inach $ 'omato
,ayam Eomato
B <otatoes & Banana
Kentang #isang
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
< > &rinking a lot of water
Minum air dengan banya!
A > =ating salt foods
Ma!an ma!anan yang
banya!
) > *ot e4ercising
Eida! mela!u!an senaman
S > <laing s!orts
,ersu!an
SULIT 4551/1
+.. &iagram 29 shows a !art of hind lim! which consists of femur/ tibia and fibula .
Raah 20 menunu!!an bahagian anggota bela!ang yang terdiri dari $emur+ tibia dan
$ibula.
&iagram 29
Which of this action cannot be done if the !atella is dislocated"
Mana!ah tinda!an beri!ut tida! berla!u i!a patela beralih tempat&
# Sitting down $ Walking
.udu! ,eralan
B Slee!ing & Straightening the leg
Eidur Melurus!an !a!i
+0. &iagram 21 shows the structures in(ol(ed in refle4 action.
Raah 2( menunu!!an stru!tur yang terlibat dalam tinda!an re$le!s.
Which of the following shows the correct se3uence for the abo(e action"
*ntara beri!ut+ mana!ah menunu!!an urutan yang betul bagi tinda!an di atas"
# < A ) S $ A ) S <
B < S ) A & A S < )
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
%ot !an
#eriu! panas
Patela
Diagram 21
SULIT 4551/1
+2. # farmer s!ras all the mangoes in his farm with hormone 1 to ensure that all the
mangoes ri!en at the same time. What is hormone 1"
Seorang petani menyembur semua buah manggadi ladang nya dengan hormon 0
bagi memasti!an semua mangganya masa! pada masa yang sama.
*pa!ah hormon 0&
# #u4in $ $tokinin
B =thlene & 6ibberilin
+8. &iagram 22 shows the structure of human brain.
Raah 22 menunu!!an stru!tur ota! manusia.
What is 1"
*pa!ah 0&
+;. 'he following statements is about hormone 1.
,eri!ut adalah pernyatan tentang hormon 0.
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
4
<roduced b cor!us lutem and !lacenta
:.ihasil!an oleh !orpus luteum dan pla"enta)
<romotes growth of endometrium and !re(ents menstruation.
:Merangsang pertumbuhan endometrium dan menghalang haid)
Diagram 22
A $erebrum
Serebrum
C S!inal cord
Sara$ tunang
B $erebellum
Serebelum
* Medula oblongata
Medula oblongata
SULIT 4551/1
What is hormone 1"
:*pa!ah hormone 0&)
#
,estrogen $ Luteinising hormone
Gstrogen 3ormon pelutinan
B
<rogesterone & -ollicle stimulating hormone
#rogesteron 3ormon perangsang $oli!el
+9. Which of the following is t!,e when the osmotic !ressure in the blood decreases"
Mana!ah di antara beri!ut benar se!iranya te!anan osmosis darah ber!urangan&
Se0!etio5 o6 A*)
Rembesan ADH
Re$+o!ptio5 o6 7$te! i5 .i-5ey t,,le+
Penyerapan air oleh tubul ginjal
# Bncrease
,ertambah
Bncrease
,ertambah
B &ecrease
,er!urang
&ecrease
,er!urang
$ &ecrease
,er!urang
Bncrease
,ertambah
& Bncrease
,ertambah
&ecrease
,er!urang
.9. &iagram 2+ shows the stages in the de(elo!ment of follicle in the o(ar of human.
Raah 23 menunu!!an pering!at per!embangan $oli!el dalam o5ari manusia.
What is the effect to the uterine wall when L de(elo!es into M"
*pa!ah !esan !epada dinding uterus apabila @ ber!embang menadi M&
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
M
L
Diagram 23
SULIT 4551/1
A Bt is re!aired $ Bt thickens
Ia diperbai!i Ia menebal
B Bt breaks down & Bts thickness maintains
Ia terurai Ketebalannya di!e!al!an
.1. Melissa who is a carrier for colour blindness married to #ron a normal
colour (ision.
What is the !robabilit that their son is colour blind"
Melisa adalah pembawa bagi buta warna ber!ahwin dengan *ron yang
mempunyai penglihatan warna normal.
*pa!ah !emung!inan ana! lela!i mere!a adalah buta warna &
# 9: $ 09:
B 20: & 199:
.2. # !air of fraternal twins are brought u! b two different families and ha(e
the following characteristics.
Sepasang !embar seiras telah dibesar!an oleh dua !eluarga yang
berbe2a
dan mempunyai "iri seperti beri!ut.
Which factor causes the differences in the characteristics"
;a!tor yang mana!ah menyebab!an perbe2aan "iri pada !embar itu&
# 6enetic
'eneti!
$ 6ene mutation
Mutasi gen
B =n(ironment
#erse!itaran
& $hromosome mutation
Mutasi !romosom
.+. &iagram 2. shows a red rose !lant is crossed with a white rose !lant.
'he -1 generations that are !roduced are two red rose !lants and two white rose
!lants. 'he allele for red rose !lant/ ) is dominant to white rose !lant/ r.
Raah 2/ menunu!!an po!o! ros merah di!a"u!!an dengan po!o! ros putih.
'enerasi ;( yang terhasil adalah dua po!o! ros merah dan dua po!o! ros putih. *lel
untu! po!o! ros merah+ R adalah dominan !epada alel ros putih+ r.
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
*ini K -at and fair com!le4ion
'emu! dan !ulit "erah
*ina K 'hin and slightl dark com!le4ion
Kurus dan !ulit aga! gelap
SULIT 4551/1
&iagram 2/
What is the genot!e of the !arents"
*pa!ah genotip bagi indu!&
Re- Ro+e 89ite Ro+e
# )) )r
B )r )r
$ )r rr
& )) rr
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
<arents
<henot!e
:;enotip
indu!)
-1
generation
<henot!e
:;enotip
generasi ;()
)ed )ose
:Ros merah)
White )ose
:Ros putih)
)ed )ose
:Ros merah)
White )ose
LRos #utih)
)ed )ose
:Ros merah)
White )ose
:Ros #utih)
X
SULIT 4551/1
... &iagram 20 shows ultrafiltration that occurs in the kidne.
Raah 25 menunu!!an ultraturasan yang berla!u dalam ginal.
&iagram 20
What are the substances that can mo(e across 1 "
*pa!ah bahan yang dapat merentasi 0&
#
B
-ibrinogen
;ibrinogen
Leucocte
@eu!osit
$
&
=rthrocte
Gritrosit
#mino acid
*mino asid
.0. &iagram 22 shows a shirt with a blood stain before and after being washed with
detergent containing en5me.
Raah 26 menunu!!an bau dengan !esan darah sebelum dan selepas dibasuh
dengan pen"u"i mengandungi en2im.
Before #fter
&iagram 22
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
#fferent arteriole
*rteriol a$eren
=fferent arteriole
*rteriol e$eren
1
Blood stain
Bowman ca!sule
Ka!sul Bowman
SULIT 4551/1
Which is the most suitable en5me and tem!erature to gi(e the result shown"
=ang mana!ah en2im dan suhu yang paling sesuai untu! menghasil!an !eputusan
seperti di atas&
.2. &iagram 28 shows a !air of chromosomes in a cell of an organism.
Raah 28 menunu!!an sepasang !romosom dalam sel suatu organisma.
&iagram 28
What is 1 "
*pa!ah 0 &
# #llele $ *ucleotide
B 6ene & $hromosome
.8. &iagram 2; shows the regulation of human bod tem!erature.
Raah 2< menunu!!an pengawalan suhu badan manusia.
