Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Faraday - Ee.emu - Edu.tr Eeng211 Exam F 09 10 Final Solutions
Загружено:
T FОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Faraday - Ee.emu - Edu.tr Eeng211 Exam F 09 10 Final Solutions
Загружено:
T FАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Faculty of Engineering
ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
EENG115/ I NFE115 I ntroduction to Logic Design
EENG211/ I NFE211 Digital Logic Design I
Fall 2009-10
Instructors:
M. K. Uygurolu
H. Demirel
Final EXAMINATION
Jan. 13, 2010
Duration : 120 minutes
Number of Problems: 8
Good Luck
STUDENTS
NUMBER
NAME
SURNAME
GROUP NO
Problem Achieved Maximum
1 10
2 10
3 15
4 15
5 10
6 15
7 15
8 15
TOTAL 105
Introduction to Logic Design/ Digital Logic Design I - Final Examination
Question 1 (10 points)
Answer the following questions regarding Boolean algebra.
a) Minimize the function F(w,x,y,z) using algebraic modifications. Show the result as a
sum of products with a minimum number of literals. (6 points)
F(w,x,y,z) = (y+wy(xz+xz))z + (xy+(x+y)+z)+ y(z+wx(w+z))
=[y` +wy`x]z + (xy` +x`y` + z`)` + y(z + wx`z)
= y`z + wxy`z + ( y` + z` )` + y (z)
= y`z ( 1 + wx) + yz + yz
= y`z + yz
= z
Algebraically minimized F =z
b) Convert the original function F(w,x,y,z) from part a) to a sum-of-product form and
minimize it using Karnaugh map. Compare the results. (4 points)
F(w,x,y,z) =(y+wy(xz+xz))z +(xy+(x+y)+z)+y(z+wx(w+z))
=[y` +wy`x]z +(xy` +x`y` +z`)` +y(z +wx`z)
=y`z +wy`xz +yz +wx`yz
K-map minimized F =_________________
00 01 11 10
00
01
11
10
z
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
z
M. K. Uygurolu, H. Demirel Jan. 13, 2010
Introduction to Logic Design/ Digital Logic Design I - Final Examination
Question 2 (10 points):
Answer the following questions regarding combinational logic.
a) Determine the outputs functions A and B as sums of minterms. You may use any
process to determine the result, but show your work. (7 points)
x y z A B A B
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1
I
0
=z I
0
=0
1 0
0 1 0 1 0
0 1 1
I
1
=z I
1
=z
0 1
1 0 0 1 0
1 0 1
I
2
=z I
2
=z
0 1
1 1 0 0 1
1 1 1
I
3
=z I
3
=1
1 1
( )
( )
1,2,4,7
3,5,6,7
A
B
=
=
b) The circuit shown in a) has the functionality of a commonly used arithmetic
component. What does the circuit do and what are other names for A and B?
(3 points)
The circuit implements a FULL ADDER
A is the SUM
B is the CARRY
M. K. Uygurolu, H. Demirel Jan. 13, 2010
Introduction to Logic Design/ Digital Logic Design I - Final Examination
Question 3 (15 points):
Design a magnitude comparator circuit for 2-bit binary numbers A=A1A0 and B=B1B0. The
outputs are F, G, and H, where F is 1 if A>B, G is 1 if A=B, and H is 1 if A<B.
a) Fill in the truth table for the three outputs of the comparator and determine their
function as sum of minterms. (9 points)
A
1
A
0
B
1
B
0
F(A>B) G(A=B) H(A<B)
0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 1
0 0 1 0 0 0 1
0 0 1 1 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 1 0 0
0 1 0 1 0 1 0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1
0 1 1 1 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 1 0 0
1 0 1 0 0 1 0
1 0 1 1 0 0 1
1 1 0 0 1 0 0
1 1 0 1 1 0 0
1 1 1 0 1 0 0
1 1 1 1 0 1 0
( )
( )
( )
4,8,9,12,13,14
0,5,10,15
1,2,3,6,7,11
F
G
H
=
=
=
M. K. Uygurolu, H. Demirel Jan. 13, 2010
Introduction to Logic Design/ Digital Logic Design I - Final Examination
b) Implement your comparator design using a 4-to-16 line decoder shown below.
