Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Note Taking Examples
Загружено:
knamarch270 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
34 просмотров23 страницыnote taking technique
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документnote taking technique
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
34 просмотров23 страницыNote Taking Examples
Загружено:
knamarch27note taking technique
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 23
College Note Taking
Another Academic Success Key!
Not to be used or distributed without
permission from the ARC.
Rules of the Brain Incoming
Information
Builds on Prior Knowledge
Seeks Patterns
Seeks Meaning
Seeks to Condense
Seeks to Order/Organize
Indicates you must DO (active learning)
something with your notes NOT just
read over them (passive learning)
Note Taking Why?
Promotes Active Listening
Provides Accurate Record of Info
Makes You Restructure Information
Interpret (give meaning)
Condense
Organize
Provides Repetition
0
10
20
30
40
60
50
70
90
80
100
P
e
r
c
e
n
t
f
o
r
g
o
t
t
e
n
Forgetting Curve:
1
hour
9
hours
48
hours
1
week
1
month
Time since review of information
~ 60% forgotten after only 9 hours
How much you forget if you dont organize and
review lecture notes
1
hour
9
hours
48
hours
1
week
1
month
0
10
20
30
40
60
50
70
90
80
100
P
e
r
c
e
n
t
f
o
r
g
o
t
t
e
n
Forgetting Curve:
How much you forget if you dont organize and review
Time since review of information
After 2 days: ~75% of information gone
1
hour
9
hours
48
hours
1
week
1
month
0
10
20
30
40
60
50
70
90
80
100
Forgetting Curve
0organize & = 0 understand = 0remember
review
Note taking must be active and ongoing.
Characteristics of Good Notes
Good Notes:
Are Organized
Distinguish Main Points from Details
Include Examples
Indicate Lecture Patterns
Allow for Self-Testing
Stand the Test of Time
Use Abbreviations
Note-taking Systems/Formats
All should include
Course Name
Date
Section for Notes
Section Summary
Section for Self-Test (such as Cue Column or
Predict Test Questions Section)
Note Taking Systems
Cornell Method
Take Notes
Here
2-3 Sentence
Summary
Key Terms
or
Predict Test
Questions
or
Equations
Split-Page
Professors Notes
(such as PowerPoint
handouts or course-
reader notes)
Your Notes Self-
testing
Method Three: Discussion
Columns
Question
Profs
Comments
Student
Comments
Method Four: T-Method
Your Notes
Summary Questions
Make Note Taking Work for
Your Brain
B D A
E
F
O
R
E
U
R
I
N
G
F
T
E
R
STEP 1: Before lecture
Format your paper
take notes here
Record lecture with as
much detail as possible.
After:
write key
points
~ 2 inches.
Keep this column empty as you
take notes. Before next class,
reduce to key points & test
questions.
summarize notes here Sum up each lecture in a few
paragraphs.
HEP 2500 Oct. 1, Fri.
Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver
5 infectious forms: A,B,C,D,E
**BCD can become chronic. Leads to
-cirrhosis of liver
-liver cancer
Noninfectious forms. Caused by toxic substances: alcohol, OD acetam.
(Tylenol)
1) A: not chronic. Transmitted by h2O contaminated by feces or
infected person or by food. Vaccine = Y. Only A or A/B vaccine
symptoms: sometimes none. Flu-like. Nausea, fever, fatigue, abd.
pain. Most people recover 100%. Lifelong immunity. Hi risk in
certain countries.
2) B: 5% of people have it chronically. Transmitted by blood, other
body fluids (sex, needles). Also mom to fetus. Vaccine=Y. B or A/B
symptoms: same as A. 40% no symptoms. Health workers increased
risk. Causes cirrhosis or liver cancer sometimes.
3) C: 85% = chronic. Thru blood, needles (before 92 thru
transfusions). Also mom > fetus. No vaccination available.
15
Step 2: During lecture
Organize, shortcuts, abbreviations
!!know symptoms for test
Def. of hepatitis
5 infectious types
What are they?