&iagram 2;
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
=n5me 'em!erature
#
Li!ase +8
o
$
B
<rotease 1;
o
$
$
Li!ase 1;
o
$
&
<rotease +8
o
$
4
*ormal bod tem!erature
Suhu badan normal
Bod tem!erature increase
Suhu badan mening!at
Bod tem!erature decrease
Suhu badan menurun
'em!erature )egulation
$entre #usat !awalan suhu
$orrection mechanism
Me!anisme pembetulan
SULIT 4551/1
Which of the following correction mechanism occur "
*ntara beri!ut yang mana!ah me!anisme pembetulan yang berla!u&
l. Dasodilation BBB Dasoconstriction
#em5asodilatan #em5aso"erutan
ll. =rector muscle contract lD &ecrease in metabolic rate
%tot ere!tor menge"ut) Kadar metabolisme menurun
#
B
l and ll
l/ ll and lll
$
&
l and lD
l/ ll and lD
.;. &iagram 29 shows the gra!hs of two t!es of (ariation .
)a?ah 29 menun?ukkan graf untuk dua enis 5ariasi.
<lant %uman
'umbuhan Manusia
*umbe
r
of indi(iduals
,ilangan indi5idu
What t!e of (ariation shown in each !o!ulation "
*pa!ah enis 5ariasi ditunu!!an dalam setiap populasi &
%uman
Manusia
<lant
'umbuhan
# $ontinuous &iscontinuous
B $ontinuous $ontinuous
$ &iscontinuous &iscontinuous
& &iscontinuous $ontinuous
.9. 'he following food chain is found in a fresh water !ond.
Rantai ma!anan beri!ut terdapat dalam !olam air tawar.
Phytoplankton water fleas fish
Fitoplankton kutu air ikan
Which of the following shows the relati(e amount of biological mass in the food
chain "
Mana!ah di antara beri!ut menunu!!an amaun isim biologi relati$ dalam rantai
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
Diagram 29
SULIT 4551/1
ma!anan &
<hto!lankton
-ito!lankton
Water flea
Kutu air
-ish
Bkan
# 0g 10g 29g
B +9g 29g 10g
$ 29g 0g +9g
& 29g +9g 0g
yang telah diberi sunti!an 5a!sin sebanya! dua !ali.
Which of the following will be the t!e of immunisation ac3uired b these two
!atients"
*ntara beri!ut yang mana!ah merupa!an enis !eimunan yang diperoleh oleh
!edua-dua pesa!it&
#
B
$
&
P /
#rtificial ac3uired acti(e immunit
Keimunan a!ti$ buatan
#rtificial ac3uired !assi(e immunit
Keimunan pasi$ buatan
#rtificial ac3uired !assi(e immunit
Keimunan pasi$ buatan
#rtificial ac3uired acti(e immunit
Keimunan a!ti$ buatan
*atural ac3uired !assi(e immunit
Keimunan pasi$ semulaadi
*atural ac3uired acti(e immunit
Keimunan a!ti$ semulaadi
*atural ac3uired acti(e immunit
Keimunan a!ti$ semulaadi
*atural ac3uired !assi(e immunit
Keimunan a!ti$ semulaadi
KERTAS S%ALAN TAMAT:
[Turn over
CONFIDENTIAL
Diagram 30
MARKING SCHEME
BIOLOGY 1 (4551/1)
SPM TRIAL EXAMINATION
2009
1. A 26. B
2. B 27. C
3. B 28. B
4. A 29 D
5. D 30. B
6. D 31. D
7. B 32. B
8. D 33. A
9. C 34. C
10
.
C 35. C
11
.
D 36. B
12
.
B 37. B
13
.
B 38. B
14
.
A 39. A
15
.
C 40. C
16
.
B 41. C
17
.
D 42. B
18
.
D 43. C
19
.
C 44. D
20
.
A 45. D
21
.
C 46. A
22 A 47. B
23
.
C 48. D
24
.
A 49. D
25
.
A 50 A
Section A
Bahagian A
+&' marks,
+&' markah,
"nswer all -uestions in this section.
Jawab *$mua soalan dalam bahagian ini.
# Diagram # shows the structure o. a plasma membrane.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan struktur membran plasma.
-a"(am 1
Rajah 1
/a0 1ame the parts labelled Q and R.
amakan bahagian !ang berlabel Q dan R.
. : ________________________________________________________
R : ________________________________________________________
+2 marks,
/b0/i0 State the component o. structure !.
!atakan komponen struktur P.
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+# mark ,
/ii0 34plain the main .unction o. !.
#/a0
#/b0/i0
/Lha& *$'$lah
2
For examiners
use
R .
P
"erangkan #ungsi utama P.
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+# mark ,
/c0 5he plasma membrane is said to be semi6permeable.
7hat is the meaning o. 8semi6permeable9:
Membran plasma dikatakan bersi#at separa$telap.
%pakah !ang dimaksudkan dengan & separa$telap'&
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+ # mark,
-a"(am 1,2
Rajah 1.2
d) ;raph in Diagram #.2 shows the percentage o. red blood cells that are
burst or shrink when placed in salt solution o. di..erent concentration.
(ra# dalam Rajah 1.) menunjukkan peratus sel darah merah !ang pe*ah
atau menge*ut apabila dimasukkan ke dalam larutan garam !ang berbe+a
kepekatan.
/i0 ased on the graph gi<en= state the concentration which is isotonic to
blood plasma.
#/b0/ii0
# /c0
/Lha& *$'$lah
3
,erdasarkan gra# !ang diberi- n!atakan kepekatan larutan !ang
isotonik terhadap plasma darah.
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
/# mark0
/ii0 34plain your answer in /b0/ii0.
"erangkan jawapan anda dalam .b/.ii/.
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
2
/# mark0
/iii0 Comment on the osmotic pressure at >.
,erikan ulasan tentang tekanan osmosis di Q.
2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+ 2 marks,
/e0 5he concentration o. ions inside root cells is up to #'' times greater than in
the soil. "nyway= the ions are still transported into the cells by acti<e
transport.
Kepekatan ion di dalam sel akar adalah 100 kali lebih tinggi berbanding di
dalam tanah. 1alau bagaimanapun- ion$ion tersebut masih diangkut ke
dalam sel se*ara pengangkutan akti#.
(i) De.ine acti<e transport.
"akri#kan pengangkutan akti#.
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+ # mark,
#/d0/i0
#/d0/ii0
#/d0/iii0
# /e0/i0
/Lha& *$'$lah
4
/ii0 34plain what will happen to the uptake o. the ions by root cells i. the
roots are immersed in a solution containing metabolic poisons such
as cyanide.
"erangkan apa akan berlaku terhadap pengangkutan ion oleh oleh
sel akar jika akar tersebut direndam di dalam larutan !ang
mengandungi ra*un metabolik seperti sianida.
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+3 marks,
#/e0/ii0
TOTAL
/Lha& *$'$lah
5
2 Diagram 2.# shows the biochemical processes in<ol<e molecule K=
en?yme @ and molecule M occur in organ A and organ B.
Rajah ).1 menunjukkan proses biokimia !ang melibatkan molekul K-
en+im 2 dan molekul M !ang berlaku di dalam organ 3 dan organ 4.
0 0 0 , , , , , ,
G l # 1 ! " $ 2
K
E 2 3 # m $ L
M
O ( " a 2 4
O ( " a 2 Y
h $ % a & 1 % ! ( & a l
5 $ 2
M u * 1 l $ 1 $ l l *
-a"(am 2,1
Rajah 2.1
/a0/i0 1ame organ A and organ B.
amakan organ 3 dan organ 4.
Crgan A D 222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
Crgan B D 222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+ 2 marks ,
/ii0 1ame molecule K= molecule M and en?yme @.
amakan molekul K- molekul M dan 5n+im 2.
Molecule K E molekul K D 222222222222222222222222222222222222222
Molecule M E molekul M D
222222222222222222222222222222222222222
3n?yme @ E en+im 2 D 222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+ 3 marks ,
/b0 State two characteristics o. en?yme @ based on Diagram 2.#.
!atakan dua *iri en+im 2 berdasarkan Rajah ).1.
666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666
666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666
666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666
2/a0/i0
2/a0/ii0
2 /b0
/Lha& *$'$lah
6
For examiners
use
+ 2 marks ,
/c0 Molecules M are transported .rom organ B to muscle cells. 34plain why
molecule M is needed in muscle cells.