(6 points)
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
8
D
9
D
10
D
11
D
12
D
13
D
14
D
15
A
1
A
0
B
0
B
1
I
0
I
1
I
2
I
3
F
G
H
M. K. Uygurolu, H. Demirel Jan. 13, 2010
Introduction to Logic Design/ Digital Logic Design I - Final Examination
Question 4 (15 points):
Answer the following questions regarding combinational logic design. Design a circuit
(combinational, not sequential) that takes an unsigned 2-bit number, X=X1X0, and
computes the square of that number, Y=X
2
a) How many outputs do you need? (2 points)
4
b) Show the truth table for this combinational circuit. Name the outputs Y
n
, , Y
1
, Y
0
(with n depending on what you have determined in a). (10 points)
X
1
X
0
Y
3
Y
2
Y
1
Y
0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 1 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 1
c) Determine the minimized output functions. (3 points)
3 1
2 1
1
0 0
0
Y X X
Y X X
Y
Y X
0
0
=
=
=
=
M. K. Uygurolu, H. Demirel Jan. 13, 2010
Introduction to Logic Design/ Digital Logic Design I - Final Examination
Question 5 (10 points):
Design a 4-to-16-line decoder by using the minimum number of 2-to-4-line decoders. The
2-to-4-line decoders have an enable input (1=enabled) and the designed 4-to-16-line
decoder does not have an enable. Name the inputs A0A3 and the outputs D0D15. Do
not draw the internal circuit diagrams for the decoders.
M. K. Uygurolu, H. Demirel Jan. 13, 2010
Introduction to Logic Design/ Digital Logic Design I - Final Examination
Question 6 (15 points):
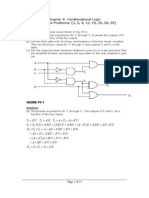
Derive the state table and the state diagram of the sequential circuit shown below.
Explain the function that the circuit performs.
( )
'
A
B
C
T B C x
T C x
T x
= +
= +
=
PS in NS FF in
A B C x A B C T
A
T
B
T
C
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0
0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1
0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0
0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1
0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1
0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0
1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1
1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0
1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1
1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0
1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1
1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0
When x=0, it counts one by one and
when x=1, it counts two by two.
M. K. Uygurolu, H. Demirel Jan. 13, 2010
Introduction to Logic Design/ Digital Logic Design I - Final Examination
Question 7 (15 points):
Use J K flip flops to design a counter with the repeated binary sequence:0,1,2.
The circuit is to be designed by treating the unused states as dont care conditions.
Analyze the circuit obtained from the design to determine the effect of the unused states.
PS NS FF Inputs
A B A B J
A
K
A
J
B
K
B
0 0 0 1 0 X 1 X
0 1 1 0 1 X X 1
1 0 0 0 X 1 0 X
1 1 X X X X
Analysis of circuit for unused state:
M. K. Uygurolu, H. Demirel Jan. 13, 2010
Introduction to Logic Design/ Digital Logic Design I - Final Examination
PS NS FF Inputs
A B A B J
A
K
A
J
B
K
B
1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1
M. K. Uygurolu, H. Demirel Jan. 13, 2010
Introduction to Logic Design/ Digital Logic Design I - Final Examination
Question 8 (15 points):
Given the state diagram below, generate the state table and design a sequential circuit
using D flip fops.
