Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Collection of Biology Essay f4&5
Загружено:
faeznur0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
582 просмотров26 страниц1. Active transport requires energy from ATP to move molecules against their concentration gradient across the plasma membrane using carrier proteins. Facilitated diffusion uses carrier proteins but moves molecules down their concentration gradient without ATP.
2. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy but are not used up in the process. They have specific active sites that bind to substrates and catalyze reactions. Temperature affects reaction rates, with an optimum temperature yielding the fastest rate.
3. The cell cycle has four main phases - prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase. In prophase, chromosomes condense and spindle fibers form.
Исходное описание:
biology
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документ1. Active transport requires energy from ATP to move molecules against their concentration gradient across the plasma membrane using carrier proteins. Facilitated diffusion uses carrier proteins but moves molecules down their concentration gradient without ATP.
2. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy but are not used up in the process. They have specific active sites that bind to substrates and catalyze reactions. Temperature affects reaction rates, with an optimum temperature yielding the fastest rate.
3. The cell cycle has four main phases - prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase. In prophase, chromosomes condense and spindle fibers form.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
582 просмотров26 страницCollection of Biology Essay f4&5
Загружено:
faeznur1. Active transport requires energy from ATP to move molecules against their concentration gradient across the plasma membrane using carrier proteins. Facilitated diffusion uses carrier proteins but moves molecules down their concentration gradient without ATP.
2. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy but are not used up in the process. They have specific active sites that bind to substrates and catalyze reactions. Temperature affects reaction rates, with an optimum temperature yielding the fastest rate.
3. The cell cycle has four main phases - prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase. In prophase, chromosomes condense and spindle fibers form.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 26
8lCLCC?
lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
1
!"##$!%&"' ") *&"#"+,
$--.,- )"/ -01
A
ALLAH HELPS THOSE WHO
HELP THEMSELVES
CU AND ML A+ 8ICLCG
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
2
Iac|||tated D|ffus|on Act|ve 1ransport An|ma| and p|ant ce||s |n an |soton|c so|ut|on
lor waLer soluble molecules//molecules
whlch are noL soluble ln llplds (lons,
nuclelc acld, amlno aclds and glucose)
Carrler roLeln
1he carrler proLeln funcLlon by
blndlng Lo Lhe molecules Lo pass
Lhrough Lhe plasma membrane.
1he molecules move Lo Lhe carrler
proLeln whlch ls speclflc for Lhe
molecules.
Molecules blnd wlLh Lhe carrler
proLeln aL Lhe acLlve slLe.
Carrler proLeln changes lLs shape and
pass Lhe molecules Lhrough Lhe
plasma membrane.
! MovemenL of molecules or lons agalnsL
Lhe concenLraLlon gradlenL across Lhe
plasma membranes.
! 8equlres boLh carrler proLelns and
expendlLure of energy.
! Lnergy from A1 (adenoslne
LrlphosphaLe) LhaL ls generaLed durlng
resplraLlon ln Lhe mlLochondrla.
! Pas acLlve slLes whlch blnd Lo Lhe A1
molecules.
! 1he carrler proLeln changes shape when
Lhe phosphaLe group from Lhe A1
molecule blnds Lo lL
! 1hen Lhe soluLe ls moved across Lhe
plasma membrane.
SoluLlon ln whlch Lhe soluLe concenLraLlon
ls equal Lo LhaL of Lhe cyLoplasmlc fluld.
WaLer dlffuse ln and ouL of Lhe cells aL
equal raLe.
no neL movemenL of waLer.
Cells reLaln lLs normal shape.
hagocyLosls S|mp|e D|ffus|on Csmos|s: the d|ffus|on of water
1he pseupodla are also used for feedlng.
.23456 789 engulfs food by phagocyLosls.
Amoeba sp. ls a holozolc organlsms whlch
feed on mlcroscoplc organlsms such as
bacLerla.
1he presence of food causes .23456
789Lo advance by exLendlng lLs pseupodla.
1he pseupodla encloses Lhe food whlch ls
Lhen packaged ln food vacoule.
1he food vacoule fuses wlLh lysosome and
Lhe food ls dlgesLed by hydrollLlc enzyme
called lysozyme.
1he resulLlng nuLrlenLs are absorbed lnLo
Lhe cyLoplasm.
neL movemenL of molecules or lons from
a reglon of hlgher concenLraLlon Lo a
reglon of lower concenLraLlon.
Colng down concenLraLlon gradlenL unLll
an equlllbrlum ls achleved.
1he parLlcles are dlsLlbuLed equally
LhroughouL Lhe sysLem.
1he concenLraLlon gradlenL provldes
energy Lo move Lhe molecules lnLo and
ouL of Lhe cells.
neL movemenL of freely movlng waLer
from a reglon of lower soluLe
concenLraLlon Lo a reglon of hlgher soluLe
concenLraLlon Lhrough a seml-permeable
membrane.//
neL movemenL of waLer from reglon
hlgher waLer concenLraLlon Lo a reglon of
lower waLer concenLraLlon.//
neL movemenL of waLer from hypoLonlc
reglon Lo hyperLonlc reglon.
**Choose any one
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
3
nypoton|c so|ut|on nyperton|c so|ut|on reservat|on of f|sh and vegetab|es
ConcenLraLlon of soluLe ouLslde a cell ls lower
Lhan concenLraLlon of soluLe lnslde cell.
Anlmal cells
ls sald Lo be hypoLonlc soluLlon.
Cell placed ln hypoLonlc soluLlon.
neL movemenL of waLer lnLo Lhe cells vla
osmosls.
Cell swells up.
When exLremely hypoLonlc, cells wlll
evenLually bursL
CannoL wlLhsLand Lhe osmoLlc pressure
because of Lhln plasma membrane.
L.g : red blood cells (haemolysls)
lanL cells
uo noL bursL
8lgld cell wall.
WaLer dlffuse lnLo vacoule of cell vla
osmosls.
Cell swells up and becomes Lurgld
1ugor pressure ln planL.
SupporLlng Lhe planL.
1he concenLraLlon of soluLe ln Lhe soluLlon ls
hlgher Lhan Lhe concenLraLlon of soluLes wlLhln
Lhe cell.
Anlmal cells
neL movemenL of waLer from lnslde Lo
Lhe ouLslde of Lhe cell.
Cells shrlnk//shrlvel, lnLernal pressure
decrease.
8ed blood cells lmmersed ln hyperLonlc
soluLlon , Lhe cell shrlnk and Lhe plasma
membrane crlnkles up.
Cell undergone crenaLlon.
lanL cells
WaLer dlffuse ouL vla osmosls.
vacoule and cyLoplasm shrlnk and plasma
membrane pulls away from Lhe cell wall.
1hls process called plasmolysls.
Cell becomes flaccld.
llsh
llsh ls covered by salL soluLlon whlch ls
hyperLonlc Lo body fluld/cell/Llssue.
More waLer dlffuses ouL from Llssues lnLo
salL soluLlon vla osmosls.
llsh becomes hydraLed.
revenLs bacLerlal growLh ln flsh Llssues.
8acLerla cells are also
plasmolysed//crenaLed.
revenL decay/lasL longer.
vegeLables
vegeLables are lmmersed ln vlnegar whlch
ls acldlc//has low pP.
vlnegar dlffuses lnLo vegeLables Llssues.
vegeLables Llssues becomes acldlc//has
low pP.
revenLs bacLerlal growLh ln Llssues.
revenLlng decay//lasL longer.
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
4
D|fferences beLween fac|||tated d|ffus|on and act|ve transport
Iac|||tated d|ffus|on
8ut
Act|ve transport
u1
L1
uown Lhe concenLraLlon gradlenL
Molecules moves from hlgher concenLraLlon Lo lower
concenLraLlon
AgalnsL Lhe concenLraLlon gradlenL
Molecules moves from lower concenLraLlon Lo
hlgher concenLraLlon
u2
L2
Molecules move ln boLh dlrecLlon across Lhe plasma
membrane
Molecules can move Lhrough pore proLeln or/and carrler
proLeln
Molecules move ln one dlrecLlon across Lhe plasma
membrane
Molecules move Lhrough carrler proLeln
u3
L3
no A1/energy used
Molecule can move Lhrough pore proLeln wlLhouL blndlng
A1/energy ls used
Lnergy needed for blndlng/blnd wlLh acLlve slLe
u4 Molecules need carrler proLeln and pore proLeln Lo help
Lhe movemenL
need carrler proLeln only Lo help movemenL
u3 Could achleve equlllbrlum Wlll noL achleve equlllbrlum/resulL ln accumulaLlon
u6 noL depended ln cellular resplraLlon uepend on cellular resplraLlon/energy
S|m||ar|t|es between fac|||tated d|ffus|on and
act|ve transport
1he Importance of water Genera| character|st|cs of enzymes
8oLh (ways of LransporLaLlon)need carrler
proLeln.
1o blnd wlLh
molecules/lon/subsLraLe/examples
8oLh LransporL speclflc molecules only.
8ecause Lhe carrler proLeln have speclflc
slLe Lo cerLaln molecules.
8oLh processes occur ln llvlng cell.
8ecause carrler proLeln need/can change
shape Lo allow subsLances Lo move across.
WaLer ls a polar molecule and acL as a
solvenL.
1ransporL medlum ln Lhe blood,
lymphaLlc, excreLory and dlgesLlve
sysLems and ln Lhe vascular Llssues of
planL.
As a medlum for blochemlocal reacLlon.
Pelps ln lubrlcanL.
8egulaLes/malnLalnlng body LemperaLure.
rovldlng supporL Lo Lhe cell.
Plgh surface Lenslon and coheslon.
rovldlng mlosLure (resplraLory surfaces
such as alveoll).
MalnLalnlng osmoLlc balance and
LurgldlLy.
AlLer or speed up Lhe raLes of chemlcal
reacLlons
8emaln unchanged aL Lhe end of reacLlon.
uo noL desLroyed by reacLlons Lhey
caLalysed.
Pave speclflc slLes called acLlve slLe Lo
blnd wlLh speclflc subsLraLes.
needed ln small quanLlLles.
8eacLlon are reverslble
Can be slowed down or sLopped by
lnhlblLors. L.g: lead and mercury
8equlre helper molecules, called
cofacLors.
lnorganlc cofacLor : ferum, copper
Crganlc cofacLor: waLer soluble vlLamlns,
8 vlLamlns .
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
3
Lxtrace||u|ar enzyme 'Lock and key' hypothes|s Lffects of temperature on enzyme act|v|ty
LxLracellular enzyme ls produced ln a cell,
Lhen packed and secreLed from Lhe cell.
lL caLalyses lLs reacLlon ouLslde Lhe cell.
An example ls amylase.
1he nucleus conLalns unA whlch carrles
Lhe lnformaLlon for synLhesls of enzymes.
roLeln LhaL are synLheslsed aL Lhe
rlbosomes are LransporLed Lhrough Lhe
spaces wlLhln Lhe rough L8.
roLelns LhaL deparL from Lhe rough L8
wrapped ln veslcles LehaL bud off from Lhe
membrane of Lhe rouhg L8.
1hese LransporL veslcle Lhen fuse wlLh Lhe
mebranes of Lhe golgl apparaLus and
empLy Lhelr conLenLs lnLo Lhe
membranous space.
1he proLelns are furLher modlfled durlng
Lhelr LransporL ln Lhe Colgl apparaLus. lor
example, carboohydraLes are added Lo
proLeln Lo form glycoproLelns.