Molekul M diangkut dari 7rgan 4 ke sel$sel otot. "erangkan kenapa
molekul M diperlukan di dalam sel$sel otot.
666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666
666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666
666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666
666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666
+ 3 marks ,
/d0 34plain the importance o. .orming glycogen.
"erangkan kepentingan pembentukan glikogen.
666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666
666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666
666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666
+ 2 marks ,
2 /c0
2 /d0
TOTAL
/Lha& *$'$lah
7
3 Diagram 3.# shows three stages A= B and F in meiosis.
Rajah 8.1 menunjukkan tiga peringkat 3- 4 dan 9 dalam meiosis.
-a"(am 6,1
Ra7ah 6,1
/a0/i0 1ame stages A and B.
amakan peringkat 3 dan 4.
A D 222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
B D 222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+2 marks,
/ii0 State two di..erences between chromosomal beha<iour at A and B.
!atakan dua perbe+aan perlakuan kromosom di 3 dan 4.
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+ 2 marks ,
/b0 i0 State the occurrence at F.
!atakan kejadian !ang berlaku di 9.
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+ 2 marks ,
3/a0/i0
/
3/a0/ii0
3/b0/i0
/Lha& *$'$lah
8
For examiners
use
X
Z
Y
S!l
R S
T
ii0 5he chromosome number in somatic cell o. this organism is #2.
State the chromosome number in each o. the daughter cell in F.
;i<e a reason .or your answer.
,ilangan kromosom dalam sel soma bagi organisma ini ialah 1).
!atakan bilangan kromosom dalam setiap sel anak 9.
,erikan alasan anda.
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
222222
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+ 2 marks ,
/c0 Diagram 3.2 shows the process o. sperm .ormation in the human testis.
Rajah 8.) menunjukkan proses pembentukan sperma di dalam testis
manusia.
-a"(am 6,2
Rajah 3.2
/i0 "re cells "= cell and cell C genetically identical: 34plain.
%dakah sel %- sel , dan sel : seiras dari segi geneti*' "erangkan.
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
3/b0/ii0
3/c0/i0
/Lha& *$'$lah
9
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+2 marks,
/ii0 I. Cell undergoes an improper cell di<ision= cell D might recei<e an e4tra
chromosome. State the number o. chromosomes in Cell D.
Jika Sel , melalui pembahagian sel !ang tidak sempurna- sel ;
berkemungkinan menerima satu kromosom tambahan. !atakan bilangan
kromosom di dalam sel ;.
2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+ # mark ,
/iii0 I. cell D .ertilises with an o<um= the ?ygote .ormed might de<elop into an
abnormal male. State the syndrome o. the indi<idual.
Jika sel ; bersen!awa denngan o<um- +igot !ang terbentuk akan
berkembang menjadi lelaki !ang abnormal. !atakan sindrom indi<idu
tersebut.
2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+ # mark ,
3/c0/ii0
3/c0/iii0
TOTAL
/Lha& *$'$lah
10
For examiners
use
$ Diagram $.# shows the apparatus set up in an e4periment to study the role
o. the <ascular tissue in the transport o. water in plants.
Rajah =.1 menunjukkan susunan radas eksperimen untuk mengkaji
peranan tisu <askular dalam pengangkutan air di dalam tumbuhan.
-a"(am 4,1
Rajah 4.1
/a0 State the .unction o. the eosin solution.
!atakan #ungsi larutan eosin.
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+ # mark ,
/b0 5he stem o. the plant is cut across at AB and <iewed under a microscope.
" cross section o. the stem is shown in Diagram $.2.
%kar tumbuhan tersebut dikerat se*ara merentas pada 34 dan
diperhatikan di bawah mikroskop. Keratan rentas akar ditunjukkan dalam
Rajah =.).
-a"(am 4,2
Rajah 4.2
$/a0
$/b0
/Lha& *$'$lah
11
K
M
1ame the parts labelled K and M.
amakan bahagian !ang berlabel K dan M.
K D 222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
M D 222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+ 2 marks ,
/c0 1ame the tissue which is responsible .or transporting water and minerals
ions .rom the roots to the upper parts o. the plant.
amakan tisu !ang terlibat dalam pengangkutan air dan ion mineral dari
akar ke bahagian atas tumbuhan.
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+ # mark ,
/d0 I. the root o. the plant is cut across= draw and label the obser<ation made.
Jika keratan rentas dibuat ke atas akar tumbuhan- lukis dan labelkan
pemerhatian anda.
+ 3 marks ,
/e0 Diagram $.3 shows the e..ect o. remo<ing tissue M .rom the stem.
$/c0
$/d0
/Lha& *$'$lah
12
For examiners
use
-a"(am 4,6
Rajah 4.3
/i0 State the type o. transport in<ol<ed in Diagram $.3.
!atakan jenis pengangkutan !ang terlibat dalam Rajah =.8.
66666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666666
+ # mark ,
/ii0 34plain why does the part abo<e the ring become swollen a.ter two weeks.
"erangkan mengapa bahagian atas gelang membengkak selepas dua
minggu.
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+2 marks,
/iii0 34plain why ha<e the lea<es not wilted a.ter two weeks.
"erangkan mengapa daun$daun tidak la!u selepas dua minggu.
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+2 marks,
$/e0/i0
$/e0/ii0
$/e0/iii0
TOTAL
/Lha& *$'$lah
13
%. Gigure % shows the re.le4 arc that occurs when the .inger is accidentally
pricked with a needle.
Rajah > menunjukkan suatu arka re#leks !ang berlaku apabila jari tangan
se*ara tidak sengaja di*u*uki oleh sebatang jarum.
-a"(am 5
Ra7ah 5
/a0 Complete the abo<e .igure by drawing the appropriate neurones in<ol<ed in
the re.le4 action.
2engkapkan rajah di atas- dengan melukis neuron !ang terlibat di dalam
tindak balas re#leks.
+2 marks,
/b0 34plain the transmission o. impulse .rom one neurone to another neurone.
"erangkan pemindahan impuls dari satu neuron ke neuron !ang
berikutn!a.
2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+ $marks ,
%/a0
%/b0
%/c0
/Lha& *$'$lah
14
/c0 1ame the structures M and 1.
amakan struktur M dan .
MD 2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
1 D 2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+2 marks,
/d0 Di..erentiate between the abo<e re.le4 action with the <oluntary action.
,e+akan di antara tindakan re#leks di atas dengan tindakan terkawal.
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
22222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
2
+# mark,
/e0 State the importance o. re.le4 action to us.
!atakan kepentingan tindakan re#leks kepada kita.
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+#
mark ,
/.0 I. e..erent neurone is injured and damaged= predict what will happen to the
person.
Jika neuron e#eren *edera dan rosak- ramalkan apa !ang akan berlaku
Kepada orang tersebut.
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
+#
mark ,
%/d0
%/e0
%/.0
TOTAL
S$1&!2 B
Baha"a2 B
+$' marks,
/Lha& *$'$lah
15
"nswer any &8! -uestions .rom this section.
Jawab mana$mana dua soalan daripada bahagian ini
&/a0 Gigure &.# shows mo<ement acti<ities in a human.
Rajah ?.1 menunjukkan akti<iti pergerakan pada manusia.
.
ased on Gigure &.#/i0 and Gigure &.#/ii0= e4plain how the abo<e
mo<ement takes place which in<ol<es muscles= tendons= bones= ligaments
and joints
,erdasarkan Rajah ?.1.i/ dan Rajah ?.1.ii/- terangkan bagaimana
pergerakan di atas berlaku !ang melibatkan otot- tendon - tulang- ligamen
dan sendi.
+#' marks,
/b0/i0 y gi<ing one e4ample o. woody plant and and non6woody= e4plain how
the support system in woody plants di..ers .rom that o. non6woody plants.
;engan men!atakan *ontoh- terangkan bagaimana sistem sokongan
pada tumbuhan berka!u berbe+a daripada tumbuhan tidak berka!u.
+#' marks,
(/a0 Diagram (.# shows how the respiratory gases are transported in the
human body.
Rajah @.1 menunjukkan bagaimana gas respirasi diangkut dalam badan
manusia.