Which types become chronic?
What two diseases are caused
by chronic hepatitis?
A transmitted by contaminated
water, food, or infected person.
Which vaccine?
What are symptoms of Type A?
How are symptoms of A and
B the same? Different?
Which type are health workers
most at risk for?
Which types can a mother
pass on to a fetus?
HEP 2500 Oct. 1, Fri.
Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver
5 infectious forms: A,B,C,D,E
**BCD can become chronic. Leads to
-cirrhosis of liver
-liver cancer
Noninfectious forms. Caused by toxic substances: alcohol, OD acetam.
(Tylenol)
1) A: not chronic. Transmitted by h2O contaminated by feces or
infected person or by food. Vaccine = Y. Only A or A/B vaccine
symptoms: sometimes none. Flu-like. Nausea, fever, fatigue,
abdominal pain. Most people recover 100%. Lifelong immunity. Hi
risk in certain countries.
2) B: 5% of people have it chronically. Transmitted by blood, other
body fluids (sex, needles). Also mom to fetus. Vaccine=Y. B or A/B
symptoms: same as A. 40% no symptoms. Health workers increased
risk. Causes cirrhosis or liver cancer sometimes.
3) C: 85% = chronic. Thru blood, needles (before 92 thru
transfusions). Also mom > fetus. No vaccination available.
After lecture
Write in key points and
create questions
15
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver and there are five infectious types A, B, C, D, E. B,C,D can become
chronic and result in cirrhosis or liver cancer. A is transmitted through contaminated water, food, or other
infected person. B & C are transmitted through blood or other body fluids as well as from mom to fetus.
A& B have vaccines, but C does not. Type C has the highest percentage of becoming chronic.
15
HEP 2500 Oct. 1, Fri.
Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver
5 infectious forms: A,B,C,D,E
**BCD can become chronic. Leads to
-cirrhosis of liver
-liver cancer
Noninfectious forms. Caused by toxic substances: alcohol, OD acetam.
(Tylenol)
1) A: not chronic. Transmitted by h2O contaminated by feces or
infected person or by food. Vaccine = Y. Only A or A/B vaccine
symptoms: sometimes none. Flu-like. Nausea, fever, fatigue,
abdominal pain. Most people recover 100%. Lifelong immunity. Hi
risk in certain countries.
2) B: 5% of people have it chronically. Transmitted by blood, other
body fluids (sex, needles). Also mom to fetus. Vaccine=Y. B or A/B
symptoms: same as A. 40% no symptoms. Health workers increased
risk. Causes cirrhosis or liver cancer sometimes.
3) C: 85% = chronic. Thru blood, needles (before 92 thru
transfusions). Also mom > fetus. No vaccination available.
Summary Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver and there are five infectious types A, B, C, D, E.
B,C,D can become chronic and result in cirrhosis or liver cancer. A is transmitted through contaminated
water, food, or other infected person. B & C are transmitted through blood or other body fluids as well as
from mom to fetus. A& B have vaccines, but C does not. Type C has the highest percentage of becoming
chronic.
After lecture
HEP 2500 Oct. 1, Fri. 15
Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver
5 infectious forms: A,B,C,D,E
**BCD can become chronic. Leads to
-cirrhosis of liver
-liver cancer
Noninfectious forms. Caused by toxic substances: alchol, OD acetam. (Tylenol)
1) A: not chronic. Transmitted by h2O contaminated by feces or infected person or
by food. Vaccine = Yes. Only A or A/B vaccine
symptoms: sometimes none. Flu-like. Nausea, fever, fatigue, abdominal pain.
Most people recover 100%. Lifelong immunity. High risk in certain countries.
2)B: 5% of people have it chronically. Transmitted by blood, other body fluids
(sex, needles). Also mom to fetus. Vaccine=yes. B or A/B
symptoms: same as A. 40% no symptoms. Health workers increased risk. Causes
cirrhosis or liver cancer sometimes.