PS In NS Out
A B x A B y
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 1 1 0 0
0 1 0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 1 1 1 0
1 1 0 1 0 1
1 1 1 0 1 0
Flip Flop inputs
D
A
=A(t+1)
D
B
=B(t+1)
Y=ABx
M. K. Uygurolu, H. Demirel Jan. 13, 2010
Introduction to Logic Design/ Digital Logic Design I - Final Examination
M. K. Uygurolu, H. Demirel Jan. 13, 2010
Вам также может понравиться
- Final Solutions PDFДокумент12 страницFinal Solutions PDFMahendra Reddy JОценок пока нет
- Faculty of Engineering: Electrical and Electronic Engineering DepartmentДокумент10 страницFaculty of Engineering: Electrical and Electronic Engineering DepartmentEndalkОценок пока нет
- EEE241fİNAL2022 1Документ4 страницыEEE241fİNAL2022 1mfp.plt453Оценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan: DL 0&preview 495460+Digital+Electronics+2020-2021 PDFДокумент18 страницLesson Plan: DL 0&preview 495460+Digital+Electronics+2020-2021 PDFapi-544757965Оценок пока нет
- Faculty of Engineering: Electrical and Electronic Engineering DepartmentДокумент10 страницFaculty of Engineering: Electrical and Electronic Engineering DepartmentEndalkОценок пока нет
- EENG (INFE) 115 F16-17 Final Exam-SOLUTIONSДокумент9 страницEENG (INFE) 115 F16-17 Final Exam-SOLUTIONSTeki ChweОценок пока нет
- Ee NG 115 Midterm SolutionsДокумент10 страницEe NG 115 Midterm SolutionsSreekanth NaraОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual 02Документ5 страницLab Manual 02Muhammad AmirОценок пока нет
- EE 213M - Mid Sem Exam Paper 1Документ3 страницыEE 213M - Mid Sem Exam Paper 1Arpit SurekaОценок пока нет
- Dl2 Comb LogicДокумент26 страницDl2 Comb Logicomgcharlie12Оценок пока нет
- 1 - 2EB - Main - Exam - 2020 - Digital - Section - FinalДокумент4 страницы1 - 2EB - Main - Exam - 2020 - Digital - Section - FinalMischka BudhaiОценок пока нет
- EENG211/INFE211 Digital Logic Design I - Final ExaminationДокумент10 страницEENG211/INFE211 Digital Logic Design I - Final ExaminationEndalkОценок пока нет
- SolutionДокумент5 страницSolutionAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Digital Design Assignment 40%Документ2 страницыDigital Design Assignment 40%Obada Ar-ruzziОценок пока нет
- CS302P - Sample PaperДокумент10 страницCS302P - Sample PaperMian GОценок пока нет
- Example 1: Simplify The Following Boolean Expression. Using Boolean Algebra Postulates andДокумент10 страницExample 1: Simplify The Following Boolean Expression. Using Boolean Algebra Postulates andMohamed ZaideОценок пока нет
- Sessional II Spring 2013Документ8 страницSessional II Spring 2013Jannat NasirОценок пока нет
- Exam Model ATED2020 ENДокумент1 страницаExam Model ATED2020 ENAna HodorogeaОценок пока нет
- 60-265-01 Computer Architecture and Digital Design: Midterm Examination # 2Документ9 страниц60-265-01 Computer Architecture and Digital Design: Midterm Examination # 2Akhil SinghОценок пока нет
- Priority EncoderДокумент45 страницPriority EncoderCtutor Ctutor100% (1)
- Computer Science Final Exam (2007)Документ15 страницComputer Science Final Exam (2007)Chantal RamezОценок пока нет
- Solution PDFДокумент5 страницSolution PDFCedric SunОценок пока нет
- STUDENT ID NO AND LECTURE SECTIONДокумент11 страницSTUDENT ID NO AND LECTURE SECTIONBala GanabathyОценок пока нет
- Dldlab6 justPreLabДокумент10 страницDldlab6 justPreLabArfaat SanitaryОценок пока нет
- Class 9 CompДокумент1 страницаClass 9 Compansuman9901Оценок пока нет