/Lha& *$'$lah
16
/i0 /ii0
Diagram &.#
Diagram (.#
/i0 ased on Diagram (.#= e4plain how the transport o. o4ygen and
carbon dio4ide takes place in the body cells
,erdasarkan Rajah @.1- terangkan bagaimanakah pengangkutan
oksigen dan karbon dioksida berlaku di dalam sel$sel badan.
+& marks,
/ii0 Describe the adaptations o. the al<eolus .or gaseous e4change.
"erangkan pen!esuaian pada al<eolus !ang membolehkann!a utuk
melakukan proses pertukaran gas.
+$ marks,
/b0 5he shaded area o. the graph in Diagram (.2 shows the intake o. o4ygen
by an athlete be.ore= during and a.ter running .or .i<e minutes.
Kawasan !ang berlorek pada gra# dalam Rajah @.) menunjukkan
pengambilan oksigen oleh seorang atlet sebelum- semasa dan selepas
/Lha& *$'$lah
17
berlari selama > minit.
Diagram (.2
ased on the graph= e4plain how an o4ygen debt is built up when an
athlete is running and how it is settled a.ter he stops running.
,erdasarkan gra#- terangkan bagaimana hutang oksigen terhasil semasa
atlet itu berlari dan bagaimana ia diselesaikan selepas beliau berlari.
+#' marks,
)/a0 Mr 1ick has group " blood while his wi.e has group blood. 5he group o.
their son is C.
34plain how this happen.
/Lha& *$'$lah
18
Mr i*k mempun!ai kumpulan darah % manakala isterin!a mempun!ai
kumpulan darah ,. Kumpulan darah anak lelaki mereka ialah 7.
"erangkan bagaimana ini boleh berlaku.
+#' marks,
/b0 1owadays= the D1" .ingerprinting techni-ue has replaced the common
.ingerprinting techni-ue in criminal in<estigations.
Pada masa kini- teknik *ap jari ;% telah menggantikan teknik *ap jari
biasa dalam pen!iasatan jena!ah.
/i0 34plain how D1" .ingerprinting is carried out.
"erangkan bagaimana *ap jari ;% dilakukan
+$ marks,
/ii0 ased on the gi<en statement= state your opinion an the
ad<antages and disad<antages o. D1" .ingerprinting.
,erdasarkan pern!ataan !ang diberikan- n!atakan pendapat kamu
tentang kebaikan dan keburukan *ap jari ;%.
+& marks,
*/a0 Diagram * shows a mangro<e swamp.
Rajah A menunjukkan kawasan pa!a bakau.
/Lha& *$'$lah
19
Diagram *
/i0 34plain why most plants cannot colonise and grow in the swamps.
"erangkan mengapa keban!akan tumbuhan tidak boleh hidup dan
tumbuh di kawasan pa!a bakau.
+% marks,
/ii0 34plain how the mangro<e trees adapt themsel<es to the harsh
li<ing conditions.
"erangkan bagaimana pokok bakau ini men!esuaikan diri dengan
keadaan hidup !ang sukar.
+% marks,
/b0 De<elopment that is not planned and managed properly has brought
negati<e e..ects to the ecosystem such as land erosion= .lash .lood=
landslides= global warming= thinning o. the o?one layer= climate change
and the e4tinction o. certain species.
Pembangunan !ang tidak teran*ang dan terurus dengan teliti boleh
membawa kesan negati# kepada ekosistem seperti hakisan tanah- banjir
kilat- tanah runtuh- pamanasan global- penipisan lapisan o+on- perubahan
iklim dan kepupusan spesis tertentu.
ased on the abo<e statement= describe the e..ects o. unplanned
de<elopment and improper management o. the ecosystem.
,erdasarkan ken!ataan di atas- terangkan kesan pembangunan !ang
tidak teran*ang dan terurus dengan teliti kepada ekosisitem.
+#' marks,
/Lha& *$'$lah
20
MARKING SCHEME
BIOLOGY 2 (4551/2)
SPM TRIAL EXAMINATION
2009
No. Ma!"#$ C"%&"a Ma!
1(a)
1(b)(i)
(ii)
1(c)
1 (d)(i)
1(d)(ii)
A'(& %o #a)& %*& +a%, (a'&((&- Q and R.
Sample answer :
Q : Carrier protein
R : Channel protein / pore protein
A'(& %o ,%a%& %*& .o)+o#&#% o/ ,%0.%0& P.
Sample answer :
It is composed of two layers of phospholipids
A'(& %o &1+(a"# %*& )a"# /0#.%"o# o/ P.
Sample answer :
Acts as a barrier between the internal and external
environment of the cell
// Allows only specific molecles to pass thro!h it
// provide the strctral basis for all cell membrane"
A'(& %o $"2& %*& )&a#"#$ o/ 3,&)"4+&)&a'(&5.
#ample answer :
A semi$permeable plasma membrane is a membrane that
allows only certain sbstances to move freely across it"
A'(& %o ,%a%& %*& .o#.&#%a%"o# 6*".* ", ",o%o#". %o
'(oo- +(a,)a.
Sample answer :
%"&' !/1%% cm
(
A'(& %o &1+(a"# %*& a#,6& "# (-)(").
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
1
1(d)(iii)
1(e)(i)
(ii)
SampleAnswer :
)oth percenta!e of haemolysis of red blood cells and
percenta!e of crenation of red blood cells are *ero (%+)"
A'(& %o .o))&#% o# %*& o,)o%". +&,,0& a% 7.
SampleAnswer :
, : -he osmotic pressre inside the red blood cells is
e.ivalent to its environment"
/0 : Amont of water movin! in and ot of the cells are
the same1
/( : therefore the si*e and strctre of the red blood cells
does not chan!e"
( 8 9 A#: P2/P; )
A'(& %o -&/"#& a.%"2& %a#,+o%.
Sample answer :
Active transport is a movement of sbstances / molecles /
ions a!ainst the concentration !radient / from low to hi!h
concentration across the plasma membrane with the help
of carrier protein and ener!y / A-/"
A'(& %o &1+(a"# 6*a% 6"(( *a++&# %o %*& 0+%a!& o/ %*&
"o#, ': oo% .&((, "/ %*& oo%, a& "))&,&- "# a
,o(0%"o# .o#%a"#"#$ )&%a'o(". +o",o#, ,0.* a,
.:a#"-&.
Sample answer :
/1 2 there is no pta3e of ions by root cells
/0 2 metabolic poisons 3ill/ dama!ed the (root) cells
/( 2 no ener!y/ A-/ is prodced
/& 2 active transport does not occr
(A#: %*&&)
1
1
1
1
(
TOTAL
4
4
1; )a!,
0(a)(i)
(ii)
(b)
(c)
(d)
A'(& %o #a)& o$a# X a#- o$a# Y.
Sample answer :
4r!an 5 : Ilem // small intestine
4r!an 6 : 7iver
A'(& %o #a)& )o(&.0(& K< )o(&.0(& M a#- &#=:)& L.
Sample answer :
8olecle 9 : #tarch
8olecle 8 : :lcose
;n*yme 7 : (/ancreatic) Amylase
A'(& %o ,%a%& %6o .*aa.%&",%"., o/ &#=:)& L 'a,&- o#
>"a$a) 2.1
Sample answer :
1. ;n*yme remains nchan!ed at the end of the
reaction (and can be sed a!ain)"
2. ;n*yme is sbstrate specific / reaction is very
specific
A'(& %o &1+(a"# 6*: )o(&.0(& M ", #&&-&- "# )0,.(&
.&((,.
Sample answer :
/t" 1 8olecle 8 / !lcose is the sbstrate for respiration
/t" 0 As the mscle cells contract and relax1 ener!y is
needed for activities
/t" ( therefore1 molecle 8 is needed in mscle cells to
provide ener!y from respiration process"
A'(& %o &1+(a"# %*& ")+o%a#.& o/ /o)"#$ $(:.o$&#.