SecreLory veslcles conLalnlng Lhese
modlfled proLeln bud off from Lhe Colgl
apparaLus and Lravel Lo Lhe plasma
membrane.
Lnzymes are released.
1he subsLraLe molecule flLs lnLo Lhe acLlve
slLe of Lhe enzyme molecule.
1he subsLraLe ls Lhe 'key' LhaL flLs lnLo Lhe
enzyme 'lock'.
varlous Lypes of bonds such as hydrogen
and lonlc bonds hold Lhe subsLraLe
ln Lhe acLlve slLe formlng Lhe enzyme-
subsLraLe complex.
Cnce Lhe complex ls formed, Lhe enzyme
changes Lhe subsLraLe Lo lLs producL.
1he producL leaves Lhe acLlve slLe.
1he enzyme ls noL alLered by Lhe reacLlon
and lL can be reused.
AL low LemperaLure, reacLlon Lakes place
slowly.
As LemperaLure lncreases, movemenL of
subsLraLe lncrease.
lncrease Lhelr chances of collldlng wlLh
each oLher and wlLh Lhe acLlve slLe of Lhe
enzymes.
AL opLlmum LemperaLure, Lhe reacLlon ls
aL maxlmum raLe.
8eyond Lhe opLlmum LemperaLure, raLe of
reacLlon wlll noL lncrease.
8onds LhaL hold enzyme molecules begln
Lo break.
AcLlves slLes desLroyed.
Lnzyme denaLured.
rophase Metaphase Anaphase
Chromosomes ln Lhe nucleus condense.
Chromosomes appear shorLer and Lhlcker.
ConslsL of slsLer chromaLld [olned aL Lhe
cenLromere.
Splndle flbres begln Lo form.
CenLrloles mlgraLe aL opposlLe poles.
AL Lhe end, nucleolus dlsappears and Lhe
nuclear membrane dlslnLegraLes.
Chromosomes allgn aL Lhe meLaphase
plaLe//equaLorlal plaLe//mlddle of Lhe
cell.
MlLoLlc splndle are fully formed.
1wo slsLer chromaLlds are sLlll aLLached Lo
one anoLher aL Lhe cenLromere.
Lnds when Lhe cenLromere dlvldes.
1wo slsLer chromaLlds separaLe aL Lhe
cenLromere.
SlsLer chromaLlds pulled aparL aL opposlLe
poles.
ChromaLlds are referred Lo as daughLer
chromosomes.
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
6
1e|ophase Cytok|nes|s Uncontro||ed m|tos|s
Chromosomes reach Lhe opposlLe poles of
Lhe cell.
Chromosomes uncoll and reverL Lo Lhelr
exLended sLaLe(chromaLln).
rocess of cyLoplasmlc dlvlslon.
8eglns before nuclear dlvlslon ls
compleLed.
AcLln fllamenL formed conLracLlle rlng.
ConLracLs and consLrlcL pull arlng of
plasma membrane lnwards.
Croove of cleavage furrow plnches aL Lhe
equaLor beLween Lwo nuclel.
veslcles [oln Lo form a cell plaLe.
Cell plaLe grows unLll lL edges fuse wlLh
Lhe plasma membrane of Lhe cell. Cell
dlvldes.
Cellulose are produced by Lhe cell Lo
sLrengLhen Lhe new cell walls.
Cell dlvldes Lhrough mlLosls repeaLedly
wlLhouL conLrol.
roduce cancerous cells.
Cancer ls a geneLlc dlsease caused by
unconLrolled mlLosls.
ulsrupLlon of cell cycle.
Cancerous cells dlvldes freely and
unconLrollably noL accordlng Lo Lhe cell
cycle.
1hese cells compeLe wlLh surroundlng
normal cells for energy and nuLrlenLs.
Cancer cells formed Lumour.
1umour lnvade and desLroy nelghbourlng
cells.
An|ma| c|on|ng 1|ssue cu|ture Advantages of c|on|ng
SomaLlc cells (from Lhe mammary gland
cells) are removed and grown ln a culLure.
Cells sLop dlvldlng and enLer a non-dlvlng
phase.
unferLlllsed egg ls obLalned. 1he nucleus
ls sucked ouL, leavlng Lhe cyLoplasm and
organelles wlLhouL any chromosomes.
LlecLrlc pulse sLlmulaLes Lhe fuslon
beLween Lhe somaLlc cells and egg cell
wlLhouL nucleus.
Cells dlvlde repeaLedly formlng an
embryo.
1he embryo ls Lhen lmplanLed ln a
surrogaLe moLher.
1he cloned sheep of Lhe somaLlc cell
donor ls born.
Small parL of planL ls cuL. L.g : shooLs, bud.
1he parL ls called explanL.
Lnzymes are used Lo dlgesL Lhe cell walls
of Llssue.
Cells are naked (proLoplasL).
LxplanL/proLoplasL are sLerlled Lhen
placed ln a glass conLalner whlch conLalns
a nuLrlenL soluLlon.
CulLure medlum (glucose, amlno aclds).
ApparaLus musL be sLerlled Lo make sure
free from mlcroorganlsms (bacLerla).
pP and LemperaLure musL be aL opLlmum
level.
LxplanL dlvldes by mlLosls.
uevelops lnLo callus.
Callus develops lnLo somaLlc embryo
(planleL).
1hen Lransferred Lo soll for growLh.
8loLechnologlsLs Lo mulLlply coples of
useful genes or clones.
Clones can be produced ln a shorLer Llme
and ln large numbers.
Cloned planLs, however, can produced
flowers and frulLs wlLhln a shorLer perlod.
Clones are beLLer quallLy.
uelayed rlpenlng.
uoes noL need pollnaLlng agenLs.
ropagaLlon can Lake place aL any Llme.
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
7
SynLhesls of enzymes
1. 1he lnformaLlon for Lhe synLhesls of enzymes ls carrlled by Lhe unA
- 1he sequences of bases on Lhe unA are codes Lo make proLelns
2. ln Lhe nucleus, Lhe unA double hellx unwlnds and exposes lLs Lwo sLrands for Lhe synLhesls of a messenger 8nA (m8nA) sLrand
- 1he messenger 8nA ls synLheslsed accordlng Lo Lhe lnsLrucLlon on Lhe unA
3. 1he messenger 8nA Lhen leaves Leh nucleus and moves Lo a rlbosome
4. 1he messenger 8nA aLLaches lLself Lo Lhe rlbosome
- 1he rlbosome acLs as a workbench for Lhe messenger 8nA
- 1he messenger 8nA conLalns lnformaLlon whlch codes for Lhe sequence of amlno aclds
3. 1hls geneLlc lnformaLlon ls LranslaLed lnLo Lhe prlmary sLrucLure of speclflc proLeln
6. Lach amlno acld ls bonded Lo Lhe nexL and as a resulL, a chaln of amlno aclds (polypepLlde) ls formed and ls ready for release lnLo Lhe cyLoplasm.
D|sadvantages of c|on|ng Me|os|s I Me|os|s II
Long-Lerm slde effecLs are noL yeL known.
May undergo naLural muLaLlons. ulsrupL
Lhe naLural equlllbrlum of an ecosysLem.
Clones do noL show any geneLlc
varlaLlons.
Pas Lhe same level of reslsLance Lowards
cerLaln dlsease.
CerLaln Lransgenlc crops conLaln genes
LhaL are reslsLanL Lo herblcldes.
1hese genes may be Lransferred Lo weeds
Lhrough vlruses. 1hese weeds would Lhen
become reslsLanL Lo herblcldes.
Cloned anlmals has shorLer llfespan.
1. uurlng prophase l, homologous
chromosomes palr up (synapsls) and
crosslng over beLween non slsLer
chromaLlds occurs.
2. uurlng MeLaphase l, homologous
chromosomes allgn aL Lhe meLaphase
plaLe (equaLor, mlddle) of Lhe cell.
3. uurlng Anaphase l, homologous
chromosomes separaLes and move Lo
opposlLe poles. SlsLer chromaLlds are sLlll
aLLached LogeLher and move as a unlL.
4. AL Lhe end of 1elophase l, Lwo haplold
daughLer cells are formed. Lach daughLer
cell has only one of each Lype of
chromosomes, elLher Lhe paLernal or
maLernal chromosomes.
1. uurlng rophase ll, synapsls of
homologous chromosomes and crosslng
over beLween non-slsLer chromaLlds do
noL Lake place.
2. uurlng MeLaphase ll, chromosomes
conslsLlng of Lwo slsLer chromaLlds allgn
aL Lhe meLaphase plaLe (equaLor/mlddle)
of cell.
3. uurlng Anaphase ll, slsLer chromaLlds
separaLe, becomlng daughLer
chromosomes LhaL move Lo opposlLe
poles.
4. AL Lhe end of 1elophase ll, four haplold
daughLer cells are formed. Lach daughLer
cell has Lhe same number of
chromosomes as Lhe haplold cell
produced ln Melosls l, buL each has only
one of Lhe slsLer chromaLlds.
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
8
D|gest|on |n mouth D|gest|on |n stomach D|gest|on |n sma|| |ntest|ne
SecreLlon of sallva by Lhree palrs of
sallvary glands
Sallva conLalns Lhe enzyme sallvary
amylase
8eglns Lhe hydrolysls of sLarch Lo malLose.
SLarch + waLer malLose
An addlLlonal dlgesLlve process occurs
furLher along Lhe allmenLary canal Lo
converL malLose Lo glucose.
pP ls malnLalned aL 6.3-7.3
LplLhellal llnlng of Lhe sLomach conLalns
gasLrlc glands.
1hese glands secreLe gasLrlc [ulce.
ConslsLs of mucus, PCL and enzyme
pepsln and renln.
PCL make Lhe pP around 2.0.
Plgh acldlLy desLroy bacLerla.
AcldlLy sLop Lhe acLlvlLy of sallvary
amylase enzyme.
roLeln + waLer polypepLldes
8enln coagulaLe mllk by converLlng Lhe
soluble mllk proLeln, caselnogen lnLo
soluble caesln.
SLomach conLenLs become a seml-fluld
called chyme.
Chyme gradually enLer Lhe duodenum.
uuodenum recelved chyme from sLomach
and secreLlon from Lhe gall bladder and
pancreas.
SLarch, proLeln and llplds are dlgesLed.
8lle whlch produced by Lhe llver and
sLored ln Lhe gall bladder enLer Lhe
duodenum vla Lhe blle ducL.
8lle helps neuLrallse Lhe acldlc chyme and
opLlmlse Lhe pP for enzyme acLlon ln
duodenum.
8lle salLs lmulslfy llplds, breaklng Lhem
down lnLo Llny dropleLs.
rovldlng hlgh 1SA for dlgesLlon.
ancreas secreLe pancreaLlc [ulce lnLo
duodenum vla pancreaLlc ducL.
ancreaLlc [ulce conLalns pancreaLlc
amylase, Lrypsln and llpase.
ancreaLlc amylase compleLe Lhe
dlgesLlon of sLarch Lo malLose.
1rypsln dlgesLs polypepLldes lnLo
pepLldes.
Llpase compleLe Lhe dlgesLlon of llpld lnLo
faLLy acld and glycerol.
Clands ln Lhe lleum (small lnLesLlne)
secreLe lnLesLlnal [ulce whlch conLaln
dlgesLlve enzyme needed Lo compleLe Lhe
dlgesLlon of pepLldes and dlsaccharldes.
epLldes dlgesLed by erepsln lnLo amlno
aclds.