3) C: 85% = chronic. Through blood or needles (before 92 thru transfusions).
Also mom > fetus. No vaccination available.
Def. of hepatitis
5 infectious types: What are
they?
Which types become chronic?
What two diseases are caused
by chronic hepatitis?
A transmitted by what?
Which vaccine for A?
What are symptoms of Type A?
How are symptoms of A and
B the same? Different?
Which type are health workers
most at risk for?
Which types can a mother
pass
it on to a fetus?
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver and there are five infectious types A, B, C, D, E. B,C,D can become chronic and
result in cirrhosis or liver cancer. A is transmitted through contaminated water, food, or other infected person. B & C are
transmitted through blood or other body fluids as well as from mom to fetus. A& B have vaccines, but C does not. Type C
has the highest percentage of becoming chronic.
HEP 2500 Oct. 1, Fri. 15
Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver
5 infectious forms: A,B,C,D,E
**BCD can become chronic. Leads to
-cirrhosis of liver
-liver cancer
Noninfectious forms. Caused by toxic substances: alchol, OD acetam. (Tylenol)
1) A: not chronic. Transmitted by h2O contaminated by feces or infected person or
by food. Vaccine = Yes. Only A or A/B vaccine
symptoms: sometimes none. Flu-like. Nausea, fever, fatigue, abdominal pain.
Most people recover 100%. Lifelong immunity. High risk in certain countries.
2)B: 5% of people have it chronically. Transmitted by blood, other body fluids
(sex, needles). Also mom to fetus. Vaccine=yes. B or A/B
symptoms: same as A. 40% no symptoms. Health workers increased risk. Causes
cirrhosis or liver cancer sometimes.
3) C: 85% = chronic. Through blood or needles (before 92 thru transfusions).
Also mom > fetus. No vaccination available.
Def. of hepatitis
5 infectious types: What are
they?
Which types become chronic?
What two diseases are caused
by chronic hepatitis?
A transmitted by what?
Which vaccine for A?
What are symptoms of Type A?
How are symptoms of A and
B the same? Different?
Which type are health workers
most at risk for?
Which types can a mother
pass it on to a fetus?
Summary: Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver and there are five infectious types A, B, C, D, E. B,C,D can become
chronic and result in cirrhosis or liver cancer. A is transmitted through contaminated water, food, or other infected person.
B & C are transmitted through blood or other body fluids as well as from mom to fetus. A& B have vaccines, but C does
not. Type C has the highest percentage of becoming chronic.
5
Order of
Operations:
Please excuse my
dear aunt sally
Please Parenthesis or grouping symbols
Excuse Exponents (and radicals)
My Dear Multiplication/Division left to right
Aunt Sally Addition/Subtraction left to right
Math 1010 J an. 16
Example 4: Simplify
*Multiply
*Add
*Subtract
When you do have more than one mathematical operation, you
need to use the order of operations PEMDAS
5
Order of
Operations:
Please excuse my
dear aunt sally
Please Parenthesis or grouping symbols
Excuse Exponents (and radicals)
My Dear Multiplication/Division left to right
Aunt Sally Addition/Subtraction left to right
Math 1010 J an. 16
Example 4: Simplify
*Multiply
*Add
*Subtract
When you do have more than one mathematical operation, you
need to use the order of operations PEMDAS
15
HEP 2500 Oct. 1, Fri.
Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver
5 infectious forms: A,B,C,D,E
**BCD can become chronic. Leads to
-cirrhosis of liver
-liver cancer
Noninfectious forms. Caused by toxic substances: alcohol, OD acetam.
(Tylenol)
1) A: not chronic. Transmitted by h2O contaminated by feces or
infected person or by food. Vaccine = Y. Only A or A/B vaccine
symptoms: sometimes none. Flu-like. Nausea, fever, fatigue,
abdominal pain. Most people recover 100%. Lifelong immunity. Hi
risk in certain countries.