Sample answer :
/t"1 : :lyco!en is the main reserve of carbohydrates in
animals
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
5
2
;
/t" 0 It can be converted bac3 to !lcose when ener!y is
needed from respiration process
1
TOTAL
2
12 )a!,
((a(i))
(ii)
(b)(i)
A'(& %o #a)& ,%a$& X a#- Y.
Sample answer :
5 : /rophase I
6 : 8etaphase I
A'(& %o A'(& %o ,%a%& %6o -"//&&#.&, '&%6&&#
.*o)o,o)a( '&*a2"o0 a% X a#- Y.
Sample Answer:
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
(ii)
(c)(i)
(ii)
(iii)
/rophase I
8etaphase I
(/aired homolo!os
chromosomes) are
arran!ed randomly"
(/aired homolo!os
chromosomes) are
arran!ed on the
metaphase plate /
e.atorial plane"
#pindle fibre does not hold
on the centromere of the
chromosomes "
#pindle fibre holds on the
centromere of the
chromosomes"
(-he homolo!os
chromosomes paired and)
crossin! over ta3e place"
(-he homolo!os
chromosomes paired)
crossin! over does not
ta3e place"
( A#: 2 )
A'(& %o ,%a%& %*& o..0&#.& a% ?.
Sample Answer:
/1 : ,or da!hter cells formed
/0 : ;ach da!hter cell has two chromosomes / haploid / n
A'(& %o ,%a%& %*& .*o)o,o)& #0)'& "# &a.* o/ %*&
-a0$*%& .&(( "# ? a#- a'(& %o $"2& &a,o#.
Sample answer :
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
TOTAL
2
2
2
12 )a!,
/1 : < (chromosomes)"
/0 :(=rin! meiosis) the da!hter cell receives half
the nmber of chromosome from the parent cell / 0n
// =a!hter cell haploid / n1 parent cell diploid / 0n
A'(& %o ,%a%& &"%*& .&(( A< .&(( B a#- .&(( C a&
$&#&%".a((: "-&#%".a( a#- &1+(a"#.
Sample answer :
, : Cell A is similar to cell ) bt is different from cell C"
/ : Cell A and cell ) are prodcts of mitosis whereas cell
C is a prodct of meiosis"
A'(& %o ,%a%& %*& #0)'& o/ .*o)o,o)& "# C&(( "/ C&((
B 0#-&$o&, a# ")+o+& .&(( -"2","o#.
Sample answer :
0& (chromosomes)
A'(& %o ,%a%& %*& ,:#-o)& o/ %*& "#-"2"-0a(.
Sample answer :
=own>s syndrome
// 9linefelter>s syndrome
&(a)
&(b)
&(c)
A'(& %o ,%a%& %*& /0#.%"o# o/ %*& &o,"# ,o(0%"o#.
Sample answer :
-o stain the xylem (vessels) (with red dye)
A'(& %o #a)& %*& +a%, (a'&((&- K a#- M.
#ample answer :
9 : 5ylem
8 : /hloem
A'(& %o #a)& %*& %",,0& 6*".* ", &,+o#,"'(& /o
%a#,+o%"#$ 6a%& a#- )"#&a( "o#, /o) %*& oo%, %o
%*& 0++& +a%, o/ %*& +(a#%"
Sample answer :
1
1
1
1
2
&(d)
(e)(i)
(ii)
(iii)
5ylem
A'(& %o -a6 a#- (a'&( %*& o',&2a%"o# o/ %*& oo% .0%
a.o,,.
Sample answer :
=rawin! 2 1 m
Any 0 labels 2 0 m
A'(& %o ,%a%& %*& %:+& o/ %a#,+o% "#2o(2&- "#
>"a$a) 4.;.
Sample answer :
-ranslocation
A'(& %o &1+(a"# 6*: -o&, %*& +a% a'o2& %*& "#$
'&.o)& ,6o((&# a/%& %6o 6&&!,.
Sample answer :
, : -he prodcts of photosynthesis cannot be transported
to the parts below the rin!
/ : as tisse 8 / phloem is removed
A'(& %o &1+(a"# 6*: *a2& %*& (&a2&, #o% 6"(%&- a/%&
%6o 6&&!,.
Sample answer :
, : ?ater can still be transported to the leaves
/ : as tisse 9 / xylem is not removed from the stem
1
1
0
1
1
1
1
1
TOTAL
1
;
5
12 )a!,
5ylem
/hloem
/ericycle
Cortex
// !rond tisse
'(a)
'(b)
'(c)
A'(& %o .o)+(&%& %*& -a6"#$ %*& a++o+"a%& #&0o#,
"#2o(2&- "# %*& &/(&1 a.%"o#.
Sample answer :
( nerones 2 0 m
0 nerones $ 1 m
A'(& %o &1+(a"# %*& %a#,)",,"o# o/ ")+0(,& /o) o#&
#&0o#& %o a#o%*& #&0o#&.
Sample answer :
/t""1 ?hen an implses arrives in the axon terminal
/t" 0 it stimlates (synaptic) vesicles to move towards and
bind with the presynaptic membrane
/t" ( -he vesicles fse / release the nerotransmitter into
the synapse
/t" & -he nerotransmitter molecles across the synapse
to the dendrite of another nerone
/t" ' #timlated to tri!!er a new implses which travels
alon! the nerone
( Ma1 4 )
A'(& %o #a)& %*& ,%0.%0& M a#- N.
Sample answer :
8 : #ensory reseptor // fin!er tip
@ : ;ffector // mscles tisses
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
4
2
'(d)
'(e)
' (f)
A'(& %o -"//&&#%"a%& %*& &/(&1 a.%"o# 6"%* %*&
2o(0#%a: a.%"o#.
Sample answer :
-he reflex action is !overned by the spinal chord whereas
the volntary action is !overned by the cerebrm"
A'(& %o ,%a%& %*& ")+o%a#.& o/ &/(&1 a.%"o# %o 0,.
Sample answer :
-o protect the body a!ainst inAries
A'(& %o +&-".% %*& &//&.% o# O "/ "% ", "#@0&- o
-a)a$&-.
Sample answer:
1" -he nerve impls will be sent from afferent nerone to
the effector
0" -he effector / mscles will not contract
(" -he hand will not be removed immediately from the
needle"
(Any one )
1
1
1
1
1
TOTAL
1
1
1
11 )a!,
<(a)
(b)
A'(& %o &(a%& %*& %",,0&, "#2o(2&- "# +o-0."#$ %*&
0##"#$ )o2&)&#%
Sample Answer:
/l$ -endons1 li!aments1 bones1 mscles and Aoints are
important featres in a movement1
/0$ -endons connect mscles to bones
/($ -endons are stron! and non elastic
/&$ ,orce is transferred to bones thro!h tendons"
/'$ 8ovement at the Aoint is possible with the aid of
li!aments"
/<$ 7i!aments connect two bones to!ether
/B$to !ive spport and stren!th to the Aoint"
/C$ 7i!aments are stron! and elastic"
/D$ -he .adriceps / extensor mscles contract while the
biceps femoris mscles relax and the le! is strai!htened"
/1%$ -he biceps femoris mscles contract while the
.adriceps / extensor mscles relax and the le! is bent"
/11$ Calf mscles contract to lift p the heels"
/10$,eet psh downward and bac3ward
/1($Repeated contraction and relaxation of mscles reslt in
the rnnin! movement"
MAXIMAMB 10 )a!,
A'(& %o $"2& &1a)+(& a#- &1+(a"# *o6 %*& ,0++o%
,:,%&) "# 6oo-: +(a#%, -"//&, /o) %*a% o/ #o#46oo-:
+(a#%,.