- UNIT WISE QUEST DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN - GIET 2019 II - I (3rd Sem)Документ18 страницUNIT WISE QUEST DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN - GIET 2019 II - I (3rd Sem)Deepak NaiduОценок пока нет
- CEG 2136 - Fall 2009 - MidtermДокумент19 страницCEG 2136 - Fall 2009 - MidtermAmin DhouibОценок пока нет
- Multiplexer Dan DemultiplexerДокумент23 страницыMultiplexer Dan Demultiplexerunhar ftkОценок пока нет
- Prelim Examination in Logic DesignДокумент5 страницPrelim Examination in Logic Designdj_eqc7227Оценок пока нет
- Digital Logic Circuits Tutorial (2014-2015) ODD SemДокумент7 страницDigital Logic Circuits Tutorial (2014-2015) ODD SemSai Er SaravananОценок пока нет
- Solution ManualДокумент14 страницSolution ManualdattadhanweОценок пока нет
- Map - K Dengan Kondisi Dont CareДокумент17 страницMap - K Dengan Kondisi Dont CareDestri HandokoОценок пока нет
- Final 2020 DLDДокумент4 страницыFinal 2020 DLDMuhammad Sufyan AliОценок пока нет
- United International University (UIU) : Dept. of Computer Science& Engineering (CSE)Документ2 страницыUnited International University (UIU) : Dept. of Computer Science& Engineering (CSE)mahbub mitulОценок пока нет
- Isc 2005Документ21 страницаIsc 2005Your Laughter DosageОценок пока нет
- Lecture 19Документ10 страницLecture 19Aviral UpadhyayОценок пока нет
- Tabular Method for Logic Function Minimization (Part 1Документ10 страницTabular Method for Logic Function Minimization (Part 1trephenaОценок пока нет
- EGR 265 Final ExamДокумент6 страницEGR 265 Final Examcompuguy1088Оценок пока нет
- Assignment 2Документ3 страницыAssignment 2Fanny CheungОценок пока нет
- Digital PDFДокумент15 страницDigital PDFthumatimadhusudhanОценок пока нет
- Lab 9 (Group 4) - 1Документ11 страницLab 9 (Group 4) - 1MUHAMMAD HUZAIFAОценок пока нет
- Ia1 DPSDДокумент2 страницыIa1 DPSDRaja BenitaОценок пока нет
- Activity 2.3.1 Octal & Hexadecimal Number SystemsДокумент5 страницActivity 2.3.1 Octal & Hexadecimal Number SystemsDark Lotus100% (1)
- CSE 231 Sample MidДокумент1 страницаCSE 231 Sample MidzalkernineОценок пока нет
- ECSE 221 Midterm W11Документ9 страницECSE 221 Midterm W11Eliran HalfonОценок пока нет
- CENG355 Final Exam Spring2019 SolutionДокумент13 страницCENG355 Final Exam Spring2019 SolutionHadi SleemОценок пока нет
- Amankwah - 040119150 - L200 - B - Morning - Digital Computer Design - It 232Документ11 страницAmankwah - 040119150 - L200 - B - Morning - Digital Computer Design - It 232Qwerku GeorgeОценок пока нет
- Digital Design LaboratoryДокумент10 страницDigital Design Laboratorykarths22Оценок пока нет
- Lab 3Документ10 страницLab 3tuan phanОценок пока нет
- Computer Science Final Exam (2012)Документ14 страницComputer Science Final Exam (2012)Chantal RamezОценок пока нет
- Function Quiz1 This Is Quiz Question 1 X Zeros (1,10) For I 1:10 X (I) I End y X 2/2+2x Plot (Y, X)Документ2 страницыFunction Quiz1 This Is Quiz Question 1 X Zeros (1,10) For I 1:10 X (I) I End y X 2/2+2x Plot (Y, X)peilin93Оценок пока нет
- DLD Ques5Документ2 страницыDLD Ques5mahbub mitulОценок пока нет
- Final Exam - Design and Analysis of Algorithms - Fall 2010 Semester - SolДокумент7 страницFinal Exam - Design and Analysis of Algorithms - Fall 2010 Semester - SolAbdul RaufОценок пока нет