2) B: 5% of people have it chronically. Transmitted by blood, other
body fluids (sex, needles). Also mom to fetus. Vaccine=Y. B or A/B
symptoms: same as A. 40% no symptoms. Health workers increased
risk. Causes cirrhosis or liver cancer sometimes.
3) C: 85% = chronic. Thru blood, needles (before 92 thru
transfusions). Also mom > fetus. No vaccination available.
Exam prep 7 steps:
1. Read notes out loud to
get info. fixed in
memory.
2. Cover your notes; leave
Left column uncovered.
3. Ask yourself question or
explain concept.
4. Uncover notes to see
how much you
remembered.
5. If you knew it, go on to
next concept. If you
missed, review notes
again.
6. Check off concepts as
you learned them.
7. Next study session:
review what you know,
but concentrate on what
you dont know.
Вам также может понравиться
- ABCs of Hepatitis.Документ13 страницABCs of Hepatitis.Ali AkhtarОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis BДокумент28 страницHepatitis BLex DgtОценок пока нет
- HepatitisДокумент8 страницHepatitisudaybujjiОценок пока нет
- Health Assignment6Документ7 страницHealth Assignment6api-275667839Оценок пока нет
- Hepatitis C Virus: Section: 3Документ43 страницыHepatitis C Virus: Section: 3Aymen OmerОценок пока нет
- Viral Hepatitis 101 A Thru C - FINAL 04-30-2014Документ3 страницыViral Hepatitis 101 A Thru C - FINAL 04-30-2014ipcsafetyofficerОценок пока нет
- IntroductionДокумент8 страницIntroductionRamandeep Singh BhullarОценок пока нет
- Your Liver Is The Largest Organ Inside Your Bod1Документ14 страницYour Liver Is The Largest Organ Inside Your Bod1Rrhandy Mae dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis A, B, C and HIV: The Hepatitis Education Project Seattle, WashingtonДокумент34 страницыHepatitis A, B, C and HIV: The Hepatitis Education Project Seattle, Washingtonkashifbutty2kОценок пока нет
- HepatitisДокумент10 страницHepatitisBheru LalОценок пока нет
- How Do You Get Hepatitis B? How Can I Protect Myself?Документ14 страницHow Do You Get Hepatitis B? How Can I Protect Myself?Dini MayrisdayaniОценок пока нет
- What Is The HepatitisДокумент14 страницWhat Is The HepatitisBlack Hack HakerОценок пока нет
- Assignment Submitted To: Mam Anum Nazir Submitted By: Zarish Sultan DND-FA16-004 TopicДокумент9 страницAssignment Submitted To: Mam Anum Nazir Submitted By: Zarish Sultan DND-FA16-004 TopicLAIBA FAISALОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis B: Your Doctor. DR Michael Jones, Medical EditorДокумент9 страницHepatitis B: Your Doctor. DR Michael Jones, Medical Editormmbrelvi2757Оценок пока нет
- Hepatitis OverviewДокумент37 страницHepatitis OverviewM Lutfi Fanani100% (1)
- Angliski SeminarskaДокумент13 страницAngliski SeminarskaMarija AleksovaОценок пока нет
- Take The Hepatitis TestДокумент2 страницыTake The Hepatitis TestJAGADISH PADHYОценок пока нет
- Viral Hepatitis: Information For Gay/Bisexual MenДокумент2 страницыViral Hepatitis: Information For Gay/Bisexual MenPatrick RamosОценок пока нет
- Recommendations: Hepatitis AДокумент1 страницаRecommendations: Hepatitis AmtnyndaОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis B OverviewДокумент8 страницHepatitis B OverviewAnnieElizabethОценок пока нет
- Haepatitis - EДокумент5 страницHaepatitis - ERatnaPrasadNalamОценок пока нет
- Causes, Incidence, and Risk Factors: Hepatitis A Hepatitis C Hepatitis DДокумент41 страницаCauses, Incidence, and Risk Factors: Hepatitis A Hepatitis C Hepatitis DAmber ShrivastavaОценок пока нет
- HepatitisДокумент43 страницыHepatitissacchandesu100% (3)
- Who-What Is HepatitisДокумент2 страницыWho-What Is HepatitisnadОценок пока нет
- HepatitisДокумент6 страницHepatitisMOHIT KUMARОценок пока нет