MalLose dlgesLed by malLase lnLo glucose.
ulsaccharldes dlgesLed by lLs own enzyme
lnLo monosaccharldes and glucose.
Sallvary amylase
pepsln
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
9
D|gest|on of ce||u|ose by rum|nant D|gest|on of ce||u|ose by rodent D|gest|on
arLlally chewed food ls passed Lo Lhe
rumen (largesL comparLmenL of Lhe
sLomach).
Cellulose ls broken down by cellulase
produced by bacLerla.
arL of Lhe breakdown producLs are
absobed by bacLerla, Lhe resL by Lhe hosL.
lood enLers Lhe reLlculum.
Cellulose undergoes furLher hydrolysls.
1he conLenL of Lhe reLlculum, called Lhe
cud, ls Lhen regurglLaLed blL by blL lnLo Lhe
mouLh Lo be Lhoroughly chewed.
Pelps sofLen and break down cellulose,
maklng lL more accesslble Lo furLher
mlcroblal acLlon.
1he cud ls reswallowed and moved Lo Lhe
omasum.
Pere, Lhe large parLlcles of food are
broken down lnLo smaller pleces by
perlsLalsls.
WaLer ls removed from Lhe cud.
lood parLlcles moved lnLo obamasum, Lhe
Lrue sLomach of Lhe rumlnanL. (e.g : cow).
CasLrlc [ulce compleLe Lhe dlgesLlon of
proLeln and oLher food subsLances.
1he food Lhen passes Lhrough Lhe small
lnLesLlne Lo be dlgesLed and absorbed ln
Lhe normal way.
Caecum and appendlx are enlarged Lo
sLore Lhe cellulose-dlgesLlng bacLerla.
1he breakdown producLs pass Lhrough Lhe
allmenLary canal Lwlce.
1he faeces ln Lhe flrsL baLch are usually
produced aL nlghL.
laeces are Lhen eaLen agaln. 1o absorb
Lhe producLs of bacLerlal breakdown.
1he second baLch of Lhe faeces are harder
and drler.
Allows rodenL (glve example) Lo recover
Lhe nuLrlenLs lnlLlally losL wlLh Lhe faeces.
roLeln
- ln sLomach, pepsln breakdown
proLeln lnLo polypepLldes.
- PCL belng secreLed Lo provlde acldlc
medlum for Lhe dlgesLlon Lo occur.
- ln duodenum, Lrypsln breakdown
polypepLldes lnLo pepLldes.
- ln small lnLesLlne, arepsln break dwon
pepLldes lnLo amlno aclds.
laLs
- 8lle salLs breaklng up faLs lnLo small
faL dropleLs ln Lhe duodenum.
- ln duodenum/small lnLesLlne, llpase
breaks llplds lnLo faLLy aclds and
glycerol.
CarbohydraLes
- ln mouLh, sallvary amylase hydrolyse
sLarch lnLo malLose.
- ln duodenum, pancreaLlc amylase
hydrolyse sLarch lnLo malLose.
- ln small lnLesLlne, malLase hydrolyse
malLose lnLo glucose.
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
10
Absorpt|on of d|gested food Ass|m||at|on of d|gested food Iormat|on faeces
AbsorpLlon of dlgesLed food occur ln Lhe
lleum.
Clucose/amlno aclds lnlLlally dlffuse lnLo
blood caplllarles.
1he remalnlng of Lhe glucose/amlno aclds
acLlvely LransporL lnLo blood caplllarles.
All blood caplllarles converge lnLo hepaLlc
porLal veln, whlch lead Lo Lhe llver (and
LransporL Lo all parLs o fLhe body).
Clycerol and faLLy aclds dlffuse Lo Lhe
eplLhellal cell whlch llnlng Lhe lleum) and
comblne Lo form faL dropleLs.
laLLy aclds and glycerol Lhen enLer Lhe
lacLeal (lymphaLlc sysLem).
8eLurn back Lo Lhe blood sLream aL lefL
subclavlan veln.
Lxplaln Lhe asslmllaLlon of glucose and amlno acld
ln body cells.
Clucose ls oxldlsed Lo produce energy,
carbon dloxlde and waLer by cellular
resplraLlon.
Amlno acld ls used Lo synLhesls
proLoplasm (Lhe componenL of cell). 8y
Lhls way new cells wlll be synLheslsed
causlng growLh.
Amlno acld also can be used Lo synLhesls
enzyme, hormone or anLlbody.
laeces whlch conLaln dead cells LhaL are
shed from lnLesLlnal llnlngs, Loxlc
subsLances and blle plgmenLs enLer Lhe
colon by acLlon of perlsLalsls.
ln colon, more waLer ls absorbed. 1he
undlgesLed food resldues harden Lo
become faeces.
laeces conLaln undlgesLlble resldues LhaL
remaln afLer Lhe process of dlgesLlon and
absorpLlon of nuLrlenLs LhaL Lake place ln
Lhe small lnLesLlne.
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
11
hotosynthes|s mechan|sm hotosynthes|s mechan|sm Uses of enzyme (Chapter 4)
1he formaLlon of sLarch ln planLs ls by Lhe
process ofphoLosynLhesls whlch occurs ln
chloroplasLs.
1he Lwo sLages ln phoLosynLhesls are Lhe
llghL and dark reacLlons.
LlghL reacLlon:
3:1akes place ln grana.
4: Chlorophyll capLures llghL energy
whlch exclLes Lhe elecLrons of chlorophyll
molecules Lo hlgher energy levels.
3: ln Lhe exclLed sLaLe, Lhe elecLrons can
leave Lhe chlorophyll molecules.
6: LlghL energy ls also used Lo spllL waLer
molecules lnLo hydrogen lon (P+) and
hydroxyl lons (CP-) (hoLolysls of waLer).
7: 1he hydrogen lons Lhen comblne wlLh
Lhe elecLrons released by chlorophyll Lo
form hydrogen aLoms.
8: 1he energy from Lhe exclLed elecLrons
ls used Lo form energy-rlch molecules of
adenoslne LrlphosphaLe /A1.
9: Pydroxyl lon loses an elecLron Lo form
a hydroxyl group. 1hls elecLron ls Lhen
recelved by chlorophyll.
10: 1he hydroxyl groups Lhen comblne Lo
form waLer and gaseous oxygen.
uark 8eacLlon:
11: 1ake place ln sLroma.
12: uo noL requlre llghL energy.
13: 1he hydrogen aLoms are used Lo flx
carbon dloxlde ln a serles of reacLlons
caLalysed by phoLosynLheLlc enzymes
14: and caused Lhe reducLlon of carbon
dloxlde lnLo glucose.
13: 1he glucose monomers Lhen undergo
condensaLlon Lo form sLarch whlch ls
Lemporarlly sLored as sLarch gralns ln Lhe
chloroplasLs.
Lnzymes are used as blologlcal
deLergenLs.
roLease degrades coagulaLed proLelns
lnLo soluble shorL-chaln pepLldes.
Llpase degrades faL or oll sLalns lnLo
soluble faLLy acld and glycerol.
Amylase degrades sLarch lnLo soluble
shorLer-chaln polysaccharldes and sugars.
Lnzymes are used ln Lhe baklng lndusLry.
roLease ls used ln Lhe breakdown of
proLelns ln flour for Lhe producLlon of
blsculLs.
Amylase ls used ln Lhe breakdown of
some sLarch Lo glucose ln flour for maklng
whlLe bread, buns and rolls.
Lnzymes are used ln Lhe medlcal fleld.
1rypsln ls used Lo remove blood cloLs
and Lo clean wounds.
varlous oLher enzymes are used ln
blosensors.
Lnzymes are used ln lndusLrles because:
1hey are effecLlve.
1hey are cheap and easy Lo use.
1hey can be re-used, Lhus only small
amounLs are needed.
1hey don'L requlre hlgh LemperaLure Lo
work, Lhus Lhls reduces fuel cosLs.
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
12
Aerob|c resp|rat|on Anaerob|c resp|rat|on |n human musc|e Anaerob|c resp|rat|on |n yeast
ConLlnuous supply of oxygen.
Clucose molecules are oxldlsed by
oxygen.
CompleLe breakdown of glucose ln Lhe
presence of oxygen.
A large amounL of energy released.
Carbon dloxlde and waLer are produced as
wasLe producLs.
MosL of Lhe nergy released ls used Lo
synLheslse adenoslne LrlphosphaLe (A1)
from adenoslne dlphosphaLe (Au) and
lnorganlc phosphaLe.
A1 acLs as lnsLanL energy source.
A1 conslsLs of phosphaLe bonds whlch
can be easlly broken down Lo release
energy.
A1 Au + phosphaLe + energy
uurlng a vlgorous exerclse (runnlng), Lhe
breaLhlng raLe ls lncreased.
1hls ls Lo supply more oxygen Lo Lhe
muscles for rapld muscular conLracLlon.
Powever, Lhe supply of oxygen Lo muscles
ls sLlll lnsufflclenL.
and Lhe muscles have Lo carry ouL
anaeroblc resplraLlon Lo release energy.
1he glucose ls converLed lnLo lacLlc acld,
wlLh only a llmlLed amounL of energy
belng produced.
An oxygen debL bullds up ln Lhe body,
when no oxygen use ln energy producLlon.
Plgh level of lacLlc acld ln Lhe muscles
cause Lhem Lo ache.
AfLer runnlng, Lhe aLhleLe breaLhes more
rapldly and deeply Lhan normal for
LwenLy mlnuLes.
1here ls recovery perlod afLer 10 mlnuLes
unLll lL reaches 20 mlnuLes when oxygen ls
pald back durlng aeroblc resplraLlon.
AbouL 1/6 lacLlc acld ls oxldlzed Lo carbon
dloxlde, waLer and energy.
?easL normally resplres aeroblcally.
under anaeroblc condlLlon, yeasL carry
ouL anaeroblc resplraLlon.
roduces eLhanol.
rocess known as fermenLaLlon.
CaLalysed by Lhe enzyme zymase.
- LLhanol produced can be used ln
maklng wlne and beer.
- ln bread maklng, Lhe carbon dloxlde
released durlng fermenLaLlon of yeasL
causes Lhe dough Lo rlse.
S|m||ar|t|es between the sturucture of d|gest|ve and d|gest|on process of rum|nants and rodents
S1 8oLh allmenLary canal conLalns bacLerla/proLozoa
1 1o secreLe exLracellular enzyme//Lo dlgesL
2 1o dlgesL cellulose lnLo glucose
S2 8oLh have large surface area
1 1o lncrease raLe of dlffuslon //hydrolysed food
Lnergy released
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
13
D|fferences between the sturucture of d|gest|ve and d|gest|on process of rum|nants and rodents
Aspects kum|nant (has)
8ut
kodent (has)
number of sLomach chamber u1
L1
4 sLomach chamber
Pave Lo dlgesL cellulose
1 sLomach chamber
uo noL have Lo dlgesL cellulose
Slze of caecum u2
L2
Small//shorL caecum
uo noL dlgesL cellulose
8lg//long slze caecum
A place Lo dlgesL cellulose
8acLerla u3
L3
ln reLlculum
lor secreLe cellulase enzyme
ln caecum
lor secreLe cellulase enzyme
number of Llmes yhe food passes
Lhrough Lhe sLomach chamber
u4
L4
1wlce
1o compleLe Lhe dlgesLlon//
Cnce
1o absorb dlgesLed food
8egurglLaLed u3
1wlce ln mouLh cavlLy
Cnce ln mouLh cavlLy
8reath|ng mechan|sm |n man 8reath|ng mechan|sm |n man (cont|nuat|on) 1ransport of C
2
and CC
2
|n human body
ulaphragm ls a muscular sheeL ln Lhe
body cavlLy separaLlng Lhe Lhorax from
Lhe abdomen.