E1a)+(&, C 2 )a!, <
8a.%, C D )a!,
Sample answers:
No#46oo-: +(a#%, (*&'a.&o0, +(a#%,)
;xample: )alsam plant/ any sitable answer
/1: (#pport in herbaceos plants is) provided by the tr!idity
of the parenchyma / collenchyma cells
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
/0: (?hen there is eno!h warm in the !rond)" the cells ta3e
in water by osmosis and become tr!id"
/(: -he tr!or pressre of the flids in the vacoles pshes
the cell contents / plasma membrane a!ainst the cell wall
/&: creatin! spport for it stem/ roots /leaves
/': -he thin thic3enin! die cell walls with celllose /
collenchyma cells !ives spport to herbacos plants
Eoo-: +(a#%, B
;xample : Rambtan tree/ hibiscs/ any sitable example
/<: ?oody plants have specialised tisses/ sclerenchyma
tisses/ xylem vessels / tracheids" to !ive them spportE
/B: -hese tisses have celllose walls which have deposits
of li!nin for added stren!th"
/C: #clerenchyma cells have very thic3 walls (which do not
allow water to pass thro!h)"
/D: (-hese cells are dead cells and) their fnction is to pro$
vide spport for the plant"
/1%: 5ylem vessels have thic3 walls of li!nin which are
deposited drin! the plantFs secondary !rowth"
/11: -he li!nified xylem vessels form the woody tisses of the
stem"
/10: -his ma3es the plant stron!er and also provides spport
for the plant"
/1(: -racheids are also dead cells with thic3 walls and very
small
diameters"
/1&: -hey are fond with the xylem vessels and to!ether they
spport the plants"
MAXIMAMB 10 )a!,
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
20 marks
TOTAL
B(a) (") A'(& %o &1+(a"# *o6 %*& %a#,+o% o/ o1:$&# a#-
.a'o# -"o1"-& %a!&, +(a.& "# %*& 'o-: .&((,
Sample answers:
/1: -he blood circlatory system transport oxy!en from the
alveoli to the body cells"
/0: 4xy!en combines with the haemo!lobin in the red blood
cells
/(: to form oxyhaemo!lobin (which is nstable")
/&: 4xy!en is carried (in form of oxyhaemo!lobin) to the
tisses (which have a low partial pressre of oxy!en")
/': -he (nstable) oxyhaemo!lobin brea3s down into oxy!en
and haemo!lobin a!ain"
/<: 4xy!en (molecles are) transferred to the body cells
/B: Carbon dioxide binds (itself) to the haemo!lobin
/C: (and is) transported in the form of carbaminohaemo!lobin"
/D: Carbon dioxide is (also) transported as dissolved carbon
dioxide (in the blood plasma")
/1%: 8ost of carbon dioxide is carried as bicarbonate ions
(dissolved in the blood plasma")
/11: ?hen the blood carryin! carbon dioxide reaches the
body cells1 the carbon dioxide diffses into the blood plasma
and combines with the red blood cells"
/10:Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form carbonic acid"
/1(:Carbonic anhydrase in the red blood cells catalyse the
formation of carbonic acid"
/1&: -he carbonic acid then dissociates into a hydro!en ions
and bicarbonate ions"
MAXIMAMB F )a!,
("") A'(& %o -&,."'& %*& a-a+%a%"o#, o/ %*& a(2&o(0, /o
$a,&o0, &1.*a#$&
Sample answer:
,1: -he millions of alveoli
/1: provide a lar!e srface area for !aseos exchan!e"
,0: -he walls of the alveoli are moist
/0: and this allows respiratory !ases to dissolve easily to
them"
,(: -he walls of the alveoli are very thin (one$cell thic3)
/(: for.ic3 / easy diffsion of !ases"
,&: -he alveoli are richly spplied with blood capillaries
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
F
(b)
/&: to increase the rate of diffsion / the rate of the
transportation of !ases
MAXIMAMB 4 )a!,
A'(& %o &1+(a"# *o6 a# o1:$&# -&'% ", '0"(% 0+ 6*&# a#
a%*(&%& ", 0##"#$ a#- *o6 "% ", ,&%%(&- a/%& *& ,%o+,
0##"#$.
Sample answer:
/1: =rin! a vi!oros exercise /rnnin!1 the breathin! rate is
increased"
/0: -his is to spply more oxy!en (.ic3ly to the mscles)
/(:for rapid msclar contraction)"
/&: Gowever1 the spply of oxy!en to mscles is still
insfficient /': and the mscles have to carry ot anaerobic
respiration (to release ener!y)"
/<: -he !lcose is converted into lactic acid1
/B: with only a limited amont of ener!y bein! prodced
/C: An oxy!en debt bilds p in the body as shown in the
!raph
/D: Gi!h levels of lactic acid in the mscles
/1%: case them to ache"
/11: After rnnin!1 the athlete breathes more rapidly / deeply
than normal for 0% mintes (shown in the !raph)
/10: -here is a recovery period (from the 1%
th
minte ntil the
0%
th
minte)
/1(:when oxy!en is paid bac3 (drin! aerobic respiration)
/1&: Abot 1/< lactic acid is oxidised to carbon dioxide1 water
and ener!y"
MAXIMAMB 10 )a!,
4
10
20 marks
TOTAL
C(a)
(b)
A'(& %o &1+(a"# *o6 %*& "#*&"%a#.& *a++&#
Answer :
/1: -he sitation involved is monohybrid inheritance"
/0: -he !enotype of blood !rop A can be I
A
I
A
/1
A
1
%
/(: while the !enotype of blood !rop ) can be I
)
I
)
or I
)
I
4
"
/&: )lood !rop % has a !enotype1 I
4
I
4
(while the
!enotype of blood !rop A) is I
A
I
)
"
/': Alleles 1
A
and I
)
are codominant
/<: I
4
allele is recessive"
/B: 8r" @ic3 is hetero*y!os dominant/I
A
I
4
(for his blood
!rop A)
/C: while his wife is hetero*y!os dominant/ I
)
I
%
(for blood
!rop ))
/D: 8r" @ic3 and his wife prodce haploid
!ametes/sperm/ovm (as a r e s l t o f m e i o s i s )
/1%: 8r" @ic3 prodces (!ametes with) !enotypes I
A
/I
4
/11: (while) his wife (will) prodce (!ametes with) !enotypes
1
A
/ l
4
/10: -he !amete (I
4
) of 8r" @ic3 fses with his wifeFs !amete
(1
%
)
/1(: to prodce a *y!ote with !enotype IHI
o
"
/1&: (-hs1 they will) prodce an offsprin! with blood !rop %"
MAXIMAMB 10 )a!,
(") A'(& %o &1+(a"# *o6 >NA /"#$&+"#%"#$ ", .a"&- o0%.
Answer:
/1: -isse samples are ta3en from the scene of a crime and
=@A is extracted"
/0: An en*yme brea3s down the =@A into fra!ments"
/(: -he =@A fra!ments are classified accordin! to si*e"
/&: An al3ali is added to separate the doble$stranded =@A
i n t o s i n ! l e s t r a n d s "
/' : ;ach sin!le strand is laid on a nylon membrane and
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
radioactive matter is added to it" A bandin! pattern appears"
/<: An 5$ray film is prodced and the positions of blac3 bands
are compared with the part of =@A treated with radioactive
matter"
MAXIMAMB 4 )a!,
("") A'(& %o ,%a%& %*& a-2a#%a$&, a#- -",a-2a#%a$&, o/
>NA /"#$&+"#%"#$
Sample answer:
A-2a#%a$&,B
/1: =@A fin!erprintin! is more accrate than common
fin!erprintin! as no two people have the same =@A
fin!erprints"
/0: =@A fin!erprintin! is more efficient than blood$type
identification becase many people have the s a m e
b l o o d t y p e
/(: =@A fin!erprintin! re.ires only a small amont of =@A to
obtain a hi!hly accrate reslt
/&: =@A samples last lon!er than fin!erprints"
/': 8ixed =@A samples can still be sed"
/<: =@A evidence is harder to clean p compared to
fin!erprints"
>",a-2a#%a$&,B
/B: =@A samples may be de!raded by addi n!
chemicals1 and this will affect the accracy of the techni.e"
/C: Gman errors are possible when different procedres and
standards are sed in =@A fin!erprintin!"
MAXIMAMB F )a!,
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
TOTAL
4
F
20 marks
D(a) (") A'(& %o &1+(a"# 6*: )o,% +(a#%, .a##o% .o(o#",& a#-
$o6 "# %*& ,6a)+,.