- Bloodborne Pathogens: NWSSB, Det. Corona Annual Sustainment Training Instructor: Richard Owens October 3, 2008Документ50 страницBloodborne Pathogens: NWSSB, Det. Corona Annual Sustainment Training Instructor: Richard Owens October 3, 2008jayand_net100% (1)
- What Is Leptospirosis?: Flulike Headaches FeverДокумент7 страницWhat Is Leptospirosis?: Flulike Headaches FeverPatrick PaternoОценок пока нет
- Viral Hepatitis Basic InformationДокумент3 страницыViral Hepatitis Basic Informationberuangmadu777Оценок пока нет
- What Is Hepatitis?: Online Q&A Reviewed July 2015Документ2 страницыWhat Is Hepatitis?: Online Q&A Reviewed July 2015Nikhilesh PrasadОценок пока нет
- HepatitisДокумент40 страницHepatitisbhaktirudani1Оценок пока нет
- The A, B, Cs of Viral HepatitisДокумент7 страницThe A, B, Cs of Viral HepatitishawllatyОценок пока нет
- What Is Hepatitis A?Документ33 страницыWhat Is Hepatitis A?zainjamilОценок пока нет
- Assignment On: HepatitisДокумент12 страницAssignment On: HepatitisAbdallah KisswaniОценок пока нет
- Biology Assignment: Submitted By: Maham Ahmed (01-171182-013) Class: BS Psychology Date: 23 Submitted To: Sir Kashif AliДокумент6 страницBiology Assignment: Submitted By: Maham Ahmed (01-171182-013) Class: BS Psychology Date: 23 Submitted To: Sir Kashif Alihurricane2010Оценок пока нет
- Immunization of Hepatitis BДокумент33 страницыImmunization of Hepatitis BibrahimОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis A & B Power PointДокумент15 страницHepatitis A & B Power PointHerlina Marshal100% (1)
- LiverДокумент26 страницLiverDinesh MishraОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis B VirusДокумент8 страницHepatitis B VirusNika AndrianiОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis A: Questions and Answers: Information About The Disease and VaccinesДокумент4 страницыHepatitis A: Questions and Answers: Information About The Disease and VaccinesSodiqa Strida SaSi TwinzОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis A Fact SheetДокумент2 страницыHepatitis A Fact SheetKUER NewsОценок пока нет
- Infectious Disease Project-NikkiДокумент10 страницInfectious Disease Project-Nikkiuglyghost0514Оценок пока нет
- Hepatitis A: Questions and Answers: Information About The Disease and VaccinesДокумент4 страницыHepatitis A: Questions and Answers: Information About The Disease and VaccinesSceptic GrannyОценок пока нет
- 2014 - 08 - (August) HepatitisДокумент1 страница2014 - 08 - (August) HepatitisEkwoh Okwuchukwu EОценок пока нет
- Jurnal Hepatitis AДокумент7 страницJurnal Hepatitis AarifОценок пока нет
- Why Do We Fall Ill 1Документ11 страницWhy Do We Fall Ill 1hakim_wasim8548Оценок пока нет
- Script-Hepa AbДокумент6 страницScript-Hepa Abkaty loОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis A: The Need For VaccinationДокумент28 страницHepatitis A: The Need For VaccinationRizki FitriantoОценок пока нет
- Infectious Disease Project-NikkiДокумент10 страницInfectious Disease Project-Nikkiuglyghost0514Оценок пока нет
- 20 - Semiotics of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disorders.Документ32 страницы20 - Semiotics of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disorders.Paramveer SinhОценок пока нет
- Viral Hepatitis: Navy Environmental and Preventive Medicine Unit No. FiveДокумент57 страницViral Hepatitis: Navy Environmental and Preventive Medicine Unit No. FiveSaad MotawéaОценок пока нет
- Emerging Diseases and Bloodborne DiseasesДокумент8 страницEmerging Diseases and Bloodborne DiseasesAngela ReyesОценок пока нет
- Jurnal Hepatitis AДокумент5 страницJurnal Hepatitis ANurul Amaliah LestariОценок пока нет