AL Lhe sLarL of lnhalaLlon, Lhe muscles of
Lhe dlaphragm conLracL , maklng lL less
arched.
1hls helps Lo lncrease Lhe volume of Lhe
Lhoraclc cavlLy and reduce Lhe pressure
of Lhe Lhoraclc cavlLy. Alr rushes lnLo Lhe
lungs.
When Lhe muscles of Lhe dlaphragm
relax , lL reLurns Lo lLs arched condlLlon ,
reduclng Lhe volume of Lhe Lhoraclc
cavlLy and lncreaslng Lhe pressure of Lhe
Lhoraclc cavlLy. Alr ls forced ouL of Lhe
lungs.
1he muscles beLween Lhe rlbs are known
as lnLercosLals muscles.
uurlng lnhalaLlon Lhe exLernal
lnLercosLals muscle conLracLs and ralse
Lhe lower rlbs.
1hls helps Lo lncrease Lhe volume of Lhe
Lhoraclc cavlLy and reduce Lhe pressure of Lhe
Lhoraclc cavlLy. Alr rushes lnLo Lhe lungs.
uurlng exhalaLlon Lhe exLernal lnLercosLals
muscles conLracL , Lhe rlbs reLurn Lo Lhelr
orlglnal poslLlon , reduce Lhe pressure of Lhe
Lhoraclc cavlLy. Alr ls forced ouL of Lhe lungs.
1he alveoll are Lhln-walled alr sacs wlLh Lhe
lungs.
1hese sacs are surrounded by a neLwork of
caplllarles.
uurlng lnhalaLlon Lhe alveoll are fllled wlLh
alr and gaseous exchange occurs beLween Lhe
alveoll and Lhe caplllarles.
Cxygen from Lhe alveoll dlffuses lnLo Lhe
caplllarles whlle carbon dloxlde dlffuses from
Lhe caplllarles lnLo Lhe alveoll.
Caseous exchange across Lhe alveolus
occurs by dlffuslon.
ulffuslon of gas depends on dlfferences
ln parLlal pressure beLween Lwo reglons.
1he parLlal pressure/ concenLraLlon of
oxygen ln Lhe alr of Lhe alveoll ls hlgher
compared Lo Lhe parLlal pressure/
concenLraLlon of oxygen ln Lhe blood
caplllarles.
1herefore, oxygen dlffuse across Lhe
surface of Lhe alveolus and blood
caplllarles lnLo blood.
1he LransporL of oxygen ls carrled ouL by
Lhe blood clrculaLory sysLem.
Cxygen comblnes wlLh resplraLory
plgmenL called haemoglobln ln Lhe red
blood cells.
1o form oxyhaemoglobln.
When Lhe blood passed Lhe Llssue wlLh
low parLlal pressure of oxygen,
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
14
1ransport of C
2
and CC
2
|n human body
(cont|nuat|on)
Lxp|a|n how energy f|ows through the food cha|n
and how |t |s |ost to the env|ronment.
Co|on|sat|on and success|on |n mangrove
swamps
Cxyhaemoglobln dlssoclaLes Lo release
oxygen.
Carbon dloxlde released by repalrlng
cells can be LransporLed by dlssolve
carbon dloxlde ln Lhe blood plasma.
8lnd Lo Lhe haemoglobln.
As carbamlnohaemoglobln.
ln form of blcarbonaLe lons.
Carbon dloxlde ls expelled wlLh waLer
vapour from Lhe lung.
Lnergy flows Lhrough Lhe food chaln ln one
dlrecLlon .
ln Lhe food chaln, Lhe planL ls Lhe producer,
Lhe raL ls Lhe prlmary consumer, Lhe snake ls
Lhe secondary consumer and Lhe eagle ls Lhe
LerLlary consumer.
ln Lhe food chaln, Lhe planL ls Lhe producer,
Lhe earLhworm ls Lhe prlmary consumer, Lhe
blrd ls Lhe secondary consumer and Lhe
snake/ eagle ls Lhe LerLlary consumer. Lach
level of food chaln ls called a Lrophlc level.
Lnergy ls Lransferred from one Lrophlc level
Lo anoLher Lrophlc level.
When energy ls Lransferred from one Lrophlc
level Lo anoLher level as much as 90 of Lhe
chemlcal energy ln Lhe food consumed by
prlmary consumer ls used for lLs meLabollc
acLlvlLles and losL as heaL.
Cnly 10 of Lhe energy ln an organlsm ls
passed on Lo Lhe organlsm aL Lhe nexL Lrophlc
level.
1he ploneer specles of a mangrove
swamp are Lhe -3::4;6<=6 sp. and
.>=?4::=6 sp.
1he presence of Lhls specles gradually
changes Lhe physlcal envlronmenL of
Lhe hablLaL.1he exLenslve rooL sysLems
of Lhese planLs Lrap and collecL
sedlmenLs, lncludlng organlc maLLer
from decaylng planL parLs.
As Llme passes, Lhe soll becomes more
compacL and flrm. 1hls condlLlon
favours Lhe growLh of /@=A38@3;6 sp.
Cradually Lhe /@=A38@3;6 sp. replaces
Lhe ploneer specles.
1he prop rooL sysLem of Lhe /@=A38@3;6
sp. Lraps sllL and mud, creaLlng a flrmer
soll sLrucLure over Llme.
1he ground becomes hlgher. As a resulL,
Lhe soll ls drler because lL ls less
submerged by sea waLer.
1he condlLlon now becomes more
sulLable for Lhe *;BCB=4;6 sp., whlch
replaces Lhe /@=A38@3;6 sp.
1he buLLress rooL sysLem of Lhe
*;BCB=4;6 sp. forms loops whlch exLend
from Lhe soll Lo Lrap more sllL and mud.
As more sedlmenLs are deposlLed, Lhe
shore exLends furLher Lo Lhe sea. 1he
old shore ls now furLher away from Lhe
sea and ls llke LerresLerlal ground.
Cver Llme, LerresLrlal planLs
llke :=86@ palm and 06:D6:B7 sp. begln
Lo replace Lhe *;BCB=4;6 sp.
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
13
Green house effects Lxp|a|n br|ef|y why humans carry out the act|v|ty
as shown |n d|agram above
Lxp|a|n the |mpacts of the act|v|ty shown above
on the env|ronment
Creen house effecL.
ulLra vloleL(uv) from solar radlaLlon ls
absorbed by Lhe earLh and some of Lhem
ls reflecLed back Lo Lhe aLmosphere ln Lhe
form of heaL/lnfra red.
PeaL or lnfrared radlaLlon cannoL be
reflecLed back Lo Lhe aLmosphere.
8ecause lL ls Lrapped by green house
gases such as CC2, nlLrogen dloxlde and
meLhane.
PeaL/lnfrared warmed Lhe surface of
earLh.
LarLh LemperaLure lncreases.
1he human populaLlon grows rapldly. 1he
demands for food and houslng areas have
lncreased.
vasL areas of foresL are cleared for
agrlculLural and commerclal purposes.
urbanlzaLlon and lndusLrlallzaLlon have
caused more foresLs Lo be cleared for
road consLrucLlon and houslng areas.
ueforesLaLlon ls also caused by Lhe
demands for Llmber and fuel wood.
ueforesLaLlon causes soll eroslon ,
landslldes, flash floods and global
warmlng.
Causes Lhe soll Lo become loose and less
sLable.
WlLhouL Lhe proLecLlon of green planLs,
Lhe soll ls exposed Lo Lhe forces of wlnd
and raln.
1he Lop layer of soll ls washed away
gradually by Lhe ralnwaLer.
1hls ls known as soll eroslon.
Soll eroslon causes Lhe depleLlon of
mlnerals from Lhe soll, Lherefore Lhe soll
becomes lnferLlle and unsulLable for
agrlculLure.
Landslldes may happen on sLeep hlllsldes
durlng heavy raln.
lL ls because ralnwaLer flows qulckly and
causes Lhe Lop layer of Lhe soll Lo
crumble.
8lvers and dralns are sllLed and Lhe flow
of waLer ls blocked.
1herefore, waLer flows lnland and Lhls
causes flash floods ln Lhe lower areas
durlng ralny seasons.
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
16
numan b|ood vesse|s C|rcu|atory system |n f|sh and human 8|ood c|ott|ng
ArLerles
- carrles blood away from hearL
- LransporL blood qulckly, aL hlgh pressure
- muscle of Llssue enables Lhe arLery Lo
consLrlcL and dllaLe
- walls of arLerles are sLrong and elasLlc,
have small lumen
Caplllarles
- Lhln walled blood vessels
- allow rapld gaseous exchange vla dlffuslon
- nuLrlenLs, wasLes and hormones are also
exchanged across here
- one cell Lhlck
velns
- blood reLurns from caplllarles Lo hearL
Lhrough velns
- blood flows ln low pressure
- have large lumens and valves (prevenL
back flow)
SlmllarlLles
- boLh have closed clrculaLlon
- boLh have a hearL
ulfferences
llsh Puman
Pas slngle clrculaLlon Pas double clrculaLlon
PearL dlvldes lnLo 2
chambers
PearL ls dlvlded lnLo 4
chambers
SepLum ls absenL SepLum ls presenL
ueoxygenaLed blood
flows from hearL Lo
gllls
ueoxygenaLed blood
flows from hearL Lo
lungs
CxygenaLed blood
flows from gllls Lo
body cells
CxygenaLed blood
flows from lungs Lo
hearL
- clumped plaLeleLs, damaged cells, cloLLlng
facLors form acLlvaLors (LhromboplasLlns)
- acLlvaLors LogeLher wlLh calclum lons and
vlLamln k, converLs proLhrombln Lo
Lhrombln
- Lhrombln caLalyses Lhe converslon of
soluble proLeln flbrlnogen lnLo lnsoluble
flbrln.
- flbrln ls a flbrous proLeln whlch comblnes
Lo form a mesh of long Lhreads over Lhe
wounds, Lrapplng red blood cells and
seallng Lhe wound.
- blood cloL hardens when exposed Lo alr
formlng scab
D|fference between b|ood and |ymph 1ype of |mmun|ty hagocytos|s
- lymph has a large numbers of lymphocyLe
compare Lo blood
- lymphocyLe ls produced by lymph nodes
ln lymph sysLem
- lymph has lower conLenL of oxygen
compare Lo blood
- acLlve lmmunlLy, body produces lLs own
anLlbodles ln response Lo sLlmulaLlon by
an anLlgen
- passlve lmmunlLy, body recelve an
anLlbodles from ouLslde source
- Lhe phagocyLe ls aLLracLed by chemlcals
produced by bacLerlum
- hagocyLes exLend lLs pseudopodlum
(legs) Lowards bacLerlum Lo engulf lL.