- 9A04306 Digital Logic DesignДокумент4 страницы9A04306 Digital Logic DesignsivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- CSEN102: Introduction To Computer Science Winter Semester 2019-2020Документ17 страницCSEN102: Introduction To Computer Science Winter Semester 2019-2020Khalid RadwanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ2 страницыChapter 1Seemab RamzanОценок пока нет
- COMP2611 Spring 2020 Homework #1 Solutions Deadline and Submission DetailsДокумент9 страницCOMP2611 Spring 2020 Homework #1 Solutions Deadline and Submission DetailsManan GoyalОценок пока нет
- Digital Signal Processing: Mathematical and Computational Methods, Software Development and ApplicationsОт EverandDigital Signal Processing: Mathematical and Computational Methods, Software Development and ApplicationsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Cellular NetworksДокумент60 страницCellular NetworksT FОценок пока нет
- OSI Physical LayerДокумент30 страницOSI Physical LayerT FОценок пока нет
- Syllabus - Introduction To Telecommunication Networks CourseДокумент2 страницыSyllabus - Introduction To Telecommunication Networks CourseT FОценок пока нет
- Integrated Services Digital Network (Isdn) : Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001Документ29 страницIntegrated Services Digital Network (Isdn) : Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001T FОценок пока нет
- Ece 374 Course Notes Telecom Networks 2012-2013Документ80 страницEce 374 Course Notes Telecom Networks 2012-2013Saptarshi ChatterjeeОценок пока нет
- Voice Communication Concepts and Technology: 1 Modified by Masud-ul-Hasan and Ahmad Al-YamaniДокумент80 страницVoice Communication Concepts and Technology: 1 Modified by Masud-ul-Hasan and Ahmad Al-YamaniT FОценок пока нет
- Sign MagnitudeДокумент25 страницSign MagnitudeT FОценок пока нет
- WWW - Montgomerycollege.edu - Kyee - EE244 - Course Handouts - Lecture Notes - Lecture Notes 07Документ8 страницWWW - Montgomerycollege.edu - Kyee - EE244 - Course Handouts - Lecture Notes - Lecture Notes 07T FОценок пока нет
- Heart To Stone by Phoenix - Flames - 1Документ6 страницHeart To Stone by Phoenix - Flames - 1T FОценок пока нет
- Acom Lab ManualДокумент58 страницAcom Lab ManualRavi ShankarОценок пока нет
- Half Adders and Full AddersДокумент12 страницHalf Adders and Full AddersmonzuracОценок пока нет
- 2 Miricles To Be SaintДокумент13 страниц2 Miricles To Be SaintT FОценок пока нет
- You Did What! by Nonjon-Harry Potter Fan FictionДокумент317 страницYou Did What! by Nonjon-Harry Potter Fan FictionT FОценок пока нет
- Ece 374 Course Notes Telecom Networks 2012-2013Документ80 страницEce 374 Course Notes Telecom Networks 2012-2013Saptarshi ChatterjeeОценок пока нет
- Mistaken Love by MzKISSEShereДокумент78 страницMistaken Love by MzKISSEShereT FОценок пока нет
- Physics EquationsДокумент5 страницPhysics Equationsanon-992211100% (64)
- 5 Hours 27 Minutes and 8 Seconds by Draco - Lover202Документ3 страницы5 Hours 27 Minutes and 8 Seconds by Draco - Lover202T FОценок пока нет
- 5 Hours 27 Minutes and 12 Seconds by Draco - Lover202Документ23 страницы5 Hours 27 Minutes and 12 Seconds by Draco - Lover202T FОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentДокумент42 страницыNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentT FОценок пока нет
- Harlequin 2Документ5 страницHarlequin 2T FОценок пока нет
- Programmable Logic Controller: This Datasheet Has Been Downloaded From at ThisДокумент12 страницProgrammable Logic Controller: This Datasheet Has Been Downloaded From at ThisEmanuel NavasОценок пока нет