Sample answer:
/1: -he !rond is too soft and nable to spport plants1
/0: -he water$lo!!ed / mddy swamps provide very little
oxy!en for root respiration"
/(: -he swamp water has a hi!h concentration of salt and is
hypertonic"
/&: -he plants !rowin! in swamp will have the problem of
dehydration"
/': #eeds that fall into the mddy swamp will die of
dehydration / insfficiency of oxy!en"
/<: -he swamp is exposed to stron! snli!ht and intense
heat"
/B: As a reslt1 the plants !rowin! there will lose water very
fast by transpiration"
MAXIMAMB 5 )a!,
("") A'(& %o &1+(a"# *o6 %*& )a#$o2& %&&, a-a+%
%*&),&(2&, %o %*& *a,* ("2"#$ .o#-"%"o#,
Sample answer:
/1: Root system which is hi!hly branched and spreads over a
bi! area to !ive !ood spport to the plants"
/0: /nematophores (breathin! roots) which !row protrdin!
pwards above the !rond"
/(: -he plant cells have hi!h concentration of cell sap"
/&: Gence1 the cells are able to withstand the hi!h salt
content of the
swamp"
/': ;xcess salt is eliminated thro!h hydatodes fond at the
lower epidermis of leaves"
/<: Iiviparos seeds which !erminate while still
attached to the parent plant"
/B: -he lon! radical prodced will let the seedlin! stic3 into
the !rond and not sbmer!e or drift away"
/C:-hic3 cticle and sn3en stomata which help to redce the
rate of transpiration"
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
5
5
(b)
MAXIMAMB 5 )a!,
A'(& %o -&,."'& %*& &//&.%, o/ 0#+(a##&- -&2&(o+)&#%
a#- ")+o+& )a#a$&)&#% o/ %*& &.o,:,%&)"
/1: -he leave canopy in the forest protects the soil from
excess rain water"
/0: ?hen the forest is cleared1 the soil is exposed to rain
(water) / wind"
/(: this will case soil erosion
/&:-he soil that is exposed to wind will be blown to
another area1
/': while soil that is exposed to rain water will be eroded
and deposited at the bottom of the river / pond /la3e"
/<:-he soil at the hill slopes can (also) be washed away by
heavy rain water
/B: resltin! in land slides"
/C: (-he deposited soil will) case the water level to increase
rapidly when it rains and
/D: this will in trn case flash floods"
/1%:?ild life species will also be threatened
/11: when their habitat is destroyed"
/10: :lobal warmin! will occr
/1(:de to an increase in the ;arthFs temperatre1
/1&:which is cased by excess emissions of carbon
dioxide/ methane/ C,C /nitro!en dioxide (into the
atmosphere)"
/1':-hese !ases trap the heat that is reflected by the ;arth"
/1<:-he thinnin! of the o*one layer occrs
/1B: when the o*one layer (that protects the ;arth from
ltraviolet radiation) is destroyed by chloroflorocarbons
(C,C)"
MAXIMAMB 10 )a!,
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
Вам также может понравиться
- Zika Virus and Diseases: From Molecular Biology to EpidemiologyОт EverandZika Virus and Diseases: From Molecular Biology to EpidemiologyОценок пока нет
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesОт EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Biology: AnalysisДокумент24 страницыBiology: AnalysisChua HcОценок пока нет
- Q Bio 2012Документ24 страницыQ Bio 2012Visva VisvamОценок пока нет
- Biology: AnalysisДокумент38 страницBiology: AnalysisYiLingTengОценок пока нет
- Biologi SkemaДокумент38 страницBiologi SkemaSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Biologi SPM Paper 1 Exercise 4551/1Документ22 страницыBiologi SPM Paper 1 Exercise 4551/1Saw CwОценок пока нет
- Soalan Biologi Tingkatan 4Документ16 страницSoalan Biologi Tingkatan 4Dekfa Miefa0% (1)
- Afterschool Biology SPM 2014 Soalan & JawapanДокумент40 страницAfterschool Biology SPM 2014 Soalan & Jawapanahmengchye0% (1)
- Solaf 1 4551/1Документ21 страницаSolaf 1 4551/1kabil86Оценок пока нет
- SPM 4551 2006 Biology k1 BerjawapanДокумент11 страницSPM 4551 2006 Biology k1 Berjawapanpss smk selandarОценок пока нет
- Lonjakan Saujana SPM 2009Документ71 страницаLonjakan Saujana SPM 2009Rozaini OthmanОценок пока нет
- Paper 1 QuestionДокумент25 страницPaper 1 QuestionNoridaAnisОценок пока нет
- Biology F4 (Paper 1)Документ18 страницBiology F4 (Paper 1)Intan RahayuОценок пока нет
- Bio P1 SPMTrialДокумент23 страницыBio P1 SPMTrialCikgu Zaid IbrahimОценок пока нет
- Bio 07 K1 (Perak Gempur)Документ14 страницBio 07 K1 (Perak Gempur)Ferguson TehОценок пока нет
- Bio k1 t4 Pptsbp07Документ19 страницBio k1 t4 Pptsbp07Anonymous 9soHe7I01lОценок пока нет
- Ulangkaji Berfokus SPM 2015 p1 Theme 2Документ99 страницUlangkaji Berfokus SPM 2015 p1 Theme 2Norizan DarawiОценок пока нет
- Trial Bio 1 2010Документ26 страницTrial Bio 1 2010Muhammad Fikri RashidОценок пока нет
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelДокумент20 страницUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456Оценок пока нет
- Kertas 1 SPM (Percubaan) 1-10Документ76 страницKertas 1 SPM (Percubaan) 1-10Hazizi HanapiОценок пока нет
- 5096 s11 QP 11Документ20 страниц5096 s11 QP 11mstudy123456Оценок пока нет
- SPM 4551 2007 Biology k1 BerjawapanДокумент17 страницSPM 4551 2007 Biology k1 Berjawapanpss smk selandar100% (1)
- Bio SPM 2003 P1Документ13 страницBio SPM 2003 P1SeanОценок пока нет
- Biology SPM Forecast PapersДокумент21 страницаBiology SPM Forecast PaperswhywhyqОценок пока нет
- Bio Paper 1 Mid Term 2011Документ22 страницыBio Paper 1 Mid Term 2011Hilmi Din100% (1)
- Biologi Kertas 1, 2, 3 Percubaan SPM 2007 MRSMДокумент53 страницыBiologi Kertas 1, 2, 3 Percubaan SPM 2007 MRSMfariss68Оценок пока нет
- Q Sci 2012Документ15 страницQ Sci 2012Chua HcОценок пока нет
- Biology Form 4 Paper 1Документ23 страницыBiology Form 4 Paper 1unieezz100% (2)
- Trial SPM Bio-P1 2018Документ21 страницаTrial SPM Bio-P1 2018CHIENG LEH ZING -Оценок пока нет
- Final Exam f4 p1 2014Документ22 страницыFinal Exam f4 p1 2014eimОценок пока нет
- Question Bio P1Документ26 страницQuestion Bio P1Marliana Iryani YaacobОценок пока нет
- SPM 4551 2005 Biology k1Документ10 страницSPM 4551 2005 Biology k1pss smk selandarОценок пока нет
- Information For CandidatesДокумент40 страницInformation For CandidatescikgunazriОценок пока нет
- Pre Trial MRSM Biology ObjectivesДокумент16 страницPre Trial MRSM Biology ObjectivesKhusyairy Daeng SailendraОценок пока нет
- BIOLOGI P1 2011 JohorДокумент27 страницBIOLOGI P1 2011 JohorNadrah Harith FadzilahОценок пока нет
- Cylindrical Shaped Smooth Outer Membrane and Folded Inner MembraneДокумент26 страницCylindrical Shaped Smooth Outer Membrane and Folded Inner MembranerhimalinyОценок пока нет
- 5090 w14 QP 12Документ20 страниц5090 w14 QP 12Rahique ShuaibОценок пока нет