- 1Hrqdwdo6Huylfhv1,&8: 300 Children's Way, 0& San Diego, CA 92123Документ2 страницы1Hrqdwdo6Huylfhv1,&8: 300 Children's Way, 0& San Diego, CA 92123deepakОценок пока нет
- Hepetitis 140722235359 Phpapp01Документ34 страницыHepetitis 140722235359 Phpapp01Dharmendra GohilОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis DДокумент24 страницыHepatitis DAgeededin HartОценок пока нет
- 04 - Typhoid FeverДокумент35 страниц04 - Typhoid Feversoheil100% (1)
- Protect Your Baby For LifeДокумент2 страницыProtect Your Baby For LifeEko Wahyu AgustinОценок пока нет
- Vitamin C in Dermatology: Drug ProfileДокумент5 страницVitamin C in Dermatology: Drug ProfileFharidha Ny GbfОценок пока нет
- IGI Cares Structuring AgentsДокумент7 страницIGI Cares Structuring Agentsknamarch27Оценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S0960982214003261 MainДокумент10 страниц1 s2.0 S0960982214003261 Mainknamarch27Оценок пока нет
- Evodiamine Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Metastasis in MDA MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells in Vitro and in VivoДокумент10 страницEvodiamine Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Metastasis in MDA MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells in Vitro and in Vivoknamarch27Оценок пока нет
- Dose-Response and Threshold Effects in Cytotoxicity and ApoptosisДокумент6 страницDose-Response and Threshold Effects in Cytotoxicity and Apoptosisknamarch27Оценок пока нет
- Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activity of Uleine From Himatanthus LancifoliusДокумент5 страницAcetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activity of Uleine From Himatanthus Lancifoliusknamarch27Оценок пока нет
- 1749 8546 6 27 PDFДокумент15 страниц1749 8546 6 27 PDFknamarch27Оценок пока нет
- Mitochondria: A Promising Target For Anticancer AlkaloidsДокумент13 страницMitochondria: A Promising Target For Anticancer Alkaloidsknamarch27Оценок пока нет
- Evodiamine Inhibits in Vitro Angiogenesis: Implication For AntitumorgenicityДокумент10 страницEvodiamine Inhibits in Vitro Angiogenesis: Implication For Antitumorgenicityknamarch27Оценок пока нет
- Zhang 2004Документ10 страницZhang 2004knamarch27Оценок пока нет
- ChemistCornerMiniCourse Lesson4 PDFДокумент21 страницаChemistCornerMiniCourse Lesson4 PDFknamarch27Оценок пока нет
- IU and Jang Yi Jeong of HISTORY Let's Meet On FridayДокумент2 страницыIU and Jang Yi Jeong of HISTORY Let's Meet On Fridayknamarch27Оценок пока нет
- 32721Документ33 страницы32721prasadbheemОценок пока нет
- Handbook For Cell Culture Basics (Gibco)Документ62 страницыHandbook For Cell Culture Basics (Gibco)Cesar PuentesОценок пока нет
- Cell Biology and CancerДокумент17 страницCell Biology and Cancersatya_chagantiОценок пока нет
- Closed Fracture OsДокумент23 страницыClosed Fracture OsDiana Lita SОценок пока нет
- Sample Health Teaching PlanДокумент1 страницаSample Health Teaching PlanGia Espinosa OcbeñaОценок пока нет
- CancerДокумент70 страницCancerapi-3735995100% (1)
- Programmed Postoperative Physiotherapy May Improve Functional Outcomes in Pneumonectomy Patients of Rare Causes Case SeriesДокумент7 страницProgrammed Postoperative Physiotherapy May Improve Functional Outcomes in Pneumonectomy Patients of Rare Causes Case SeriesAtu KaushalОценок пока нет
- Diagnosis and Management of COPD: A Case Study: RespiratoryДокумент4 страницыDiagnosis and Management of COPD: A Case Study: RespiratoryUssy TsnnnОценок пока нет
- Pricelist 13 Juli 2020Документ21 страницаPricelist 13 Juli 2020Achmad Sya'idОценок пока нет
- وسيلة منصوريДокумент126 страницوسيلة منصوريhouda houdaОценок пока нет
- The Benefits of ChocolateДокумент2 страницыThe Benefits of ChocolateHanna FairussaniaОценок пока нет