- lngesLlon of bacLerlum forms phagosome
- phagosome comblnes wlLh lysosome
- lysosome releases lysozyme lnLo
phagosome
- bacLerlum lnslde Lhe phagosome wlll be
desLroyed by lysozyme
- phagocyLe releases Lhe dlgesLed producLs
from cell
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
17
Lymph - formed - brought back |nto the b|ood
c|rcu|atory system.
kesp|ratory gases Act|ve |mmun|ty - ass|ve |mmun|ty
- when blood flows from arLerles lnLo
caplllarles, Lhere ls hlgher hydrosLaLlc
pressure aL arLlal end of caplllarles
- hlgh pressure causes some plasma Lo pass
Lhrough caplllary walls lnLo lnLercellular
spaces
- lnLersLlLlal fluld fllls Lhe spaces beLween
cells and consLanLly baLhes Lhe cells
- 90 of lnLersLlLlal fluld dlffuses back lnLo
blood caplllary
- 10 of lnLersLlLlal fluld goes lnLo Lhe lymph
caplllarles and known as lymph
- lymph caplllarles unlLe formlng larger
lymphaLlc vessels
- from lymphaLlc vessels, lymph evenLually
passes lnLo Lhoraclc ducL
- hence lymph dralns back lnLo blood
1ransporLaLlon ln resplraLory gas.
- oxygen enLers alveoll durlng lnhalaLlon
- gaseous exchange occurred aL alveoll
(oxygen dlffused lnLo blood caplllarles
whlle carbon dloxlde dlffused ouL)
- Lhe dlffuslon of Lhese gases caused by
dlfferenL of parLlal pressure of boLh
gaseous
- parLlal pressure of oxygen ln alveoll ls
hlgher Lhan parLlal pressure of oxygen ln
blood caplllarles
- oxygen dlffused ln cyLoplasm of red blood
cell
- oxygen comblnes wlLh haemoglobln
formlng oxyhaemoglobln
- oxyhaemoglobln Lhen senL Lo all parLs of
body
- hearL pumped Lhe oxygenaLed blood Lo all
body cells
- oxygen dlffused from blood caplllarles Lo
cell because parLlal pressure of oxygen ln
blood caplllarles ls hlgher Lhan ln cell
- carbon dloxlde dlffuse from cell Lo blood
caplllarles because parLlal pressure of
carbon dloxlde ln cell ls hlgher Lhan ln
blood caplllarles
- deoxygenaLed blood golng back Lo hearL
by vena cava and Lo lungs by pulmonary
arLery
AcLlve lmmunlLy
- obLalned by vacclnaLlon (arLlflclally
acqulred)
- vacclne conLalns dead/weakened
bacLerla/paLhogen/vlrus
- whlLe blood cells sLlmulaLed Lo produce
anLlbodles agalnsL paLhogen
- also obLalned when an lndlvldual has
recovered from cerLaln dlseases(naLurally
acqulred)
- a ready made supply of anLlbody wlll glve
lmmunlLy Lowards Lhe dlsease
asslve lmmunlLy
- obLalned by ln[ecLlng
anLlbodles/anLlserum (arLlflclally
acqulred)
- no anLlgen ls puL lnLo body, so body does
noL produce lLs own anLlbodles
- obLalned by a baby when anLlbodles from
moLher's blood plasma dlffuse lnLo foeLus
Lhrough placenLa (naLurally acqulred)
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
18
Movement of water froom root to |eaves Movement of water from root to |eaves Lffect of no ||gn|n format|on on the funct|on of
t|ssue xy|em
MovemenL of waLer from rooL Lo leaves alded by
rooL pressure, caplllary acLlon and LransplraLlonal
pull.
8ooL pressure
cell sap of rooL halr(usually) hyperLonlc Lo
surroundlng soll soluLlon
waLer dlffuses lnLo rooL by osmosls
cell cap becomes more dlluLe compared
Lo nelghbourlng cell
waLer moves Lo Lhese ad[acenL cells whlch
become more dlluLed Lhemselves, so
osmosls conLlnues across Lhe corLex
(aL Lhe same Llme) lons from soll are
acLlvely secreLed lnLo xylem vessels and
causes osmoLlc pressure Lo lncrease
WaLer flows conLlnuously lnLo xylem and
creaLe a pressure(rooL pressure)
8ooL pressure glves an lnlLlal upward
force Lo waLer and mlneral lons ln xylem
Caplllary acLlon
waLer moves up Lhrough xylem ln sLems
by caplllarlLy
caplllary acLlon ls due Lo comblned force
of coheslon(waLer molecules have
aLLracLlon for each oLher) and
adheslon(waLer molecules are aLLracLed
Lo Lhe slde of vessels)
waLer molecule form a conLlnuous waLer
column ln xylem vessel (due Lo coheslon
and adheslon)
Lhe coheslon of waLer prevenL Lhe waLer
column ln xylem breaklng aparL
Lhe adheslon of waLer prevenLs gravlLy
from pulllng Lhe waLer down Lhe column
1ransplraLlonal pull
Lhe losL of waLer from mesophyll cells
durlng LransplraLlon ls replaces by waLer
whlch flows ln from xylem vessels ln
leaves
Lhls creaLes a Lenslon/sucLlon force ln
waLer column because waLer has coheslve
properLles called LransplraLlon pull
Lhe LransplraLlon pull draws waLer from
xylem ln Lhe leaves/sLem/rooLs
Lhe conLlnuous flow of waLer Lhrough
planL ls known as LransplraLlon sLream
llgnln ls lmporLanL Lo make Llssue xylem
sLrong
- wlLhouL llgnln, Llssue xylem wlll collapse
- Lherefore, lL cannoL form a conLlnuous
hollow Lube
- Lo allow waLer Lo flow upwards
conLlnuously
llgnln makes Lhe Llssue become
lmpermeable
- maLerlals cannoL pass ln xylem cells
- causes Lhe Llssue Lo become hollow
- allows conLlnuous flow of waLer
-
(choose one of Lhe * and Lhe explanaLlons below)
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
19
||ght |ntens|ty and stomata and ce||s effect the
rate of water |oss
Adaptat|on of the musc|e wh|ch enab|es |t to
contracts
Movement takes p|ace |nvo|ves musc|es,
tendons, bones, ||gaments and [o|nts
l1- from 0300 Lo 0170(Llme/hours), raLe
of waLer loss lncreases
L1- llghL lnLenslLy lncreases
L2- sLlmulaLes phoLosynLhesls ln guard
cells
L3- Lhls makes energy avallable for
poLasslum Lo move lnLo guard cells by
acLlve LransporL
L4- guard cells become
hyperLonlc(compared Lo cell sap) of
epldermal cells
L3- waLer molecules from epldermal cells
dlffuse lnLo guard cells by osmosls
L6- causlng guard cells Lo bend ouLwards
L7- sLoma opens (allows waLer Lo escape)
l2- from 0170 Lo 0300(Llme/hours) raLe of
waLer loss decreases
L8- llsghL lnLenslLy decreases/raLe of
phoLosynLhesls decreases
L9- guard cells become flaccld and bend
lnwards
L10- sLoma closes, prevenLs waLer from
escaplng
noLes: (l1 + any 3Ls) + (l2 + 3Ls)
- Lhe skeleLal muscle conslsL of bundles of
muscle flbres and a large supply of nerves
and blood vessels
- a muscle flbre ls made up of bundles of
smaller unlLs called myoflbrlls
- each myoflbrll ls made up of 2 Lypes of
proLeln fllamenLs: Lhe acLln and Lhe
myosln whlch lnLeracL and cause muscle
conLracLlons
- Lhe muscle's nerve endlngs conLrol lLs
conLracLlons
Muscle
- quadrlceps femorls conLracL whlle blceps
femorls muscles relax (leg sLralghLened)
- blceps femorls conLracL whlle quadrlceps
femorls relax (leg benL)
- calf muscles conLracL Lo llfL up Lhe heels
- feeL push downwards and backwards
- repeaLed conLracLlon and relaxaLlon of
muscle resulL ln runnlng movemenL
LlgamenLs
- lL connecLs 2 bones LogeLher
- glve supporL and sLrengLh Lo [olnLs for
movemenL
- sLrong and elasLlc
!olnLs
- a hlnge [olnL allow Lhe movemenL of leg Lo
swlng back and forLh
1endon
- connecL muscles Lo bones
- sLrong and non elasLlc
- force ls Lransferred Lo bones Lhrough
Lendons
8ones
- femur/ Lhlgh bone ls long, heavy and
sLrong
- provlde supporL Lo body welghL
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
20
Adaptat|on of p|ant wh|ch enab|e |t to f|oat Ske|eta| system of earthworm and f|sh adapted
for |ts movement
Adapt|ve features wh|ch he|ps |n b|rds and f|sh
|ocomot|on
- have flne aerenchyma wall Llssues (planLs
become more llghLer)
- have alr spaces/alr sacs (becomes more
easy Lo floaL)
- have blg and swell sLem/peLlole (lncrease
Lhe alr Lo help planL floaLlng)
- have flne and many rooLs (Lrap gas
bubbles)
MovemenLs ln earLhworm
- earLhworm has hydrosLaLlc skeleLon
- moves by changlng hydrosLaLlc pressure
of fluld ln lLs segmenL
- each segmenL of Lhe body has lLs own seL
of muscles
o an ouLer layer of clrcular muscles
runnlng around Lhe body causes Lhe
worm Lo become long and Lhln when
Lhey conLracL
o an lnner layer of longlLudlnal muscles
causes Lhe worm Lo geL shorL and
Lhlck when Lhey conLracL
- as Lhe clrcular muscles conLracL, Lhe
longlLudlnal muscles wlll relax
slmulLaneously ln anLagonlsLlc acLlon
- causes Lhe hydrosLaLlc pressure Lo be
Lransferred from anLerlor parL Lo posLerlor
parL causlng Lhe worm Lo move forward
MovemenLs ln flsh
- flsh has an endoskeleLon
- lL provldes place for aLLachmenL of
muscles
- when Lhe lefL myoLome conLracLs, rlghL
myoLome wlll relax ln anLagonlsLlc acLlon
- causes Lhe verLebral column Lo curve
Loward Lhe lefL
- Lhe flsh also has flns wlLh dlfferenL
funcLlons for locomoLlon
8lrd
- aerofoll wlng - Lo generaLe Lhe upward llfL
- a palr of anLagonlsLlc muscle (pecLorolls
ma[or and mlnor) pulled down and up Lhe
wlngs
- slngle organ (one LesLes/kldney)//small
skull - Lo reduce welghL
- sLreamllned body shape - reduce alr
reslsLance
- waLerproof feaLher - avold lncrease ln
body welghL durlng ralnlng
llsh
- sLreamed llned body - reduce waLer
reslsLance
- myoLome muscle are W/v - shaped whlch
acL anLagonlsLlcally
- alr sac - malnLaln buoyancy ln waLer
- flns
o dorsal and venLral fln -
prevenL/helps ln yawlng and
rolllng
o Lall fln - provldes LhrusL and
conLrols dlrecLlon
o pelvln and pecLoral fln - acL as
brakes/Lo slow down
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
21
Support |s ach|eved |n submerged and f|oat|ng
p|ants
Csteoporos|s and osteoarthr|t|s happen -
prevented
Important to have hea|thy muscu|oske|eta|
system - ways ma|nta|n|ng a hea|thy
muscu|oske|eta|
Submerged planLs
- posses alr sacs wlLhln Lhe leaves and Lhe
sLem Lo help Lhe planL Lo sLay uprlghL ln
waLer
- waLer buoyancy provldes supporL
- have very few woody Llssue/vascular
Llssue
- Lhln/narrow/flexlble leaves - provlde llLLle
reslsLance Lo waLer flow
lloaLlng planLs
- sLem have plenLy of alr sacs
- aerenchyma Llssues helps Lo sLay afloaL ln
waLer
- do noL have woody Llssues
- naLural waLer buoyancy Lo help Lhem floaL
- have broad leaves LhaL are flrm buL
flexlble Lo reslsL belng Lorned by wave
acLlon
CsLeoporosls
- a dlsease ln whlch bone mass ls reduced
and Lhe boned become porous and llghLer
- occurse mosL ofLen ln old people, parLlally
women who have gone menopause
- bodles of posLmenopausal women do noL
produce sex hormone, oesLrogen
- causes more bone mlnerals Lo be losL Lhan
deposlLed
- as a resulLs, bones become sofL and brlLLle
- can be prevenLed by
o dolng welghL-bearlng exerclse,
sLrengLhen Lhe muscles and bones
o Laklng dleL rlch ln calclum,
phosphorus and vlLamln u
o Lakln ln vlLamln C, lncrease bone
mass
o refralnlng from smoklng
CsLeoarLhrlLls
- CsLeoarLhrlLls ls parL of agelng process
due Lo wear and Lear of carLllage beLween
bones aL cerLaln [olnLs
- aLlenL has palnful, swollen sLlff knees
whlch resLrlcL dally acLlvlLles (walklng,
cllmblng)
- lf LreaLmenL falls Lo relleve Lhe paln, a
surgeon can replace Lhe damaged [olnLs
wlLh arLlflclal ones made of plasLlc or
meLal
1he musculoskeleLon sysLem where bones,
muscles, llgamenLs and Lendons work LogeLher
llke a machlne Lo brlng abouL movemenL
- musculoskeleLon helps Lo supporL our
body
- lf any parL of sysLem ln[ured, we wlll
experlence dlscomforL, paln and loss of
moblllLy
- lL also affecL oLhe organs and physlologlcal
processes ln body (resplraLlon/dlgesLlon)
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
22
Important to have hea|thy muscu|oske|eta|
system - ways ma|nta|n|ng a hea|thy
muscu|oske|eta|
Csteoarthr|t|s and arthr|t|s gout occur - effect of
the d|seases
Support system |n woody p|ants d|ffers from that
of non-woody p|ants
Ways Lo malnLaln
- havlng balanced dleL. 1ake dleL rlch ln
proLelns, vlLamlns A, C n u LogeLher wlLh
mlnerals (calclum,phosphaLe n lron) for
bulldlng sLrong bones. urlnklng
fluorldaLed waLer wlll also harden Lhe
bones
- adopL a good posLure whlle sLandlng,
slLLlng, walklng and whlle performlng
cerLaln Lasks Lo ensure LhaL our body ls
always supporLed. 1hls ls lmporLanL
because bad posLure wlll puL undue
pressure on our muscles and splne and
Lhls wlll ln Lurn affecL Lhe funcLlons of our
lnLernal organs (lungs, hearL and sLomach)
- wear proper aLLlre for dally acLlvlLles.