- Ujian Prestasi 2 / 2015 Biologi Tingkatan 4Документ16 страницUjian Prestasi 2 / 2015 Biologi Tingkatan 4Fadhliana UzalliОценок пока нет
- Biologi Kertas 1Документ29 страницBiologi Kertas 1ain_senseiОценок пока нет
- Soalan Bio K1 Midyear (Repaired)Документ25 страницSoalan Bio K1 Midyear (Repaired)hanafizaОценок пока нет
- p1 BioДокумент25 страницp1 BioIsmaliza IshakОценок пока нет
- Kertas 1 PercubaanДокумент28 страницKertas 1 PercubaanHerdawati HamdanОценок пока нет
- Q Sci 2011Документ15 страницQ Sci 2011Asim RusliОценок пока нет
- As Trial Jan 14 p1 QДокумент15 страницAs Trial Jan 14 p1 QArvin DiNozzoОценок пока нет
- Bio Penilaian 2 f4Документ11 страницBio Penilaian 2 f4Sara GrayОценок пока нет
- Question Section AДокумент25 страницQuestion Section AFatin Liyana AhmadОценок пока нет
- Soalan P1 Trial 2015Документ33 страницыSoalan P1 Trial 2015Tajul Azhar BaharudinОценок пока нет
- Percubaan Biologi Kertas 1 Melaka 2016Документ29 страницPercubaan Biologi Kertas 1 Melaka 2016Siti Norliana JohariОценок пока нет
- Trial SPM 2012 Ssem Bio Paper 1Документ29 страницTrial SPM 2012 Ssem Bio Paper 1Aisyahumaira_hidayahОценок пока нет
- Bahan Biologi Kertas 1 2017Документ25 страницBahan Biologi Kertas 1 2017nizampermaiОценок пока нет
- SPM 2005 & 2006 - Kertas 1 Set 2Документ28 страницSPM 2005 & 2006 - Kertas 1 Set 2kiongocОценок пока нет
- 9700 s11 QP 12Документ16 страниц9700 s11 QP 12Ahmed Kaleem Khan NiaziОценок пока нет
- (667209331) Question-Paper-1-Final-F4-Sbp-2011Документ39 страниц(667209331) Question-Paper-1-Final-F4-Sbp-2011Fadhliana UzalliОценок пока нет
- FRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRДокумент11 страницFRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRAnonymous Igsm89AОценок пока нет
- Albumin: Structure, Biosynthesis, Function: Federation of European Biochemical Societies 11Th Meeting Copenhagen 1977От EverandAlbumin: Structure, Biosynthesis, Function: Federation of European Biochemical Societies 11Th Meeting Copenhagen 1977Оценок пока нет
- Biochemical Correlates of Brain Structure and FunctionОт EverandBiochemical Correlates of Brain Structure and FunctionA.N. DavisonОценок пока нет
- Current Topics in Bioenergetics: Volume 12От EverandCurrent Topics in Bioenergetics: Volume 12D. Rao SanadiОценок пока нет
- Rekod Kewangan Bulan Oct 2013Документ1 страницаRekod Kewangan Bulan Oct 2013shazy7Оценок пока нет
- Corporate Communications Specialist Job DescriptionДокумент2 страницыCorporate Communications Specialist Job Descriptionshazy7Оценок пока нет
- Children Learn What They LiveДокумент1 страницаChildren Learn What They Liveshazy7Оценок пока нет
- What Has A Face and Two Hands But No Arms or LegsДокумент3 страницыWhat Has A Face and Two Hands But No Arms or Legsshazy7Оценок пока нет
- Translation AgreementДокумент3 страницыTranslation Agreementshazy750% (2)
- Chapter 1 StudДокумент40 страницChapter 1 Studshazy7Оценок пока нет
- Rabies: Dr. Fitzroy A. Orrett, MB - BS, MSC, D (Abmm), Fccm. Clinical MicrobiologistДокумент42 страницыRabies: Dr. Fitzroy A. Orrett, MB - BS, MSC, D (Abmm), Fccm. Clinical MicrobiologistPatriceОценок пока нет
- Effect of The Rho-Associated Kinase Inhibitor Eye Drop (Ripasudil) On Corneal Endothelial Wound HealingДокумент9 страницEffect of The Rho-Associated Kinase Inhibitor Eye Drop (Ripasudil) On Corneal Endothelial Wound HealingRaúl Plasencia SaliniОценок пока нет
- Cell Structure Function Review PresentationДокумент8 страницCell Structure Function Review PresentationCharles IppolitoОценок пока нет
- Genetics in AquacultureДокумент100 страницGenetics in AquacultureDave DaveОценок пока нет
- Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemДокумент12 страницChapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine System蔡旻珊Оценок пока нет
- Topics in Biology Form 4Документ7 страницTopics in Biology Form 4IMELDA75% (12)
- Control of Gene Expression Questions AQA OCR EdexcelДокумент5 страницControl of Gene Expression Questions AQA OCR EdexcelMeeta DeviОценок пока нет
- Gene MappingДокумент5 страницGene MappingC/fataax C/xakiimОценок пока нет
- HumaCount 5D ENДокумент8 страницHumaCount 5D ENAhmed MoeenОценок пока нет
- Early DevelopmentДокумент2 страницыEarly DevelopmentyelloweverglowОценок пока нет
- Foundation Tier Biology 1: P.M. TUESDAY, 7 June 2011 45 MinutesДокумент14 страницFoundation Tier Biology 1: P.M. TUESDAY, 7 June 2011 45 MinutessureshthevanОценок пока нет
- Biology Practical Class 12Документ2 страницыBiology Practical Class 12ManishОценок пока нет
- Markscheme HL Paper3Документ8 страницMarkscheme HL Paper3Jane ChangОценок пока нет
- AnthropologyДокумент209 страницAnthropologyStiff Yilma50% (2)
- Bioremediation of PesticidesДокумент3 страницыBioremediation of PesticidesSunil VohraОценок пока нет
- Diet and FitnessДокумент23 страницыDiet and FitnessMariam El KhatibОценок пока нет
- Biofertilizer For Crop Production and Soil Fertility: August 2018Документ9 страницBiofertilizer For Crop Production and Soil Fertility: August 2018GnanakumarОценок пока нет
- Student Exploration: Evolution: Mutation and Selection Gizmo AnswersДокумент8 страницStudent Exploration: Evolution: Mutation and Selection Gizmo Answersthanossssss57% (7)
- Concepts of BiologyДокумент1 007 страницConcepts of BiologyEduardo Panadero CuarteroОценок пока нет
- Lecture Slides-01 02 Functional Microanatomy of NeuronsДокумент4 страницыLecture Slides-01 02 Functional Microanatomy of NeuronsAna LeucaОценок пока нет
- Entrez Digital Tools and UtilitiesДокумент80 страницEntrez Digital Tools and UtilitiesGeorge Sebastian AntonyОценок пока нет
- Biotechnology For SustainabilityДокумент552 страницыBiotechnology For SustainabilitySubhash Janardhan Bhore, PhD100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Advanced GeneticsДокумент31 страницаChapter 6 Advanced GeneticsRochelleCasador180Оценок пока нет
- Topical Test Biology Form 4Документ14 страницTopical Test Biology Form 4Siti Wahida SuleimanОценок пока нет
- PH Optimo de InvertasaДокумент11 страницPH Optimo de InvertasapsykhodelykОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis PDFДокумент22 страницыPhotosynthesis PDFbhaskar rayОценок пока нет
- 10 Biology EM 2023-24GДокумент257 страниц10 Biology EM 2023-24Gdishitagarwal22Оценок пока нет
- Biodiversity and Ecosystem ServicesДокумент18 страницBiodiversity and Ecosystem Servicessameer AhadОценок пока нет
- November 2006 MS - Paper 3 CIE Biology IGCSEДокумент6 страницNovember 2006 MS - Paper 3 CIE Biology IGCSEUzair ZahidОценок пока нет
- Class 9th Cell - The Unit of LifeДокумент40 страницClass 9th Cell - The Unit of LifeKabir RaiОценок пока нет