- Apple Macbook Pro 13 A1278 (K24, 820-2530)Документ81 страницаApple Macbook Pro 13 A1278 (K24, 820-2530)Vio Chi100% (1)
- Lab No 4 - ReportДокумент18 страницLab No 4 - ReportZainab Ali Naveed IrshadОценок пока нет
- Wireless Media: 802.11 802.11b 802.11a 802.11g 802.11nДокумент16 страницWireless Media: 802.11 802.11b 802.11a 802.11g 802.11nkhakestary1363Оценок пока нет
- Dell Intel XXV710 Dual Port 25GbE SFP28 PCIe Adapter, Full Height, Customer Install - Networking - DellДокумент5 страницDell Intel XXV710 Dual Port 25GbE SFP28 PCIe Adapter, Full Height, Customer Install - Networking - DellGabriela PopescuОценок пока нет
- Monitoring of Electrical System Using Internet of Things With Smart Current Electric SensorsДокумент8 страницMonitoring of Electrical System Using Internet of Things With Smart Current Electric SensorsMarcela VelasteguíОценок пока нет
- Projector Spec: TechnologyДокумент2 страницыProjector Spec: TechnologyTathokoza MpondaОценок пока нет
- 1000-Series Data SheetДокумент1 страница1000-Series Data SheetChaitannya MahatmeОценок пока нет
- Experiment No. (5) Single Sideband Modulation: ObjectДокумент4 страницыExperiment No. (5) Single Sideband Modulation: ObjectFaez FawwazОценок пока нет
- Radio 9310Документ79 страницRadio 9310YoSoloYoОценок пока нет
- Calculating RTU TransmissionДокумент2 страницыCalculating RTU Transmissionceleritas81Оценок пока нет
- Vsat Bandwidth Efficiency On Satpath SystemДокумент10 страницVsat Bandwidth Efficiency On Satpath SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- LP8072CДокумент2 страницыLP8072Cmostafa ashrafОценок пока нет
- MBI Driver IC For LED Display ScreenДокумент14 страницMBI Driver IC For LED Display ScreenAcido CinicoОценок пока нет
- Analog and Digital Electronics Laboratory 18CSL37 2019 20Документ68 страницAnalog and Digital Electronics Laboratory 18CSL37 2019 20Riti JainОценок пока нет
- Syllabus: India'S Best Institute For EngineersДокумент6 страницSyllabus: India'S Best Institute For EngineersGaurav ShrimaliОценок пока нет
- NVJ Series ValvesДокумент46 страницNVJ Series ValvesjoxenoОценок пока нет
- ES 1 MarkДокумент5 страницES 1 MarkVenkatesan SundaramОценок пока нет
- 123 2.ministar Manual Rev3 EngДокумент44 страницы123 2.ministar Manual Rev3 EngMilovan JanićijevićОценок пока нет
- 19v From A Car BatteryДокумент4 страницы19v From A Car Batterysafet100% (1)
- Alcatel-Lucent Short Message Service CenterДокумент3 страницыAlcatel-Lucent Short Message Service CenterLL ABОценок пока нет
- Input and Output. Supervisor Mode, Exceptions, Traps. Co-ProcessorsДокумент53 страницыInput and Output. Supervisor Mode, Exceptions, Traps. Co-ProcessorsLordwin MichealОценок пока нет
- JunipericonsДокумент30 страницJunipericonsAndri AndriyanОценок пока нет
- MSP430 GPIO and Watchdog Timer Lab/TITLEДокумент13 страницMSP430 GPIO and Watchdog Timer Lab/TITLEsreekanth2728Оценок пока нет
- Power HarmonicsДокумент18 страницPower HarmonicsSwagat Pradhan100% (2)
- L-2/T-L/Eeef.: .Tul - I. - CB) - .Документ44 страницыL-2/T-L/Eeef.: .Tul - I. - CB) - .MeowОценок пока нет
- Pyro LaserДокумент2 страницыPyro LaserWilder Ortiz VelasquezОценок пока нет
- Advanced Paper Cutting Machine Using ARM7: SenseДокумент3 страницыAdvanced Paper Cutting Machine Using ARM7: SensechotichanduОценок пока нет
- Ion ManualДокумент6 страницIon ManualkosarobОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringДокумент6 страницLesson Plan: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringSandeep PatilОценок пока нет