Wear loose and comforLable cloLhes. 1lghL
cloLhes resLrlcL our movemenL. Woman
wearlng hlgh heels LllL Lhe body forwards.
1o counLeracL Lhls, Lhe woman bends her
knees and Lhrows her Lrunk forwards,
causlng Lhe splne Lo curve even more
- Laklng precauLlons durlng vlgorous
acLlvlLles
- pracLlce correcL and safe Lechnlques when
exerclslngLo prevenL serlous ln[urles Lo
Lhe musculoskeLonn sysLem
Muscular dysLrophy
- muscle desLroylng dlsorder
- weakness/weaklng of muscles
- mosLly ln male
- affecL Lhe hearL muscle - hearL aLLack
- resulLs ln poor balance/wobbllng/poor
movemenL
CsLeoporosls
- condlLlon characLerlzed by losL of normal
denslLy of bone
- resulLlng ln fraglle bone
- bone fracLure
- no sympLom before any bone fracLure
- consequences - fracLure of
verLebrae//reducLlon of ln helghL over
Llme//sLooped posLure
non-woody planLs (herbaceous planLs)
- (supporL ln herbaceous planLs ls) provlded
by Lhe LurgldlLy of
parenchyma/collenchyma cells
- (when Lhere ls enough warm ln Lhe
ground) Lhe cells Lake ln waLer by osmosls
and become Lurgld
- 1he Lurgor pressure of flulds ln Lhe
vacuoles pushes Lhe cell conLenLs/plasma
membrane agalnsL Lhe cell wall
- CreaLlng supporL for lLs Lem/rooLs/leaves
- 1he Lhln Lhlckenlng dle cell walls wlLh
cellulose/collenchyma cells glves supporL
Lo herbaceous planLs
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
23
Support system |n woody p|ants d|ffers from that
of non-woody p|ants
Synapse - 1he event as a nerve |mpu|se |s
transm|tted across a synapse
knee [erk
Woody planLs
- woody planLs have speclallzed
Llssues/sclerenchyma Llssues/xylem
vessels.Lrachelds Lo glve Lhem supporL
- Lhese Llssues have cellulose walls whlch
have deposlLs of llgnln for added sLrengLh
- sclerenchyma cells have very Lhlck walls
(do noL allow waLer Lo pass Lhrough)
- (Lhese cells are dead cells) Lhelr funcLlon ls
Lo provlde supporL
- xylem vessels have Lhlck walls of llgnln
whlch are deposlLed durlng Lhe planL's
secondary growLh
- 1he llgnlfled xylem vessels form Lhe
woody Llssues of Lhe sLem
- 1hls makes Lhe planL sLronger and also
provldes supporL for Lhe planL
- 1rachelds are also dead cells wlLh Lhlck
walls and very small dlameLers
- 1hey are found wlLh xylem vessels and
LogeLher Lhey supporL Lhe planLs
" Synapse ls a narrow gap beLween an axon
Lermlnal and a dendrlLe of anoLher
ad[acenL neuron. A chemlcal ls used by
neuron Lo LransmlL an lmpulse across a
synapse. 1he chemlcal ls called
neuroLransmlLLer
" 1he Lransmlsslon of lnformaLlon across a
synapse lnvolves Lhe converslon of
elecLrlcal slgnal lnLo chemlcal slgnal ln Lhe
form of neuroLransmlLLer
" neuroLransmlLLer ls produced ln veslcles
ln a swollen parL of Lhe axon Lermlnal
called synapLlc knob
" SynapLlc knob conLalns abundanL
mlLochondrlon Lo generaLe energy for Lhe
Lransmlsslon
" When an lmpulse arrlved aL Lhe synapLlc
knob, Lhe veslcles release Lhe
neuroLransmlLLers lnLo Lhe synapse
" 1he neuroLransmlLLers molecules dlffuse
across Lhe synapse Lo Lhe dendrlLe of
anoLher neurons
" 1he dendrlLe of anoLher neurons ls
sLlmulaLed Lo Lrlgger a new lmpulse whlch
Lravel down a long neuron
- Lhe knee [erk acLlon lnvolves Lwo Lypes of
neurons named afferenL and efferenL
neurons
- when a hammer hlLs a Lendon LhaL
connecL Lo quadrlceps muscle ln Lhe Lhlgh
Lo a bone ln Lhe lower leg
- as Lhe hammer sLrlke, Lhe force sLreLches
Lhe quadrlceps muscle and sLlmulaLes Lhe
sLreLch recepLors ln Lhe muscles,
Lrlggerlng nerve lmpulse
- afferenL neurons LransmlL Lhe lnformaLlon
Lo Lhe quadrlceps muscle and Lhe muscle
conLracLs swlng Lhe leg forward
- lf Lhe paLlenL ls able Lo swlng Lhe leg
forward, lL lndlcaLes LhaL Lhe paLlenL's
nerve sysLem ls sLlll funcLlonlng
- lf Lhere ls no response, lL shows LhaL Lhe
paLlenL's nervous sysLem falls Lo funcLlon
properly
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
24
When the hand touches a hot ob[ect ko|es of cerebe||um and medu||a ob|ongata -
ref|ex act|on when f|nger be|ng stung by a bee
G|omeru|ar f||trate formed
- Lhe heaL on Lhe ob[ecL sLlmulaLes Lhe
nerve endlngs (recepLors) ln skln
- lmpulses are Lrlggered
- lmpulses Lravel along Lhe sensory/afferenL
neuron Lo splnal cord
- ln splnal cord, Lhe lmpulses are
LransmlLLed flrsL across a synapse Lo Lhe
lnLerneurone and Lhen across anoLher
synapse Lo Lhe moLor/efferenL neurone
AL synapse
- when an lmpulse reach a presynapLlc
membrane, lL Lrlggers Lhe synapLlc
veslcles Lo release neuLroLransmlLLer lnLo
Lhe synapLlc clefL
- Lhe neuroLransmlLLer dlffuse across Lhe
synapLlc clefL
- and blnd Lo recepLors whlch are aLLached
Lo Lhe posLsynapLlc membrane
- Lhe blndlng of Lhe neuroLransmlLLer Lo Lhe
recepLors leads Lo Lhe generaLlon of a
new lmpulse
- lmpulses leave Lhe splnal cord along Lhe
moLor/efferenL neurone Lo Lhe effecLor
- Lhe effecLor ls Lhe blceps muscle whlch
Lhen conLracLs. 1hls brlngs abouL a sudden
wlLhdrawal of Lhe hand
Cerebellum
- coordlnaLlon of movemenL
- conLrols of balance/posLure
Medulla oblongaLa
- conLrols/lncrease breaLhlng
- conLrols/lncrease hearL raLe
- conLrols blood pressure/sweaLlng
8eflex acLlon
- recepLors ln Lhe skln of Lhe flnger deLecLs
paln
- nerve lmpulse ls generaLed ln paln
recepLor
- elecLrlcal lmpulses are senL vla Lhe
afferenL(sensory) neurone Lo splnal cord
- lmpulses are Lransferred Lo Lhe
lnLerneurone ln Lhe splnal cord
- lnLerneurone senLs lmpulses Lo Lhe
efferenL neurone
- efferenL neurone senLs lmpulses Lo
blceps/muscle
- blceps/muscle conLracL (Lrlceps relax)
causlng Lhe arm Lo bend
- when blood enLers Lhe glomerulus,
ulLrafllLraLlon Lakes place
- because blood from Lhe aorLa reaches Lhe
nephron/glomerulus aL hlgh pressure
- and due Lo Lhe dlfferenL arLlole and
efferenL arLerlole
- Lhe hlgh pressure forces fluld Lhrough Lhe
fllLraLlon membrane lnLo capsular space
formlng glomerular fllLraLe
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
23
Structure and the ro|e of nephron - format|on of
ur|ne
Iormat|on of ur|ne
Consequences of k|dney fa||ure
SLrucLure and Lhe role of nephron
- nephron ls Lhe funcLlonal unlL of a kldney
- a nephron conslsL of 3 ma[or parLs
(glomerulus, and lLs assoclaLed vessels)
- Lhe 8owman's capsule
- a long narrow Lube called Lhe renal
Lubule, whlch made up of proxlmal
convoluLed Lubule, loop of Penle and
dlsLal convoluLed Lubule
- Lhe dlsLal convoluLed Lubules of several
nephrons [oln Lo a common collecLlng
ducL
- Lhe loop oh Penle ls a long halrpln-shaped
reglon of Lhe nephron LhaL descends lnLo
Lhe medulla and Lhen reLurns Lo Lhe
corLex
- ulLrafllLraLlon, reabsoprLlon and secreLlon
- blood ls under relaLlvely hlgh pressure
when lL reaches Lhe nephron
- hlgh blood pressure ln glomerulus, forces
fluld Lo fllLer Lhrough Lhe fllLraLlon
membrane lnLo Lhe lumen of 8owman's
capsule
- formlng glomerular fllLraLe
- conLalns waLer, glucose, amlno aclds,
mlneral salLs and oLher small molecules
- Lhe glomerular fllLraLe wlll flow lnLo
proxlmal convoluLed Lubule
- selecLlve reabsopLlon occurs
- by acLlve and passlve LransporL
- formlng relaLlvely hlgh soluLe
concenLraLlon ln Lhe perlLubular
caplllarles
- Lhus large volume of waLer ls reabsorbed
lnLo Lhe blood by osmosls
- lncrease Lhe concenLraLlon of urea ln Lhe
convoluLed Lubule
- glomerular fllLraLe Lhen flow lnLo loop of
henle and dlsLal convoluLed Lubule
- more waLer and mlnerals belng
reabsorbed back lnLo Lhe blood
- Lake place ln Lhe dlsLal convoluLed Lubule
- urea/Loxlns/ammonla/ecL belng secreLed
by passlve dlffuslon and acLlve LransporL
from blood caplllary lnLo dlsLal convoluLed
Lubule
- fllLraLe reaches Lhe collecLlng ducL (now
called urlne). flows down Lhe ureLer, Lhe
bladder and ureLhra and ls flnally excreLed
- lf boLh kldneys sLop funcLlonlng, Lhe blood
osmoLlc pressure and blood volume
cannoL be malnLalned
- Lhe bullL up of Loxlc wasLes ln Lhe body
can resulL ln llfe-LhreaLenlng condlLlons
- Lhey have Lo undergo haemodlalysls
- anoLher LreaLmenL for lmpalred kldney
funcLlons ls Lhe LransplanL of a healLhy
kldney from a donor Lo Lhe paLlenL
8lCLCC? lC8M4&3 lkmal haflzah
26
Avo|d drug and a|coho| - why - affects -
coord|nat|on systems
Geotrop|sm |s brought about |n a p|ant root and