- Diagnostic Report: Patient Name: Razia Sultana FH.11964170 0026VI003012Документ2 страницыDiagnostic Report: Patient Name: Razia Sultana FH.11964170 0026VI003012Zeeshan QureshiОценок пока нет
- Pediatric Diabetes InsipidusДокумент11 страницPediatric Diabetes InsipidusVictor Matias BarriosОценок пока нет
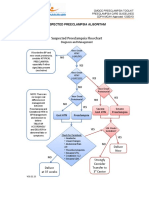
- Suspected Preeclampsia AlgorithmДокумент1 страницаSuspected Preeclampsia Algorithmmisstina.19876007100% (1)
- Akshata Sawant Final Article 1Документ16 страницAkshata Sawant Final Article 1SonuОценок пока нет
- Computational Fluid Dynamics and Trigeminal Sensory Examinations of Empty Nose Syndrome PatientsДокумент60 страницComputational Fluid Dynamics and Trigeminal Sensory Examinations of Empty Nose Syndrome Patientsmadhumitha srinivasОценок пока нет
- Manual of Contact Lens Prescribing and Fitting, 3rd Edition: The Ocular Fundus Offers The Clinician AnДокумент2 страницыManual of Contact Lens Prescribing and Fitting, 3rd Edition: The Ocular Fundus Offers The Clinician AnphenixousОценок пока нет
- Effects of Cuscuta Chinensis Lam. Versus Fluoxetine For Treatment of Major Depression: A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled TrialДокумент10 страницEffects of Cuscuta Chinensis Lam. Versus Fluoxetine For Treatment of Major Depression: A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled TrialBaru Chandrasekhar RaoОценок пока нет
- Journal of Health Education: Medication Adherence of Tuberculosis Patients in Yogyakarta: A Cross Sectional StudyДокумент12 страницJournal of Health Education: Medication Adherence of Tuberculosis Patients in Yogyakarta: A Cross Sectional StudyDesy AmaliaОценок пока нет
- Acute Necrotizing Sinusitis Caused by Staphylococcus Lugdunensis 2011Документ3 страницыAcute Necrotizing Sinusitis Caused by Staphylococcus Lugdunensis 2011J Sebastian PeinadoОценок пока нет
- WHO Drug Information: Herbal Medicines Regulatory ActionДокумент91 страницаWHO Drug Information: Herbal Medicines Regulatory ActionLia PuspitasariОценок пока нет
- Categorical and Hypothetical ImperativesДокумент4 страницыCategorical and Hypothetical ImperativesKathe KiunisalaОценок пока нет
- Booklet Bcu Revisi 5Документ8 страницBooklet Bcu Revisi 5irza nasutionОценок пока нет
- NIV - Past, Present and FutureДокумент9 страницNIV - Past, Present and FutureDejan ŽujovićОценок пока нет
- Low-Cost Breath AnalyzerДокумент20 страницLow-Cost Breath AnalyzeradnanОценок пока нет
- Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Booklet For Parents and CarersДокумент40 страницAutism Spectrum Disorders: A Booklet For Parents and CarersAndreea SanduОценок пока нет
- PTSD - Diagnostic CriteriaДокумент5 страницPTSD - Diagnostic Criteriagreg sОценок пока нет
- 3.trauma Vaskular Richard SДокумент79 страниц3.trauma Vaskular Richard SAdang SunandarОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Nursing Assistant A Nursing Process Approach 11th EditionДокумент7 страницTest Bank For Nursing Assistant A Nursing Process Approach 11th EditionLarry Cessor100% (26)
- 2015 To 2019 Super Speciality Dissertation Topics PDFДокумент35 страниц2015 To 2019 Super Speciality Dissertation Topics PDFJoseph John Crasto100% (4)
- Guidelines On Dental Record KeepingДокумент8 страницGuidelines On Dental Record KeepingXubair AhmedОценок пока нет
- 3 - SДокумент45 страниц3 - SFarnoush ShahriariОценок пока нет
- The Gut Microbiota in Anxiety and Depression - A Systematic Review (Simpson Et Al, 2020)Документ18 страницThe Gut Microbiota in Anxiety and Depression - A Systematic Review (Simpson Et Al, 2020)GokushimakОценок пока нет