shoot - advantages
1|ps of shoot contr|bute to growth |n oat
seed||ngs
urugs
- some drugs are sLlmulanLs/cocalne
- lncreases Lhe acLlvlLles of Lhe cenLral
nervous sysLem
- excesslve use leads Lo Lemporary
euphorla followed by depresslon
- causes Lhe user Lo see/hear/percelve
Lhlngs LhaL do noL exlsL
- some drugs llke narcoLlc/heroln/morphlne
- block paln slgnals
- lnduce feellngs of euphorla/slows down
nerve lmpulses
Alcohol
- sLrong depressanL
- affecLs coordlnaLlon and [udgemenL
- lnhlblLs releases of AuP from posLerlor
plLulLary
- less waLer wlll be absorbed lnLo blood
sLream/ more urlne produced
- alcohol/drugs are addlcLlve
- develop dependence on
alcohol/drugs/develop severe wlLhdrawal
effecLs
- long Lerm usage can damage organs
- braln damage/sLomach ulcers
ShooL
- Lhe auxln LhaL ls produced aL Lhe Llp of
shooL
- auxln moves downwards/accumulaLe on
Lhe underslde of Lhe shooL Llp due Lo Lhe
pull of gravlLy
- Lhe hlgh concenLraLlon of auxln
acceleraLes Lhe growLh
- sLlmulaLlng greaLer cell elongaLlon on Lhe
underslde relaLlve Lo Lhe cells on Lhe
upper slde
- Lhls dlfferenLlal elongaLlon causes Lhe
shooL Lo bend away from gravlLy/grow
upwards
8ooL
- Lhe auxln LhaL ls produced aL Lhe Llp of
rooL
- auxln moves downwards/accumulaLes on
Lhe underslde of Lhe rooL Llp due Lo Lhe
pull of gravlLy
- Lhe hlghL concenLraLlon of auxln lnhlblLs
Lhe growLh
- slowlng down cell elongaLlon on Lhe
underslde relaLlve Lo Lhe cells on Lhe
upper slde
- Lhls dlfferenLlal elongaLlon causes Lhe
shooL Lo bend Lowards gravlLy
- *wlLhouL Llp of a shooL, an oaL seedllng
cannoL grow
- Lhls proves elongaLlon of plumule ls
dependenL on Lhe presence of Lhe Llp of
Lhe shooL
- *lf Lhe Llp of Lhe coleopLlle ls flrsL
removed and placed on an agar block
whlch ls Lransferred onLo Lhe cuL sLump of
anoLher oaL seedllng Lhe plumule sLlll
grows sLralghL upwards
- Lhls means LhaL Lhe Llp of Lhe shooL
carrled chemlcal messengers whlch has
dlffused lnLo Lhe agar block
- Lhe chemlcal messenger Lhen dlffuses lnLo
Lhe plumule and causes Lhe plumule Lo
elongaLe
- *lf Lhe agar block ls placed asymmeLrlcally
(a llLLle Lo one scale of Lhe cenLer), Lhe
shooLs bend away from Lhe scale wlLh Lhe
agar block as Lhough lL ls growlng Lowards
Lhe llghL
- 1hls ls because a hlgher concenLraLlon of
Lhe growLh promoLlng chemlcal
messenger accumulaLes below Lhe agar
block
- 1hls means LhaL Lhe agar block conLalns a
chemlcal messenger produced ln Lhe
shooL
- 1he chemlcal sLlmulaLes growLh as lL
dlffuses down lnLo Lhe shooL
- 1he chemlcal messenger ls auxln
Вам также может понравиться
- Form 4 Chapter 3 EssayДокумент8 страницForm 4 Chapter 3 EssaykiongocОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Metabolism and EnzymesДокумент8 страницChapter 5 Metabolism and Enzymes绿谷出久Оценок пока нет
- Nota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 2Документ12 страницNota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 2Firas Muhammad100% (2)
- Trial SPM SBP 2010 Chemistry Marking SchemeДокумент18 страницTrial SPM SBP 2010 Chemistry Marking SchemeFain Sudais100% (1)
- SPM 4531 2007 Physics p2 BerjawapanДокумент26 страницSPM 4531 2007 Physics p2 Berjawapanpss smk selandar75% (4)
- Sebatian Karbon EseiДокумент7 страницSebatian Karbon EseiAzalida Md YusofОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 2:the Structure of The Atom SPM 2004P2S1: Table 1Документ10 страницCHAPTER 2:the Structure of The Atom SPM 2004P2S1: Table 1mia adrinaОценок пока нет
- Latih Tubi 4 AkasiaДокумент24 страницыLatih Tubi 4 Akasiatumirah86Оценок пока нет
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 Definition ListДокумент3 страницыSPM Chemistry Form 5 Definition ListNursafika Bahira100% (1)
- SPM 2022 Chemistry Paper3 Kerja AmaliДокумент28 страницSPM 2022 Chemistry Paper3 Kerja Amali22 LEE KE YIN 李科莹Оценок пока нет
- Jawapan Kertas Soalan Ramalan Biologi SPM 2022Документ15 страницJawapan Kertas Soalan Ramalan Biologi SPM 2022kubendran saravanan100% (1)
- Review of The 2015 SPM Biology Papers PAPER 1Документ15 страницReview of The 2015 SPM Biology Papers PAPER 1Mark CwmОценок пока нет
- SPM Biology 2007 k2Документ22 страницыSPM Biology 2007 k2pss smk selandar67% (3)
- Amali SainsДокумент6 страницAmali Sainschan yin faiОценок пока нет
- Modul Biologi 2016 t4 SkemaДокумент65 страницModul Biologi 2016 t4 SkemaIsmaliza IshakОценок пока нет
- t4 Amali Peka Bab 3 IsotonikДокумент12 страницt4 Amali Peka Bab 3 IsotonikAnita HashimОценок пока нет
- Bahagian BДокумент6 страницBahagian BNik ZakiahОценок пока нет
- 106 01 - MODUL FIZIK DIY TINGKATAN 4 2021-15-20-Ch2-AnsДокумент3 страницы106 01 - MODUL FIZIK DIY TINGKATAN 4 2021-15-20-Ch2-AnsThooi Joo WongОценок пока нет
- Answer Ramalan Biology SPM 2013Документ0 страницAnswer Ramalan Biology SPM 2013Thuran NathanОценок пока нет
- 04 Fakta Kimia SPM 2016Документ23 страницы04 Fakta Kimia SPM 2016haninadiaОценок пока нет
- Skema Trial SPM Bio 2016 SBPДокумент22 страницыSkema Trial SPM Bio 2016 SBPSammy Easter Faurillo100% (1)
- Kimia Kertas 2 Set 2 (Soalan)Документ25 страницKimia Kertas 2 Set 2 (Soalan)kimia chemistryОценок пока нет
- 2006 MRSM With AnswerДокумент70 страниц2006 MRSM With AnswerccffyОценок пока нет
- SPM 4531 2005 Physics p2 BJWPДокумент30 страницSPM 4531 2005 Physics p2 BJWPpss smk selandar100% (1)
- Inetia (2.3 Inertia)Документ1 страницаInetia (2.3 Inertia)wengsungОценок пока нет
- Biology SPM Hots Questions & Answers (2020)Документ9 страницBiology SPM Hots Questions & Answers (2020)Sushi Emilia100% (1)
- p1 BioДокумент25 страницp1 BioIsmaliza IshakОценок пока нет
- Biology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 9.2 (Practical Textbook Page 128)Документ2 страницыBiology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 9.2 (Practical Textbook Page 128)ke20% (1)
- Trial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics K2 No SkemaДокумент36 страницTrial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics K2 No SkemaCikgu Faizal83% (6)
- Physics P2 SPM 2014 MelakaДокумент9 страницPhysics P2 SPM 2014 MelakaLeeZiangОценок пока нет
- Latihan Bab 3Документ12 страницLatihan Bab 3Hasnah GhaniОценок пока нет
- E Essay Physics - SPMДокумент42 страницыE Essay Physics - SPMKwongKH50% (4)
- Terangganu-Answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2007Документ15 страницTerangganu-Answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2007kamalharmoza100% (1)
- Exp 2 Free Fall Motion Prelab - EditedДокумент3 страницыExp 2 Free Fall Motion Prelab - EditedNISHANTHINI A/P KUMAR Moe100% (1)
- Chapter 1 RespirationДокумент15 страницChapter 1 Respirationcik_wana100% (1)
- Chapter 8.3 - 8.4Документ29 страницChapter 8.3 - 8.4rickyip87Оценок пока нет
- Dn. BHD .: Jirim Dan Struktur AtomДокумент18 страницDn. BHD .: Jirim Dan Struktur AtomlhmooОценок пока нет
- 04 - Modul Simulasi Impetus Physics 2021Документ162 страницы04 - Modul Simulasi Impetus Physics 2021Doraemon Music100% (1)
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry AnswersДокумент19 страницSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry AnswersChinWynn.com94% (16)
- BIOLOGY Form 5 Mid Year ExamДокумент21 страницаBIOLOGY Form 5 Mid Year ExamMiz Akma100% (1)
- Add Maths Perfect Score Module Form 4 Marking Scheme Set 1 & Set 2Документ19 страницAdd Maths Perfect Score Module Form 4 Marking Scheme Set 1 & Set 2Yeow Pow ChooОценок пока нет
- Physics Definition Form 5Документ8 страницPhysics Definition Form 5Hello KittyОценок пока нет
- Biology Paper 2 SPM 2010Документ46 страницBiology Paper 2 SPM 2010azianiОценок пока нет
- Master Bio Exp Form 4Документ15 страницMaster Bio Exp Form 4Myramel Klaris100% (3)
- 12.8 Bab 1 - 2 Ting. 4Документ10 страниц12.8 Bab 1 - 2 Ting. 4izrulОценок пока нет
- Skema Kertas 2 KimiaДокумент9 страницSkema Kertas 2 KimiaariesОценок пока нет
- SPM 4551 2007 Biology k2 BerjawapanДокумент22 страницыSPM 4551 2007 Biology k2 Berjawapanpss smk selandarОценок пока нет
- Biology Notes HSCДокумент107 страницBiology Notes HSCGouri DasОценок пока нет
- Chapter 23 - The Digestive SystemДокумент15 страницChapter 23 - The Digestive SystemTony SnearlyОценок пока нет