- The Bodies of Others: The New Authoritarians, COVID-19 and The War Against the HumanОт EverandThe Bodies of Others: The New Authoritarians, COVID-19 and The War Against the HumanРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (12)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (9)
- Do You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineОт EverandDo You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineОценок пока нет
- Uncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicОт EverandUncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicОценок пока нет
- Mama Might Be Better Off Dead: The Failure of Health Care in Urban AmericaОт EverandMama Might Be Better Off Dead: The Failure of Health Care in Urban AmericaОценок пока нет
- Epic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.От EverandEpic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (13)
- There Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceОт EverandThere Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (11)
- The Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsОт EverandThe Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- The Varicose Veins Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint for Complete Varicose Veins ManagementОт EverandThe Varicose Veins Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint for Complete Varicose Veins ManagementОценок пока нет
- Clean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyОт EverandClean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (18)
- There Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceОт EverandThere Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (15)
- The Price of Health: The Modern Pharmaceutical Industry and the Betrayal of a History of CareОт EverandThe Price of Health: The Modern Pharmaceutical Industry and the Betrayal of a History of CareРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeОт EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (21)
- Heat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoОт EverandHeat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (40)
- The Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusОт EverandThe Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (10)
- The Hair Color Mix Book: More Than 150 Recipes for Salon-Perfect Color at HomeОт EverandThe Hair Color Mix Book: More Than 150 Recipes for Salon-Perfect Color at HomeРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (7)
- The Wuhan Cover-Up: And the Terrifying Bioweapons Arms RaceОт EverandThe Wuhan Cover-Up: And the Terrifying Bioweapons Arms RaceОценок пока нет
- Fatal Conveniences: The Toxic Products and Harmful Habits That Are Making You Sick—and the Simple Changes That Will Save Your HealthОт EverandFatal Conveniences: The Toxic Products and Harmful Habits That Are Making You Sick—and the Simple Changes That Will Save Your HealthРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (7)
- Inflamed: Deep Medicine and the Anatomy of InjusticeОт EverandInflamed: Deep Medicine and the Anatomy of InjusticeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (12)
- Beyond the Next Village: A Year of Magic and Medicine in NepalОт EverandBeyond the Next Village: A Year of Magic and Medicine in NepalОценок пока нет
- COVID-19: The Victims, The Heroes, The Comlicit, and Our New NormalОт EverandCOVID-19: The Victims, The Heroes, The Comlicit, and Our New NormalОценок пока нет
- Mercury, Mining, and Empire: The Human and Ecological Cost of Colonial Silver Mining in the AndesОт EverandMercury, Mining, and Empire: The Human and Ecological Cost of Colonial Silver Mining in the AndesОценок пока нет
- Healthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityОт EverandHealthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)