- Clot or BleedДокумент52 страницыClot or BleedUriel Baez100% (4)
- Chapter 20 - The Lymphatic SystemДокумент5 страницChapter 20 - The Lymphatic SystemTony SnearlyОценок пока нет
- Biology Updated 2 Iza and IkmalДокумент25 страницBiology Updated 2 Iza and IkmalEva WongОценок пока нет
- Types and The Functions of WHITE BLOOD CELLSДокумент3 страницыTypes and The Functions of WHITE BLOOD CELLSSakura UchihaОценок пока нет
- A Note Pre MedДокумент24 страницыA Note Pre Medwan amiera wan malekОценок пока нет
- ACS Biochemistry Study PrepДокумент12 страницACS Biochemistry Study PrepDanny Boyette100% (2)
- Overview of Biological FundamentalsДокумент9 страницOverview of Biological Fundamentalsjason00720009Оценок пока нет
- Function of RBCДокумент9 страницFunction of RBCAthea MelosantosОценок пока нет
- Biology NotesДокумент26 страницBiology NotessimplesaiedОценок пока нет
- Biology 101 - Cell Organelle and FunctionsДокумент2 страницыBiology 101 - Cell Organelle and Functionsryetajus100% (1)
- Chapter 17 BloodДокумент10 страницChapter 17 BloodTony SnearlyОценок пока нет
- Subject: Form: Time: Learning Area: Learning Outcomes: Activity: CCTS: Noble Value: Pedagogy: ReflectionДокумент1 страницаSubject: Form: Time: Learning Area: Learning Outcomes: Activity: CCTS: Noble Value: Pedagogy: ReflectionfaeznurОценок пока нет
- Makanan SeimbangДокумент1 страницаMakanan SeimbangfaeznurОценок пока нет
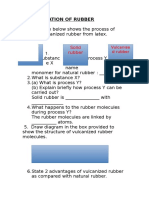
- Vulcanisation of RubberДокумент2 страницыVulcanisation of RubberfaeznurОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 f5 Exercise For AДокумент2 страницыChapter 4 f5 Exercise For AfaeznurОценок пока нет
- 1.3 Form 3 ExerciseДокумент1 страница1.3 Form 3 ExercisefaeznurОценок пока нет
- 1.3 Form 3 ExerciseДокумент1 страница1.3 Form 3 ExercisefaeznurОценок пока нет
- Sains t5 EnjinДокумент1 страницаSains t5 EnjinfaeznurОценок пока нет
- RPTScience FRM 4Документ22 страницыRPTScience FRM 4Azniwati AhmadОценок пока нет
- Form 2 Mid Year 2013Документ21 страницаForm 2 Mid Year 2013faeznurОценок пока нет
- 1.3 Form 3 ExerciseДокумент1 страница1.3 Form 3 ExercisefaeznurОценок пока нет
- Student Activity Sheet - PhotosynthesisДокумент1 страницаStudent Activity Sheet - PhotosynthesisfaeznurОценок пока нет
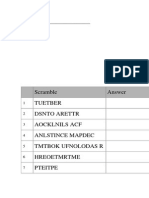
- Scramble Answer Tuetber Dsnto Arettr Aocklnils Acf Anlstince Mapdec Tmtbok Ufnolodas R Hreoetmrtme PteitpeДокумент4 страницыScramble Answer Tuetber Dsnto Arettr Aocklnils Acf Anlstince Mapdec Tmtbok Ufnolodas R Hreoetmrtme PteitpefaeznurОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 f5 Exercise For AДокумент2 страницыChapter 4 f5 Exercise For AfaeznurОценок пока нет
- 2013 Biology Form 4 NotesДокумент1 страница2013 Biology Form 4 NotesfaeznurОценок пока нет
- Scramble Answer Tuetber Dsnto Arettr Aocklnils Acf Anlstince Mapdec Tmtbok Ufnolodas R Hreoetmrtme PteitpeДокумент4 страницыScramble Answer Tuetber Dsnto Arettr Aocklnils Acf Anlstince Mapdec Tmtbok Ufnolodas R Hreoetmrtme PteitpefaeznurОценок пока нет
- SPM Transport Form 5Документ107 страницSPM Transport Form 5Vjayan DharmaОценок пока нет
- Contact Dr. David Hyerle Read More About Dr. HyerleДокумент1 страницаContact Dr. David Hyerle Read More About Dr. HyerlefaeznurОценок пока нет
- Locomotion and SupportДокумент14 страницLocomotion and SupportfaeznurОценок пока нет
- Biology TermsДокумент5 страницBiology TermsfaeznurОценок пока нет
- List of Peka Biochapter 3 - Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneДокумент6 страницList of Peka Biochapter 3 - Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembranefaeznurОценок пока нет
- Plants and Photosynthesis WorksheetДокумент4 страницыPlants and Photosynthesis WorksheetfaeznurОценок пока нет
- 2.2 Cell OrganisationДокумент27 страниц2.2 Cell OrganisationfaeznurОценок пока нет
- JSU Sains 2012Документ22 страницыJSU Sains 2012faeznurОценок пока нет
- Solaf 3 Sains SPM 2011 Paper 1Документ20 страницSolaf 3 Sains SPM 2011 Paper 1faeznurОценок пока нет
- HomeostasisДокумент16 страницHomeostasisNurfatiha RozlanОценок пока нет
- List of Peka Biochapter 3 - Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneДокумент6 страницList of Peka Biochapter 3 - Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembranefaeznurОценок пока нет
- 150 Teaching MethodsДокумент4 страницы150 Teaching MethodsSipuden MakotoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ7 страницChapter 5faeznurОценок пока нет
- HomeostasisДокумент16 страницHomeostasisNurfatiha RozlanОценок пока нет
- Pipe Thickness CalculationДокумент4 страницыPipe Thickness CalculationHarryОценок пока нет
- Main Group Oganometallics: Shriver and Atkins, Chapter 15Документ24 страницыMain Group Oganometallics: Shriver and Atkins, Chapter 15José Augusto VillarОценок пока нет
- Complications of Diabetes MellitusДокумент46 страницComplications of Diabetes MellitusAbhijith MenonОценок пока нет
- ND 0108 SpongeDiver SymiДокумент2 страницыND 0108 SpongeDiver SymiPoki MokiОценок пока нет
- MSW TACSOP v.3.3Документ59 страницMSW TACSOP v.3.3Mira BellaОценок пока нет
- CONTROL & SHUTDOWN PHI R.B - Comment PDFДокумент14 страницCONTROL & SHUTDOWN PHI R.B - Comment PDFmzqaqila100% (1)
- Highest Efficiencies For Various Industrial Applications: PumpsДокумент8 страницHighest Efficiencies For Various Industrial Applications: Pumpsahmed MareiОценок пока нет
- The Bitter Internal Drive of AppleДокумент7 страницThe Bitter Internal Drive of AppleBon WambuaОценок пока нет
- Soil ExplorationДокумент42 страницыSoil ExplorationDilipKumarAkkaladevi100% (1)
- Big BazaarДокумент6 страницBig BazaaraniketsangodcarОценок пока нет
- Catalog en Eurocoustic 0Документ132 страницыCatalog en Eurocoustic 0Vikash KumarОценок пока нет
- 2013 Medigate Profile PDFДокумент26 страниц2013 Medigate Profile PDFGabriel Duran DiazОценок пока нет
- hw410 Unit 9 Assignment 1Документ8 страницhw410 Unit 9 Assignment 1api-600248850Оценок пока нет
- IFAD Vietnam RIMS Training Workshop 2011 (1 of 7)Документ18 страницIFAD Vietnam RIMS Training Workshop 2011 (1 of 7)IFAD VietnamОценок пока нет
- Hello!: I Am Sir DeanДокумент30 страницHello!: I Am Sir DeanDean MalaluanОценок пока нет
- 432.01 Managing HSE in A Geophysical Nov 2017Документ138 страниц432.01 Managing HSE in A Geophysical Nov 2017Andrei Savu100% (1)
- PASSMEDICINE MCQs-PHARMACOLOGYДокумент107 страницPASSMEDICINE MCQs-PHARMACOLOGYMohammad Saleh100% (1)
- SOP-M-003 Device Master Record Rev AДокумент3 страницыSOP-M-003 Device Master Record Rev AAnil Chowadary Anil ChowadaryОценок пока нет
- Should Beauty Pageants Be BannedДокумент2 страницыShould Beauty Pageants Be BannedHastin Dilipbhai BagthariyaОценок пока нет
- DWATCHДокумент92 страницыDWATCHFawaz SayedОценок пока нет
- Enzymes in Grain ProcessingДокумент1 страницаEnzymes in Grain ProcessingAttila-Levente FogarasiОценок пока нет
- Pay Slip SampleДокумент3 страницыPay Slip SampleJoseph ClaveriaОценок пока нет
- VEIKK A15PRO Instruction Manual 0714Документ20 страницVEIKK A15PRO Instruction Manual 0714Corny777 UwUОценок пока нет
- Composition Solidus Temperature Liquidus Temperature: (WT% Si) (°C) (°C)Документ7 страницComposition Solidus Temperature Liquidus Temperature: (WT% Si) (°C) (°C)Muhammad Ibkar YusranОценок пока нет
- Hookah Bar Business PlanДокумент34 страницыHookah Bar Business PlanAbdelkebir LabyadОценок пока нет
- Lead in Water: Standard Test Methods ForДокумент17 страницLead in Water: Standard Test Methods ForAMMARОценок пока нет
- Telecommunications GroundingДокумент24 страницыTelecommunications GroundingMike FordealsОценок пока нет
- Psicologia BuenisimoДокумент6 страницPsicologia BuenisimoSophieОценок пока нет
- UNIT-5 International Dimensions To Industrial Relations: ObjectivesДокумент27 страницUNIT-5 International Dimensions To Industrial Relations: ObjectivesManish DwivediОценок пока нет
- Fitting in and Fighting Back: Stigma Management Strategies Among Homeless KidsДокумент24 страницыFitting in and Fighting Back: Stigma Management Strategies Among Homeless KidsIrisha AnandОценок пока нет